-
摘要:
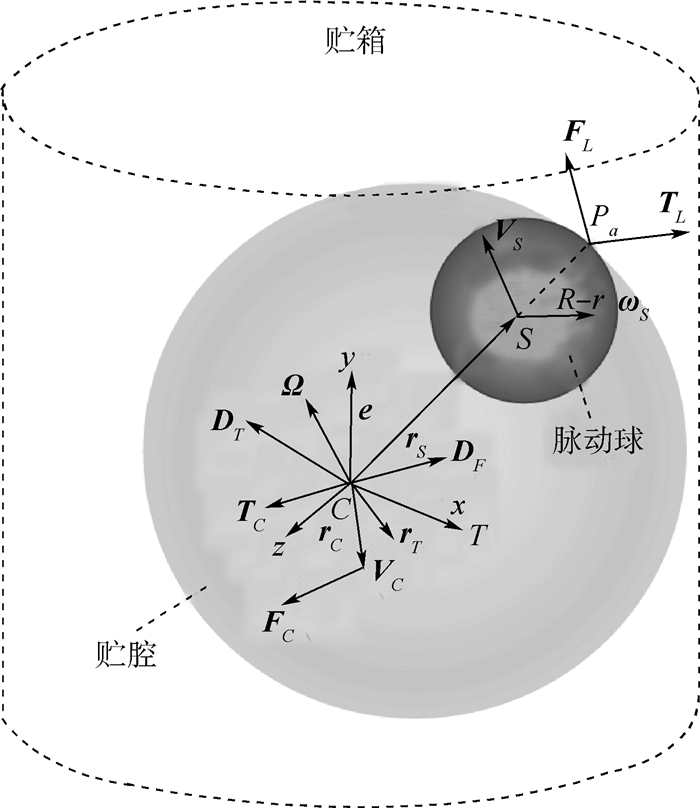
针对液体大幅晃动、通信资源受限的充液航天器姿态控制系统,提出一种自适应滑模控制与事件触发机制相结合的控制策略。首先,针对固-液耦合的充液航天器姿态控制系统,选用滑模变结构控制来削弱液体大幅晃动的非线性影响,并设计自适应更新律在线估计不确定参数来提高系统的鲁棒性。然后,考虑星载计算机资源的限制,设计相对阈值的事件触发机制来决定控制输入信号的更新,从而减少控制器与执行器之间的信号更新对通信网络的占用。最后,仿真结果表明,在液体大幅晃动下,所提控制策略不但可以使航天器姿态控制系统最终收敛到任意小的界内,而且可以减少96%的控制信号传输,减轻航天器的通信负载。
Abstract:Aimed at the attitude system of liquid-filled spacecraft with large-amplitude liquid sloshing and limited communication resources, a control strategy combining adaptive sliding mode control and event-triggering mechanism is proposed. First, sliding mode variable structure control is used to weaken the nonlinear effect of large-amplitude liquid sloshing for a liquid-solid coupled spacecraft attitude system, and an adaptive updating law is designed to estimate the uncertain parameters online to improve the robustness of the system. Then, considering the limitation of onboard computer resources, an event-triggering mechanism with relative threshold is designed to determine the update of control input signal, so as to reduce the occupation of communication network caused by signal update between controller and actuator. Finally, the simulation results show that, under large-amplitude liquid sloshing, the control strategy can not only make the spacecraft attitude system converge to an arbitrary small boundary, but also reduce the control signal transmission by 96% and reduce the communication load of spacecraft.
-
-
[1] 朱宁昌. 中国液体火箭发动机发展之我见[J]. 宇航学报, 1990(3): 5-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YHXB199003001.htmZHU N C. Viewpoint on the development of China's liquid propellant rocket engines[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 1990(3): 5-9(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YHXB199003001.htm [2] VREEBURG J P B. Spacecraft maneuvers and slosh control[J]. IEEE Control Systems, 2005, 25(3): 12-16. doi: 10.1109/MCS.2005.1432593 [3] VREEBURG J P B. Dynamics and control of a spacecraft with a moving, pulsating ball in a spherical cavity[J]. Acta Astronautics, 1997, 40(2-8): 257-274. doi: 10.1016/S0094-5765(97)00095-7 [4] BERRY R L, TEGART J R.Experimental study of transient liquid motion in orbiting spacecraft: NASA-CR-144003[R].Wshington, D.C.: NASA, 1975. [5] 董瑞琦, 吴爱国, 张颖, 等. 转动惯量存在不确定性的挠性航天器动态自适应滑模姿态控制[J]. 飞控与探测, 2019, 2(5): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FKTC201905002.htmDONG R Q, WU A G, ZHANG Y, et al. Dynamic adpative sliding attitude control for flexibel spacecraft with inertia uncertainty[J]. Flight Control & Detection, 2019, 2(5): 1-8(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FKTC201905002.htm [6] 杜辉, 张洪华. 一类带液体晃动航天器的姿态控制[J]. 空间控制技术与应用, 2010, 36(2): 25-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJKZ201002006.htmDU H, ZHANG H H. Attitude control of a spacecraft with liquid sloshing[J]. Aerospace Control and Application, 2010, 36(2): 25-30(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJKZ201002006.htm [7] DENG M L, YUE B Z. Attitude tracking control of flexible spacecraft with large amplitude slosh[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2017, 33(6): 1095-1102. doi: 10.1007/s10409-017-0700-9 [8] ZHU Z, XIA Y Q, FU M Y. Attitude stabilization of rigid spacecraft with finite-time convergence[J]. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2011, 21(6): 686-702. doi: 10.1002/rnc.1624 [9] SONG X J, LU S F. Attitude maneuver control of liquid-filled spacecraft with unknown inertia and disturbances[J]. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2019, 25(8): 1460-1469. doi: 10.1177/1077546318820414 [10] MAZMANYAN L, AYOUBI M A. Fuzzy attitude control of spacecraft with fuel sloshing via linear matrix inequalities[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(5): 2526-2536. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2820419 [11] REYHANOGLU M.Modeling and control of space vehicles with fuel slosh dynamics[M]//HALL D J.Advances in spacecraft technologies.[S.l.]: InTech, 2011: 549-562. [12] DENG M L, YUE B Z. Attitude dynamics and control of liquid filled spacecraft with large amplitude fuel slosh[J]. Journal of Mechanics, 2017, 33(1): 125-136. doi: 10.1017/jmech.2016.60 [13] 顾黄兴, 齐瑞云. 带液体晃动航天器的非线性自适应反馈控制[J]. 航天控制, 2013, 31(4): 72-77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HTKZ201304014.htmGU H X, QI R Y. Nonlinear adaptive feedback controller for spacecraft with fuel slosh[J]. Aerospace Control, 2013, 31(4): 72-77(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HTKZ201304014.htm [14] 王婕, 马晓, 宗群. 四旋翼无人飞行器的轨迹跟踪与滑模事件驱动控制[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2019, 36(7): 1083-1089. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZLY201907008.htmWANG J, MA X, ZONG Q. Trajectory tracking and sliding mode event-triggered control for a quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2019, 36(7): 1083-1089(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZLY201907008.htm [15] 于灏, 欧阳利, 郝飞. 事件触发控制在倒立摆系统中的仿真与实验[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(10): 2107-2117. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2015.0631YU H, OUYANG L, HAO F. Simulation and experiment of event -triggered control for inverted pendulum system[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42(10): 2107-2117(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2015.0631 [16] SUN S, YANG M, WANG L.Event-triggered nonlinear attitude control for a rigid spacecraft[C]//The 36th Chinese Control Conference, 2017: 7582-7586. [17] WANG F, HOU M Z, CAO X B. Event-triggered backstepping control for attitude stabilization of spacecraft[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2019, 356(16): 9474-9501. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2019.09.010 [18] YI H, LIU M, LI M. Event-triggered fault tolerant control for spacecraft formation attitude synchronization with limited data communication[J]. European Journal of Control, 2018, 48: 97-103. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcon.2018.11.003 [19] 杨飞生, 汪璟, 潘泉. 基于事件触发机制的网络控制研究综述[J]. 控制与决策, 2018, 33(6): 969-977. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC201806001.htmYANG F S, WANG J, PAN Q. A survey of network control based on event triggering mechanism[J]. Control and Decision, 2018, 33(6): 969-977(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC201806001.htm [20] 邓明乐, 岳宝增, 黄华. 液体大幅晃动等效力学模型研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2016, 37(6): 631-638. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YHXB201606001.htmDENG M L, YUE B Z, HUANG H. Study on the equivalent mechanical model for large amplitude slosh[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2016, 37(6): 631-638(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YHXB201606001.htm [21] WU B, QIANG S, CAO X. Event-triggered attitude control of spacecraft[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2018, 61(3): 927-934. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2017.11.013 [22] ZHANG J, FENG G. Event-driven observer-based output feedback control for linear systems[J]. Automatica, 2014, 50(7): 1852-1859. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.04.026 [23] 张嘉芮, 陈弈澄, 董新蕾, 等. 基于事件触发的航天器姿态自适应容错控制[J]. 飞控与探测, 2020, 3(2): 17-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FKTC202002003.htmZHANG J R, CHEN Y C, DONG X L, et al. Event-triggered adaptive fault-tolerant control of spacecraft attitude[J]. Flight Control & Detection, 2020, 3(2): 17-25(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FKTC202002003.htm -







 下载:
下载: