Human motion direction prediction method based on eye tracking, pose and scene video
-
摘要:
外骨骼机器人作为新提出的改善、提高人类生活能力的智能设备,同样需要高效智能的人机交互系统,而人机交互的第一步,则是精准预测人的行为意图。从外骨骼机器人的顶层控制角度出发,介绍了人体运动意图识别和外骨骼机器人智能交互能力的研究现状,并对人体运动方向识别进行了研究。提出了一种结合眼动信息、位姿信息及场景视频信息的多信息融合的人体运动意图识别网络架构,并进行了采集设备的穿戴实验。利用实验数据,对提出的网络方法进行了实验验证。结果表明:所提出的人体运动方向的识别系统,可以预测出人体运动过程中的运动方向。
Abstract:Exoskeleton robots, as newly proposed smart devices to improve and enhance human life ability, require efficient and intelligent human-computer interaction systems, and the first step of human-computer interaction is to accurtely predict human behavior intention. From the perspective of top-level control of exoskeleton robots, the current states and progress of human motion intention recognition and the intelligent interaction capabilities of exoskeleton robots are reported. Then, the recognition of human motion direction is studied. A network framework of human motion intention recognition combining eye tracking information, position and posture information, and scene video information is proposed, and wearable experiments of acquisition devices are carried out. The predictive capability of the network has been proved by experiments. The results show that the proposed recognition system can predict the movement direction during human movement.
-
Key words:
- eye tracking /
- prediction method /
- direction of movement /
- human behavior /
- human computer interaction
-
层名 输出大小 各卷积层结构 conv1 112×112 7×7, 64, 步长2 maxpool 56×56 3×3, 最大池化,步长2 conv2_x 56×56 
conv3_x 28×28 
conv4_x 14×14 
conv5_x 7×7 
avgpool 1×1 平均池化,1 000维全连接层,softmax层 表 2 用于构建训练集的数据类型
Table 2. Data type used to build training set
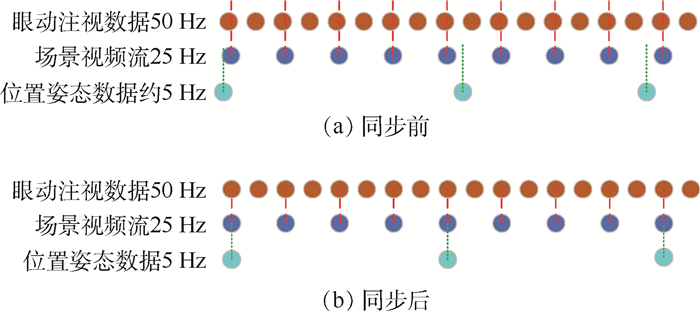
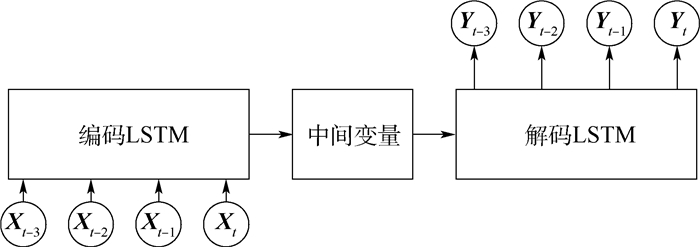
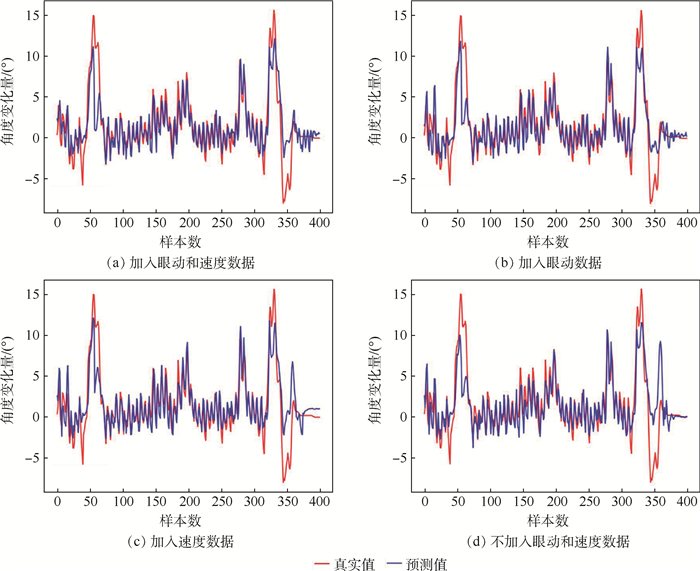
数据名称 数据大小 采样频率/Hz 位置坐标 3×1 5 姿态坐标 3×1 5 场景特征向量 2 048×1 25 眼动注视数据 2×1 25 相对转角(标签) 1×1 5 表 3 4种训练数据的结果
Table 3. Results of four training experiment
训练数据 MAE MSE R2 ① 1.383 4.863 0.676 ② 1.337 4.413 0.705 ③ 1.415 4.681 0.688 ④ 1.484 5.873 0.608 -
[1] JACOBSEN S C, OLIVIER M, SMITH F M, et al. Research robots for applications in artificial intelligence, teleoperation and entertainment[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2004, 23(4-5): 319-330. doi: 10.1177/0278364904042198 [2] LIANG J W, JIANG L, NIEBLES J C, et al. Peeking into the future: Predicting future person activities and locations in videos[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 2960-2963. [3] 王昕. 面向下肢康复机器人的运动意图识别技术研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2019: 97-98.WANG X. Research on motion intention recognition technology for lower limb rehabilitation robot[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2019: 97-98(in Chinese). [4] ALAHI A, GOEL K, RAMANATHAN V, et al. Social LSTM: Human trajectory prediction in crowded spaces[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 961-971. [5] BHATTACHARYYA A, FRITZ M, SCHIELE B. Long-term on-board prediction of people in traffic scenes under uncertainty[C]//2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workships (CVPRW). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 4194-4202. [6] CHANDRA R, GUAN T R, PANUGANTI S, et al. Forecasting trajectory and behavior of road-agents using spectral clustering in graph-LSTMs[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020, 5(3): 4882-4890. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2020.3004794 [7] CHANDRA R, BHATTACHARYA U, BERA A, et al. TraPHic: Trajectory prediction in dense and heterogeneous traffic using weighted interactions[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 8475-8484. [8] XU Y Y, PIAO Z X, GAO S H. Encoding crowd interaction with deep neural network for pedestrian trajectory prediction[C]//2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 5275-5284. [9] HAYASHI T, KAWAMOTO H, SANKAI Y. Control method of robot suit HAL working as operator's muscle using biological and dynamical information[C]//2005 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2005: 3063-3068. [10] 张富平. 图像去噪增强算法的研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2014: 1-2.ZHANG F P. Research of image enhancement and image denoising[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2014: 1-2(in Chinese). [11] 苏泫. 基于IMU预积分的视觉惯性里程计系统[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2018: 5-7.SU X. Visual-inertial odometry based on IMU pre-integration[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2018: 5-7(in Chinese). [12] QIN T, LI P L, SHEN S J. VINS-Mono: A robust and versatile monocular visual-inertial state estimator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2018, 34(4): 1004-1020. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2018.2853729 [13] 张裕天. 基于视觉感知的多模态多任务端到端自动驾驶方法研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2019: 43-45.ZHANG Y T. Research on multi-modal multi-task end-to-end autonomous driving method based on visual perception[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2019: 43-45(in Chinese). [14] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [15] FLETCHER D, IAN P. 3D数学基础: 图形与游戏开发[M]. 史银雪, 陈洪, 王荣静, 译. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2005: 154-157. [16] FLETCHER D, IAN P. 3D math primer for graphics and game development[M]. SHI Y X, CHEN H, WANG R J, translated. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2005: 154-157(in Chinese). [17] FU R, ZHANG Z, LI L. Using LSTM and GRU neural network methods for traffic flow prediction[C]//2016 31st Youth Academic Annual Conference of Chinese Association of Automation (YAC). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 324-328. [22] KINGMA D P, BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[EB/OL]. (2015-07-23)[2020-06-23]. -








 下载:
下载: