Imperialist competitive optimized dual-objective comprehensive decision algorithm for satellite selection
-
摘要:
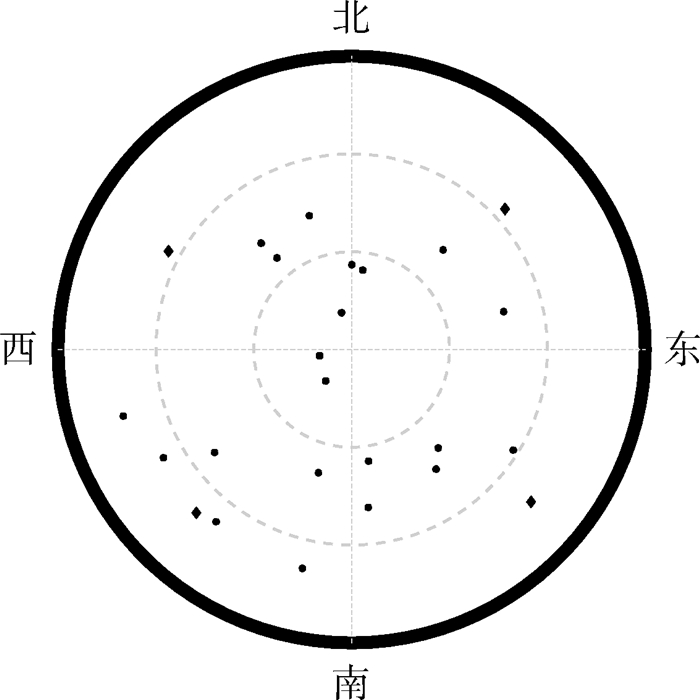
全球卫星导航系统(GNSS)的应用前景已经得到世界各国的普遍承认,其应用领域也趋于多样化,在此背景下,卫星接收机也要求其具有更快的解算速度和可靠的精度。针对目前多数接收机的选星算法都是固定选星数目从而限制算法机动性的问题,提出基于帝国竞争优化算法(ICA)的双目标综合决策选星算法。为了更好获取几何构型较好的卫星星座,引入可见卫星的卫星仰角和方向角先验信息,进行先验性约束,通过构建几何精度因子(GDOP)以及选星数目2个目标,进行综合决策的快速选星,提高了选星的灵活度,并且在满足用户精度的要求下减轻了多星座卫星接收机的计算负担。通过仿真实验和实测数据对双目标综合决策选星算法验证的结果表明:所提算法在高度截止角5°下引入先验性约束条件后平均选星数目在仿真数据和实测数据中缩减率分别为51.8%和45.4%,平均GDOP值较无约束下分别减少0.209 2和0.248 4。同时,所提算法单次选星平均耗时分别为0.168 4 s和0.303 1 s,与遍历法的选星耗时4 s相比,提高了95.79%和92.42%。
-
关键词:
- 全球卫星导航系统(GNSS) /
- 多星座组合导航 /
- 帝国竞争优化算法(ICA) /
- 几何精度因子(GDOP) /
- 选星
Abstract:With the development of Global Navigation Satellite System(GNSS), the prospect of GNSS has been widely recognized in the world. In particular, the positioning solutions with fast and accuracy calculation are essential for the GNSS receiver design. The most of the current satellite selection algorithms in the GNSS receiver fix the number of satellites in advance, which limits the performance of the algorithm. This paper proposes an Imperialist Competitive Algorithm (ICA) for satellite selection. In order to obtain better geometric configuration of satellite constellation, the prior information (elevation and azimuth of visible satellite) is introduced for prior constraint. The Geometric Dilution of Precision (GDOP) and number of satellites are two objectives of the optimization algorithm. Comprehensive decisions are used to quickly select satellites, making the selection of satellites more flexible, as well as reducing the computational burden of multi-constellation satellite receivers. Experiment results based on simulation and field data showed that, after priori constraints are introduced, at elevation angle 5°, the average number of satellites selected by the algorithm proposed in this paper is 51.8% of the maximum visible satellites based on simulation data and the average number of satellites is 45.4% of the maximum visible satellites based on field data. The average GDOP is decreased by 0.209 2 and 0.248 4 compared to the satellite selection without a priori constraint. At the same time, the average calculation time for once satellite selection is about 0.168 4 s and 0.303 1 s, with an improvement of 95.79% and 92.42% compared to the time consumption (i.e. 4 s) of the traversal method.
-
表 1 GPS+GLONASS+BDS下不同选星数目后的最小GDOP
Table 1. Minimum GDOP with different numbers of selected satellites (GPS+GLONASS+BDS)
选星数目/颗 最小GDOP 选星数目/颗 最小GDOP 6 2.477 16 1.717 7 2.277 17 1.692 8 2.146 18 1.673 9 2.026 19 1.658 10 1.954 20 1.643 11 1.898 21 1.631 12 1.855 22 1.620 13 1.819 23 1.612 14 1.781 24 1.607 15 1.747 25(全部) 2.015 表 2 GPS+GLONASS+BDS下选星前后对比分析
Table 2. Comparative analysis before and after satellite selection (GPS+GLONASS+BDS)
高度截止角/(°) 算法 选星数目/颗 GDOP值 最小值 最大值 平均值 最小值 最大值 平均值 5 选星前 24 34 28.777 2 1.051 8 1.752 2 1.341 3 无先验性约束选星后 7 19 11.045 1 1.436 6 2.572 5 1.896 6 先验性约束下选星后 10 22 14.907 7 1.261 4 2.117 1 1.687 4 10 选星前 22 32 26.283 1 1.246 5 2.092 2 1.559 9 无先验性约束选星性 7 17 10.641 2 1.586 9 3.022 6 2.121 2 先验性约束下选星后 10 20 14.092 3 1.471 2 2.516 0 1.916 3 表 3 有/无先验性约束下平均选星数目对比
Table 3. Comparison of average satellite selection number with /without a priori constraint
本文算法 平均选星数目/颗 缩减率/% 选星前 选星后 无先验性约束高度截止角5°下 28.777 2 11.045 1 38.4 先验性约束高度截止角5°下 28.777 2 14.907 7 51.8 表 4 选星前和先验性约束下选星后GDOP差值在各区间下的百分比
Table 4. Percentage of GDOP difference before and after satellite selection with a priori constraint in each interval
高度截止角/(°) GDOP差值在各区间下百分比 差值方差 [0, 0.1) [0.1, 0.2) [0.2, 0.3) [0.3, 0.4) [0.4, 0.5] 5 0 2.29 24.36 48.92 24.427 4 0.005 3 10 0.35 3.05 20.47 44.21 31.92 0.002 7 表 5 截止高度角5°下有/无先验性约束单次选星耗时数据统计
Table 5. Statistics of time consumption for one-time satellite selection with/without prior constraint at an elevation angle of 5°
算法 耗时/s 方差 最小值 最大值 平均值 先验性约束下 0.067 3 0.893 2 0.168 4 0.003 2 无先验性约束 0.158 8 0.931 3 0.412 9 0.012 7 表 6 单次选星平均耗时算法性能比较
Table 6. Comparison of time consumption of one-time satellite selection by candidate algorithms
算法 平均耗时/s 遍历法 4.0 无先验性约束下本文算法 0.412 9 先验性约束下本文算法 0.168 4 表 7 实测数据下选星前后对比分析
Table 7. Comparative analysis before and after satellite selection based on field data
高度截止角/(°) 不同算法 选星数目/颗 GDOP值 最小值 最大值 平均值 最小值 最大值 平均值 5 选星前 20 32 24.743 1 1.361 7 2.715 5 2.060 0 先验性约束下选星后 10 19 11.237 9 1.564 5 3.102 0 2.237 3 先验性无约束选星后 7 18 8.831 5 1.699 3 3.535 9 2.485 7 表 8 实测数据下, 选星前和先验性约束下选星后GDOP差值在各区间下百分比
Table 8. Percentage of GDOP difference before and after satellite selection with a priori constraint in each interval based on field data
高度截止角/(°) GDOP差值在各区间下百分比 差值方差 [-0.4, -0.2) [-0.2, 0) [0, 0.2) [0.2, 0.4) [0.4, 0.5] 5 0.47 17.78 39.67 26.14 15.94 0.032 2 表 9 实测数据下有/无先验性约束单次选星耗时数据统计
Table 9. Statistics of time consumption for one-time satellite selection with/without prior constraint based on field data
高度截止角/(°) 算法 耗时/s 方差 最小值 最大值 平均值 5 先验性约束下 0.086 0 1.169 4 0.303 1 0.005 54 无先验性约束 0.193 8 1.341 0 0.400 8 0.005 15 -
[1] 曹冲. 全球卫星导航系统的最新动向与发展趋势[J]. 卫星与网络, 2010(4): 22-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-965X.2010.04.004CAO C. The latest trends and development trends of global satellite navigation systems[J]. Satellite and Network, 2010(4): 22-25(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-965X.2010.04.004 [2] LI X X, ZHANG X, REN X, et al. Precise positioning with current multi-constellation global navigation satellite systems: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and BeiDou[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1): 1-14. doi: 10.9734/JSRR/2015/14076 [3] 杨丽新, 苏建峰. GPS/北斗组合导航系统的快速选星算法研究[J]. 电子设计工程, 2017, 25(11): 167-169. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6236.2017.11.042YANG L X, SU J F. Research on fast selection algorithm for GPS/BeiDou integrated navigation system[J]. Electronic Design Engineering, 2017, 25(11): 167-169(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6236.2017.11.042 [4] KAPLAN E D, HEGARTY C J. GPS原理与应用[M]. 2版. 寇艳红, 译. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2007: 240-268.KAPLAN E D, HEGARTY C J. Understanding GPS: Principles and applications[M]. 2nd ed. KOU Y H, translated. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2007: 240-268(in Chinese). [5] 白雅庆, 陈栋. 卫星导航几何精度因子的计算及选星方法[J]. 导航, 2006, 42(3): 88-94.BAI Y Q, CHEN D. The calculation of geometric dilution of precision and satellite selection method for satellite navigation[J]. Navigition, 2006, 42(3): 88-94(in Chinese). [6] MOSAVI M R, DIVBAND M. Calculation of geometric dilution of precision using adaptive filtering technique based on evolutionary algorithms[C]//International Conference on Electrical and Control Engineering. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 4842-4845. [7] 王尔申, 贾超颖, 曲萍萍, 等. 基于混沌粒子群优化的北斗/GPS组合导航选星算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(2): 36-42. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0281WANG E S, JIA C Y, QU P P, et al. BDS/GPS integrated navigation satellite selection algorithm based on chaos particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(2): 36-42(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0281 [8] 霍航宇, 张晓林. 组合卫星导航系统的快速选星方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2015, 41(2): 273-282. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2014.0138HUO H Y, ZHANG X L. Fast satellite selection method for integrated navigation systems[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2015, 41(2): 273-282(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2014.0138 [9] AZAMI H, SANEI S. GPS GDOP classification via improved neural network trainings and principal component analysis[J]. International Journal of Electronics, 2014, 101(9): 1300-1313. doi: 10.1080/00207217.2013.832390 [10] 宋丹, 许承东, 胡春生, 等. 基于遗传算法的多星座选星方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2015, 36(3): 300-308. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2015.03.008SONG D, XU C D, HU C S, et al. Satellite selection with gen-etic algorithm under multi-constellation[J]. Journal of Astrona-utics, 2015, 36(3): 300-308(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2015.03.008 [11] WU C H, SU W H, HO Y W. A study on GPS GDOP approximation using support-vector machines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2011, 60(1): 137-145. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2010.2049228 [12] 刘季, 张小红, 徐运. GPS/GLONASS组合单点定位中选星算法的研究[J]. 测绘信息与工程, 2012, 37(2): 8-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHXG201202003.htmLIU J, ZHANG X H, XU Y. Satellite selection algorithm for combined GPS and GLONASS single point positioning[J]. Journal of Geomatics, 2012, 37(2): 8-10(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHXG201202003.htm [13] 徐小钧, 马利华, 艾国祥. 基于多目标遗传算法的多星座选星方法[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2017, 51(12): 1520-1528. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHJT201712016.htmXU X J, MA L H, AI G X. Satellite selection with multi-obje-ctive genetic algorithm for multi-GNSS constellations[J]. Jour-nal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2017, 51(12): 1520-1528(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHJT201712016.htm [14] 徐小钧, 马利华, 艾国祥. 基于NSGA-Ⅱ算法的多目标快速选星方法[J]. 天文研究与技术, 2018, 15(3): 292-301. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTWT201803006.htmXU X J, MA L H, AI G X. Multi-objective and fast satellite selection method based on the NSGA-Ⅱ algorithm[J]. Astronomical Research and Technology, 2018, 15(3): 292-301(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTWT201803006.htm [15] 郭婉青, 叶东毅. 帝国竞争算法的进化优化[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2014, 8(4): 473-482. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTS201404010.htmGUO W Q, YE D Y. Evolutionary optimization of imperialist competitive algorithm[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology, 2014, 8(4): 473-482(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTS201404010.htm [16] 孙丽, 王珂, 孟广伟, 等. 基于帝国竞争算法的车架优化[J]. 汽车工程学报, 2013, 3(6): 427-432. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1469.2013.06.06SUN L, WANG K, MENG G W, et al. Optimization of a truck frame based on imperialist competitive algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Automotive Engineering, 2013, 3(6): 427-432(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1469.2013.06.06 [17] 刘帅, 赵国荣, 高超, 等. GPS/北斗组合卫星导航系统快速选星算法[J]. 电光与控制, 2017, 24(3): 36-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGKQ201703012.htmLIU S, ZHAO G R, GAO C, et al. A fast satellite selection algorithm for GPS/BDS integrated navigation system[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2017, 24(3): 36-39(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGKQ201703012.htm -







 下载:
下载: