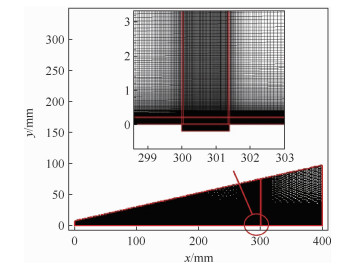
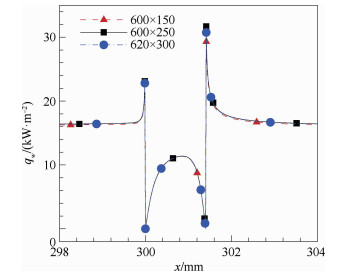
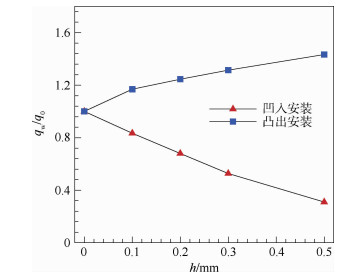
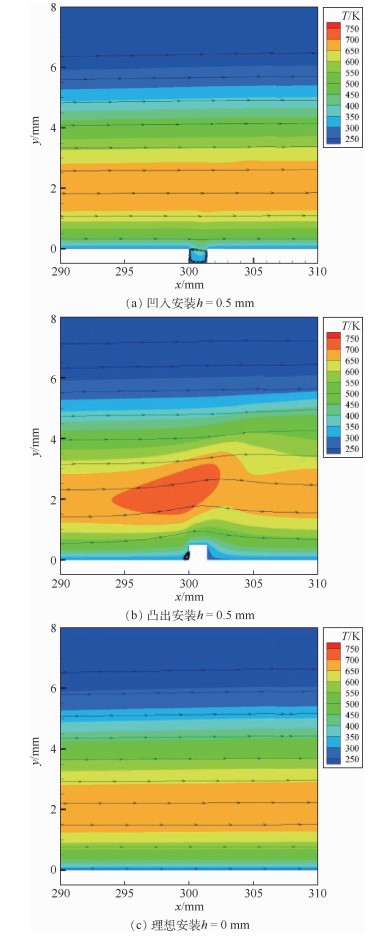
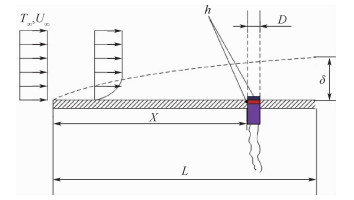
Influence of sensor installation on accuracy of aerodynamic heating measurement on flat plate
-
摘要:
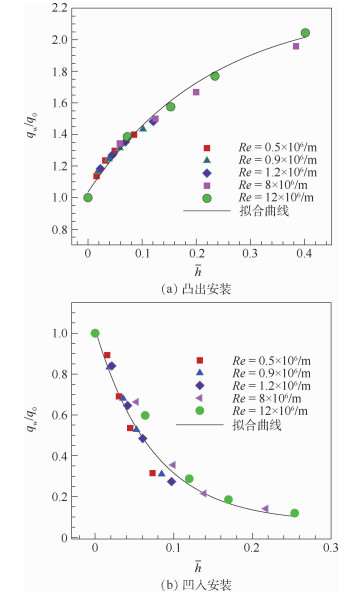
对高超声速飞行器来说,气动热的准确预测是其合理选择防热材料及热结构设计的重要依据,但目前在激波风洞试验中气动热的高精度测量仍较为困难,热流的测量精度受到诸多非理想因素的影响,但传感器安装对热流测量精度的影响却鲜见研究。选取平板模型来研究传感器非理想安装对气动热测量精度的影响,针对不同的传感器安装偏差(凸出或凹入模型表面0.1~0.5 mm),分析不同雷诺数下传感器安装对气动热测量精度的影响规律及机理。研究结果表明:传感器安装对气动热测量精度有较大影响,凸出安装会导致热流测量结果偏大,而凹入安装则会导致测量结果偏小,热流偏差会随着安装偏差的增大而增大,且高来流雷诺数下传感器非理想安装所引起的热流误差更大;以边界层当地厚度对凹凸程度无量纲化,非理想安装带来的测量偏差只与该无量纲参数相关。研究结果能够为气动热测量的实验方案设计及测量误差分析提供一定的理论指导。
Abstract:Accurate measurement of aerodynamic heating is an important issue for hypersonic vehicles to choose reasonable heat resistant materials and thermal structure design. However, it is still difficult to measure the heat flux accurately in shock tunnel experiments, and any slight deviation from ideal conditions may lead to inaccuracy. In-depth investigations are needed to carry out. In this study, the flat plate model is selected to study the influence of the non-ideal sensor installation on the accuracy of heat flux measurement. The sensors examined are protruding or recessed from the model surface in the order of 0.1 mm to 0.5 mm and different Reynolds numbers are considered. Related rules and mechanism of the influence of sensor installation on the accuracy of aerodynamic heating measurement are analyzed in detail. The results show that the sensor installation has great influence on the accuracy of the heat flux measurement. Protruding sensor installation results in larger deviation from actual heat transfer and recessed sensor installation results in smaller deviation compared to the results obtained with a smoothly installed sensor. The larger the protruding/recessed depth, the more severe the deviation, and this deviation will be larger under higher Reynolds number conditions. Using the non-dimensional form of protruding/recessed depth to the thickness of boundary layer, the level of deviation is only related to the non-dimensional value regardless of Reynolds number. In all, the results can provide theoretical guidance for the design and error analysis of aerodynamic heating measurement experiments.
-
Key words:
- flat plate /
- aerodynamic heating /
- installation precision /
- Reynolds number /
- boundary layer
-
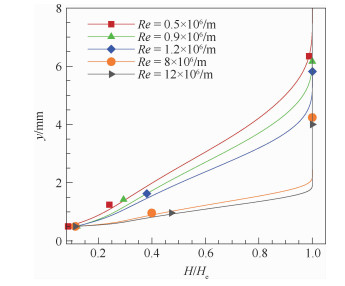
表 1 不同工况下的来流参数
Table 1. Incoming flow parameters under different working conditions
工况 p∞/Pa T∞/K Re/(106 m-1) h/mm D/mm Case 1 390 324 0.5 1.4 Case 2 394 221 0.9 1.4 Case 3 575 236.5 1.2 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.5 1, 1.4, 1.7, 2 Case 4 3 833.3 236.5 8 1.4 Case 5 5 750 236.5 12 1.4 表 2 平板热流自相似解与CFD的对比
Table 2. Comparison of theoretical and simulated plate heat flux values
工况 q0/(104 W·m-2) 偏差/% CFD 理论值 Case 1 2.36 2.45 3.67 Case 2 1.59 1.65 3.64 Case 3 2.04 2.09 2.39 Case 4 5.02 5.23 4.02 Case 5 6.04 6.40 5.63 -
[1] ANDERSON J D. Hypersonic and high-temperature gas dynamics[M]. 2nd ed. Reston: AIAA, 2006. [2] WANG Q, LI J P, ZHAO W, et al. Influence of thermal sensor installation on measuring accuracy at stagnation points[J]. Journal of Thermophysics & Heat Transfer, 2016, 31(2): 1-6. [3] COBLISH J, COULTER S, NORRIS J. Aerothermal measurement improvements using coaxial thermocouples at AEDC hypervelocity wind tunnel No. 9[C]//AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting & Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 2013: 1467. [4] CHADWICK K. Stagnation heat transfer measurement techniques in hypersonic shock tunnel flows over spherical segments[C]//AIAA Thermophysics Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2008: 2493. [5] VAN DRIEST E R. Investigation of laminar boundary layer in compressible fluids using the Crocco method[J]. Technical Report Archive & Image Library, 1952, 10(1): 15-31. [6] FAY J A, RIDDELL F R. Theory of stagnation point heat transfer in dissociated air[J]. Journal of the Aeronautical Sciences, 2012, 25(2): 73-85. [7] 彭治雨, 石义雷, 龚红明, 等. 高超声速气动热预测技术及发展趋势[J]. 航空学报, 2015, 36(1): 325-345.PENG Z Y, SHI Y L, GONG H M, et al. Hypersonic aeroheating prediction technique and its trend of development[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2015, 36(1): 325-345(in Chinese). [8] GUELHAM A, ESSER B. A study on heat flux measurements in high enthalpy flows[C]//AIAA Thermophysics Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2013: 3011. [9] 曾磊, 桂业伟, 王安龄, 等. 激波风洞驻点热流测量误差机理及其不确定度研究[J]. 实验流体力学, 2015, 29(5): 15-25.ZENG L, GUI Y W, WANG A L, et al. Study on error mechanism and uncertainty assessment of heat flux measurement in shock tunnel[J]. Journal of Experiments in Fluid Mechanics, 2015, 29(5): 15-25(in Chinese). [10] 阎超, 禹建军, 李君哲. 热流CFD计算中格式和网格效应若干问题研究[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2006, 24(1): 125-130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-1825.2006.01.023YAN C, YU J J, LI J Z. Scheme effect and grid dependency in CFD computations of heat transfer[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2006, 24(1): 125-130(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-1825.2006.01.023 [11] KANDULA M, HADDAD G F, CHEN R H. Three-dimensional thermal boundary layer corrections for circular heat flux gauges mounted in a flat plate with a surface temperature discontinuity[J]. International Journal of Heat & Mass Transfer, 2007, 50(3): 713-722. [12] WANG Q, LI J P, ZHAO W, et al. Comparative study on aerodynamic heating under perfect and nonequilibrium hypersonic flows[J]. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 2016, 59(2): 77-83. [13] 秦峰, 何川, 曾磊, 等. 驻点热流测量试验技术研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2013, 48(6): 1072-1077. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2013.06.016QIN F, HE C, ZENG L, et al. Experimental research of heat-transfer measurements on stagnation points[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2013, 48(6): 1072-1077(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2013.06.016 [14] 傅德薰. 计算空气动力学[M]. 北京: 宇航出版社, 2006.FU D X. Computational aerodynamics[M]. Beijing: China Asteonautic Publishing House, 2006(in Chinese). [15] KIM K H, KIM C, RHO O H. Methods for the accurate computations of hypersonic flows: I. AUSMPW+scheme[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2001, 174(1): 38-80. doi: 10.1006/jcph.2001.6873 [16] JAMESON A, YOON S. Lower-upper implicit schemes with multiple grids for the Euler equations[J]. AIAA Journal, 1987, 25(7): 929-935. doi: 10.2514/3.9724 [17] 郭永怀. 边界层理论讲义[M]. 北京: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2008.GUO Y H. Lecture notes on boundary layer theory[M]. BeiJing: University of Science and Technology of China Press, 2008(in Chinese). [18] 李素循. 激波与边界层主导的复杂流动[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007.LI S X. Complex flow dominated by shock wave and boundary layer[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2007(in Chinese). [19] LI X D, HU Z M, JIANG Z L. Numerical investigation on the thermal protection mechanism for blunt body with forward-facing cavity[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2016, 59(7): 1120-1129. doi: 10.1007/s11431-016-6015-4 [20] KUMAR C S, REDDY K P J. Experimental investigation of aerodynamic interference heat transfer around a protuberance on a flat plate subjected to hypersonic flow[C]//International Symposium on Shock Waves, 2012: 471-476. [21] 吴云鹏. 壁面温度控制对平板边界层影响的数值研究[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2016, 34(5): 674-679.WU Y P. Numerical simulation of wall temperature control influence on flat plate boundary layer[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2016, 34(5): 674-679(in Chinese). [22] 李俊红, 张亮, 俞继军, 等. 高超声速可压缩流中粗糙壁热流研究[J]. 计算物理, 2017, 34(2): 165-174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-246X.2017.02.006LI J H, ZHANG L, YU J J, et al. Study of rough wall heat flux in hypersonic turbulent flow[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2017, 34(2): 165-174(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-246X.2017.02.006 -







 下载:
下载: