A geomagnetic reference map reconstruction method based on sparse representation and dictionary learning
-
摘要:
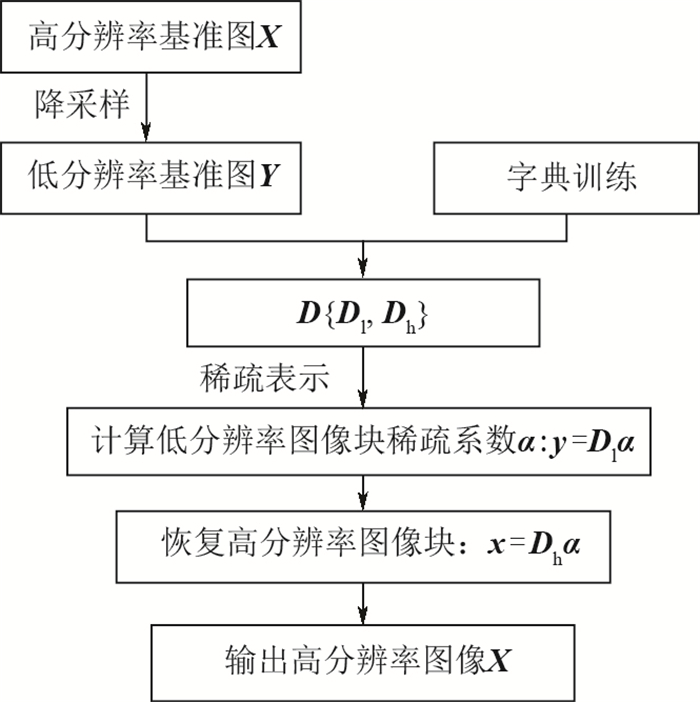
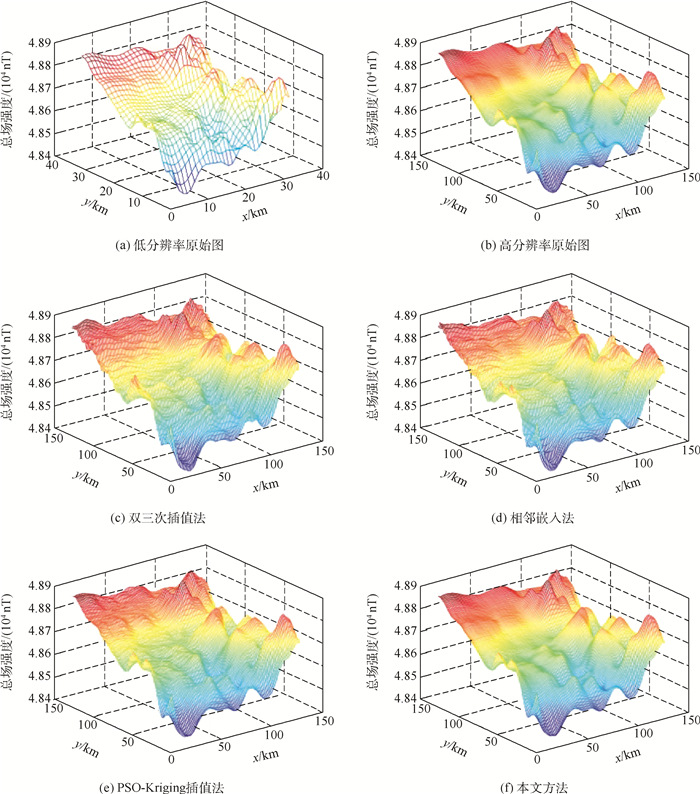
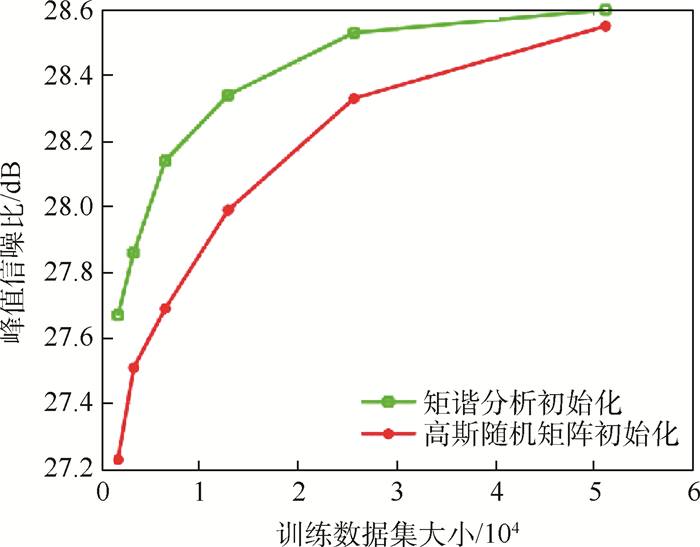
地磁匹配导航在导航制导领域具有重要作用,地磁基准图的构建精度决定了地磁匹配导航的有效性。针对现有地磁基准图构建精度难以满足实际应用需求的问题,提出了基于稀疏表示和字典学习的高精度地磁基准图构建方法。首先,利用矩谐分析(RHA)进行稀疏字典的初始化;其次,利用K-SVD算法对稀疏字典进行训练;最后,利用低分辨率和高分辨率基准图具有相同稀疏系数的特点重建高分辨率地磁基准图。实验结果表明:所提方法对地磁基准图具有更高的构建精度,对训练所需的数据集有更低的需求,同时对噪声有更好的鲁棒性。与PSO-Kriging插值法相比,在4倍放大倍数下峰值信噪比(PSNR)由26.31 dB提高至26.73 dB,结构相似度(SSIM)由0.498提高至0.524,均方根误差(RMSE)由14.96 nT减小至13.78 nT。
Abstract:Geomagnetic matching navigation plays an important role in the field of navigation guidance. The construction accuracy of geomagnetic reference map determines the effectiveness of geomagnetic matching navigation. Aimed at the problem that the existing geomagnetic reference map construction accuracy is difficult to meet the needs of practical applications, a high-precision geomagnetic reference map construction method based on sparse representation and dictionary learning is proposed. First, the sparse dictionary is initialized using Rectangular Harmonic Analysis (RHA). Then, K-SVD is used to train the sparse dictionaries. Finally, the feature that the low-resolution and high-resolution reference maps have the same sparse coefficients is used to reconstruct the high-resolution geomagnetic reference maps. Experimental results show that the proposed method has higher construction accuracy for geomagnetic reference maps, lower requirements for training datasets, and better robustness to noise. Compared with the PSO-Kriging interpolation method, with a magnification factor of 4, the Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR) value is increased from 26.31 dB to 26.73 dB; the Structural Similarity Index (SSIM) is increased from 0.498 to 0.524; the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) is decreased from 14.96 nT to 13.78 nT.
-
表 1 二倍放大倍数下不同方法PSNR、SSIM和RMSE指标对比
Table 1. Comparison of PSNR, SSIM and RMSE of different methods with magnification factor 2
方法 PSNR/dB SSIM RMSE/nT 双三次插值法 32.16 0.789 3.07 相邻嵌入法 32.14 0.787 3.12 PSO-Kriging插值法 32.31 0.796 2.89 本文方法 32.44 0.823 2.77 表 2 三倍放大倍数下不同方法PSNR、SSIM和RMSE指标对比
Table 2. Comparison of PSNR, SSIM and RMSE of different methods with magnification factor 3
方法 PSNR/dB SSIM RMSE/nT 双三次插值法 27.66 0.565 7.65 相邻嵌入法 27.59 0.561 7.83 PSO-Kriging插值法 28.28 0.606 7.23 本文方法 28.54 0.637 6.91 表 3 四倍放大倍数下不同方法PSNR、SSIM和RMSE指标对比
Table 3. Comparison of PSNR, SSIM and RMSE of different methods with magnification factor 4
方法 PSNR/dB SSIM RMSE/nT 双三次插值法 24.89 0.431 16.77 相邻嵌入法 24.81 0.435 16.47 PSO-Kriging插值法 26.31 0.498 14.96 本文方法 26.73 0.524 13.78 表 4 不同噪声等级下各种方法PSNR值对比
Table 4. Comparison of PSNR of different methods under different noise levels
方法 PSNR/dB σ=0 σ=3 σ=6 σ=9 σ=12 双三次插值法 28.89 28.80 28.45 28.17 27.74 相邻嵌入法 28.84 28.73 28.47 28.13 27.86 PSO-Kriging插值法 29.35 29.30 29.21 29.11 28.97 本文方法 29.78 29.76 29.73 29.69 29.67 表 5 不同噪声等级下各种方法SSIM值对比
Table 5. Comparison of SSIM of different methods under different noise levels
方法 SSIM σ=0 σ=3 σ=6 σ=9 σ=12 双三次插值法 0.603 0.587 0.573 0.551 0.533 相邻嵌入法 0.599 0.584 0.571 0.555 0.541 PSO-Kriging插值法 0.637 0.626 0.611 0.597 0.581 本文方法 0.664 0.661 0.659 0.658 0.654 表 6 不同噪声等级下各种方法RMSE值对比
Table 6. Comparison of RMSE of different methods under different noise levels
方法 RMSE/nT σ=0 σ=3 σ=6 σ=9 σ=12 双三次插值法 9.72 9.83 9.96 10.14 10.30 相邻嵌入法 9.81 9.89 9.99 10.12 10.24 PSO-Kriging插值法 9.11 9.20 9.31 9.44 9.61 本文方法 8.77 8.82 8.85 8.89 8.95 -
[1] HOLLAND R A, THORUP K, VONHOF M J, et al. Navigation: Bat orientation using Earth's magnetic field[J]. Nature, 2006, 444(7120): 702. doi: 10.1038/444702a [2] ECKENHOFF K, GENEVA P, HUANG G. Direct visual-inertial navigation with analytical preintegration[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1429-1435. [3] CUNTZ M, KONOVALTSEV A, MEURER M. Concepts, development and validation of multi-antenna GNSS receivers for resilient navigation[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2016, 104(6): 1-14. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2016.2566740 [4] LOHMANN K J, LOHMANN C M F, EHRHART L M, et al. Geomagnetic map used in seaturtle navigation[J]. Nature, 2004, 428(6986): 909-910. doi: 10.1038/428909a [5] 岳建平, 甄宗坤, 基于粒子群算法的Kriging插值在区域地面沉降中的应用[J]. 测绘通报, 2012(3): 59-62.YUE J P, ZHEN Z K. Application of particle swarm optimization based Kriging interpolation method in regional land subsidence[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2012(3): 59-62(in Chinese). [6] 李晨霖, 王仕成, 张金生, 等. 基于改进的Kriging插值方法构建地磁基准图[J]. 计算机仿真, 2018, 35(12): 278-282.LI C L, WANG S C, ZHANG J S, et al. Construction of geomagnetic datum map based on improved Kriging interpolation method[J]. Computer Simulation, 2018, 35(12): 278-282(in Chinese). [7] GOLDENBERG F. Geomagnetic navigation beyond the magnetic compass[C]//Position, Location & Navigation Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2006: 684-694. [8] AKESSON S, LUSCHI P, BRODERICK A C. Oceanic long-distance navigation: Do experienced migrants use the Earth's magnetic field [J]. Journal of Navigation, 2001, 54(3): 415-427. [9] LIN Y, YAN L, TONG Q. Underwater geomagnetic navigation based on ICP algorithm[C]//IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2008: 2115-2120. [10] CAI Q, YANG G, SONG N, et al. Analysis and calibration of the gyro bias caused by geomagnetic field in a dual-axis rotational inertial navigation system[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2016, 27(10): 105001. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/27/10/105001 [11] LIU M, LIU K, YANG P, et al. Bio-inspired navigation based on geomagnetic[C]//IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 2339-2344. [12] GAO X, ZHANG K, TAO D, et al. Image super-resolution with sparse neighbor embedding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(7): 3194-3205. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2190080 [13] WANG G, LI L, LI Q. Perceptual evaluation of single-image super-resolution reconstruction[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing(ICIP). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 3145-3149. [14] ROMANO Y, ISIDORO J, MILANFAR P. RAISR: Rapid and accurate image super resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2016, 3(1): 110-125. [15] YEGANLI F, NAZZAL M, UNAL M, et al. Image super-resolution via sparse representation over multiple learned dictionaries based on edge sharpness[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2016, 10(3): 535-542. doi: 10.1007/s11760-015-0771-7 [16] VILLENA S, VEGA M, BABACAN S D, et al. Bayesian combination of sparse and non-sparse priors in image super resolution[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2013, 23(2): 530-541. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2012.10.002 [17] LIU D, WANG Z, WEN B, et al. Robust single image super-resolution via deep networks with sparse prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(7): 1. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2585779 [18] LEDIG C, THEIS L, HUSZAR F, et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network[EB/OL]. (2017-05-25)[2020-05-28]. [19] FARHADIFARD F, ABAR E, NAZZAL M, et al. Single image super resolution based on sparse representation via directionally structured dictionaries[C]//Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 1718-1721. [20] QI N, SHI Y, SUN X, et al. Single image super-resolution via 2D sparse representation[C]//2015 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1-6. [21] 乔玉坤, 王仕成, 张金生, 等. 采用矩谐分析和支持向量机的地磁导航基准图构建方[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2010, 44(10): 47-51.QIAO Y K, WANG S C, ZHANG J S, et al. A constructing method of reference maps for geomagnetic navigation using rectangular harmonic analysis and support vector machine[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2010, 44(10): 47-51(in Chinese). [22] YANG S, WANG M, CHEN Y, et al. Single-image super-resolution reconstruction via learned geometric dictionaries and clustered sparse coding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(9): 4016-4028. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2201491 [23] ZHANG Y, LIU Y. Single image super-resolution reconstruction method based on LC-KSVD algorithm[C]//1st International Conference on Materials Science, Energy Technology, Power Engineering(MEP 2017), 2017: 1-6. [24] YANG J, WRIGHT J, HUANG T S, et al. Image super-resolution as sparse representation of raw image patches[C]//2008 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2008: 1-8. [25] MOUSAVI H, MONGA V. Sparsity-based color image super resolution via exploiting cross channel constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(11): 5094-5106. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2704443 -








 下载:
下载: