A geomagnetic reference map construction method based on convolutional neural network
-
摘要:
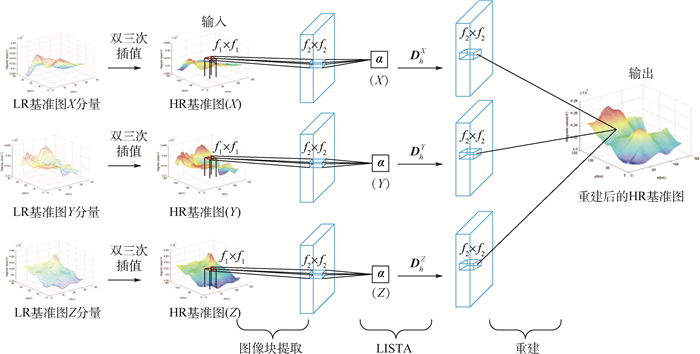
地磁匹配导航技术是一种重要的辅助导航制导方法,地磁基准图的构建精度对地磁匹配制导的精准度起着决定性作用。针对现有地磁基准图构建精度难以满足实际地磁匹配导航需求的问题,提出了一种基于卷积神经网络的地磁基准图构建方法。首先,利用卷积层提取低分辨率基准图中的特征图像块;然后,利用基于学习的阈值收缩算法(LISTA)实现图像块的稀疏表示;最后,利用三通道的地磁信息得到重建后的高分辨率基准图。实验结果表明:所提方法对地磁基准图具有更高的构建精度,同时对噪声有更好的鲁棒性,各种客观评价指标均高于现有的超分辨率重建方法。
Abstract:Geomagnetic matching navigation technology is an important auxiliary navigation guidance method. The construction accuracy of geomagnetic reference map plays a decisive role in the accuracy of geomagnetic matching guidance. Aimed at the problem that the construction accuracy of the existing geomagnetic reference maps is difficult to meet the actual requirements of geomagnetic matching navigation, a construction method of geomagnetic reference maps based on convolutional neural network is proposed. First, the convolutional layer is used to extract the feature image patches in the low-resolution reference image. Then, the Learned Iterative Shrinkage and Thresholding Algorithm (LISTA) is used to realize the sparse representation of the low-resolution image patches. Finally, the three-channel geomagnetic information is used to obtain the final reconstructed high-resolution reference map. The experimental results show that the proposed method has a higher construction accuracy for geomagnetic reference map and better robustness to noise. Various objective evaluation indexes of the proposed method are higher than those of the existing super-resolution reconstruction algorithms.
-
表 1 2倍放大下不同方法PSNR、SSIM和RMSE指标对比
Table 1. Comparison of PSNR, SSIM and RMSE of different methods with magnification factor 2
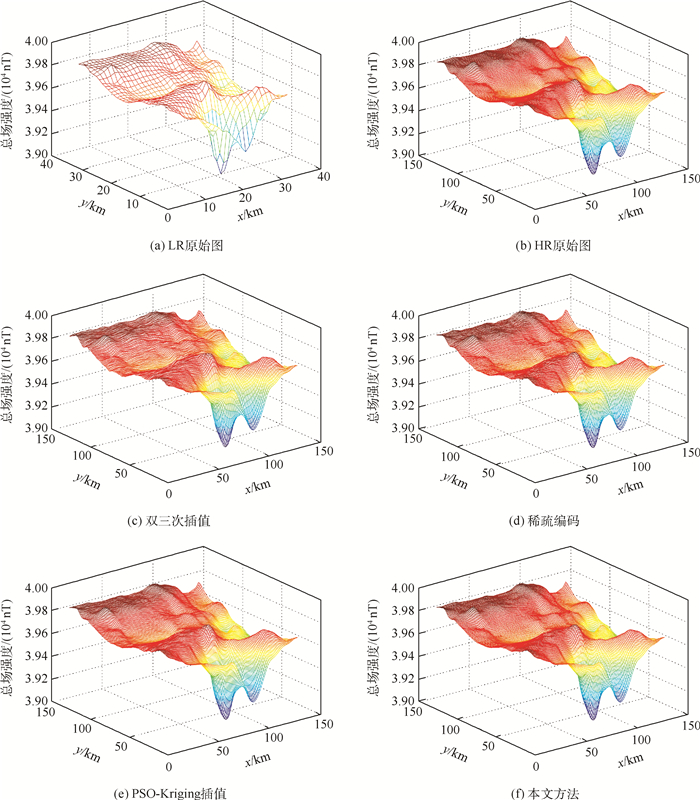
方法 PSNR/dB SSIM RMSE/nT 双三次插值 30.56 0.801 3.02 稀疏编码 31.51 0.835 3.82 PSO-Kriging 31.44 0.831 2.93 本文方法 31.67 0.847 2.77 表 2 3倍放大下不同方法PSNR、SSIM和RMSE指标对比
Table 2. Comparison of PSNR, SSIM and RMSE of different methods with magnification factor 3
方法 PSNR/dB SSIM RMSE/nT 双三次插值 27.66 0.571 8.19 稀疏编码 28.39 0.634 7.62 PSO-Kriging 28.18 0.623 7.88 本文方法 28.64 0.664 7.31 表 3 4倍放大倍数下不同方法PSNR、SSIM和RMSE指标对比
Table 3. Comparison of PSNR, SSIM and RMSE of different methods with magnification factor 4
方法 PSNR/dB SSIM RMSE/nT 双三次插值 25.13 0.446 15.47 稀疏编码 26.12 0.508 12.87 PSO-Kriging 25.99 0.501 13.45 本文方法 26.55 0.561 12.11 表 4 不同噪声等级下各种方法PSNR值对比
Table 4. Comparison of PSNR of different methods under different noise levels
方法 PSNR/dB σ=0 σ=5 σ=10 σ=15 σ=20 稀疏编码 28.39 28.31 28.22 28.13 28.05 SRCNN 28.44 28.34 28.22 28.13 28.02 PSO-Kriging 28.18 28.09 28.01 27.94 27.85 本文方法 28.64 28.58 28.52 28.48 28.44 表 5 不同噪声等级下各种方法SSIM值对比
Table 5. Comparison of SSIM of different methods under different noise levels
方法 SSIM σ=0 σ=5 σ=10 σ=15 σ=20 稀疏编码 0.634 0.629 0.623 0.616 0.609 SRCNN 0.642 0.634 0.627 0.620 0.611 PSO-Kriging 0.623 0.614 0.606 0.599 0.589 本文方法 0.664 0.661 0.657 0.652 0.648 表 6 不同噪声等级下各种方法RMSE值对比
Table 6. Comparison of RMSE of different methods under different noise levels
方法 RMSE/nT σ=0 σ=5 σ=10 σ=15 σ=20 稀疏编码 7.62 7.69 7.77 7.84 7.92 SRCNN 7.45 7.58 7.69 7.78 7.89 PSO-Kriging 7.88 7.97 8.11 8.23 8.35 本文方法 7.31 7.37 7.42 7.47 7.55 -
[1] HOLLAND R A, THORUP K, VONHOF M J, et al. Bat orientation using Earth's magnetic field[J]. Nature, 2006, 444(7120): 702. doi: 10.1038/444702a [2] ECKENHOFF K, GENEVA P, HUANG G Q. Direct visual-inertial navigation with analytical preintegration[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1429-1435. [3] CUNTZ M, KONOVALTSEV A, MEURER M. Concepts, development, and validation of multiantenna GNSS receivers for resilient navigation[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2016, 104(6): 1288-1301. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2016.2525764 [4] LOHMANN K J, LOHMANN C M F, EHRHART L M, et al. Geomagnetic map used in sea-turtle navigation[J]. Nature, 2004, 428(6986): 909-910. doi: 10.1038/428909a [5] 岳建平, 甄宗坤. 基于粒子群算法的Kriging插值在区域地面沉降中的应用[J]. 测绘通报, 2012(3): 59-62.YUE J P, ZHEN Z K. Application of particle swarm optimization based Kriging interpolation method in regional land subsidence[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2012(3): 59-62(in Chinese). [6] 李晨霖, 王仕成, 张金生, 等. 基于改进的Kriging插值方法构建地磁基准图[J]. 计算机仿真, 2018, 35(12): 262-266. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2018.12.062LI C L, WANG S C, ZHANG J S, et al. Construction of geomagnetic datum map based on improved Kriging interpolation method[J]. Computer Simulation, 2018, 35(12): 262-266(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2018.12.062 [7] GOLDENBERG F. Geomagnetic navigation beyond the magnetic compass[C]//2006 IEEE/ION Position, Location, and Navigation Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2006: 684-694. [8] 张涛, 郑建华, 高东. 一种利用磁强计和星敏感器的自主导航方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2017, 38(2): 152-158. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2017.02.006ZHANG T, ZHENG J H, GAO D. A method of autonomous navigation using the magnetometer and star sensor[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2017, 38(2): 152-158(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2017.02.006 [9] 华冰, 张志文, 王峰, 等. 基于地磁/光谱红移/太阳光信息的FAUKF自主定轨[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(1): 154-161.HUA B, ZHANG Z W, WANG F, et al. FAUKF autonomous orbit determination based on geomagnetic/spectral redshift/sunlight information[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(1): 154-161(in Chinese). [10] CAI Q Z, YANG G L, SONG N F, et al. Analysis and calibration of the gyro bias caused by geomagnetic field in a dual-axis rotational inertial navigation system[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2016, 27(10): 105001. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/27/10/105001 [11] LIU M Y, LIU K, YANG P P, et al. Bio-inspired navigation based on geomagnetic[C]//2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 2339-2344. [12] 杨宇翔. 图像超分辨率重建算法研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2013: 14-28.YANG Y X. Image super resolution reconstruction[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2013: 14-28(in Chinese). [13] WANG Z Y, YANG Y Z, WANG Z W, et al. Learning super-resolution jointly from external and internal examples[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(11): 4359-4371. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2462113 [14] DENG C, XU J, ZHANG K B, et al. Similarity constraints-based structured output regression machine: An approach to image super-resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2016, 27(12): 2472-2485. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2468069 [15] LI X, ORCHARD M T. New edge-directed interpolation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2001, 10(10): 1521-1527. doi: 10.1109/83.951537 [16] WEN B H, RAVISHANKAR S, BRESLER Y. Structured overcomplete sparsifying transform learning with convergence guarantees and applications[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 114(2-3): 137-167. doi: 10.1007/s11263-014-0761-1 [17] IRANI M, PELEG S. Improving resolution by image registration[J]. CVGIP: Graphical Models and Image Processing, 1991, 53(3): 231-239. doi: 10.1016/1049-9652(91)90045-L [18] YANG J C, LIN Z, COHEN S. Fast image super-resolution based on in-place example regression[C]//2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 1059-1066. [19] YANG J C, WANG Z W, LIN Z, et al. Coupled dictionary training for image super-resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(8): 3467-3478. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2192127 [20] DONG C, LOY C C, HE K M, et al. Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2014: 184-199. [21] KIM J, LEE J K, LEE K M. Deeply-recursive convolutional network for image super-resolution[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1637-1645. [22] MACKAY D J C. Good error-correcting codes based on very sparse matrices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1999, 45(2): 399-431. doi: 10.1109/18.748992 [23] LIU D, WANG Z W, WEN B H, et al. Robust single image super-resolution via deep networks with sparse prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(7): 3194-3207. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2564643 期刊类型引用(4)
1. 杨朝永,赵冬青,郭文卓,赖路广,张乐添,贾晓雪. 一种5G辅助地磁匹配的室内定位方法. 山东科技大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(03): 26-34 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 任钰琳,王伟,王召巴,程诚,刘昱彤,赵子文. 基于生成对抗网络的超分辨率室内地磁基准图构建. 国外电子测量技术. 2023(07): 74-79 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 赵鹤达,张宁,林春生,林朋飞,徐磊. 基于零边界值Kriging插值的地磁异常场稳定向上延拓法. 海军工程大学学报. 2022(01): 49-54 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 于晓彤,李夕海,曾小牛,刘继昊,谭笑枫. 基于生成对抗网络的地磁数据重建. 地球物理学进展. 2022(03): 989-997 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(5)
-








 下载:
下载:


 百度学术
百度学术

