-
摘要:
针对目前大型飞机机翼常见的单点优化设计方法在考虑多巡航工况情况下非设计点性能较差的问题,提出了一种多工况气动弹性综合优化框架,考虑了不同的巡航工况,对大型飞机复合材料机翼开展气动弹性优化的研究。以最小机翼结构质量为目标,在气动弹性、应力/应变、强度等条件的约束下,通过遗传算法对机翼型架外形的蒙皮、腹板、凸缘等复合材料部件的铺层厚度展开设计,并根据优化结果进行了型架外形设计,采用高精度CFD/CSD耦合方法分析和校验了优化结果的升阻特性。研究表明:在不低于设计巡航外形气动性能的条件下,综合多巡航工况的气动弹性优化能有效减轻结构质量,从而减少整体燃油消耗。进一步对比分析了多巡航工况优化与单巡航工况优化,研究了巡航工况数目与优化结果之间的关系,结果表明:综合考虑多巡航工况的优化结果性能更好,且优化结果的整体性能随着优化巡航工况数目的增加而提升。
Abstract:Aiming at the problem of poor performance at off-design points in the current common single-point optimization design method of large aircraft wings considering multiple cruise conditions, a synthetical aeroelastic optimization framework with multiple cruise conditions is proposed, and the multi-point aeroelastic optimization of a large aircraft composite wing is studied. The laminate thickness of skin, web, flange and other composite components of the jig shape is optimized to minimize the wing structure weight using genetic algorithm, subjected to the constraints of aeroelasticity, stress/strain, strength and other conditions, and the jig shape design is carried out according to the optimization results. The lift-to-drag characteristics of the optimization results are analyzed and verified by the high-precision CFD/CSD coupling method. The results show that the multi-point aeroelastic optimization can effectively reduce the structure weight and maintain the aerodynamic performance of the pre-designed cruise configuration, thus reducing the overall fuel consumption. Furthermore, the results of multi-point optimization and single-point optimization are compared and the relationship between the considered cruise conditions number and the optimization results is analyzed. The results show that the performance of the multi-point aeroelastic optimization is better than that of the single-point aeroelastic optimization, and the overall performance increases with the increase of the number of cruise conditions considered in the optimization.
-
表 1 复合材料单向层压板主要性能参数
Table 1. Main performance parameters of composite unidirectional laminate
材料性能 具体参数 典型值 B基值 拉伸强度/MPa 纵向Xt 1 747 1 342 横向Yt 67 56 压缩强度/MPa 纵向Xc 1 357 1 069 横向Yc 170 147 纵横剪切强度/MPa Ys 124 117 层间剪切强度/MPa τb 93 85 泊松比 γ12 0.312 0.312 拉伸弹性模量/GPa 纵向E1t 137 127 横向E2t 9.3 8.5 压缩弹性模量/GPa 纵向E1c 136 127 横向E2c 9.4 8.5 纵剪切弹性模量/GPa G12 5.3 4.5 表 2 优化中的强度/应变约束条件
Table 2. Strength/strain constraint conditions in optimization
约束指标 约束范围 长桁应力约束/MPa [-324, 446] 梁突缘应力约束/MPa [-324, 446] 纵向拉压许用应变约束/με [-4 000, 5 500] 纵横向剪切许用应变约束/με [-7 600, 7 600] 失效约束(Tsai-Wu失效准则) [-1, 1] 表 3 各巡航工况半模质量分布
Table 3. Half model mass distribution of each cruise condition
巡航工况编号 半模质量/kg 1 42 258 2 41 258 3 40 258 4 39 258 5 36 258 6 33 258 表 4 各优化条件所考虑巡航工况
Table 4. Cruise conditions considered in each optimization condition
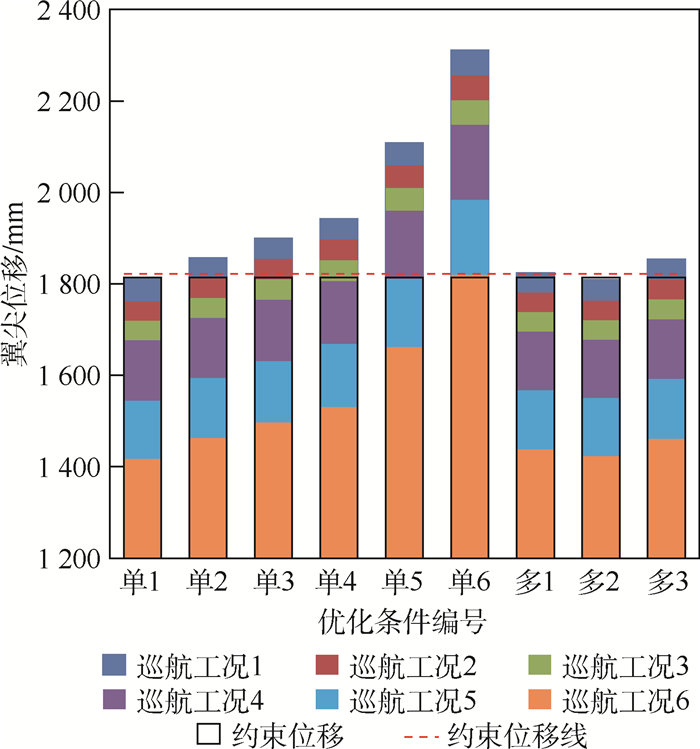
单巡航工况
优化条件编号单1 单2 单3 单4 单5 单6 所考虑巡航
工况编号1 2 3 4 5 6 多巡航工况
优化条件编号多1 多2 多3 所考虑巡航
工况编号1, 4 1, 2, 3, 4 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 表 5 优化后油耗变化
Table 5. Fuel consumption change after optimization
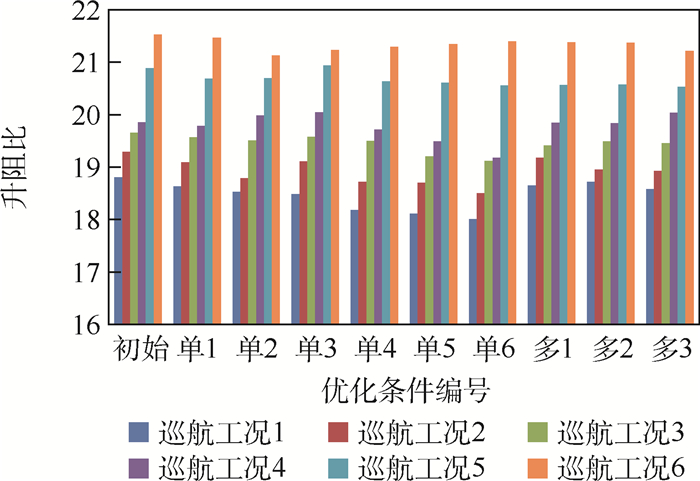
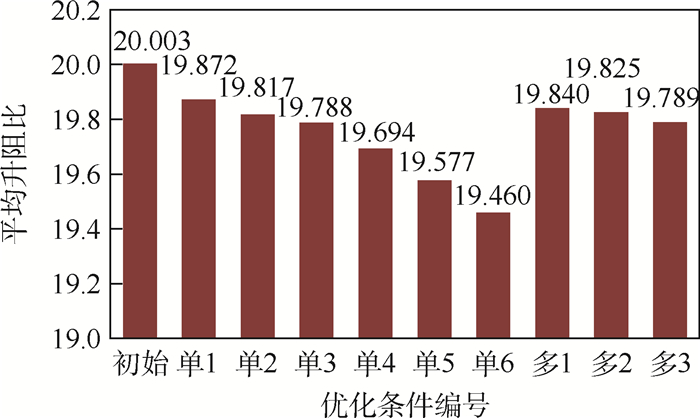
优化条件 工况数目 升阻比变化对油耗影响 结构质量变化对油耗影响 总油耗变化/% 平均升阻比 升阻比变化/% 油耗变化/% 结构质量/kg 结构质量变化/% 油耗变化/% 初始 0 20.003 0 0 1 076.2 0 0 0 单1 1 19.872 -0.65 0.65 1 018.6 -5.35 -3.88 -3.23 多1 2 19.840 -0.82 0.82 1 015.1 -5.68 -4.12 -3.30 多2 4 19.825 -0.89 0.89 1 013.4 -5.84 -4.23 -3.34 多3 6 19.789 -1.07 1.07 991.4 -7.88 -5.71 -4.64 -
[1] 崔勇. 提高航油使用效率控制航油成本[J]. 中国民用航空, 2008, 8: 22-25.CUI Y. Fuel cost control by fuel efficiency improvement[J]. China Civil Aviation, 2008, 8: 22-25(in Chinese). [2] CLIFF S E, REUTHER J J, SAUNDERS D A, et al. Single-point and multipoint aerodynamic shape optimization of high-speed civil transport[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2001, 38(6): 998-1005. doi: 10.2514/2.2886 [3] LEOVIRIYAKIT K, JAMESON A. Multipoint wingplanform optimization via control theory: AIAA-2005-450[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2005: 1-12. [4] 王晓鹏. 基于遗传算法的飞机气动优化设计[J]. 计算力学学报, 2002, 19(2): 188-191. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4708.2002.02.012WANG X P. Optimization and design for aerodynamic configuration of aircraft based on genetic algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2002, 19(2): 188-191(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4708.2002.02.012 [5] 王晓璐, 朱自强, 刘周, 等. 基于N-S方程的翼型双设计点双目标优化设计[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2006, 32(5): 503-507. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2006.05.002WANG X L, ZHU Z Q, LIU Z, et al. Bi-point/bi-objective optimization design of ailfoil using N-S equations[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2006, 32(5): 503-507(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2006.05.002 [6] 朱自强, 王晓璐. 高升阻比翼型和机翼的多点优化设计[J]. 航空科学技术, 2008(1): 20-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5453.2008.01.006ZHU Z Q, WANG X L. Multipoint optimization design of high lift-to-drag ratio for airfoil and wing[J]. Aeronautical Science and Technology, 2008(1): 20-25(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5453.2008.01.006 [7] 詹浩, 许晓平, 朱军. 气动外形多点优化设计研究[J]. 航空计算技术, 2007, 37(1): 19-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-654X.2007.01.006ZHAN H, XU X P, ZHU J. Multipoint optimization for aerodynamic shape[J]. Aeronautic Computing Technique, 2007, 37(1): 19-21(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-654X.2007.01.006 [8] 林宇, 王和平. 基于遗传算法的负弯度翼型亚音速多点设计[J]. 航空计算技术, 2009, 39(1): 45-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-654X.2009.01.012LIN Y, WANG H P. Subsonic multi-point design of a reflex foil based on genetic algorithm[J]. Aeronautic Computing Technique, 2009, 39(1): 45-47(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-654X.2009.01.012 [9] 刘晓冬, 杨旭东. 基于伴随方法的机翼多设计点气动反设计方法[J]. 航空计算技术, 2012, 42(5): 60-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-654X.2012.05.015LIU X D, YANG X D. Inverse design for wing of multi-point aerodynamic based on adjoint method[J]. Aeronautic Computing Technique, 2012, 42(5): 60-64(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-654X.2012.05.015 [10] 丁存伟, 杨旭东. 一种旋翼翼型多点多约束气动优化设计策略[J]. 航空计算技术, 2013, 43(1): 52-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-654X.2013.01.014DING C W, YANG X D. Multi-point aerodynamic optimization design strategy of rotor airfoil with multi-constrain conditions[J]. Aeronautic Computing Technique, 2013, 43(1): 52-57(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-654X.2013.01.014 [11] 陈学孔, 郭正, 易凡, 等. 低雷诺数翼型的气动外形优化设计[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2014, 32(3): 300-307.CHEN X K, GUO Z, YI F, et al. Aerodynamic shape optimization and design of airfoil with Reynolds number[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2014, 32(3): 300-307(in Chinese). [12] 张德虎, 李军府, 李士途. 前加载翼型多点综合优化设计[J]. 航空工程进展, 2015, 6(1): 32-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8190.2015.01.005ZHANG D H, LI J F, LI S T. Multipoints integrated optimization design of fore-loaded airfoil[J]. Advancesin Aeronautical Science and Engineering, 2015, 6(1): 32-37(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8190.2015.01.005 [13] 杨体浩, 白俊强, 史亚云, 等. 考虑吸气分布影响的HLFC机翼优化设计[J]. 航空学报, 2017, 38(12): 6-20.YANG T H, BAI J Q, SHI Y Y, et al. Optimization design for HLFC wings considering influence of suction distribution[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2017, 38(12): 6-20(in Chinese). [14] 柴啸. 客机总体参数与发动机参数综合优化研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2017: 81-107.CHAI X. A study on integrated optimization of airframe and engine parameters in conceptual design of airliners[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017: 81-107(in Chinese). [15] CHAI X, YU X Q, WANG Y. Multipoint optimization on fuel efficiency in conceptual design of wide-body aircraft[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2018, 31(1): 99-106. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2017.10.006 [16] 蒋城, 刘峰博, 李典, 等. 面向阻力发散的CRM机翼气动优化设计[J]. 航空计算技术, 2018, 48(5): 46-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-654X.2018.05.012JIANG C, LIU F B, LI D, et al. Aerodynamic optimization design of CRM wing faced on drag divergence[J]. Aeronautic Computing Technique, 2018, 48(5): 46-49(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-654X.2018.05.012 [17] 雷国东, 李岩. 跨声速飞机高可信度多设计点多约束气动优化设计技术研究[J]. 航空科学技术, 2019, 30(9): 9-18.LEI G D, LI Y. Research of the multiple design-points high-fidelity aerodynamics optimization technologies for the transonic aircraft with the multiple constraints[J]. Aeronautical Science and Technology, 2019, 30(9): 9-18(in Chinese). [18] 刘蕾, 胡磊, 郭雪岩, 等. 轴流风扇叶型多工况点气动优化设计[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2019, 40(11): 2551-2558.LIU L, HU L, GUO X Y, et al. Multipoint optimization of axial-flow fan airfoil[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2019, 40(11): 2551-2558(in Chinese). [19] TOAL D J J, KEANE A J. Efficient multipoint aerodynamic design optimization via cokriging[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2011, 48(5): 1685-1695. doi: 10.2514/1.C031342 [20] GALLAR F, MEAUX M, MONTAGNAC M, et al. Aerodynamic aircraft design for mission performance by multipoint optimization: AIAA-2013-2582[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2013: 1-17. [21] LIEM R P, KENWAY G K, MARTINSJ R R A. Multi-point, multi-mission, high-fidelity aerostructural optimization of a long-range aircraft configuration: AIAA-2012-5706[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2012: 1-25. [22] LIEM R P, KENWAY G K, MARTINS J R R A. Multimission aircraft fuel-burn minimization via mulitipoint aerostructural optimization[J]. AIAA Journal, 2015, 53(1): 104-122. doi: 10.2514/1.J052940 [23] KENWAY G K, MARTINS J R R A. Multipoint high-fidelity aerostructural optimization of a transport aircraft configuration[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2014, 51(1): 144-160. doi: 10.2514/1.C032150 [24] BURDETTE D A, KENWAY G K, MARTINS J R R A. Performance evaluation of a morphing trailing edge using multipoint aerostructural design optimization: AIAA-2016-0159[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2016: 1-15. [25] BROOKS T R, MARTINS J R R A, KENNEDY G J. High-fidelity multipoint aerostructural optimization of a high aspect ratio tow-steered composite wing: AIAA-2017-1350[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2017: 1-16. [26] 罗志凡, 荣见华, 杜海珍. 基于遗传算法和梯度算法的桁架结构动力学形状优化[J]. 振动与冲击, 2003, 22(2): 42-44.LUO Z F, RONG J H, DU H Z. Shape optimization for truss dynamic problems based on genetic algorithm and gradient algorithm[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2003, 22(2): 42-44(in Chinese). [27] 万志强, 杨超, 郦正能. 混合遗传算法在气动弹性多学科优化中的应用[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2004, 30(12): 1142-1146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2004.12.002WAN Z Q, YANG C, LI Z N. Application of hybrid genetic algorithm in aeroelastic multidisciplinary optimization[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2004, 30(12): 1142-1146(in Chinese. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2004.12.002 [28] RODDEN W P, JOHNSON E H. MSC/Nastran aeroelastic analysis user's guide[Z]. 68ed. Los Angeles: MSC Corporation, 1994: 35-65. [29] NEILL D J, HERENDEEN D L, VENKAYYA V B. ASTROS enhancements: ASTROS theoretical manual: WL-TR-95-3006[R]. New York: Wright Laboratory, 1995: 5-11. [30] 管德. 飞机气动弹性力学手册[M]. 北京: 航空工业出版社, 1994: 126-134.GUAN D. Manual of aircraft aeroelastic mechanics[M]. Beijing: Aviation Industry Press, 1994: 126-134(in Chinese). [31] 万志强, 杨超. 大展弦比复合材料机翼气动弹性优化[J]. 复合材料学报, 2005, 22(3): 145-149. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2005.03.028WAN Z Q, YANG C. Aeroelastic optimization of a high aspect ratio composite wing[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2005, 22(3): 145-149(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2005.03.028 [32] 杨乃宾, 章怡宁. 复合材料飞机结构设计[M]. 北京: 航空工业出版社, 2002: 102-120.YANG N B, ZHANG Y N. Composite aircraft structural design[M]. Beijing: Aviation Industry Press, 2002: 102-120(in Chinese). [33] 杨国伟, 郑冠男. 基于静气动弹性效应的飞机型架外形修正方法研究[J]. 航空工程进展, 2011, 2(2): 143-150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8190.2011.02.003YANG G W, ZHENG G N. Aircraft jig-shape correction method based on static aeroelastic analyses[J]. Advances in Aeronautical Science an Engineering, 2011, 2(2): 143-150(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8190.2011.02.003 [34] 梁强, 杨永年, 叶正寅. 三维机翼的型架外形设计研究[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2002, 20(2): 262-264. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2002.02.022LIANG Q, YANG Y N, YE Z Y. Analysis of jig-shape design for elastic wing[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2002, 20(2): 262-264(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2002.02.022 [35] 梁路. 大型飞机弹性机翼型架外形设计与气动弹性优化研究[D]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学, 2011: 46-64.LIANG L. Study of jig shape design and aeroelastic optimization on flexible wings of large aircraft[D]. Beijing: Beihang University, 2011: 46-64(in Chinese). [36] 王晓宇. 基于QAR的飞机燃油消耗特性及节油飞行研究[D]. 天津: 中国民航大学, 2015: 37-48.WANG X Y. Research on aircraft fuel consumption characteristics and fuel-efficient flight based on QAR[D]. Tianjin: Civil Aviation University of China, 2015: 37-48(in Chinese). -








 下载:
下载: