-
摘要:
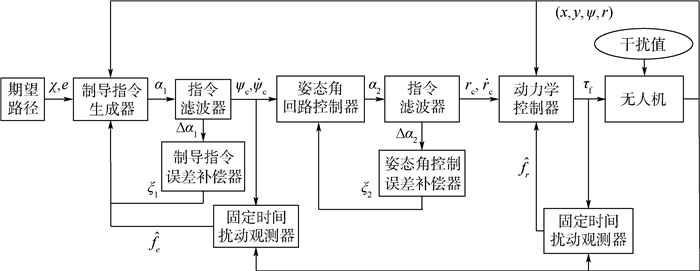
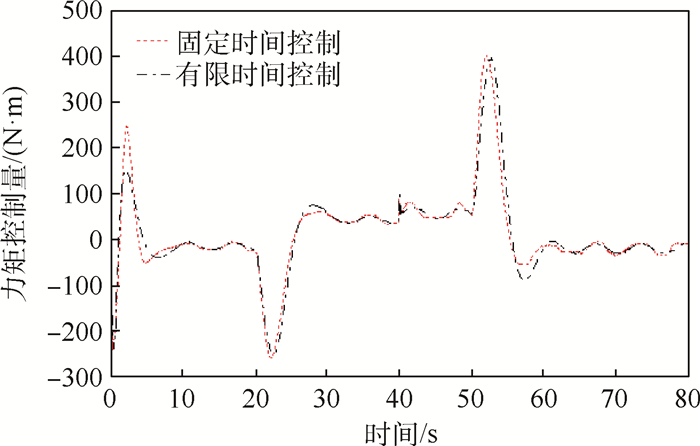
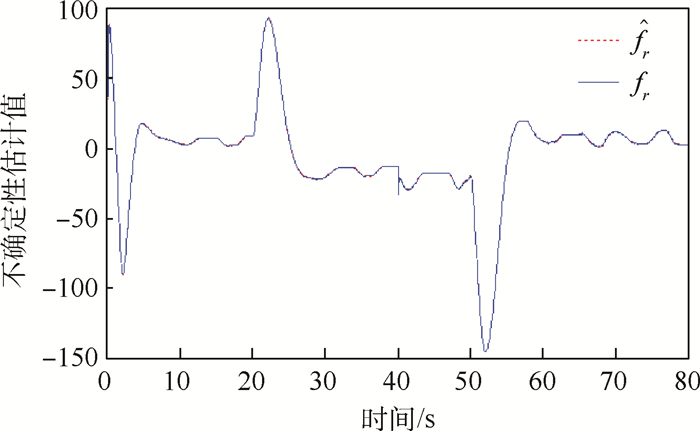
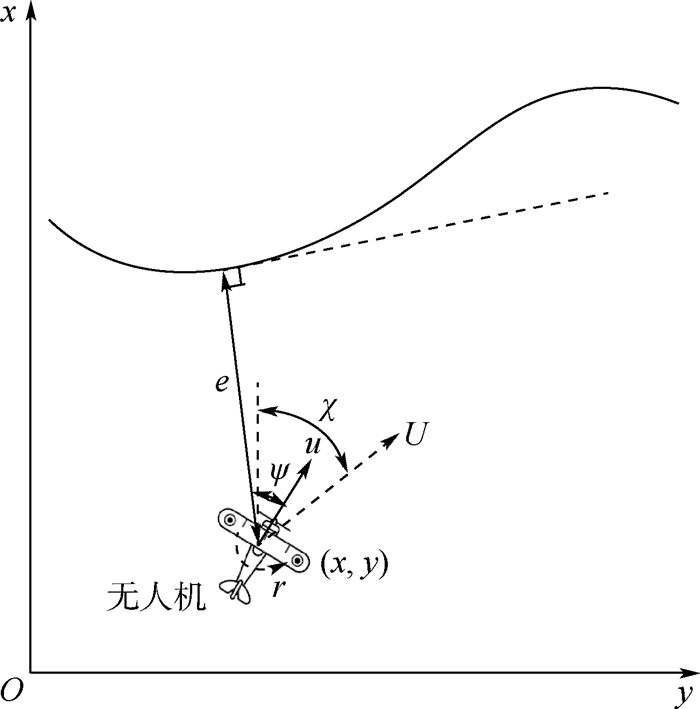
针对无人机存在外部环境干扰及执行机构故障情况下的固定时间路径跟踪容错制导控制进行研究,提出了固定时间收敛的视线制导控制算法,利用反步法及固定时间收敛的视线制导控制算法确保无人机路径跟踪误差在固定时间内收敛。通过在视线制导控制算法中引入指令滤波器及误差补偿器,避免反步法中虚拟控制量微分项的复杂计算。为了抑制制导控制过程中系统状态剧烈变化,引入障碍李雅普诺夫函数对偏航角速度误差进行限制。通过非线性固定时间观测器对不确定性进行估计补偿,消除执行机构故障及外部环境干扰等因素对跟踪性能的影响。仿真结果表明:所提算法具备有效性和鲁棒性,具有良好的路径跟踪容错制导控制性能。
Abstract:A fault-tolerant fixed-timepath following guidance control method for the UAVs subject to thedisturbancesand actuator faults is studied. Both backstepping and fixed-time convergence techniques are employed for developing the line-of-sight path following control strategies to guarantee the convergence of the UAV to its reference trajectory in fixed time with elegant transient performance. Command filters and auxiliary systems are introduced in the guidance control algorithms design to avoid the arduous calculation of derivatives of virtual control terms in backstepping. To address turning rates constraints of the UAV, the barrier Lyapunov functions are incorporated with the control scheme to prevent the drastic change of the guidance control system states. A nonlinear fixed-time observer is designed for estimating complex unknown external disturbances and eliminating the actuator faults and the influence of external environment disturbance on following performance. Simulation results show the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed line-of-sight path following guidance control algorithm, and it has good path following fault-tolerant control performance.
-
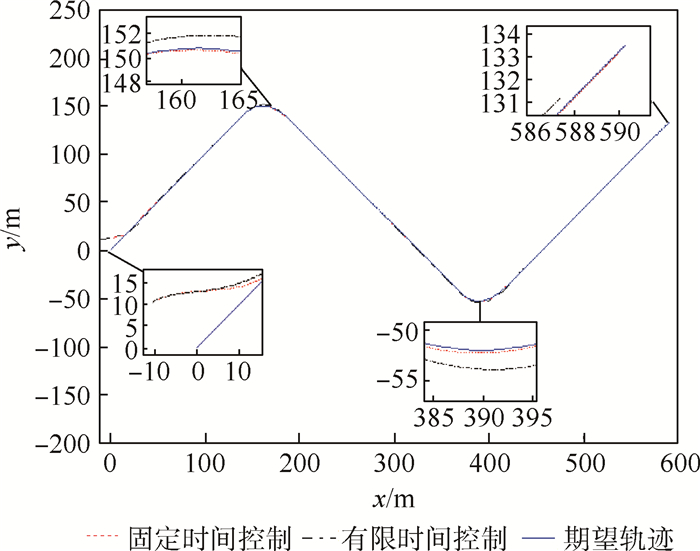
表 1 100次仿真统计结果
Table 1. Statistic results of 100 simulations
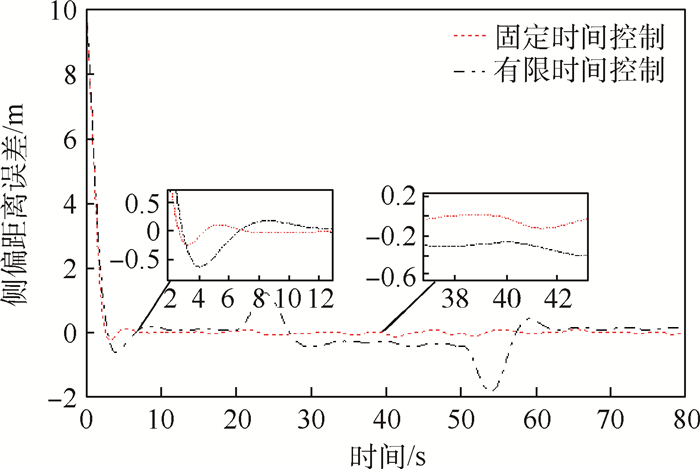
控制算法 收敛时间均值/s 收敛时间方差 固定时间控制算法 7.72 0.003 有限时间控制算法 12.32 1.394 -
[1] BERNARD M, KONDAK K, MAZA I, et al. Autonomous transportation and deployment with aerial robots for search and rescue missions[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2011, 28(6): 914-931. doi: 10.1002/rob.20401 [2] METNI N, HAMEL T. A UAV for bridge inspection: Visual servoing control law with orientation limits[J]. Automation in Construction, 2007, 17(1): 3-10. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2006.12.010 [3] MAZA I, KONDAK K, BERNARD M, et al. Multi-UAV cooperation and control for load transportation and deployment[C]//The 2nd International Symposium on UAVs. Berlin: Springer, 2009: 417-449. [4] ESCAREÑ J, SALAZAR S, ROMERO H, et al. Trajectory control of a quadrotor subject to 2D wind disturbances[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2013, 70(1-4): 51-63. doi: 10.1007/s10846-012-9734-1 [5] MELLINGER D, MICHAEL N, KUMAR V. Trajectory generation and control for precise aggressive maneuvers with quadrotors[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2012, 31(5): 664-674. doi: 10.1177/0278364911434236 [6] MICHAEL N, FINK J, KUMAR V. Cooperative manipulation and transportation with aerial robots[J]. Autonomous Robots, 2011, 30(1): 73-86. doi: 10.1007/s10514-010-9205-0 [7] RYSDYK R. UAV path following for constant line-of-sight[C]//2nd AIAA "Unmanned Unlimited" Conference and Workshop & Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 2003: 6626. [8] SUJIT P B, SARIPALLI S, SOUSA J B. Unmanned aerial vehicle path following: A survey and analysis of algorithms for fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicless[J]. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 2014, 34(1): 42-59. doi: 10.1109/MCS.2013.2287568 [9] RUBÍ B, PÉREZ R, MORCEGO B. A survey of path following control strategies for UAVs focused on quadrotors[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2019, 98(8): 1-25. [10] ZHAO S, WANG X, ZHANG D, et al. Model predictive control based integral line-of-sight curved path following for unmanned aerial vehicle[C]//AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2017: 1511. [11] FOSSEN T I, PETTERSEN K Y. On uniform semiglobal exponential stability (USGES) of proportional line-of-sight guidance laws[J]. Automatica, 2014, 50(11): 2912-2917. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.10.018 [12] FOSSEN T I, PETTERSEN K Y, GALEAZZI R. Line-of-sight path following for dubins paths with adaptive sideslip compensation of drift forces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2014, 23(2): 820-827. [13] CUI Z, WANG Y. Nonlinear adaptive line-of-sight path following control of unmanned aerial vehicles considering sideslip amendment and system constraints[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2020(5): 1-11. [14] POLYAKOV A. Nonlinear feedback design for fixed-time stabilization of linear control systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2011, 57(8): 2106-2110. [15] 李锋, 叶川, 李广佳, 等. 临近空间太阳能飞行器横航向稳定性[J]. 航空学报, 2016, 37(4): 1148-1158.LI F, YE C, LI G J, et al. Lateral-directional stability of near-space solar-powered aircraft[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2016, 37(4): 1148-1158(in Chinese). [16] 马东立, 张良, 杨穆清, 等. 超长航时太阳能无人机关键技术综述[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(3): 29-58.MA D L, ZHANG L, YANG M Q, et al. Review of key technologies of ultra-long-endurance solar powered unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(3): 29-58(in Chinese). [17] YAN X G, EDWARDS C. Nonlinear robust fault reconstruction and estimation using a sliding mode observer[J]. Automatica, 2007, 43(9): 1605-1614. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2007.02.008 [18] TAN C P, EDWARDS C. Sliding mode observers for detection and reconstruction of sensor faults[J]. Automatica, 2002, 38(10): 1815-1821. doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(02)00098-5 [19] ZHAO L, ZHANG B, YANG H, et al. Finite-time tracking control for pneumatic servo system via extended state observer[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2017, 11(16): 2808-2816. [20] BASIN M, PANATHULA C B, SHTESSEL Y. Multivariable continuous fixed-time second-order sliding mode control: Design and convergence time estimation[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2016, 11(8): 1104-1111. doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2016.0572 [21] CUI R, GE S S, HOW B V, et al. Leader-follower formation control of underactuated autonomous underwater vehicles[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2010, 37(17): 1491-1502. [22] ZHANG Y, HUA C, LI K. Disturbance observer-based fixed-time prescribed performance tracking control for robotic manipulator[J]. International Journal of Systems Science, 2019, 50(13): 2437-2448. doi: 10.1080/00207721.2019.1622818 [23] FORSSELL L, NILSSON U. ADMIRE the aero-data model in a research environment version 4.0, model description: FOI-R-1624-SE[R]. Stockholm: FOI, 2005. -







 下载:
下载: