-
摘要:
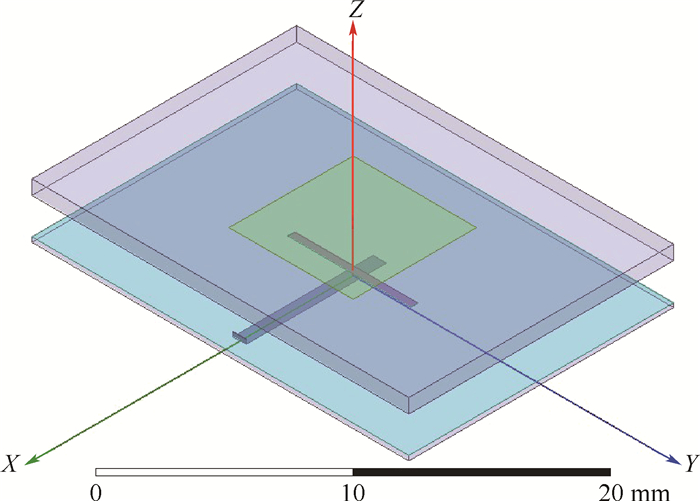
为降低天线副瓣电平(SLL)和展宽带宽,设计了一款谐振频率为14.25 GHz的16阵元非均匀间距的耦合馈电微带阵列天线。天线采用多层设计,通过在接地板开矩形槽进行耦合馈电,并引入空气层,降低天线Q值,增大带宽。区别于均匀间距阵列天线的激励幅值加权,从阵元间距角度入手,利用差分进化算法降低副瓣电平,构建非均匀间距并联线阵天线。用槽面辐射的能量近似代替阵元接收的能量,观察阵元功率分配情况,并建立馈电网络所有馈线段的数学关系,保证非均匀间距条件下所有阵元为等幅同相激励。测试结果显示,天线在14~14.5 GHz范围内电压驻波比小于2,满足了卫星动中通的带宽要求;工作带宽内增益大于16 dB,副瓣电平低于-16 dB,性能优于均匀间距阵列天线。
Abstract:To reduce the Sidelobe Level (SLL) of the antenna and widen the bandwidth, a 16-element coupled-feed microstrip array antenna with non-uniform spacing at 14.25 GHz frequency was designed. The antenna adopts a multi-layer design, and a rectangular groove is formed in the ground layer to perform coupling feeding. And the air layer is introduced to reduce the antenna Q value and increase the bandwidth. Different from the excitation amplitude weighting of uniformly spaced antennas, this paper starts from the perspective of array element spacing, differential evolution algorithm is used to reduce the SLL, and a non-uniform spacing parallel linear array antenna is constructed. The energy received by the array element is approximately replaced with the energy passing through the rectangular slot, and the power distribution of the array element is observed. And the mathematical relationship of all feeder sections of the feed network is established to ensure that all array elements are excited with equal amplitude and in phase under the condition of unequal spacing. The measurement results show that the antenna has a voltage standing wave ratio of less than 2 in the range of 14 GHz to 15.2 GHz, which satisfies the bandwidth requirements of satcom on the move. The gain is more than 16 dB and the SLL is less than -17 dB within the operating bandwidth, which shows that the performance is better than that of the array antenna with uniform spacing.
-
表 1 天线设计指标
Table 1. Antenna design index
天线参数 指标要求 工作频段 Ku波段 中心频率/GHz 14.25 带宽/MHz 500 极化方式 线极化 阵列形式 线阵 辐射方向 边射阵 天线增益/dB ≥16 副瓣电平/dB ≤-16 表 2 阵元位置
Table 2. Array element position
序号 位置 1 0 2 0.810 4λ 3 1.593 3λ 4 2.245 7λ 5 2.750 2λ 6 3.302 3λ 7 3.754 2λ 8 4.235 9λ 9 4.685 9λ 10 5.167 5λ 11 5.619 4λ 12 6.171 5λ 13 6.676 1λ 14 7.328 4λ 15 8.111 3λ 16 8.921 7λ 表 3 馈电网络端口功率分配和相位值
Table 3. Power distribution and phase value of feed network port
端口 功率值/dB 相位值/(°) 1 -12.08 86.84 2 -12.29 87.33 3 -12.15 87.24 4 -12.47 87.38 5 -12.60 87.77 6 -12.34 87.04 7 -12.25 87.06 8 -12.30 89.58 9 -12.43 89.67 10 -12.22 91.40 11 -12.11 91.39 12 -12.41 88.84 13 -12.50 88.90 14 -12.25 90.11 15 -12.16 89.86 16 -11.99 86.91 表 4 流过矩形槽的功率
Table 4. Power passing through rectangular slots
序号 功率/W 1 0.042 2 0.041 3 0.039 4 0.048 5 0.049 6 0.048 7 0.040 8 0.040 9 0.044 10 0.048 11 0.046 12 0.039 13 0.040 14 0.041 15 0.043 16 0.039 表 5 天线参数
Table 5. Antenna parameters
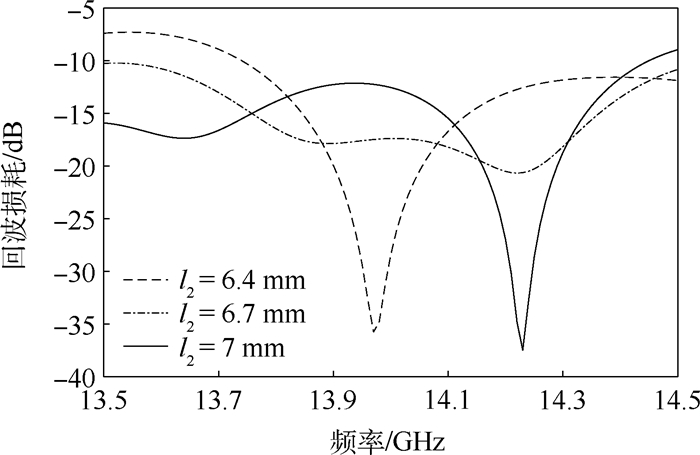
参数 数值/mm 参数 数值/mm LP 7 l510 0.21 W1 2.43 l512 16.81 l501 7 l514 5 l503 5 l516 5 l505 2.09 w501 1.90 l507 0.99 h2 2 l509 5.96 q1 17.83 l511 5 q2 35.05 l513 25.17 q3 49.41 l515 46.46 q4 60.50 w50 2.43 q5 72.65 h1 0.787 q6 82.59 l0 1.4 q7 93.19 W2 0.4 q8 103.1 l502 3.83 w70 1.37 l504 10.70 l70 3.87 l506 12.44 l2 6.80 l508 5.19 h3 0.254 表 6 不同频点性能对比
Table 6. Performance comparison at different frequencies
频率/GHz 增益/dB 副瓣电平/dB 主瓣宽度/(°) 仿真值 测试值 仿真值 测试值 仿真值 测试值 14 17.32 16.53 -18.55 -17.9 5.18 5.58 14.25 16.83 16.31 -19.17 -16.75 4.99 5.38 14.5 16.22 16.04 -18.32 -17.82 5.05 5.36 -
[1] 尹文禄. 微带天线设计与天线测量系统构建[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2004.YIN W L. The design of microstrip antenna and construction of antenna-measuring system[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2004(in Chinese). [2] BAHL J, GARG R, BHARTIA P, et al. Microstrip antenna design handbook[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2001. [3] LOGHMANNIA P, KAMYAB M, RANJBAR NIKKHAH M, et al. Analysis and design of a lowsidelobe level and wide-band aperture coupled microstrip antenna array using FDTD[C]//2013 21st Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 1-4. [4] 段雷. 77 GHz微带阵列天线的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2016.DUAN L. Research on 77 GHz microstrip array antenna[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2016(in Chinese). [5] ABREU D, FREITAS G T. A modified Dolph-Chebyshev approach for the synthesis of low sidelobe beampatterns with adjustable beamwidth[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2003, 51(10): 3014-3017. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2003.817989 [6] CHEN K D, ZHONG S S, TANG X R, et al. Low-sidelobe circularly-polarized microstrip array for RFID reader applications[C]//2007 IET Conference on Wireless, Mobile and Sensor Networks (CCWMSN07), 2007: 482-484. [7] HA B V, MUSSETTA M, PIRINOLI P, et al. Modified compact genetic algorithm for thinned array synthesis[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2016, 15: 1105-1108. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2015.2494839 [8] GOUDOS S. Antenna design using binary differential evolution: Application to discrete-valued design problems[J]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 2017, 59(1): 74-93. doi: 10.1109/MAP.2016.2630041 [9] CHENG Y F, SHAO W, ZHANG R, et al. Thinning and weighting of planar/conformal arrays considering mutual coupling effects[J]. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2016: 1-10. [10] ZAINAL N A, KAMARUDIN M R, YAMADA Y, et al. Sidelobe reduction of unequally spaced arrays for 5G applications[C]//2016 10th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1-4. [11] WIN M Z, SCHOLTZ R A. On the energy capture of ultrawide bandwidth signals in dense multipath environments[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 1998, 2(9): 245-247. doi: 10.1109/4234.718491 [12] RATHI V, KUMAR G, RAY K P. Improved coupling for aperture coupled microstrip antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1996, 44(8): 1196-1198. doi: 10.1109/8.511831 [13] 李勋. X波段宽带微带阵列天线设计[J]. 无线通信技术, 2016, 25(1): 41-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8329.2016.01.009LI X. Design of broadband microstrip array antenna for X-band[J]. Wireless Communication Technology, 2016, 25(1): 41-45(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8329.2016.01.009 [14] DESHMUKH A, RAY K P. Analysis of broadband variations of U-slot cut rectangular microstrip antennas[J]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 2015, 57(2): 181-193. doi: 10.1109/MAP.2015.2414533 [15] 钟顺时. 天线理论与技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2011: 290-296.ZHONG S S. Antenna theory and techniques[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics industry, 2011: 290-296(in Chinese). [16] WANG X J, YAO M L, DAI D C, et al. Synthesis of linear sparse arrays based on dynamic parameters differential evolution algorithm[J]. IET Microwaves, Antennas & Propagation, 2019, 13(9): 1491-1497. -








 下载:
下载: