-
摘要:
针对全球定位系统(GPS)多普勒观测值在城市环境中受多路径效应影响,从而导致测速误差大的问题,从多普勒频移产生的原理入手,通过运动学理论分析,构建了接收机、反射点与卫星整体运动与多普勒频移误差关系模型。模型分析结果表明:多普勒频移误差与卫星观测向量、反射点切线法向量、接收机运动速度及反射点运动速度有关。最后通过5种不同场景的GPS数据验证了所提模型的正确性。在多路径情况下,当接收机或反射点运动时,可能会导致巨大的测速误差,使得结果不具备可靠性。
-
关键词:
- 全球定位系统(GPS) /
- 多路径效应 /
- 多普勒频移 /
- 测速 /
- 误差模型
Abstract:Global Positioning System (GPS) Doppler observation is affected by multipath, which leads to a huge error in velocity calculation. In response to this problem, starting from the causes of Doppler observations, through kinematic analysis, a model of the relationship between the overall motion of receiver, reflection point and the satellite, and the error of Doppler observations is constructed. The results show that: the error of Doppler observations is related to the satellite observation vector, the tangent normal vector of the reflection point, the speed of the receiver and the reflection point. The effectiveness of the proposed model is verified by the results in 5 different scenarios. When receiver and reflection point are moving, multipath may cause a huge error in velocity, which makes the velocity unreliable.
-
表 1 不同场景实验情况
Table 1. Tests under different scenarios
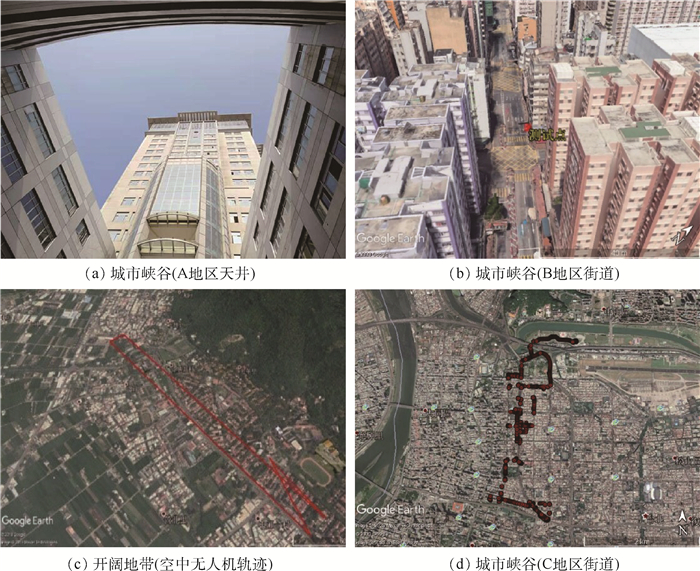
实验 载体运动状态 载体周围环境 接收机类型 有效历元数 实验1 静态 开阔地带(A地区校园) NovAtel 36 180 实验2 静态 城市峡谷(A地区天井) NovAtel 390 实验3 静态 城市峡谷(B地区街道) NovAtel 38 798 实验4 动态 开阔地带(空中无人机) Trimble 12 371 实验5 动态 城市峡谷(C地区街道) NovAtel 3 712 表 2 不同实验的RMSE
Table 2. RMSE under different tests
实验 RMSE/(m·s-1) 东向 北向 天向 总向 实验1 0.014 0.017 0.031 0.038 实验2 0.021 0.040 0.088 0.099 实验3 0.888 0.667 2.811 3.023 实验4 0.071 0.058 0.221 0.239 实验5 0.547 0.259 1.407 1.532 -
[1] GU C L. Urbanization: Positive and negative effects[J]. Science Bulletin, 2019, 64(5): 281-283. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2019.01.023 [2] 顾朝林, 曹根榕. 基于城镇化发展趋势的中国交通网战略布局[J]. 地理科学, 2019, 39(6): 865-873.GU C L, CAO G R. Strategic layout of China's future transportation network based on urbanization trends[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2019, 39(6): 865-873(in Chinese). [3] 肖云, 孙中苗, 程广义. 利用GPS多普勒观测值精确确定运动载体的速度[J]. 武汉测绘科技大学学报, 2000, 25(2): 113-118.XIAO Y, SUN Z M, CHENG G Y. Precise determination of velocity for airborne gravimetry using the GPS Doppler observations[J]. Journal of Wuhan Technical University of Surveying and Mapping, 2000, 25(2): 113-118(in Chinese). [4] 何海波, 杨元喜, 孙中苗. 几种GPS测速方法的比较分析[J]. 测绘学报, 2002, 31(3): 32-36.HE H B, YANG Y X, SUN Z M. A comparison of several approaches for velocity determination with GPS[J]. Acta Geodaeyica et Cartographica Sinica, 2002, 31(3): 32-36(in Chinese). [5] SUN R, HSU L T, XUE D, et al. GPS signal reception classification using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system[J]. The Journal of Navigation, 2019, 72(3): 685-701. doi: 10.1017/S0373463318000899 [6] SUN W, DUAN S, KONG Y, et al. Velocity and acceleration of Doppler calculation for carrier based on GPS broadcast ephemeris[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 2017, 30(11): 1630-1635. [7] 张明, 王宏涛, 王强. 利用GPS多普勒观测值精确确定运动载体的速度[J]. 电光与控制, 2006, 13(3): 97-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2006.03.027ZHANG M, WANG H T, WANG Q. Accurate determination of moving vehicle speed with GPS Doppler observed values[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2006, 13(3): 97-101(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2006.03.027 [8] GRAAS F V, SOLOVIEV A. Precise velocity estimation using a stand-alone GPS receiver[J]. Navigation, 2004, 51(4): 283-292. doi: 10.1002/j.2161-4296.2004.tb00359.x [9] WANG Q X, XU T H. Combining GPS carrier phase and Doppler observations for precise velocity determination[J]. Science China Physics, Mechanics and Astronomy, 2011, 54(6): 1022-1028. doi: 10.1007/s11433-011-4331-z [10] 王甫红, 张小红, 黄劲松. GPS单点测速的误差分析及精度评估[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2007, 32(6): 515-519.WANG F H, ZHANG X H, HUANG J S. Error analysis and accuracy assessment of GPS absolute velocity determination with SA off[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2007, 32(6): 515-519(in Chinese). [11] 何海波, 杨元喜, 孙中苗, 等. GPS多普勒频移测量速度模型与误差分析[J]. 测绘学院学报, 2003, 20(2): 79-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6338.2003.02.001HE H B, YANG Y X, SUN Z M, et al. Mathematic model and error analyses for velocity determination using GPS Doppler measurements[J]. Journal of Institute of Surveying and Mapping, 2003, 20(2): 79-82(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6338.2003.02.001 [12] 李乐乐, 贺凯飞, 王振杰, 等. GPS实时单站测速和相对测速的误差比较与精度分析[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2019, 39(10): 1063-1069.LI L L, HE K F, WANG Z J, et al. Error comparison and accuracy analysis between stand-alone and relative velocity determination using GPS[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamic, 2019, 39(10): 1063-1069(in Chinese). [13] 孙伟, 段顺利, 丁伟, 等. GPS单点测速方法的比较分析[J]. 导航定位学报, 2017, 5(1): 81-85.SUN W, DUAN S L, DING W, et al. Comparative analysis on velocity determination by GPS single point[J]. Journal of Navigation and Position, 2017, 5(1): 81-85(in Chinese). [14] 单瑞, 赵铁虎, 于得水, 等. 单点GPS多普勒测速模型比较与精度分析[J]. 测绘通报, 2013(3): 7-9.SHAN R, ZHAO T H, YU D S, et al. Model comparison and accuracy analysis of single-stationed GPS velocity estimation using GPS Doppler measurements[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2013(3): 7-9(in Chinese). [15] TRAJKOVSKI K K, STERLE O, STOPAR B. Robust statistics, Doppler observations and multipath effect in GNSS in adverse conditions[J]. Geodetski Vestnik, 2016, 60(1): 42-52. doi: 10.15292/geodetski-vestnik.2016.01.42-52 [16] SOBOLEV V S, UTKIN E N, KASHCHEEVA G A, et al. Doppler shift of the modulation frequency of laser radiation scattered by a moving object[J]. Optics and Spectroscopy, 2019, 119(2): 291-294. doi: 10.1134/s0030400x15080214 [17] 谢钢. GPS原理与接收机设计[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2009: 74-75.XIE G. Principles of GPS and receiver design[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2009: 74-75(in Chinese). [18] XU L, RIFE J H. Doppler-aided line-of-sight identification and localization in future cellular networks[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+2018). Hoboken: Wiley, 2018: 3018-3027. [19] XU L, RIFE J. NLOS and multipath detection using Doppler shift measurements[C]//Proceedings of the 32nd International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+2019). Hoboken: Wiley, 2019: 4064-4075. [20] XU L, RIFE J. Modeling multipath effects on frequency locked loops[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 International Technical Meeting of the Institute of Navigation. Hoboken: Wiley, 2020: 698-712. 期刊类型引用(3)
1. 别秭锟,王鑫宇,刘万科. 城市动态场景GNSS信号特征及其对NLOS自主识别影响分析. 测绘地理信息. 2025(02): 83-88 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 杨少帅,陈小江. 基于GNSS差分的实时动态相对定位技术研究. 舰船电子工程. 2024(11): 70-75 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 王秀境,肖建华,刘岑俐,陈肖,杨诚. 基于改进的卡尔曼滤波无人机抗欺骗BDS导航方法. 电力大数据. 2022(04): 1-8 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(10)
-








 下载:
下载:


 百度学术
百度学术

