-
摘要:
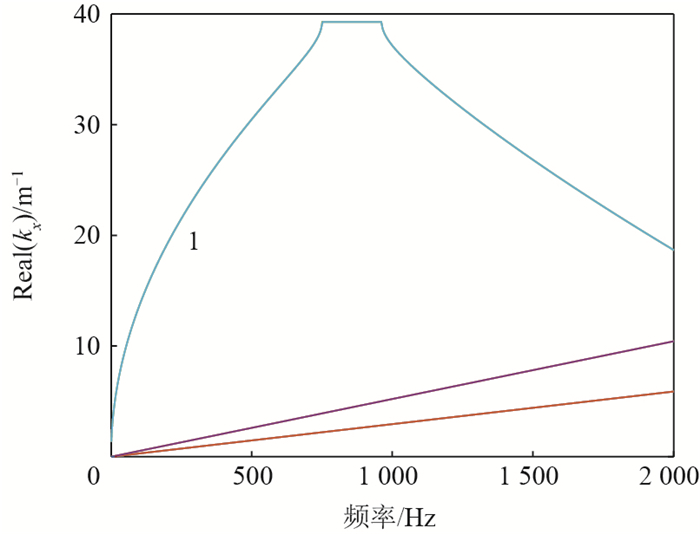
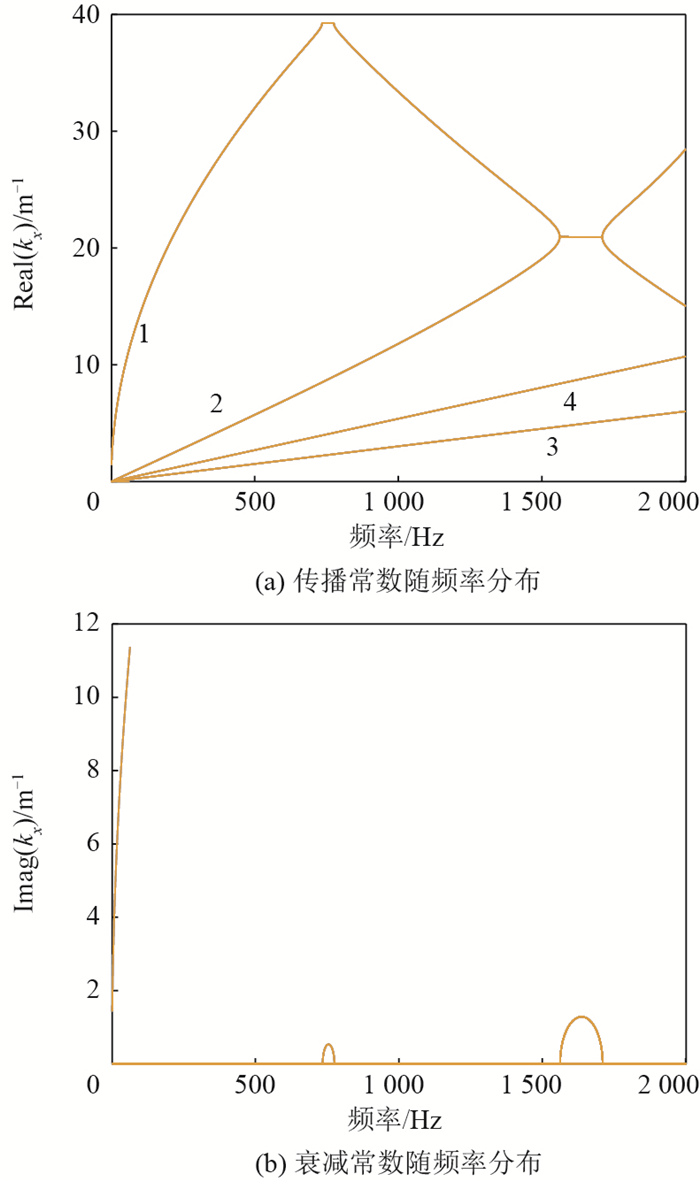
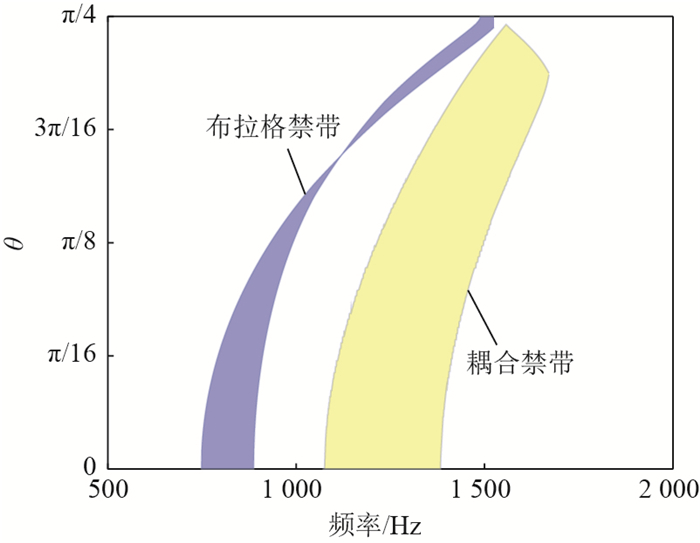
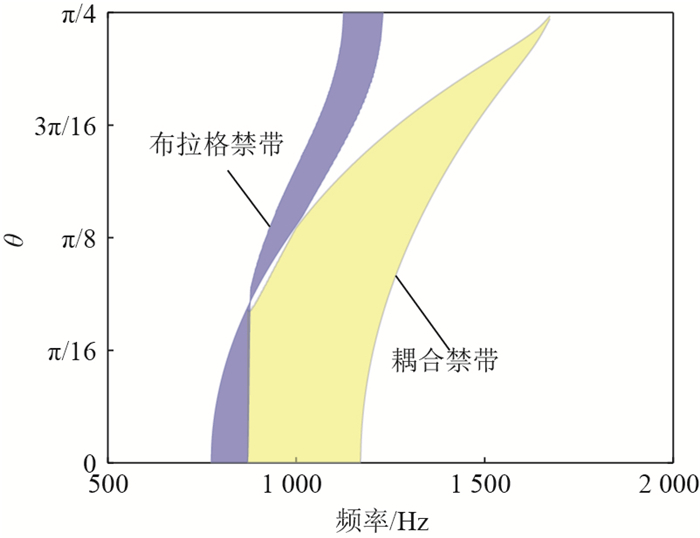
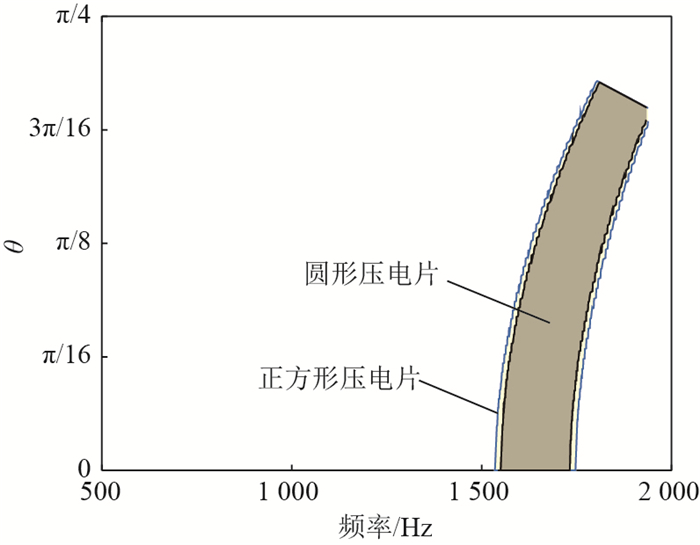
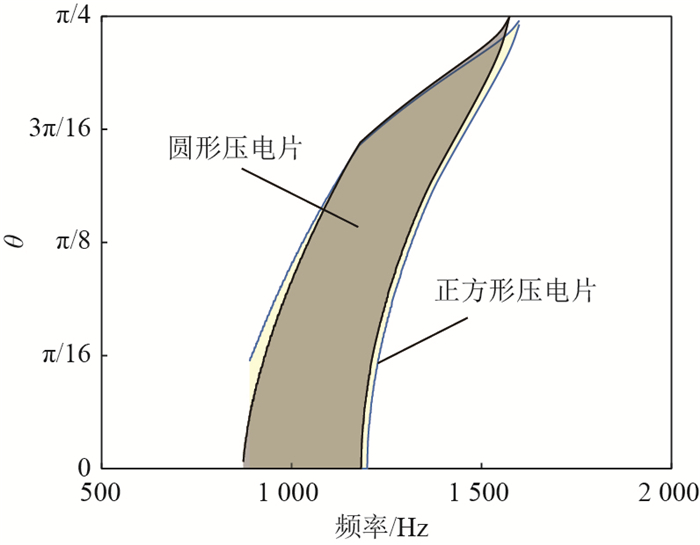
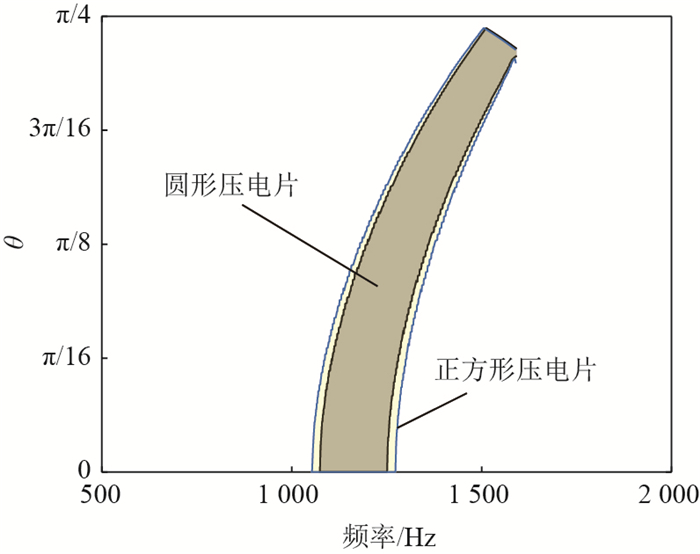
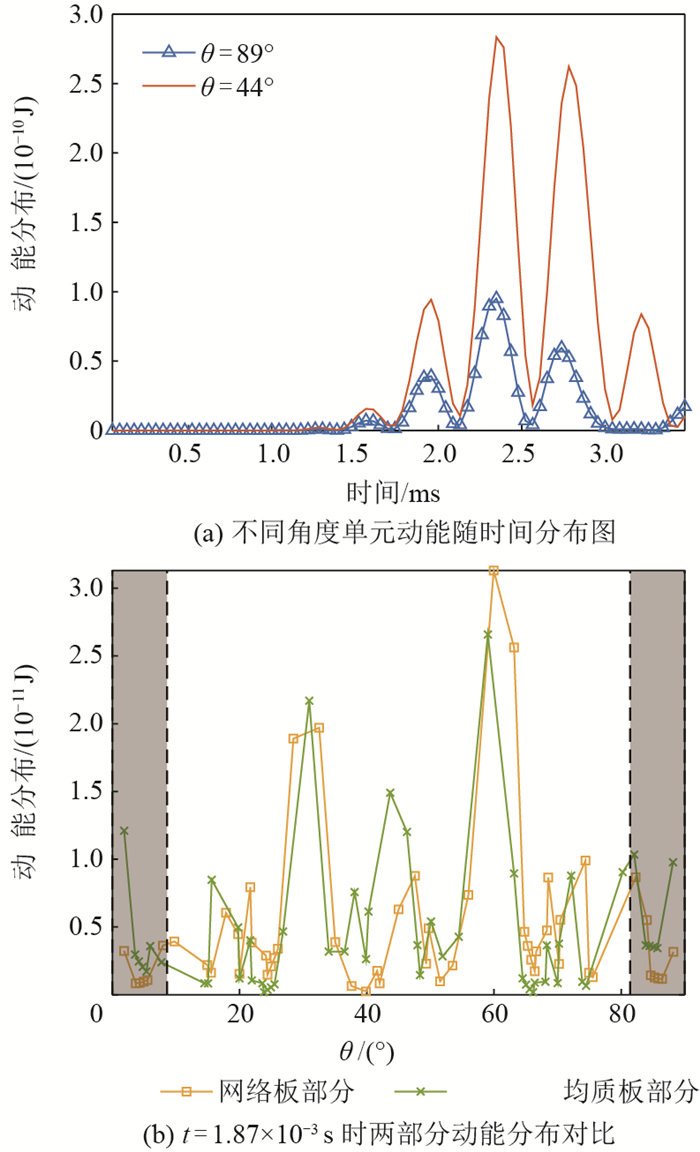
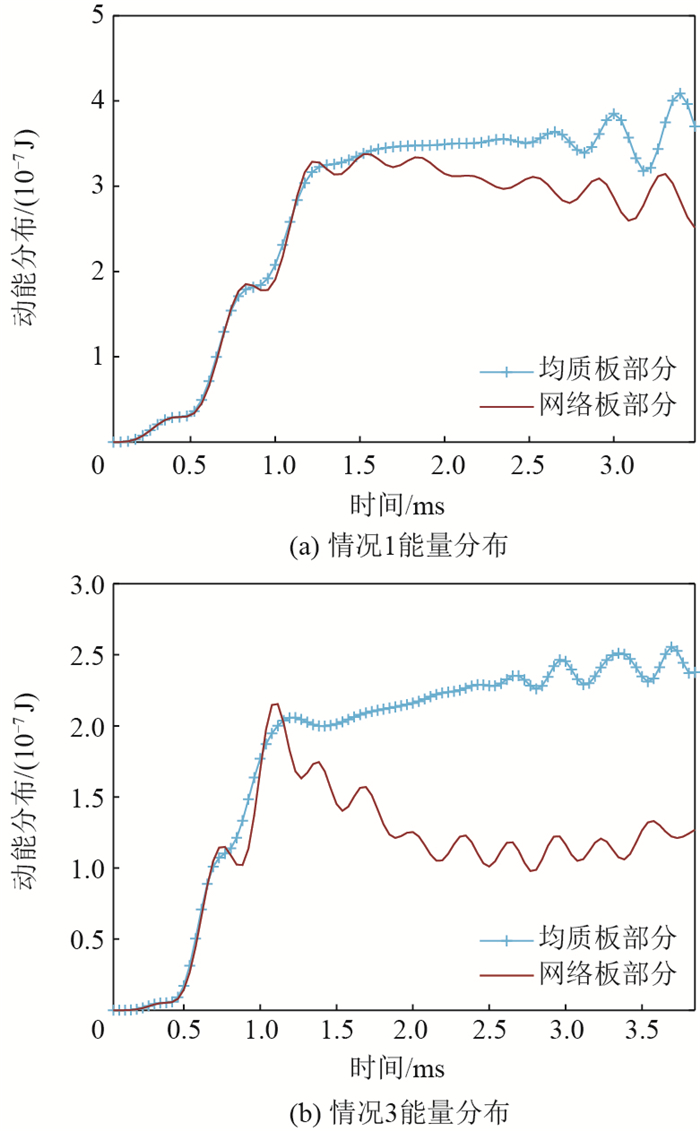
近年来,利用周期结构中弹性波禁带特性减振的研究思路受到了广泛关注。针对以往周期结构难以实现宽频且可调禁带的问题,设计了一种含电路网络的压电周期结构。该结构中的弯曲波和电路网络中的电波通过压电效应可以产生一个较宽的耦合禁带,且通过调整电路参数就可以达到调节禁带位置的目的。首先,为了高效计算该结构的波动特性,开发了适用于压电周期结构的减缩波有限元算法,该算法可以在保证结果准确性的基础上节约90%以上的计算时间。利用该算法研究了压电材料尺寸和形状对耦合禁带性能的影响。结果表明:相同电学参数下,随着压电片尺寸的增大,耦合禁带向低频移动,且禁带带宽增加;相同面积下含圆形和方形压电片的机电系统内耦合禁带差异较小,即形状对耦合禁带的分布影响不大。其次,针对不同尺寸和形状的机电系统,设计了电学参数使得在同一频率附近产生耦合禁带,并分析了其性能差异。最后,为了证明耦合禁带的减振效果,设计了一种有限压电周期板模型,其强迫响应的结果证明了耦合禁带对结构内弹性波可以进行有效调控。
Abstract:In recent years, researches on the elastic band gaps in periodic structures to reduce vibration have attracted widespread attention. However, it is difficult to design a band gap with wide bandwidth and good tunability. Aiming at this problem, we designed a periodic structure with piezoelectric network. By bonding piezoelectric patches periodically into structure, a coupled band gap can be created between the elastic waves and electric waves thanks to the piezoelectric effect. This band gap can be tailored with the help of external circuits. In order to calculate the propagation characteristics of the structure efficiently, a reduced wave finite element method suitable for piezoelectric periodic structures was developed to improve the calculation efficiency. It was found that more than 90% of the calculation time can be saved with great accuracy. Using this method, the influence of the size and shape of the piezoelectric material on the performance of the coupled band gap was studied. The results show that when fixing the electrical parameters, as the size of the piezoelectric patches increases, the coupled band gap moves to lower frequency range and its bandwidth increases. Moreover, the bandwidth in the system with square patches is slightly wider than that with circular patches. However, these two shapes have little impact on the directional distribution of coupled band gap. Then, the guideline is proposed for designing electrical parameters to make sure that coupled band gaps are generated around the desired frequency for electromechanical systems with different sizes and shapes. Finally, in order to prove the vibration reduction effect of the coupled band gap, a finite periodic piezoelectric plate was employed. The results show that the coupled band gap can effectively control the elastic wave in structure.
-
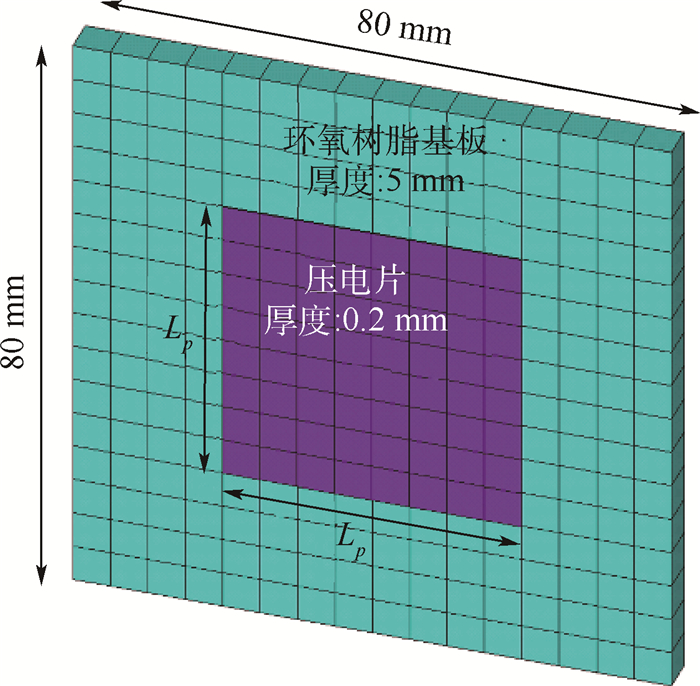
表 1 压电片材料参数
Table 1. Material parameters of piezoelectric patches
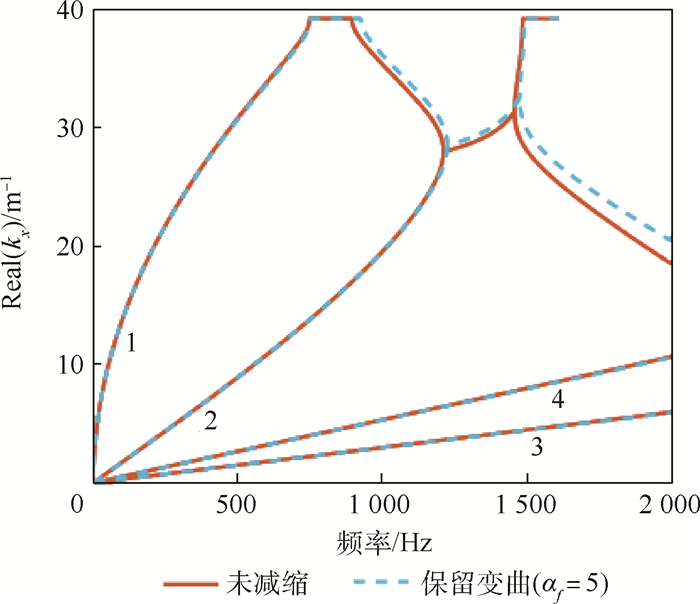
参数 数值 ρp/(kg·m-3) 7 500 s11E/(m2·N-1) 13×10-12 s12E/(m2·N-1) -4.29×10-12 s55E/(m2·N-1) 22×10-12 d31/(C·N-1) -1.86×10-10 ε33T/(F·m-1) 3.009×10-8 表 2 减缩模型对比
Table 2. Comparison between full model and reduced model
模型对比 计算时间/s 矩阵规模 自由度数 完整模型 2 843.17 8 365×8 365 1 175 减缩模型 227.98 313×313 297 增益/% 91.98 96.25 74.72 表 3 压电片结构参数
Table 3. Structural parameters of piezoelectric patches
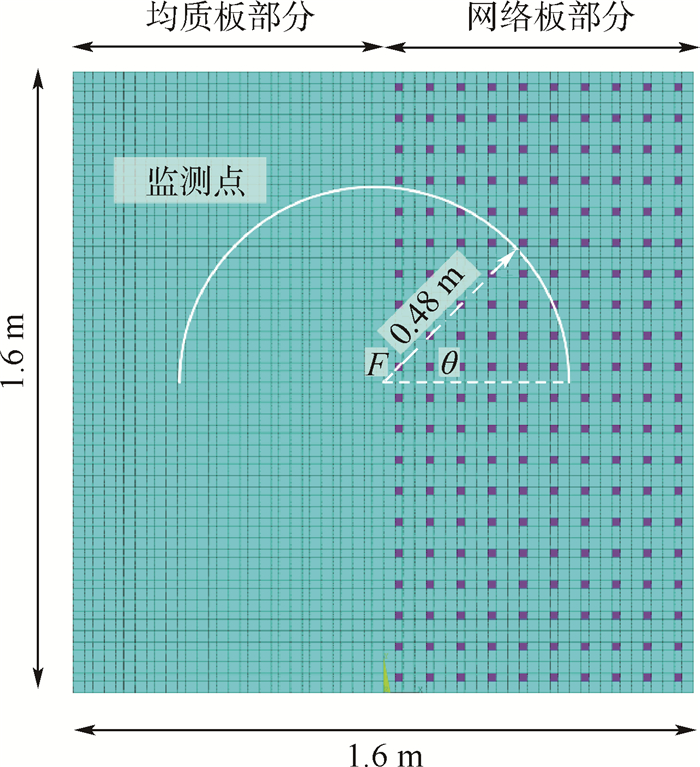
情况编号 长度/mm 直径/mm 电感/H 覆盖率/% 1 20 22.567 6 0.319 6.25 2 35 39.493 3 0.1 19.14 3 40 45.135 2 0.078 25.00 4 45 50.777 1 0.060 6 31.64 5 50 56.419 0 0.051 2 39.06 注:表中覆盖率为压电片面积与基板总面积之比。 -
[1] HUSSEIN M I, LEAMY M J, RUZZENE M. Dynamics of phononic materials and structures: Historical origins, recent progress, and future outlook[J]. Applied Mechanics Reviews, 2014, 66(4): 1-38. [2] 张荣英, 姜根山, 王璋奇, 等. 声子晶体的研究进展及应用前景[J]. 声学技术, 2006, 25(1): 35-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3630.2006.01.009ZHANG R Y, JIANG G S, WANGE Z Q, et al. Progress in researches of phononic crystal and the application perspectives[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2006, 25(1): 35-42(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3630.2006.01.009 [3] ROCA D, YAGO D, CANTE J, et al. Computational design of locally resonant acoustic metamaterials[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 345(1): 161-182. [4] NING L, WANG Y Z, WANG Y S, et al. Active control of elastic metamaterials consisting of symmetric double Helmholtz resonator cavities[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2019, 153-154: 287-298. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.02.007 [5] PELAT A, GALLOT T, GAUTIER F. On the control of the first Bragg band gap in periodic continuously corrugated beam for flexural vibration[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2019, 446: 249-262. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2019.01.029 [6] FAN Y, COLLET M, ICHCHOU M, et al. Energy flow prediction in built-up structures through a hybrid finite element/wave and finite element approach[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2016, 66-67(1): 137-158. [7] QI S, OUDICH M, LI Y, et al. Acoustic energy harvesting based on a planar acoustic metamaterial[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2016, 108(26): 1-4. doi: 10.1063/1.4954987 [8] WU Y G, LI L, FAN Y, et al. Design of dry friction and piezoelectric hybrid ring dampers for integrally bladed disks based on complex nonlinear modes[J]. Computers and Structures, 2020, 233: 1-19. [9] WEN S R, XIONG Y H, HAO S M, et al. Enhanced band-gap properties of an acoustic metamaterial beam with periodically variable cross-sections[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2020, 166: 1-10. [10] MOSCATELLI M, ARDITO R, DRIEMEIER L, et al. Band-gap structure in two- and three-dimensional cellular locally resonant materials[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, Academic Press, 2019, 454(18): 73-84. [11] LI L, JIANG Z, FAN Y, et al. Creating the coupled band gaps in piezoelectric composite plates by interconnected electric impedance[J]. Materials, 2018, 11(9): 1656. doi: 10.3390/ma11091656 [12] 舒海生, 张法, 刘少刚, 等. 一种特殊的布拉格型声子晶体杆振动带隙研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2014, 33(19): 147-151.SHU H S, ZHANG F, LIU S G, et al. Vibration band gap of a special rod of phononic crystals[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2014, 33(19): 147-151(in Chinese). [13] 舒海生, 董立强, 李世丹, 等. 布拉格型声子晶体弦的横向振动带隙研究[J]. 人工晶体学报, 2013, 42(9): 1918-1923. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2013.09.036SHU H S, DONG L Q, LI S D, et al. Study on the lateral band gap of string of phononic crystals[J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2013, 42(9): 1918-1923(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2013.09.036 [14] 张若军, 肖勇, 温激鸿, 等. 四边固支局域共振型板的低频隔声特性研究[J]. 振动工程学报, 2016, 29(5): 905-912.ZHANG R J, XIAO Y, WEN J H, et al. Analysis of sound transmission through clamped locally resonant plate in low frequency[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2016, 29(5): 905-912(in Chinese). [15] LIU L, HUSSEIN M I. Wave motion in periodic flexural beams and characterization of the transition between bragg scattering and local resonance[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2012, 79(1): 1-17. [16] XIAO Y, WEN J, WANG G, et al. Theoretical and experimental study of locally resonant and bragg band gaps in flexural beams carrying periodic arrays of beam-like resonators[J]. Journal of Vibration and Acoustics, 2013, 135(4): 1-17. [17] DONG Y, YAO H, DU J, et al. Research on local resonance and Bragg scattering coexistence in phononic crystal[J]. Modern Physics Letters B, 2017, 31(11): 1-10. doi: 10.1142/S0217984917501275 [18] CAI C, WANG Z, CHU Y, et al. The phononic band gaps of Bragg scattering and locally resonant pentamode metamaterials[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2017, 50(41): 1-7. [19] LIU Z, ZHANG X, MAO Y, et al. Locally resonant sonic materials[J]. Science, 2000, 289(5485): 1734-1736. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5485.1734 [20] 朱兴一, 钟盛, 叶安珂, 等. 声子晶体禁带特性及局域共振现象的试验研究[J]. 人工晶体学报, 2014(11): 2852-2859. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2014.11.016ZHU X Y, ZHONG S, YE A K, et al. Experimental study on band gap properties and local resonance phenomenon of phononic crystals[J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2014(11): 2852-2859(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2014.11.016 [21] LEE T, IIZUKA H. Bragg scattering based acoustic topological transition controlled by local resonance[J]. Physical Review B, 2019, 99(6): 1-11. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.99.064305 [22] MANCONI E, MACE B. Veering and strong coupling effects in structural dynamics[J]. Journal of Vibration and Acoustics, 2017, 139(2): 1-10. [23] MACE B R, MANCONI E. Wave motion and dispersion phenomena: Veering, locking and strong coupling effects[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2012, 131(2): 1015-1028. doi: 10.1121/1.3672647 [24] THOMPSON D J, FERGUSON N S, YOO J W, et al. Structural waveguide behaviour of a beam-plate system[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2008, 318(1): 206-226. [25] YU D, WEN J, ZHAO H, et al. Vibration reduction by using the idea of phononic crystals in a pipe-conveying fluid[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2008, 318(1): 193-205. [26] LIU J, LI L, FAN Y. A comparison between the friction and piezoelectric synchronized switch dampers for blisks[J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2018, 29(12): 2693-2705. doi: 10.1177/1045389X18778360 [27] LIU J, LI L, HUANG X, et al. Dynamic characteristics of the blisk with synchronized switch damping based on negative capacitor[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2017, 95: 425-445. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2017.03.049 [28] YE G, YAN J, WONG Z J, et al. Optimisation of a piezoelectric system for energy harvesting from traffic vibrations[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2009: 759-762. [29] WANG W, LI L, FAN Y, et al. Piezoelectric transducers for structural health monitoring of joint structures in cylinders: A wave-based design approach[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(3): 1-25. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2964488 [30] LI L, JIANG Z, FAN Y, et al. Coupled band gaps in the piezoelectric composite plate with interconnected electric impedance[C]//ASME 2018 Conference on Smart Materials, Adaptive Structures and Intelligent Systems, 2018: 1-27. [31] MEITZLER A H, BERLINCOURT D, WELSH F S, et al. IEEE standard on piezoelectricity: ANSI/IEEE Std 176-1987[S]. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1988. [32] CHEN S, WANG G, SONG Y. Low-frequency vibration isolation in sandwich plates by piezoelectric shunting arrays[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2016, 25(12): 1-8. [33] WANG G, CHEN S. Large low-frequency vibration attenuation induced by arrays of piezoelectric patches shunted with amplifier-resonator feedback circuits[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2015, 25(1): 1-15. [34] DUHAMEL D, MACE B R, BRENNAN M J. Finite element analysis of the vibrations of waveguides and periodic structures[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2006, 294(1): 205-220. [35] FAN Y, COLLET M, ICHCHOU M, et al. A wave-based design of semi-active piezoelectric composites for broadband vibration control[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2016, 25(5): 1-15. [36] ZHOU C W, LAINÉ J P, ICHCHOU M N, et al. Numerical and experimental investigation on broadband wave propagation features in perforated plates[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2016, 75: 556-575. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2015.12.006 [37] ZHOU C W, LAINÉ J P, ICHCHOU M N, et al. Multi-scale modelling for two-dimensional periodic structures using a combined mode/wave based approach[J]. Computers and Structures, 2015, 154: 145-162. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruc.2015.03.006 [38] BAMPTON M C C, CRAIG J R R. Coupling of substructures for dynamic analyses[J]. AIAA Journal, 1968, 6(7): 1313-1319. doi: 10.2514/3.4741 [39] WILCOX C H. Theory of Bloch waves[J]. Journal d'Analyse Mathématique, 1978, 33(1): 146-167. doi: 10.1007/BF02790171 [40] MING-HUI L U, ZHANG C, FENG L, et al. Negative birefraction of acoustic waves in a sonic crystal[J]. Nature Materials, 2007, 6(10): 744-748. doi: 10.1038/nmat1987 [41] YANG W P, WU L Y, CHEN L W. Refractive and focusing behaviours of tunable sonic crystals with dielectric elastomer cylindrical actuators[J]. Journal of Physics D Applied Physics, 2008, 41(13): 135408. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/41/13/135408 -








 下载:
下载: