-
摘要:
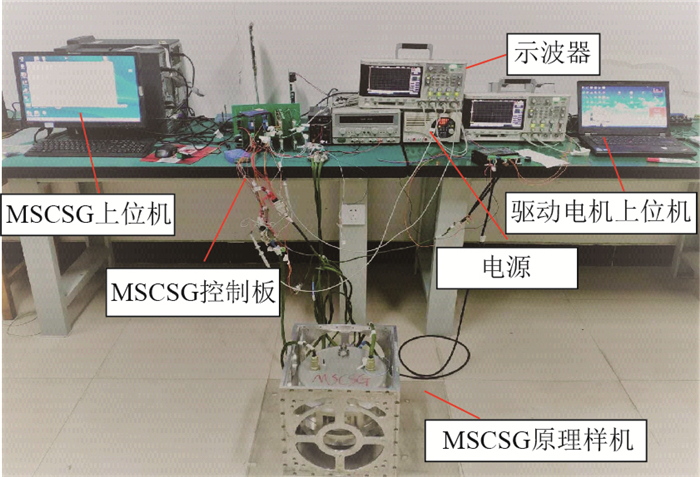
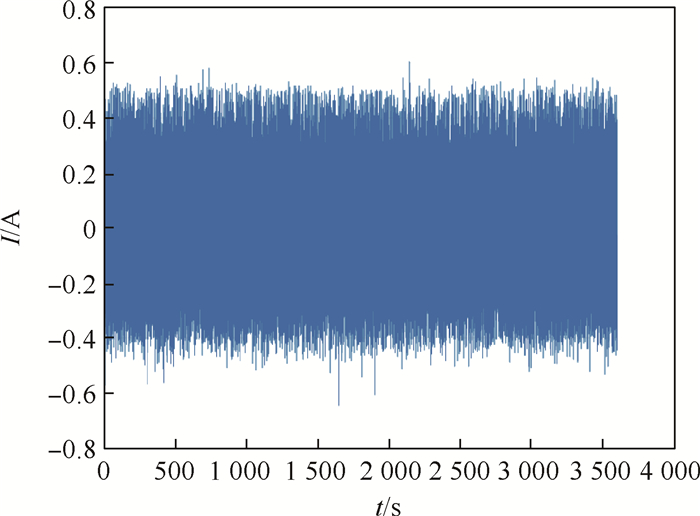
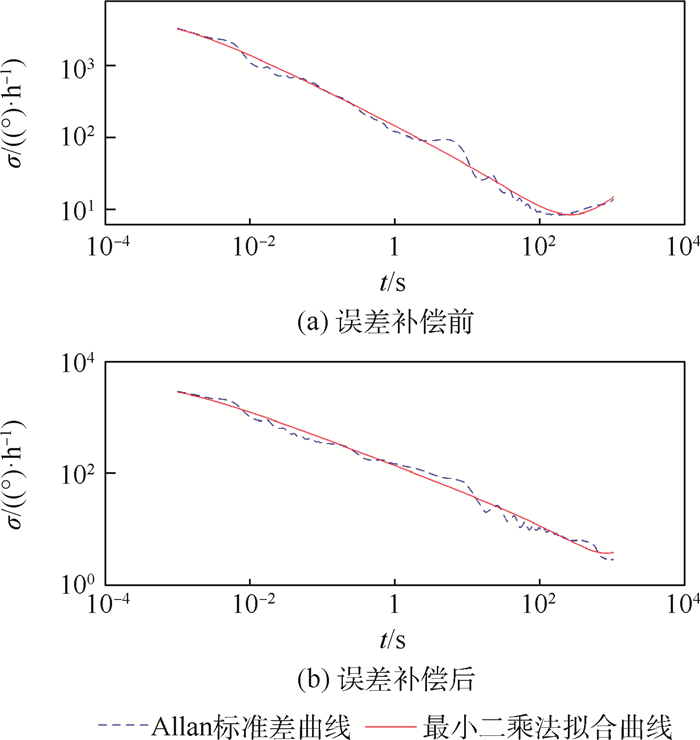
针对磁悬浮控制敏感陀螺(MSCSG)的角速率测量信号中存在较大的随机误差,不利于提高MSCSG敏感精度,以MSCSG原理样机为研究对象,提出采用Allan方差分析法对MSCSG实测数据进行随机误差分析。首先,根据MSCSG角速率敏感原理推导出MSCSG转子偏转角速率的量测公式;其次,应用Allan方差分析法和最小二乘拟合方法计算出5种典型随机误差系数。计算结果显示:在MSCSG随机误差中,零偏不稳定性、速率随机游走以及速率斜坡占主要成分,而量化噪声和角度随机游走误差所占比重较小。依此,对MSCSG误差来源进行了指向性分析,并给出了随机误差的抑制补偿方法,为MSCSG敏感精度的提高奠定了理论基础。
-
关键词:
- 磁悬浮控制敏感陀螺(MSCSG) /
- 随机误差 /
- Allan方差分析法 /
- 最小二乘拟合 /
- 误差补偿
Abstract:There is a large random error in the angular rate measurement signal of Magnetically Suspended Control & Sensing Gyroscope (MSCSG), which is not conducive to improving the sensitivity accuracy of MSCSG. In this paper, taking the principle prototype of MSCSG as the research object, the Allan variance analysis method is proposed to analyze the random error of the measured data of MSCSG. According to the principle of MSCSG angular velocity sensitivity, the measurement formula of MSCSG rotor deflection angular velocity is derived. Five typical random error coefficients are calculated by Allan variance analysis and least square fitting. The calculation results show that, among MSCSG random errors, zero deviation instability, rate following and rate slope are the main components, while quantization noise and angle random walk error account for the smaller proportion. According to this, the directivity of MSCSG error source is analyzed, and the method of restraining and compensating random error is given, which lays a theoretical foundation for improving the sensitivity accuracy of MSCSG.
-
表 1 Allan标准差与5项典型误差的对应关系
Table 1. Corresponding relations between Allan standard deviation and five typical errors
随机误差项 Allan标准差 量化噪声Q/(°) 


零偏不稳定性B/((°)·h-1) σB=B/0.664 8 

速率斜坡R/((°)·h-2) 
注:τ为时间变量。 表 2 MSCSG各项随机误差统计
Table 2. Statistics of random errors in MSCSG
随机误差项 结果 量化噪声Q/(°) 0.963 036 
2.525 648 零偏不稳定性B/((°)·h-1) 12.023 988 
32.724 570 速率斜坡R/((°)·h-2) 38.789 995 表 3 误差补偿后MSCSG各项随机误差统计
Table 3. Statistics of random errors of MSCSG after error compensation
随机误差项 补偿后结果 误差降低率/% 量化噪声Q/(°) 0.916 159 4.87 
2.365 199 6.35 零偏不稳定性B/((°)·h-1) 3.235 266 73.09 
10.682 979 36.80 速率斜坡R/((°)·h-2) 23.970 946 38.20 -
[1] 任元, 王卫杰, 刘强, 等. 一种磁悬浮控制敏陀螺: 中国, ZL201510006597.5[P]. 2017-04-28.REN Y, WANG W J, LIU Q, et al. A kind of magnetically suspended control sensitive gyroscope: China, ZL201510006597.5[P]. 2017-04-28(in Chinese). [2] 夏长峰, 蔡远文, 任元, 等. MSCSG转子不平衡振动原理分析与建模[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(11): 2321-2328. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0044XIA C F, CAI Y W, REN Y, et al. Principle analysis and modeling of rotor imbalance vibration in magnetically suspended control and sensing gyroscope[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(11): 2321-2328(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0044 [3] ZHENG S Q, LI H T, HAN B C, et al. Power consumption reduction for magnetic bearing systems during torque output of control moment gyros[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2017, 32(7): 5752-5759. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2016.2608660 [4] HAN B C, ZHENG S Q, LI H T, et al. Weight-reduction design based on integrated radial-axial magnetic bearing of a large-scale MSCMG for space station application[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 64(3): 2205-2214. [5] LIU X K, ZHAO H, YAO Y, et al. Modeling and analysis of micro-spacecraft attitude sensing with gyrowheel[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(8): 1321. doi: 10.3390/s16081321 [6] FANG J C, ZHENG S Q, HAN B C. Attitude sensing and dynamic decoupling based on active magnetic bearing of MSDGCMG[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2012, 61(2): 338-348. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2011.2164289 [7] 霍元正. MEMS陀螺仪随机漂移误差补偿技术的研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2015: 12-19.HUO Y Z. Research in measurement of MEMS gyroscope random drift compensation[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2015: 12-19(in Chinese). [8] 熊必凤. 低成本MEMS陀螺仪随机漂移误差的建模及修正[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2017: 13-16.XIONG B F. Modeling and correction of random drift error of low cost MEMS gyroscope[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2017: 13-16(in Chinese). [9] ALLAN D W, LEVINE J. A historical perspective on the development of the allan variances and their strengths and weaknesses[J]. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 2016, 63(4): 513-519. doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2016.2524687 [10] REN Y F, KE X Z, LIU Y J. MEMS gyroscope performance estimate based on allan variance[C]//2007 8th International Conference on Electronic Measurement and Instruments. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2007: 301-304. [11] 杜少林, 陈书钊, 陈鹏光, 等. 基于Allan方差的MEMS陀螺仪噪声分析[J]. 仪表技术与传感器, 2018(5): 20-22, 27.DU S L, CHEN S Z, CHEN P G, et al. Analysis of MEMS gyroscope noise based on allan variance[J]. Instrument Technique and Sensor, 2018(5): 20-22, 27(in Chinese). [12] 马群, 王庆, 阳媛, 等. 基于Allan方差的MEMS陀螺仪随机误差辨识与抑制[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2019, 38(6): 62-65.MA Q, WANG Q, YANG Y, et al. Random error identification and suppression of MEMS gyroscope based on Allan variance[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2019, 38(6): 62-65(in Chinese). [13] 贾瑞才. 低成本IMU误差辨识与补偿算法[J]. 四川兵工学报, 2014, 35(5): 97-101.JIA R C. Algorithm of error identification and compensation for low cost IMU[J]. Journal of Sichuan Ordnance, 2014, 35(5): 97-101(in Chinese). [14] 严恭敏, 李四海, 秦永元. 惯性仪器测试与数据分析[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2015: 142-143.YAN G M, LI S H, QIN Y Y. Inertial instrument test and data analysis[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2015: 142-143(in Chinese). [15] 夏长峰, 蔡远文, 任元, 等. MSCSG转子系统的扩展双频Bode图稳定性分析方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2018, 39(2): 168-176.XIA C F, CAI Y W, REN Y, et al. Stability analysis method with extended double-frequency bode diagram for rotor of MSCSG[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2018, 39(2): 168-176(in Chinese). [16] 辛朝军, 蔡远文, 任元, 等. 磁悬浮敏感陀螺动力学建模与关键误差源分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(10): 2048-2058. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2015.0650XIN C J, CAI Y W, REN Y, et al. Dynamic modeling and key error sources analysis of magnetically suspended sensitive gyroscopes[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42(10): 2048-2058(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2015.0650 [17] YU C M, WANG Z, REN Y, et al. MSCSG two degree of freedom attitude measurement method[C]//Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Electrical, Control and Automation(ICECA2018). Beijing: Space Engineering University, 2018: 390-396. [18] 李磊, 任元, 陈晓岑, 等. 基于ADRC和RBF神经网络的MSCSG控制系统设计[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(10): 1966-1972. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0536LI L, REN Y, CHEN X C, et al. Design of MSCSG control system based on ADRC and RBF neural network[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(10): 1966-1972(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0536 [19] REN Y, CHEN X C, CAI Y W, et al. Attitude-rate measurement and control integration using magnetically suspended control and sensitive gyroscopes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(6): 4921-4932. [20] 中国人民解放军战略支援部队航天工程大学. 一种基于磁悬浮控制敏感陀螺平行构型的角运动测量方法: 中国,CN110068336A[P]. 2019-07-30. Space Engineering University, Strategic Support Force of the People's Liberation Army of China. Angular motion measuring method based on parallel configuration of magnetic suspension control sensitive gyroscopes: China, CN110068336A[P]. 2019-07-30(in Chinese). [21] 辛朝军. 磁悬浮控制敏感陀螺误差分析与补偿方法研究[D]. 北京: 航天工程大学, 2017: 121-162.XIN C J. Compensation method investigation and error analysis for a magnetically suspended control & sensing gyroscope[D]. Beijing: Space Engineering University, 2017: 121-162(in Chinese). -








 下载:
下载: