Satellite time series data classification method based on trend symbolic aggregation approximation
-
摘要:
作为在时间序列数据挖掘中广泛使用的主要符号化表示方法,符号聚合近似(SAX)使用段的平均值作为符号表示,由于无法区分具有不同趋势但具有相同平均值符号的不同时间序列,某些情况下可能会导致错误的分类。提出了一种改进的符号表示——趋势符号聚合近似(TrSAX),集成SAX与最小二乘法,用以描述时间序列的均值和斜率,并由此构建出BOTS分类器。此外,对卫星的模拟量遥测时序数据中的角度序列、转速序列、电流序列进行分析,并从UCR公开数据集中筛选出与3种序列类似的3个数据集进行分类实验验证。与应用了SAX和2个改进的SAX、经典的欧氏距离(ED)、动态时间规整(DTW)的1-NN分类方法进行对比,结果表明:提出的BOTS分类方法的分类错误率明显低于其他5种分类方法。
Abstract:As the main symbolic representation method widely used in time series data mining, the Symbolic Aggregation Approximation (SAX) uses the mean value of segments as the symbolic representation. Since it is impossible to distinguish different time series that have different trends but the same mean value, it may lead to incorrect classification. This paper presents an improved symbol representation-Trend Symbol Aggregation Approximation (TrSAX), which integrates SAX and least squares method to describe the mean and slope value of the time series, and constructs the BOTS classifier. In addition, this paper analyzes the angle sequence, rotation speed sequence, and current sequence in the satellite analog telemetry time series data, and selects three datasets similar to these three sequences from the UCR public dataset for classification experiment verification. They are compared with the 1-NN classification methods using SAX, two improved SAX, classic Euclidean Distance (ED) and Dynamic Time Warping (DTW). The results show that the classification error rate of the proposed BOTS classification method is significantly lower than the other five classification methods.
-
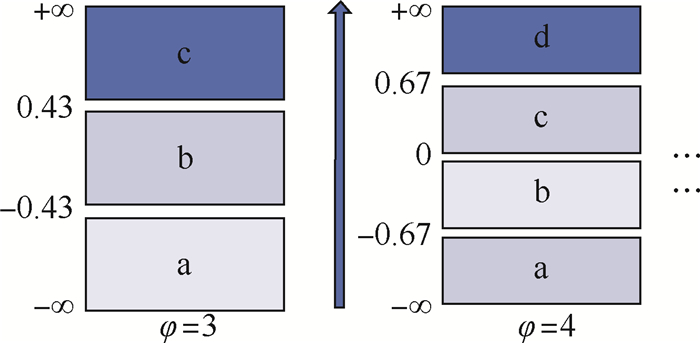
表 1 字母数为3~9的断点查找表
Table 1. Look up table from breakpoints with alphabet sizes from 3 to 5
βi 3 4 5 β1 -0.43 -0.67 -0.84 β2 0.43 0 -0.25 β3 0.67 0.25 β4 0.84 表 2 时间序列的BOTS表示形式的虚拟示例
Table 2. Visual example of BOTS representation for time series
时间序列号 AaAaAa AaAaAb … EaEaEa … EdEdEd 1 2 2 … 13 … 0 2 3 1 … 0 … 0 3 1 2 … 12 … 0 ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ m 2 2 … 14 … 0 表 3 时间序列数据集详细信息
Table 3. Details on time series datasets
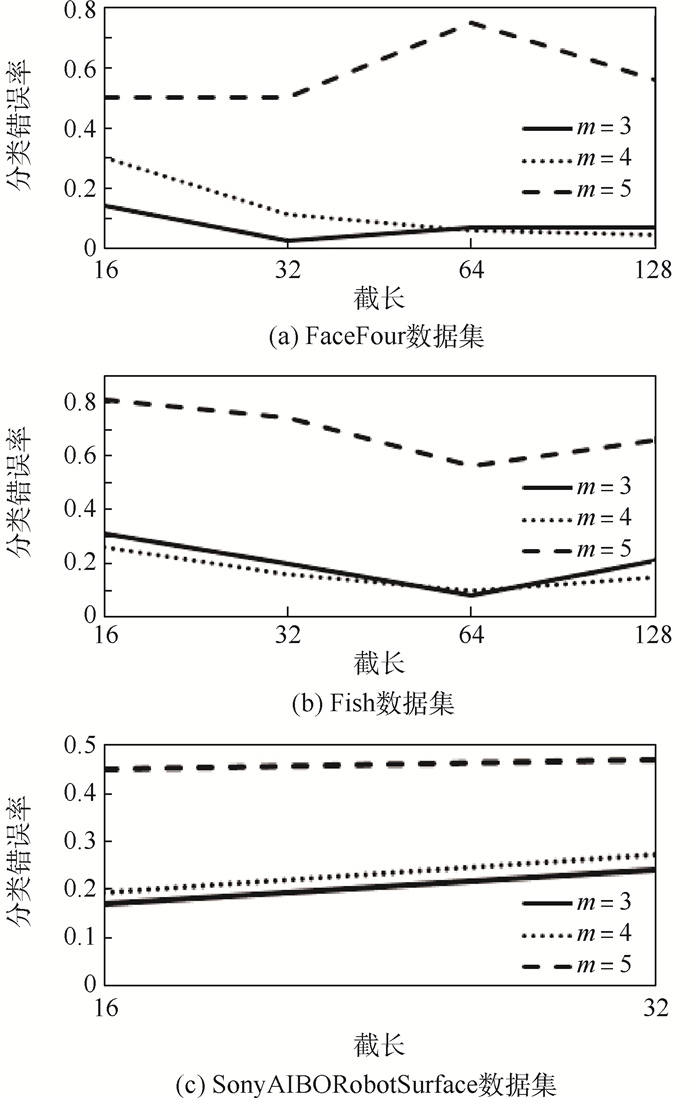
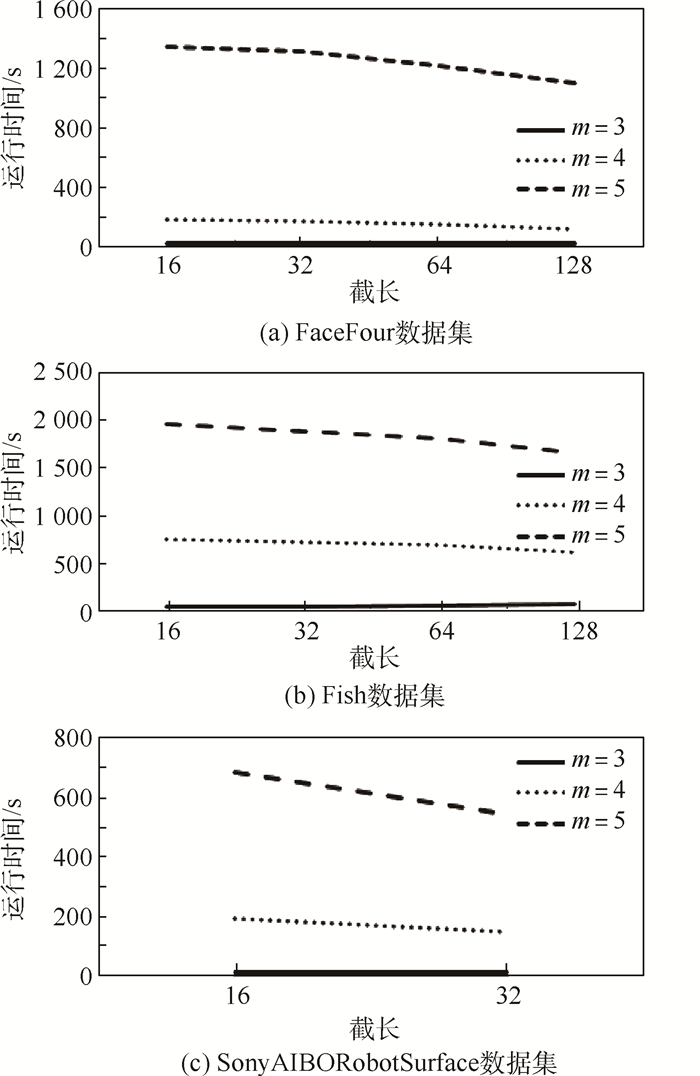
数据集编号 名称 训练集/测试集 类别数 序列长度 1 SonyAIBO
RobotSurface20/601 2 70 2 Fish 175/175 7 115 3 FaceFour 24/88 4 116 表 4 不同表示算法的分类结果
Table 4. Classification results of different representation algorithms
数据集 1-NN ED 1-NN DTW 1-NN SAX 1-NN ESAX 1-NN TSAX BOTS SongAIBO Robot 0.215 0.199 0.236 0.217 0.187 0.171 Fish 0.198 0.237 0.109 0.469 0.192 0.080 FaceFour 0.222 0.151 0.053 0.182 0.06 0.023 平均秩 4.67 4 3.33 5.33 2.67 1 -
[1] 杨海民, 潘志松, 白玮. 时间序列预测方法综述[J]. 计算机科学, 2019, 46(1): 21-28.YANG H M, PAN Z S, BAI W. Review of time series prediction methods[J]. Computer Science, 2019, 46(1): 21-28(in Chinese). [2] 史欣田, 庞景月, 张新, 等. 基于集成极限学习机的卫星大数据分析[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2018, 39(12): 81-91.SHI X T, PANG J Y, ZHANG X, et al. Satellite big data analysis based on bagging extreme learning machine[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2018, 39(12): 81-91(in Chinese). [3] 彭喜元, 庞景月, 彭宇, 等. 航天器遥测数据异常检测综述[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2016, 37(9): 1929-1945.PENG X Y, PANG J Y, PENG Y, et al. Review on anomaly detection of spacecraft telemetry data[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2016, 37(9): 1929-1945(in Chinese). [4] YANG T, CHEN B, GAO Y, et al. Data mining-based fault detection and prediction methods for in-orbit satellite[C]//IEEE International Conference on Measurement, Information and Control.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 805-808. [5] 肇刚, 李言俊. 基于时间序列数据挖掘的航天器故障诊断方法[J]. 飞行器测控学报, 2010, 29(3): 1-5.ZHAO G, LI Y J. Spacecraft fault diagnosis method based on time series data mining[J]. Journal of Spacecraft TT & C Technology, 2010, 29(3): 1-5(in Chinese). [6] 鲍军鹏, 杨科, 周静. 卫星时序数据挖掘节点级并行与优化方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(12): 2470-2478. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0334BAO J P, YANG K, ZHOU J. Node level parallel and optimization method of satellite time serial data mining[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(12): 2470-2478(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0334 [7] 张弓, 翟君武, 杨海峰. 导航卫星遥测数据趋势预测技术研究[J]. 航天器工程, 2017, 3(3): 74-81.ZHANG G, ZHAI J W, YANG H F. Research on telemetry data tendency prognosis for navigation satellite[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2017, 3(3): 74-81(in Chinese). [8] WAN Y, SI Y W. A hidden semi-Markov model for chart pattern matching in financial time series[J]. Soft Computing, 2017, 22(3): 1-20. doi: 10.1007/s00500-017-2703-7 [9] MUEEN A, KEOGH E, YOUNG N E.Logical-Shapelets: An expressive primitive for time series classification[C]//ACM Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining.New York: ACM, 2011: 1154-1162. [10] GAO Z K, CAI Q, YANG Y X, et al. Multiscale limited penetrable horizontal visibility graph for analyzing nonlinear time series[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 35622. doi: 10.1038/srep35622 [11] XI X, KEOGH E, SHELTON C, et al.Fast time series classification using numerosity reduction[C]//International Conference On Machine Learning, 2006: 1033-1040. [12] SAKOE H, CHIBA S. Dynamic programming algorithm optimization for spoken word recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing, 1978, 26(1): 43-49. doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1978.1163055 [13] RAKESH A, CHRISTOS F, ARUN S.Efficient similarity search in sequence databases[C]//Foundations of Data Organization and Algorithms.Berlin: Springer, 1993: 69-84. [14] CHEN Q, CHEN L, LIAN X, et al.Indexable PLA for efficient similarity search[C]//VLDB Endowment in Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Very Large Data Bases.2007: 435-446. [15] LIN J, KEOGH E, LI W, et al. Experiencing SAX: A novel symbolic representation of time series[J]. Data Mining & Knowledge Discovery, 2007, 15(2): 107-144. [16] KEOGH E, CHAKRABARTI K, PAZZANI M, et al. Dimensionality reduction for fast similarity search in large time series databases[J]. Knowledge & Information Systems, 2001, 3(3): 263-286. [17] LIN J, KHADE R, LI Y. Rotation-invariant similarity in time series using bag-of-patterns representation[J]. Journal of Intelligent Information Systems, 2012, 39(2): 287-315. doi: 10.1007/s10844-012-0196-5 [18] PHAM N D, LE Q L, DANG T K.Two novel adaptive symbolic representations for similarity search in time series databases[C]//Proceedings of the 12th Asia-Pacific Web Conference (APWeb).Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 181-187. [19] LKHAGVA B, SUZUKI Y, KAWAGOE K.New time series data representation ESAX for financial applications[C]//International Conference on Data Engineering Workshops.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2006: 17-22. [20] ZHANG K, LI Y, CHAI Y, et al.Trend-based symbolic aggregate approximation for time series representation[C]//2018 Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC).Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 2234-2240. [21] 陈静. 卫星遥测数据的时间序列相似性度量方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2015: 22-23.CHEN J.Similarity measure of time series for satellite telemetry data[D].Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2015: 22-23(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: