-
摘要:
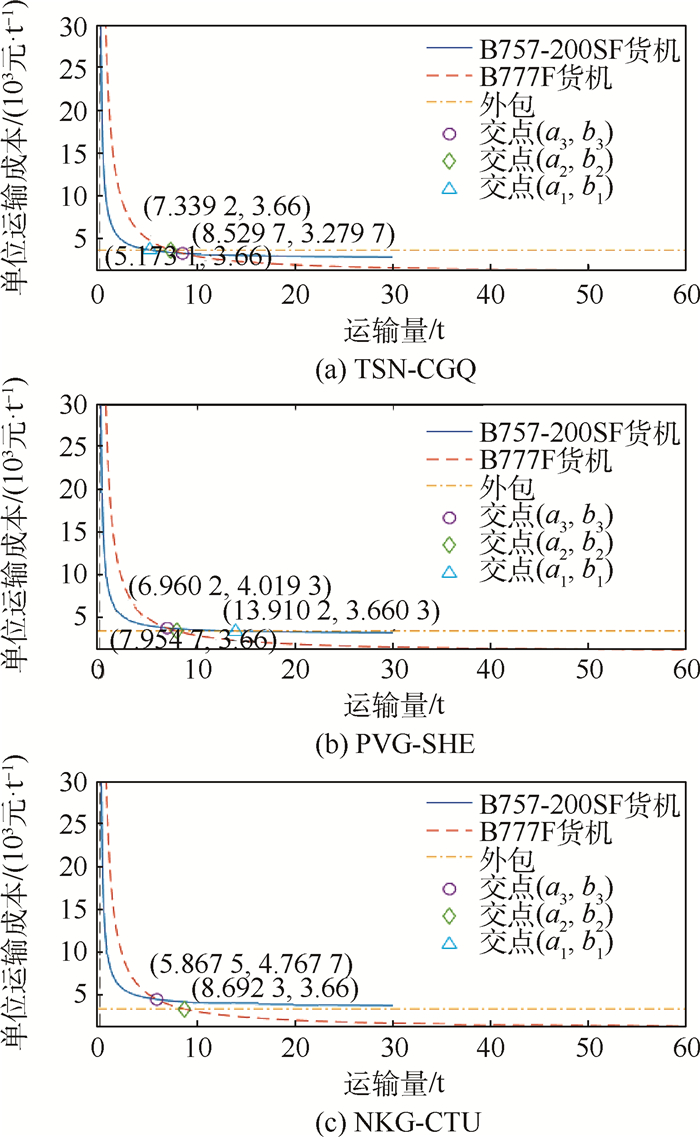
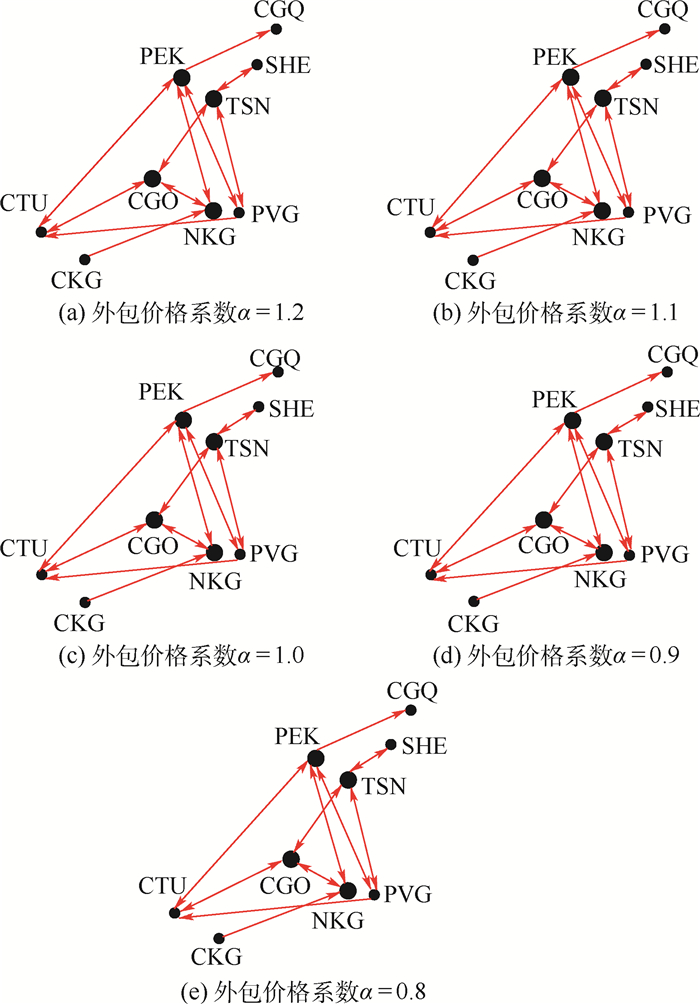
针对货运航空公司大量、纷繁交错的航空货运需求,制定合理的路径规划和配流方案可以降低运输成本、提高运输效率。考虑货机运输和外包运输2种运输方式,建立了运力配置和货流分配一体化的混合整数规划模型。以中国国际货运航空有限公司为例进行算例求解,根据不同运输距离对货流进行预分配,根据OD对机场所在集合预先规定货流可以中转的机场,不仅缩小了搜索空间,比两者均不处理时节省了85.12%的计算时间,而且中转货流运输路径总长度和中转货流周转量与不处理相比也分别降低了17.19%和28.99%,减少了大量绕路。得到的结果与不考虑外包的模型相比节省了4.87%的成本。引入外包价格系数进行灵敏度分析,随着外包价格系数从1.2到0.8不断减小,货运航空公司通过外包运输的货物量增加,同时小型货机执飞的航段不断减少,而大型货机执飞的航段没有变化。对不同运输方式的单位运输成本随运输量变化的曲线进行分析,当货运航空公司在面临新增局部货运需求时,可以不改变全局方案,而根据曲线及剩余运力情况做出较优的决策。
Abstract:For cargo airlines, in the face of a large number of complicated air cargo demands, formulating reasonable route planning and distribution schemes can reduce transportation costs and improve transportation effciency. We established a mixed integer programming model that integrates transport capacity allocation and cargo flow distribution and took Air China Cargo as an example to solve the model, in which airlines can use their self-owned cargo aircraft or outsourcing service for transportation. We proposed two data processing ways: pre-allocating cargo flow according to different transportation distances and pre-specifying transit airports according to OD pairs, which not only reduces the search space, but also saves 85.12% of the calculation time compared to the situation without data processing. The total length of freight transportation path and the turnover of transit freight flow are also reduced by 17.19% and 28.99% compared with non-preprocessing, which reduces a large number of detours. Compared with the model without outsourcing, the integrated model saves 4.87% of the cost. Then the outsourcing price coeffcient was introduced for sensitivity analysis. As the outsourcing price coeffcient decreases from 1.2 to 0.8, the outsourcing cargo volume increases. At the same time, the flight segments operated by small aircraft decrease, and the flight segments allocated to large aircraft do not change. Finally, we analyzed the curves of unit transportation cost varying with transportation volume on the same flight segment for different modes of transportation, which provides a reference for airlines to respond to the temporary segment demand, and provides a better solution according to curves and residual transport capacity without changing the overall plan.
-
表 1 各机场间的货运需求
Table 1. Freight demands among airports
机场 需求/t PEK PVG CTU CKG TSN CGO NKG CGQ SHE PEK 0 224 112 26.775 0 11.375 105 25.9 23.1 PVG 210 0 73.5 24.5 59.5 9.8 0 23.1 33.6 CTU 101.5 35.875 0 0 18.9 16.1 70 17.15 21.875 CKG 49 29.4 0 0 6.3 7.525 36.75 7.7 3.325 TSN 0 48.125 11.55 7.875 0 22.75 17.15 4.2 4.025 CGO 35 11.55 16.1 7.525 24.5 0 3.15 3.325 2.1 NKG 69.3 0 45.5 27.3 26.6 11.9 0 10.5 7.875 CGQ 26.95 14.35 11.2 7 9.625 6.475 3.15 0 0 SHE 23.1 12.6 9.275 13.405 15.4 17.15 14.875 0 0 表 2 部分OD对货流分配结果
Table 2. Cargo flow distribution results of some OD pairs
OD对 货流分配/t OD对 货流分配/t PEK-CTU PEK-CTU: 106.5; PEK-CGO-CTU: 5.5 CKG-TSN CKG-NKG-CGO-TSN: 6.3 CTU-NKG CTU-CGO-NKG: 70 CTU-CGQ CTU-PEK-CGQ: 2;外包: 12.15 NKG-CTU NKG-CGO-CTU: 45.5 TSN-CKG TSN-CGO-CKG: 3.95;外包: 3.925 PVG-SHE PVG-TSN-SHE: 33.6 CGO-CGQ CGO-PEK-CGQ: 3.325 CKG-PEK CKG-NKG-PEK: 26.7;CKE-NKG-CGO-PEK: 0.8;外包: 21.5 PVG-CGQ PVG-PEK-CGQ; 3;外包: 20.1 NKG-TSN NKG-CGO-TSN: 26.6 CGO-SHE CGO-TSN-SHE: 2.1 CTU-TSN CTU-CGO-TSN: 18.9 CTU-SHE CTU-CGO-TSN-SHE: 1.5;外包: 20.375 TSN-NKG TSN-CGO-NKG: 17.15 CGQ-NKG CGQ-PEK-NKG: 1.5;外包: 1.65 SHE-CGO SHE-TSN-CGO: 17.15 CTU-PVG 外包: 35.875 SHE-NKG SHE-TSN-CGO-NKG: 14.875 CKG-PVG 外包: 29.4 CGQ-PVG CGQ-TSN-PVG: 14.35 PEK-CKG 外包: 26.775 SHE-PVG SHE-TSN-PVG: 12.6 PVG-CKG 外包: 24.5 CGO-PVG CGO-TSN-PVG: 11.55 SHE-CKG 外包: 13.405 TSN-CTU TSN-CGO-CTU: 11.55 CGQ-CTU 外包: 11.2 NKG-CGQ NKG-PEK-CGQ: 10.5 CKG-CGQ 外包: 7.7 PVG-CGO PVG-TSN-CGO: 9.8 CGQ-CKG 外包: 7 SHE-CTU SHE-TSN-CGO-CTU: 9.275 CGQ-CGO 外包: 6.475 NKG-SHE NKG-CGO-TSN-SHE: 7.875 TSN-CGQ 外包: 4.2 CKG-CGO CKG-NKG-CGO: 7.525 CKG-SHE 外包: 3.325 表 3 是否进行预处理的求解结果对比
Table 3. Comparison of solving results with and without preprocessing
处理方式 求解时间/s 中转货流运输距离/km 中转货流周转量/(t·km) 总成本/(103元) 两者均处理 826 53 912 719 171.025 3 620.441 货流分配方式未处理 — 61 110 1 112 919.575 3 339.996 中转机场未处理 5 550 61 201 831 750.115 3 607.828 两者均未处理 — 65 105 1 012 728.775 3 328.502 注:“—”表示无法在合理时间内求得最优解,设置最大运算时间为7 200 s。 -
[1] O'KELLY M E. A quadratic integer program for the location of interacting hub facilities[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 1987, 32(3): 393-404. doi: 10.1016/S0377-2217(87)80007-3 [2] CAMPBELL J F. Integer programming formulations of discrete hub location problems[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 1994, 72(2): 387-405. doi: 10.1016/0377-2217(94)90318-2 [3] ERNST A T, KRISHNAMOORTHY M. Efficient algorithms for the uncapacitated single allocationp-hub median problem[J]. Location Science, 1996, 4(3): 139-154. doi: 10.1016/S0966-8349(96)00011-3 [4] ELHEDHLI S, HU F X. Hub-and spoke network design with congestion[J]. Computers and Operations Research, 2005, 32(6): 1615-1632. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2003.11.016 [5] 邓亚娟, 陈小鸿, 杨超. 需求不确定的枢纽辐射式航线网络设计[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2009, 9(6): 69-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2009.06.014DENG Y J, CHEN X H, YANG C. Hub-and-spoke airline network design with uncertainty demand[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2009, 9(6): 69-74(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2009.06.014 [6] 吴小欢, 朱金福, 吴薇薇. 航线网络区间型相对鲁棒优化设计[J]. 系统工程学报, 2012, 27(1): 69-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5781.2012.01.009WU X H, ZHU J F, WU W W. Relative interval robust optimization of airline network designing[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering, 2012, 27(1): 69-78(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5781.2012.01.009 [7] OKTAL H, OZGER A. Hub location in air cargo transportation: A case study[J]. Journal of Air Transport Management, 2013, 27: 1-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jairtraman.2012.10.009 [8] 高娇蛟. 我国快递企业航空运输网络的优化设计研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2011.GAO J J. Research on optimization design of air transport network of express enterprises in China[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2011(in Chinese). [9] 何明珂, 程红晶. 快递企业航空货运网络的构建[J]. 运筹与管理, 2013, 22(6): 232-242. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3221.2013.06.034HE M K, CHENG H J. Construction of air freight network for express company[J]. Operations Research and Management Science, 2013, 22(6): 232-242(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3221.2013.06.034 [10] 乐美龙, 郑文娟, 吴明功, 等. 不确定需求下航空公司枢纽网络优化设计[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(4): 674-682. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0319LE M L, ZHENG W J, WU M G, et al. Airline hub network optimization design under uncertain demand[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(4): 674-682(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0319 [11] ZHANG D, YU C H, LAU H Y K. An integrated flight scheduling and fleet assignment method based on a discrete choice model[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2016, 98: 195-210. [12] ZHANG C R, XIE F R, HUANG K, et al. MIP models and a hybrid method for the capacitated air-cargo network planning and scheduling problems[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2017, 103: 158-173. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2017.05.003 [13] KENAN N, JEBALI A, DIABAT A. An integrated flight scheduling and fleet assignment problem under uncertainty[J]. Computers and Operations Research, 2018, 100: 333-342. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2017.08.014 [14] 杨忠振, 于述南, 陈刚. 混合式航空货运网络优化[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2016, 16(1): 103-114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2016.01.013YANG Z Z, YU S N, CHEN G. Optimzation of mixed air cargo transportation network[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2016, 16(1): 103-114(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2016.01.013 [15] 贺政纲, 石雨禾. 考虑需求时间上限的航空货运模式选择[J]. 交通运输工程与信息学报, 2018, 16(4): 34-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4747.2018.04.005HE Z G, SHI Y H. The choice of air freight mode considering time limit of demand[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information, 2018, 16(4): 34-40(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4747.2018.04.005 [16] 国家计划委员会建设部. 建设项目经济评价方法与参数: 第2部分建设项目经济评价方法: 7-80058-286-8[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 1993: 16-17.Ministry of Construction of the State Planning Commission. Economic evaluation methods and parameters of construction projects: Part 2. Economic evaluation methods of construction projects: 7-80058-286-8[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 1993: 16-17(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: