Comparative analysis of linear/nonlinear static aeroelasticity of fishbone flexible wing
-
摘要:
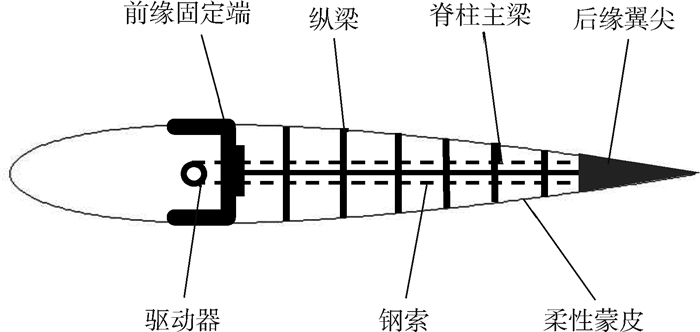
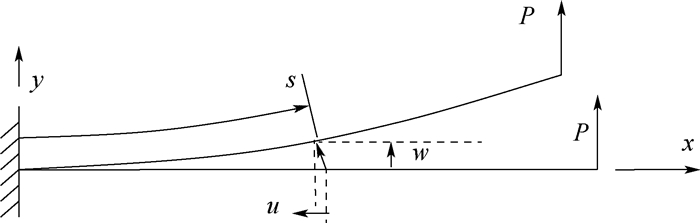
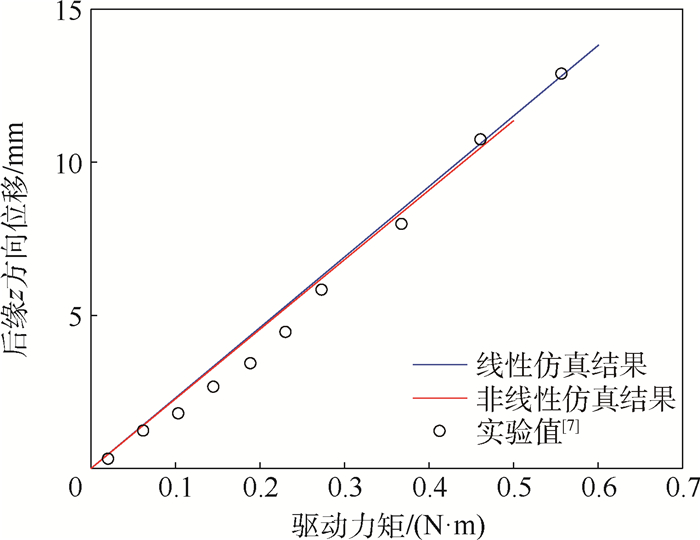
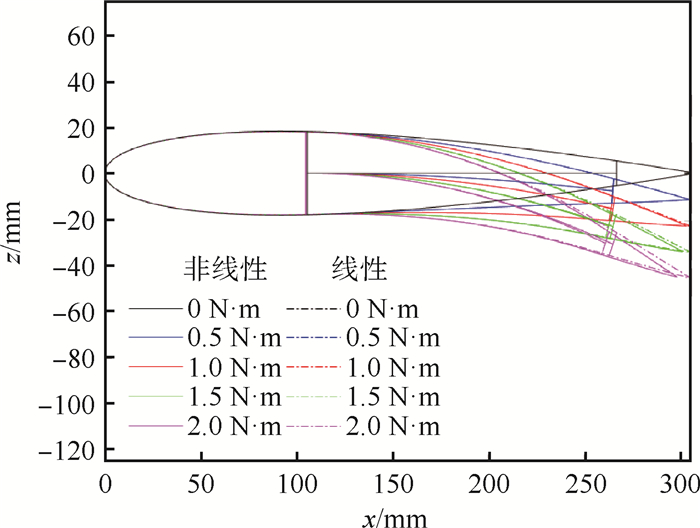
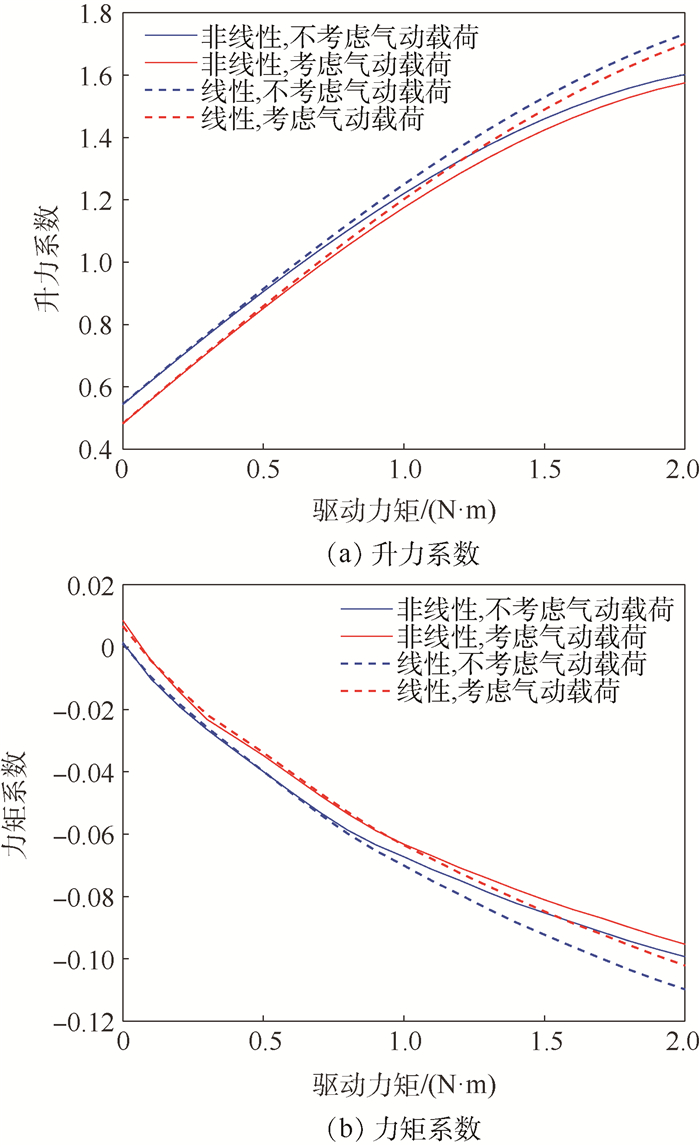
鱼骨柔性翼作为一种性能优越的主动变弯度机翼机构形式,具有弦向抗弯刚度低、翼型厚度方向刚度高的特点,其在进行大弯度主动变形时结构存在较强的几何非线性且气动弹性效应显著。针对传统线性静气动弹性分析方法并不适用于鱼骨柔性翼段的气动弹性分析问题,以Bristol大学的公开鱼骨柔性翼段模型为研究对象,采用曲面涡格法(VLM)和非线性有限元耦合的非线性静气动弹性方法,以及传统气动弹性分析中常用的平面涡格法和线性有限元耦合的线性静气动弹性方法,分别对鱼骨柔性翼段进行大变形下的静气动弹性分析,并进行结果对比。对比验证了所用曲面涡格法与XFOIL软件气动计算结果。算例结果表明:鱼骨柔性翼段大变形下气动弹性效应显著,相比传统线性静气动弹性分析方法,非线性静气动弹性分析方法得到的鱼骨柔性翼段在大变形状态下升力系数最多减少8.28%,力矩系数最多减少6.86%,且能准确快速得到真实变形结果,更具有实际工程应用价值。
-
关键词:
- 鱼骨柔性翼段 /
- 几何非线性 /
- 曲面涡格法(VLM) /
- 结构大变形 /
- 静气动弹性分析
Abstract:Fishbone flexible wing is a excellent design of active morphing camber wing. Ithas low chordwise bending stiffness and high stiffness along the thickness direction of airfoil, and it has strong geometric nonlinearity and significant aeroelastic effect when undergoing active deformation with large deformation. The traditional linear static aeroelastic analysis method is not fit for this problem. Therefore, this paper takes the public fishbone flexible wing model of Bristol University as the research object, adopts the nonlinear aeroelastic analysis method which is based on non-planar Vortex Lattice Method (VLM) and nonlinear finite element analysis and the traditional linear aeroelastic analysis method which is based on linear finite element analysis and planar VLM to analyze the static aeroelasticity of the fishbone wing under large deformation and compare the results. Similarly, the aerodynamic calculation results of the non-planar VLM and XFOIL software used in this paper are verified. The results show that the aeroelastic effect of the fishbone flexible wing under large deformation is significant. Compared to the results of traditional linear static aeroelasticity analysis method, the lift coefficient of fishbone wing under large deformation by nonlinear static aeroelasticity analysis method is 8.28% smaller at most, and the moment coefficient is 6.86% smaller at most. The real deformation under the aerodynamic load can be obtained accurately and quickly by the nonlinear aeroelasticity analysis method proposed in this paper, which is more valuable for practical engineering application.
-
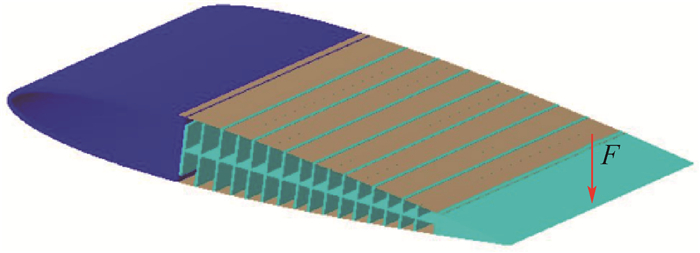
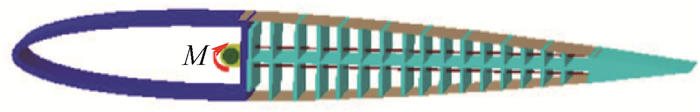
表 1 鱼骨结构模型参数
Table 1. Structural parameters of fishbone structure model
参数 数值 基础翼型 NACA0012 弦长c/mm 305 展长b/mm 150 变形起始位置/mm 107 变形结束位置/mm 260 纵墙数量 14 纵墙厚度/mm 0.8 蒙皮厚度/mm 1.5 脊柱主梁厚度/mm 2 纵梁弹性模量/GPa 2.14 脊柱主梁弹性模量/GPa 2.14 蒙皮弹性模量/MPa 4.56 钢索弹性模量/GPa 131 表 2 鱼骨柔性翼段模态频率
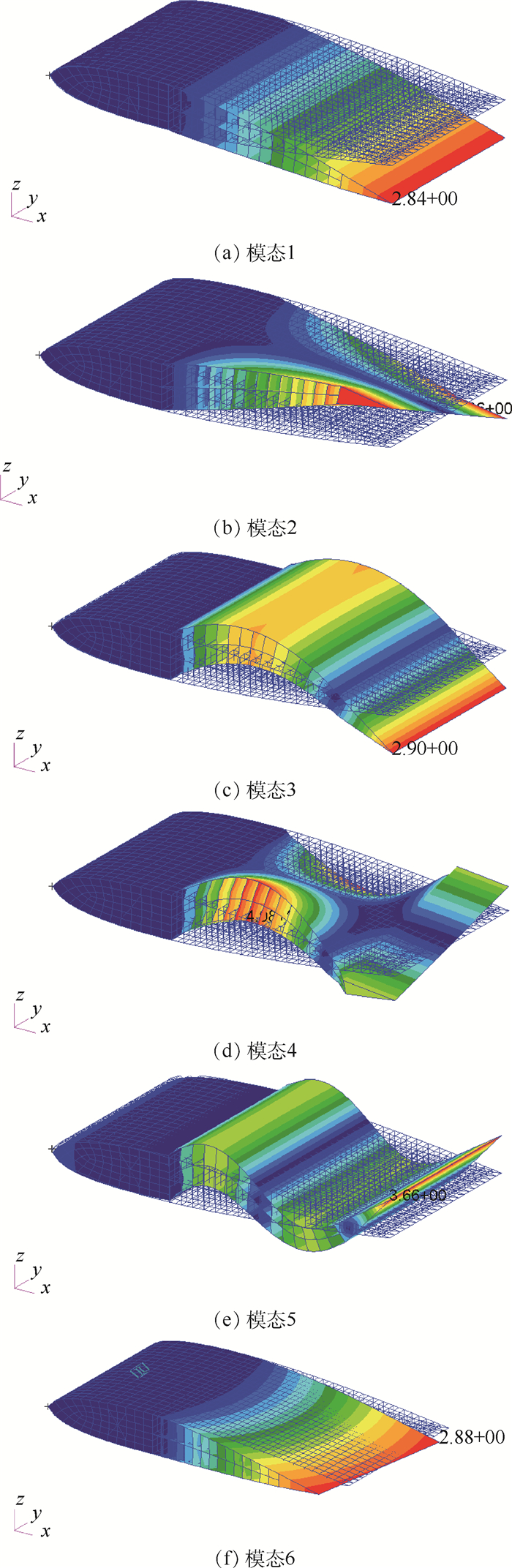
Table 2. Modal frequency of fishbone flexible wing
阶数 模态名称 频率/Hz 1 一阶弯曲 8.314 1 2 一阶扭转 15.359 3 二阶弯曲 22.495 4 二阶扭转 44.228 5 三阶弯曲 45.852 6 面内模态 61.048 -
[1] RAYMER D. Aircraft design: A conceptual approach[M]. Reston: AIAA, 2018. [2] WOODS B K, FRISWELL M I. Preliminary investigation of a fishbone active camber concept[C]//Proceedings of the ASME 2012 Conference on Smart Materials, Adaptive Structures and Intelligent Systems. New York: ASME, 2012: 1-8. [3] BARBARINO S, BILGEN O, AJAJ R M, et al. A review of morphing aircraft[J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2011, 22(9): 823-877. doi: 10.1177/1045389X11414084 [4] WOODS B K, FINCHAM J H, FRISWELL M I. Aerodynamic modelling of the fish bone active camber morphing concept[C]//Proceedings of the RAeS Applied Aerodynamics Conference, 2014: 737-748. [5] WOODS B K, FRISWELL M I. Structural characterization of the fish bone active camber morphing airfoil: AIAA 2014-1122[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2014. [6] RIVERO A E, WEAVER P M, COOPER J E, et al. Progress on the design, analysis and experimental testing of a composite fish bone active camber morphing wing[C]//ICAST 2017: 28th International Conference on Adaptive StructUres and Technologies, 2017: 1-11. [7] WOODS B K, FRISWELL M I. Fluid-structure interaction analysis of the fish bone active camber mechanism: AIAA 2013-1908[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2013. [8] WOODS B K, FRISWELL M I. Multi-objective geometry optimization of the fish bone active camber morphing airfoil[J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2016, 27(6): 808-819. doi: 10.1177/1045389X15604231 [9] DRELA M. Integrated simulation model for preliminary aerodynamic, structural, and control-law design of aircraft: AIAA 99-1394[R]. Reston: AIAA, 1999. [10] MURUA J, PALACIOS R, GRAHAM J M R. Applications of the unsteady vortex-lattice method in aircraft aeroelasticity and flight dynamics[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2012, 55: 46-72. [11] DANG H X, YANG Z, LI Y. Accelerated loosely-coupled CFD/CSD method for nonlinear static aeroelasticity analysis[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2010, 14(4): 250-258. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2010.01.004 [12] WERTER N P M, DE BREUKER R, ABDALLA M M. Continuous-time state-space unsteady aerodynamic modeling for efficient loads analysis[J]. AIAA Journal, 2017, 56(3): 905-916. doi: 10.2514/1.J056068 [13] XIE C C, WANG L B, YANG C, et al. Static aeroelastic analysis of very flexible wings based on non-planar vortex lattice method[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2013, 26(3): 514-521. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2013.04.048 [14] 谢长川, 胡锐, 王斐, 等. 大展弦比柔性机翼气动弹性风洞模型设计与试验验证[J]. 工程力学, 2016, 33(11): 249-256. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2015.04.0254XIE C C, HU R, WANG F, et al. Aeroelastic wind tunnel test model design and experiment on very flexible high-aspect-ratio wings[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2016, 33(11): 249-256(in Chinese). doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2015.04.0254 [15] 刘燚, 杨澜, 谢长川. 基于曲面涡格法的柔性飞机静气动弹性分析[J]. 工程力学, 2018, 35(2): 249-256.LIU Y, YANG L, XIE C C. Study on the static aeroelasticity for flexible aircraft based on non-planar vortex lattice method[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2018, 35(2): 249-256(in Chinese). [16] 王勖成. 有限单元法基本原理和数值方法[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 1997.WANG X C. Basic principle and numerical method of finite element method[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 1997(in Chinese). [17] 宋天霞, 郭建生, 杨元明. 非线性固体计算力学[M]. 武汉: 华中科技大学出版社, 2002.SONG T X, GUO J S, YANG Y M. Nonlinear solid computational mechanics[M]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press, 2002(in Chinese). [18] KATZ J, PLOTKIN A. Low-speed aerodynamics-from wing theory to panel methods[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2001: 400-404. [19] RODDEN W P, JOHNSON E H. MSC/NASTRAN aeroelastic analysis user's guide[Z]. Los Angeles: MSC, 1994. [20] CHEN P C, LIU D D, KARPEL M. ZAERO user's manual(Version 6.2)[Z]. Scottsdale: ZONA Technology, 2006. [21] XIE C C, YANG C. Surface splines generalization and large deflection interpolation[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2007, 44(3): 1024-1026. doi: 10.2514/1.24571 -








 下载:
下载: