Regional object detection of remote sensing airport based on improved deep neural network
-
摘要:
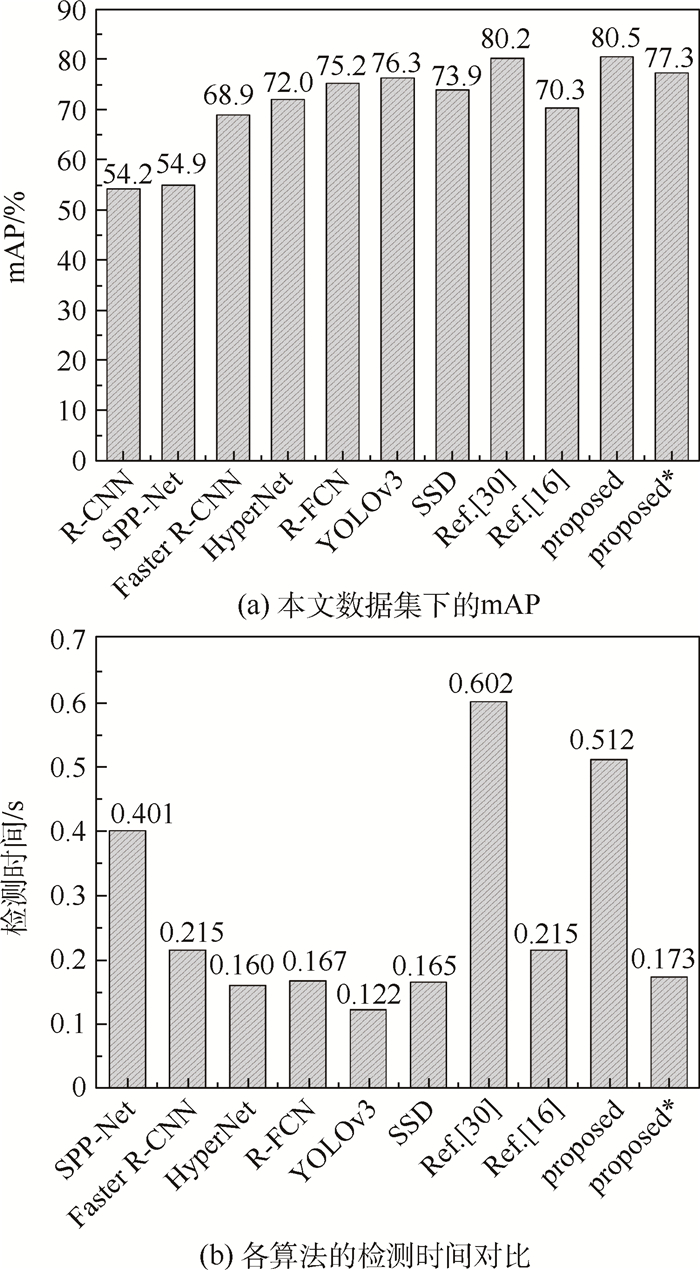
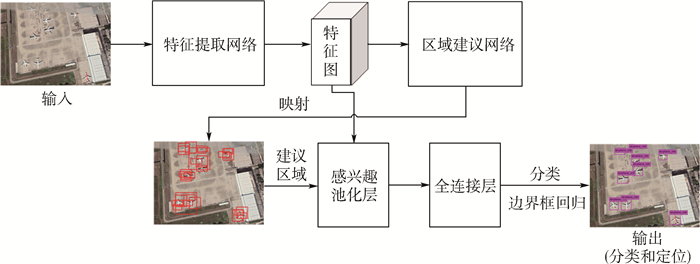
卫星遥感监测器下的机场区域多类目标检测在实际生活中有着重大的军用和民用意义。为了有效提升机场区域遥感图片的检测精确率,以主流目标检测方法中更快的区域卷积神经网络(Faster R-CNN)为基础框架,针对数据侧提出了ReMD数据增强算法。同时使用更具深度的残差神经网络(ResNet)以及特征融合部件-特征金字塔网络(FPN)来提取机场区域目标更鲁棒的深层区分性特征。在末端检测网络添加新的全连接层并根据目标的类间关联性组合softmax分类器以及4个logistic regression分类器进行机场区域多类目标的精确分类。实验结果表明:相比原网络改进后的网络带来了11.6%的多类平均检测精确率的提升,达到了80.5%的mAP,与其他主流网络进行对比也有更好的精确率;同时通过适当减小建议区域的输入量,可以在降低3.2%精确率的前提下将0.512 s的检测时间提速3倍,至0.173 s,根据具体任务可以合理权衡精确率和检测速度,体现了该网络的有效性以及实用性。
Abstract:The detection of multiple types of targets in the airport area under the satellite remote sensing monitor is of great military and civilian significance in real life. In order to effectively improve the detection accuracy of remote sensing images in the airport area, based on the representative deep network Faster R-CNN in the mainstream target detection method, the ReMD data enhancement algorithm is proposed for the data side. The deep ResNet network and the feature fusion component-FPN are used to extract more robust deep distinguishing features of airport area target. Finally, a new fully connected layer is added to the end detection network, and the softmax classifier and 4 logistic regression classifiers are combined to accurately classify airport area multi-class targets according to the target class correlation. Experiments show that the improvement of the original network brings a 11.6% increase in the average detection accuracy rate of the original network, reaching 80.5% mAP. Compared with other mainstream networks, it also has a better accuracy rate. At the same time, by appropriately reducing the input amount of the recommended area, under the premise of 3.2% reduction of accuracy rate, the detection time of 0.512 s is improved by 3 times to 0.173 s. According to the specific task, the accuracy and detection speed can be reasonably weighed, which reflects the effectiveness and practicability of the network.
-
Key words:
- object detection /
- image processing /
- remote sensing /
- airport area /
- neural network
-
表 1 目标-标签对应表
Table 1. Object-label correspondence table
目标 airport civil airplane transport plane fighter helicopter bridge oil tank 标签 airport airplane_mh airplane_y airplane_z airplane_zs bridge oil tank 表 2 目标-类别号对应表
Table 2. Object-number correspondence table
目标
标签airplane airport
airportbridge
bridgeoil tank
oil tankcivil airplane
airplane_mh类别号 1 2 3 4 5 目标 transport
planefighter helicopter background 标签 airplane_y airplane_z airplane_zs 类别号 6 7 8 0 表 3 各数据增强算法效果
Table 3. Effect of each data enhancement algorithm
数据增强算法 各算法使用情况 Spin √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ Mirror √ √ √ √ √ √ √ Scaling √ √ √ √ √ √ Pan √ √ √ √ √ Brightness Change √ √ √ √ Crop √ √ √ Gaussian Noise √ √ ReMD(proposed) √ mAP/% 68.9 69.4 69.8 69.9 70.4 71.1 71.3 72.6 表 4 基础网络对比实验结果
Table 4. Comparison of experiment results of basic network
模型 mAP/% Average IOU ZFNet 58.4 0.392 VGG_CNN_M_1024 63.5 0.425 VGG-16 72.6 0.566 VGG-19 73.9 0.571 ResNet-50 74.1 0.572 ResNet-101 75.8 0.574 ResNet-50+FPN 78.9 0.643 ResNet-101+FPN 80.2 0.645 表 5 加入新型末端检测器前后对比实验结果
Table 5. Comparison of experiment results before and after adding the new end detector
网络 AP/% mAP/% airport bridge oil tank Civil airplane Transport plane fighter helicopter T1 89.7 75.8 76.9 89.6 78.5 72.0 78.9 80.2 T2 89.8 75.9 76.9 90.1 79.1 72.6 79.4 80.5 表 6 各检测部件与所带来的时间成本
Table 6. Summary of each testing component and time cost
Faster R-CNN网络及增加的部件 原网络 ReMD ResNet-101 FPN N2 N1 检测时间/s 0.215 0.215 0.483 0.510 0.512 0.217 Δt/s 0 0 0.268 0.027 0.002 0.002 表 7 不同检测网络间的对比实验结果
Table 7. Comparison of experiment results between different detection networks
-
[1] RICHARDS J R. Remote sensing digital image analisis[M]. Berlin: Springer, 1999: 20-21. [2] 杨四海, 陈锻生, 谢维波. Hough变换的特性分析: 一种全局观点[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2006, 18(8): 1197-1204. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-9775.2006.08.020YANG S H, CHEN D S, XIE W B. Characteristics of hough transform: A global view[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2006, 18(8): 1197-1204(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-9775.2006.08.020 [3] 梁浩然. 自然图像的视觉显著性特征分析与检测方法及其应用研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2016: 16-17.LIANG H R. Research on saliency detection of natural image and its application[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2016: 16-17(in Chinese). [4] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. DeepLab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4): 834-848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184 [5] LI W, XIANG S M, WANG H B, et al. Robust airplane detection in satellite images[C]//2011 18th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 2821-2824. [6] 林煜东, 和红杰, 尹忠科, 等. 基于稀疏表示的可见光遥感图像飞机检测算法[J]. 光子学报, 2014, 43(9): 196-201.LIN Y D, HE H J, YIN Z K, et al. Airplane detection in optical remote sensing image based on sparse-representation[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2014, 43(9): 196-201(in Chinese). [7] 仇建斌, 李士进, 王玮. 角点与边缘信息相结合的遥感图像飞机检测新方法[J]. 微电子学与计算机, 2011, 28(9): 214-216.QIU J B, LI S J, WANG W. A new approach to detect aircrafts in remote sensing images based on corner and edge information fusion[J]. Microelectronics & Computer, 2011, 28(9): 214-216(in Chinese). [8] AN Z Y, SHI Z W, TENG X C, et al. An automated airplane detection system for large panchromatic image with high spatial resolution[J]. Optik, 2014, 125(12): 2768-2775. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2013.12.003 [9] ZHANG P, NIU X, DOU Y, et al. Airport detection on optical satellite images using deep convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(8): 1183-1187. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2673118 [10] ZHU T H, LI Y H, YE Q K, et al. Integrating saliency and ResNet for airport detection in large-size remote sensing images[C]//20172nd International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 20-25. [11] CHEN X Y, XIANG S M, LIU C L, et al. Aircraft detection by deep belief nets[C]//20132nd IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 54-58. [12] WU H, ZHANG H, ZHANG J F, et al. Fast aircraft detection in satellite images based on convolutional neural networks[C]//2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 4210-4214. [13] REN S Q, HE K M, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [14] 戴陈卡, 李毅. 基于Faster RCNN以及多部件结合的机场场面静态飞机检测[J]. 计算机应用, 2017, 37(S2): 85-88.DAI C K, LI Y. Aeroplane detection in static aerodrome based on Faster RCNN and multi-part model[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2017, 37(S2): 85-88(in Chinese). [15] 朱明明, 许悦雷, 马时平, 等. 基于特征融合与软判决的遥感图像飞机检测[J]. 光学学报, 2019, 39(2): 71-77.ZHU M M, XU Y L, MA S P, et al. Airplane detection based on feature fusion and soft decision in remote sensing images[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39(2): 71-77(in Chinese). [16] CHEN F, REN R L, VAN DE VOORDE T, et al. Fast automatic airport detection in remote sensing images using convolutional neural networks[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(3): 443. doi: 10.3390/rs10030443 [17] RUSSAKOVSKY O, DENG J, SU H, et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 115(3): 211-252. doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y [18] ZEILER M D, FERGUS R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks[M]//Computer Vision-ECCV 2014. Berlin: Springer, 2014: 818-833. [19] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]//Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 121-124. [20] SZEGEDY C, LIU W, JIA Y Q, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]//2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1-9. [21] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [22] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 936-944. [23] EVERINGHAM M, GOOL L, WILLIAMS C K I, et al. The pascal visual object classes (VOC) challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2010, 88(2): 303-338. doi: 10.1007/s11263-009-0275-4 [24] REDMON J, FARHADI A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement[EB/OL]. (2018-04-08)[2019-07-18]. [25] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]//2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 580-587. [26] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904-1916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824 [27] KONG T, YAO A B, CHEN Y R, et al. HyperNet: Towards accurate region proposal generation and joint object detection[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 845-853. [28] DAI J F, LI Y, HE K M, et al. R-FCN: Object detection via region-based fully convolutional networks[C]//Neural Information Processing Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 379-387. [29] LIU W, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector[M]//Computer Vision-ECCV 2016. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 21-37. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2 [30] SHRIVASTAVA A, SUKTHANKAR R, MALIK J, et al. Beyond skip connections: Top-down modulation for object detection[C]//Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 256-266. -







 下载:
下载: