-
摘要:
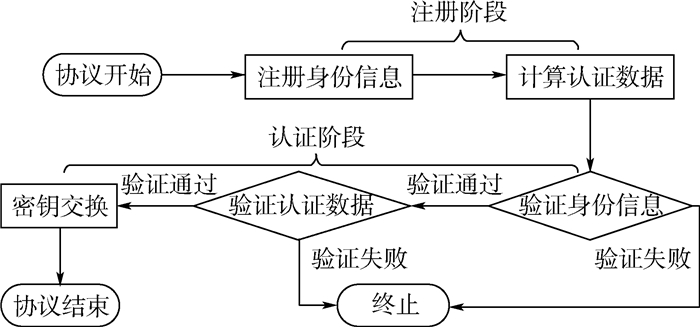
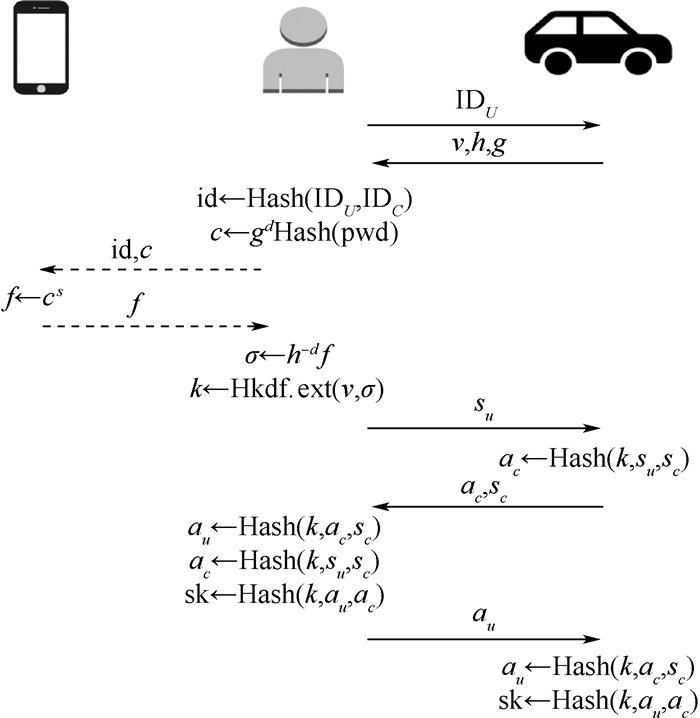
车联网的快速发展促进了电子车钥匙的研发,为解决基于智能手机的电子车钥匙与车锁之间的通信安全问题,提出了电子车钥匙场景下的安全模型和口令认证密钥交换协议。所提协议通过智能手机的协助,完成车钥匙与车锁之间的认证,即使智能手机被恶意代码侵袭或者丢失,所提协议也能保护用户的隐私。在安全模型下进行的安全性证明和性能分析表明,所提协议能够抵御字典攻击、中间人攻击、重放攻击、用户伪装攻击、内部攻击等。在计算消耗方面,所提协议性能优于同类型其他协议,减少了50.7%的计算消耗总量。
Abstract:The rapid development of Internet of vehicles has promoted the research and development of digital key. In order to solve the communication security problem between digital key and car locks, a security model and password authentication key exchange protocol are proposed. The protocol completes the authentication between the digital key and the car lock through the assistance of the smartphone. Even if the smartphone is attacked by malicious code or is lost, the protocol can protect the privacy of the user. The security proof and performance analysis of the protocol under the security model show that the protocol can resist dictionary attacks, man-in-the-middle attacks, replay attacks, malicious code attacks, disguise attacks, internal attacks, etc. The performance of this protocol in computing consumption is better than that of other protocols of the same type, reducing the total computing consumption by 50.7%.
-
表 1 DK-PAKE协议的初始化定义
Table 1. Initial definition of DK-PAKE protocol
对象 描述 G 阶为素数P的循环群 g G的生成元 pwd 用户口令 Hash() 哈希函数 Hkdf() 密钥派生函数,分为加密和解密2部分 IDU 用户的身份信息 IDC 汽车的身份信息 -
[1] BELLOVIN S M, METTITT M. Encrypted key exchange: Password-based protocols secure against dictionary attacks[C]//Proceedings 1992 IEEE Computer Society Symposium on Research in Security and Privacy. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1992: 72-84. [2] WANG D, WANG N, WANG P, et al. Preserving privacy for free: Efficient and provably secure two-factor authentication scheme with user anonymity[J]. Information Sciences, 2015, 321: 162-178. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2015.03.070 [3] XIE Q, WONG D, WANG G, et al. Provably secure dynamic ID-based anonymous two-factor authenticated key exchange protocol with extended security model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2017, 12(6): 1382-1392. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2017.2659640 [4] LI X, YANG D, ZENG X, et al. Comments on "Provably secure dynamic ID-based anonymous two-factor authenticated key exchange protocol with extended security model"[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2019, 14(12): 3344-3345. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2018.2866304 [5] REDDY A, YOON E, DAS A, et al. Design of mutually authenticated key agreement protocol resistant to impersonation attacks for multi-server environment[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 3622-3639. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2666258 [6] LI W, LI X, GAO J, et al. Design of secure authenticated key management protocol for cloud computing environments[J/OL]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2019(2019-04-09)[2020-05-26]. https: //ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8684256. [7] XIAO L, DENG Y, BEN C, et al. Two-factor authentication key agreement protocol based on biometric feature and password[J]. Journal on Communications, 2017, 38(7): 89-95. [8] DHILLON P, KALRA S. Lightweight biometrics based remote user authentication scheme for IoT services[J]. Journal of Information Security and Applications, 2017, 34(Part2): 255-270. [9] CHEN C, XU L, FANG W, et al. A three-party password authenticated key exchange protocol resistant to stolen smart card attacks[J]. Advances in Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing, 2017, 63: 331-336. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50209-0_40 [10] OM H, BANERIEE S. A password authentication method for remote users based on smart card and biometrics[J]. Journal of Discrete Mathematical Sciences and Cryptography, 2017, 20(3): 595-610. doi: 10.1080/09720529.2013.876780 [11] CHALLA S, DAS A, ODELU V, et al. An efficient ECC-based provably secure three-factor user authentication and key agreement protocol for wireless healthcare sensor networks[J]. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 2017, 69: 534-554. [12] LI X, NIU J, KUMARI S, et al. A three-factor anonymous authentication scheme for wireless sensor networks in internet of things environments[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2018, 103: 194-204. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2017.07.001 [13] WAZID M, DAS A, ODELU V, et al. Design of secure user authenticated key management protocol for generic IoT networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(1): 269-282. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2780232 [14] DAMMAK M, BOUDIA O, MESSOUS M, et al. Token-based lightweight authentication to secure IoT networks[C]//Proceedings 2019 16th IEEE Annual Consumer Communications & Networking Conference (CCNC). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1-4. [15] 董晓露, 黎妹红, 杜晔, 等. 基于切比雪夫混沌映射和生物识别的身份认证方案[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(5): 1052-1058. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0512DONG X L, LI M H, DU Y, et al. A biometric verification based authentication scheme using Chebyshev chaotic mapping[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(5): 1052-1058(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0512 [16] TAHER B, JIANG S, YASSIN A, et al. Low-overhead remote user authentication protocol for IoT based on a fuzzy extractor and feature extraction[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 148950-148966. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2946400 [17] 安迪, 杨超, 姜奇. 一种新的基于指纹与移动端协助的口令认证方法[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2016, 53(10): 2400-2411. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2016.20160439AN D, YANG C, JIANG Q. A new password authentication method based on fingerprint and mobile phone assistance[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2016, 53(10): 2400-2411(in Chinese). doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2016.20160439 [18] ZHANG R, XIAO Y, SUN S, et al. Efficient multi-factor authenticated key exchange scheme for mobile communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2019, 16(4): 625-634. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2017.2700305 [19] ARSHAD H, NIKOOGHADAM M. An efficient and secure authentication and key agreement scheme for session initiation protocol using ECC[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2016, 75(1): 181-197. doi: 10.1007/s11042-014-2282-x [20] LIN H, WEN F, DU C. An anonymous and secure authentication and key agreement scheme for session initiation protocol[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2017, 76(2): 2315-2329. doi: 10.1007/s11042-015-3220-2 [21] SRINIVAS J, DAS A, WAZID M, et al. Anonymous lightweight chaotic map-based authenticated key agreement protocol for industrial internet of things[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2020, 17(6): 1133-1146. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2018.2857811 [22] CHALLA S, WAZID M, DAS A, et al. Secure signature-based authenticated key establishment scheme for future IoT application[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 3028-3043. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2676119 [23] HE J, YANG Z, ZHANG J. On the security of a provably secure, efficient, and flexible authentication scheme for ad hoc wireless sensor networks[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2018, 14(1): 155014771875631. doi: 10.1177/1550147718756311 [24] MA M, HE D, WANG H, et al. An efficient and provably secure authenticated key agreement protocol for fog-based vehicular Ad-Hoc networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(5): 8065-8075. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2902840 [25] LYU Q, ZHENG N, LIU H, et al. Remotely access 'my' smart home in private: An anti-tracking authentication and key agreement scheme[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 41835-41851. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2907602 -








 下载:
下载: