Distributed optimal rendezvous of multi-UAV systems in prescribed time based on time-domain mapping
-
摘要:
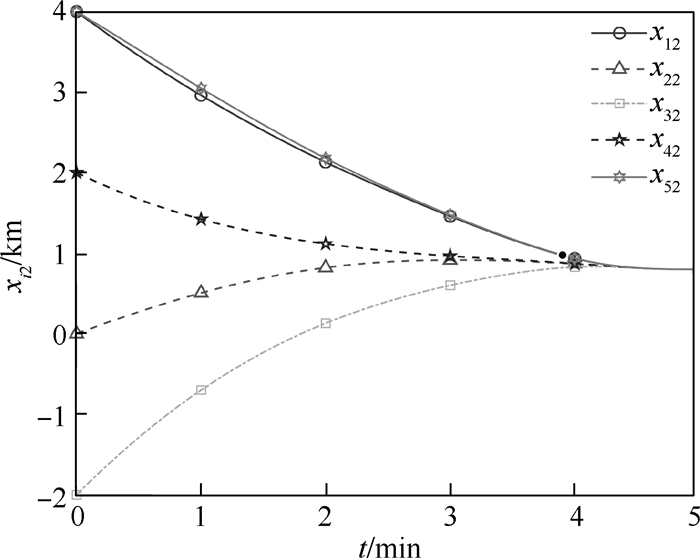
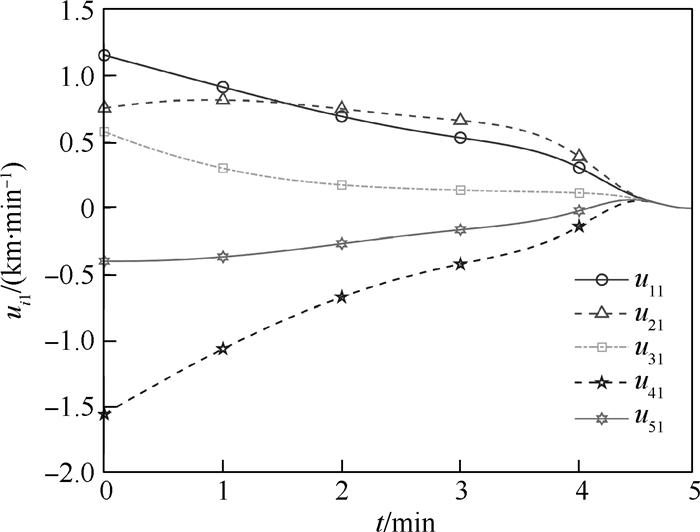
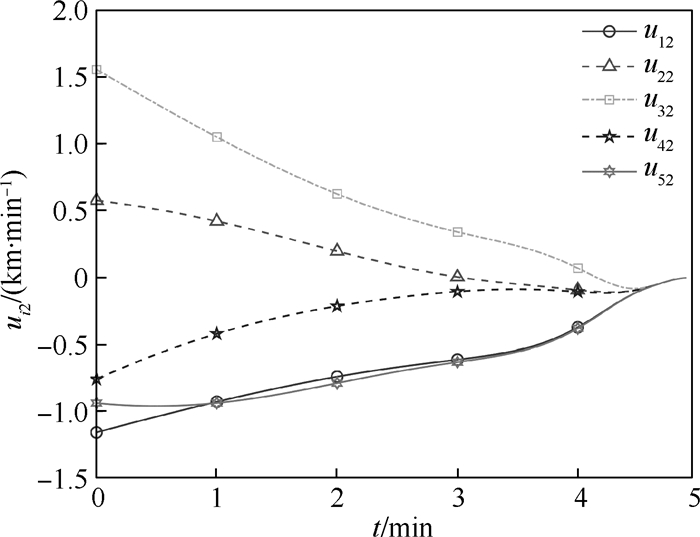
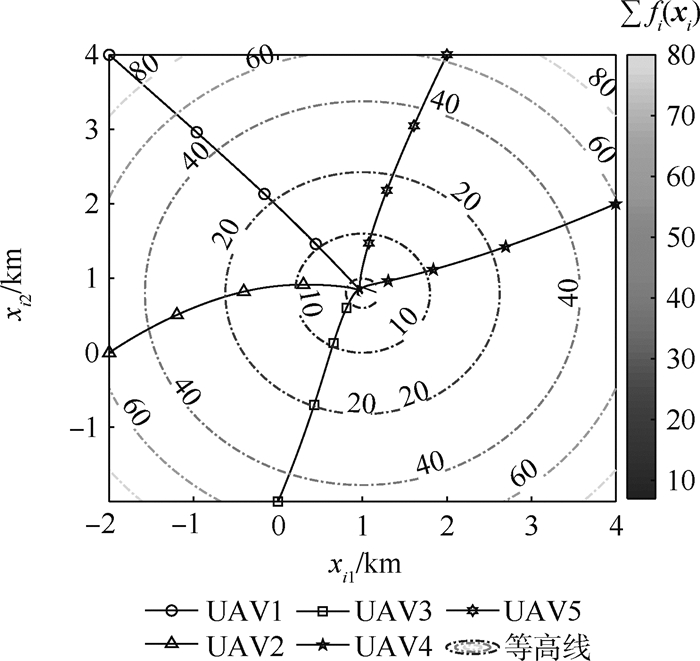
针对多无人机系统给定时间最优集结问题,建立了基于时域映射的分布式优化框架。首先,引入一类特殊的时域映射,将原时域的给定时间决策问题转化为了无限域中的渐近稳定问题,简化了分析设计流程。其次,进一步设计了给定时间梯度下降算法,其收敛时间与系统初始条件及其他参数无关,能够被预先给定,且算法时变增益的使用消除了参数选择过程,在全局信息严重匮乏的情况下仍然适用。仿真结果表明:所提方法能够在给定时间内实现多无人机分布式最优集结,并保证任务时间内闭环系统全局有界。
Abstract:To solve the prescribed-time optimal rendezvous problem for multi-UAV systems, a distributed optimization framework is established based on time-domain transformation technique. By introducing a specific time-domain transformation, the prescribed-time decision problem in original time-domain is transformed into an asymptotically stable problem in the infinite domain, which simplifies the analysis and design process. Then, we design a prescribed-time gradient descent algorithm whose convergence time is independent of the initial states as well as other parameters and therefore can be pre-specified. Besides, the application of time-varying gain removes the parameter selection process, which enables the proposed method in the context of a serious lack of global information. The simulation results show that this method is able to achieve the distributed optimal rendezvous for multiple UAVs in prescribed time, and the closed-loop system remains globally bounded in mission time.
-
Key words:
- multi-UAV systems /
- prescribed-time /
- time-domain transformation /
- distributed optimization /
- consensus
-
[1] BEARD R D, MCLAIN T W, GOODRICH M A, et al. Coordinated target assignment and intercept for unmanned air vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 2002, 18(6): 911-922. doi: 10.1109/TRA.2002.805653 [2] SCARDOVI L, SEPULCHRE R. Synchronization in networks of identical linear systems[J]. Automatica, 2009, 48(8): 2557-2562. [3] SHI G D, JOHANSSON K. Robust consensus for continuous time multi-agent dynamics[J]. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 2013, 48(5): 3673-3691. [4] DIMAROGONAS D, KYRIAKOPOULOS K. On the rendezvous problem for multiple nonholonomic agents[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2007, 52(5): 916-922. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2007.895897 [5] DING C, DONG X M, SHI C, et al. Leaderless output consensus of multi-agent systems with distinct relative degrees under switching directed topologies[J]. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2019, 13(3): 313-320. doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2018.5140 [6] 何吕龙, 张佳强, 侯岳奇, 等. 有向通信拓扑和时延条件下的无人机集群时变编队控制[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(2): 314-323. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0206HE L L, ZHANG J Q, HOU Y Q, et al. Time-varying formation control for UAV swarm with directed interaction topology and communication delay[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(2): 314-323(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0206 [7] NEDIC A, OZDAGLAR A. Distributed subgradient methods for multi-agent optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2009, 54(1): 48-61. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2008.2009515 [8] ZHU M H, MARTÍNEZ S. On distributed convex optimization under inequality and equality constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2012, 57(1): 151-164. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2011.2167817 [9] DUCHI J, AGARWAL A, WAINWRIGHT M. Dual averaging for distributed optimization: Convergence and network scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2012, 57(3): 592-606. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2011.2161027 [10] LIN P, REN W, SONG Y. Distributed multi-agent optimization subject to nonidentical constraints and communication delays[J]. Automatica, 2016, 65: 120-131. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2015.11.014 [11] KIA S S, CORTÉS J, MARTÍNEZ S. Distributed convex optimization via continuous-time coordination algorithms with discrete-time communication[J]. Automatica, 2015, 55: 254-264. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2015.03.001 [12] ZHAO Y, LIU Y F, WEN G H, et al. Distributed optimization for linear multiagent systems: Edge- and node-based adaptive designs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2017, 62(7): 3602-3609. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2017.2669321 [13] LIN P, REN W.Distributed shortest distance consensus problem in multi-agent systems[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Decision and Control.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 4696-4701. [14] LIN P, REN W, SONG Y D, et al.Distributed optimization with the consideration of adaptivity and finite-time convergence[C]//Proceedings of 2014 American Control Conference.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 3177-3182. [15] LIN P, REN W, FARRELL J A. Distributed continuous-time optimization: Nonuniform gradient gains, finite-time convergence, and convex constraint set[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2017, 62(5): 2239-2253. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2016.2604324 [16] NING B D, HAN Q L, ZUO Z Y. Distributed optimization for multiagent systems: An edge-based fixed-time consensus approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(1): 122-132. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2766762 [17] GODSIL C, ROYLE G. Algebraic graph theory[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2001. [18] FACCHINEI F, PANG J. Finite-dimensional variational inequalities and complementarity problems[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2003. [19] REN W, NATHAN S. Distributed coordination architecture for multi-robot formation control[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2008, 56(2): 324-333. [20] DING C, SHI C, CHEN Y. Nonsingular prescribed-time stabilization of a class of uncertain nonlinear systems: A novel coordinate mapping method[J]. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2020, 30(9): 3566-3581. doi: 10.1002/rnc.4949 [21] CHEN F, CAO Y, REN W. Distributed average tracking of multiple time-varying reference signals with bounded derivatives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2012, 57(12): 3169-3174. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2012.2199176 -







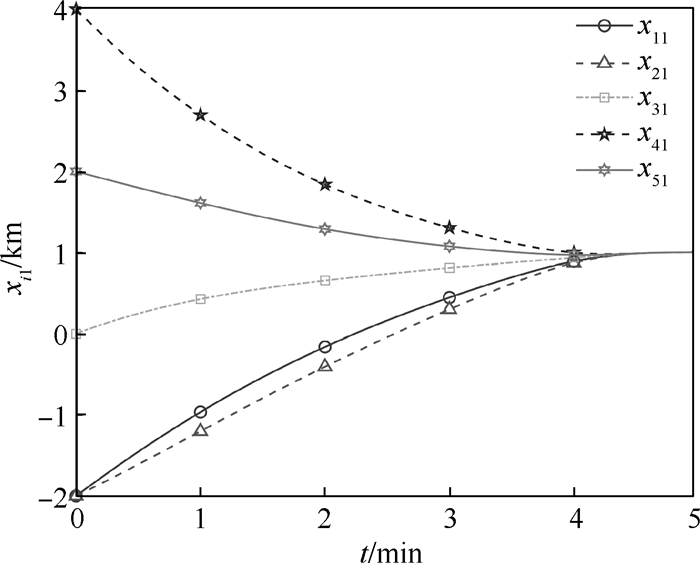
 下载:
下载: