-
摘要:
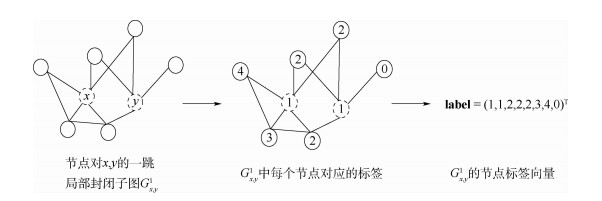
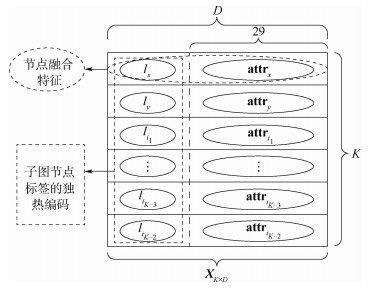
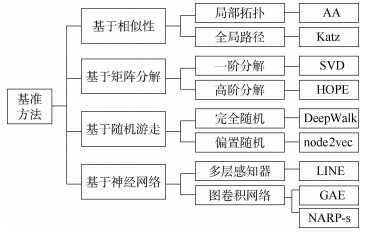
针对新增航线发现研究中存在的航线选择主观化、网络信息挖掘不充分等问题,考虑航空运输网络的拓扑结构特征和节点(通航城市)层次属性,提出了一种基于链路预测的未来新增航线发现(NARP)模型。NARP模型提取局部封闭子图构建子图邻接矩阵,基于距离标记子图节点结构重要性,采用因子分析和层次聚类提取节点层次属性。在此基础上,融合子图结构和节点属性2类特征,采用深度图卷积神经网络(DGCNN)进行链路预测,实现新增航线发现。在中国航空运输网络实际运行数据上的实验结果表明:较之基准方法,NARP模型的预测准确率最高提升9.28%;在网络极度不完整时,预测准确率可以保持在80%左右;预测结果符合航空运输网络的实际演变情况。
-
关键词:
- 航空运输网络 /
- 链路预测 /
- 未来新增航线发现(NARP) /
- 节点层次属性 /
- 深度图卷积神经网络(DGCNN)
Abstract:In view of the problems of subjective route selection and insufficient network information mining in the research of new air routes discovery, and considering the topological structure characteristics and nodes (navigable cities) hierarchical attributes of air transport network, a New Air Routes Prediction (NARP) model based on link prediction is proposed. The NARP model extracted local enclosing subgraphs to construct subgraph adjacency matrices, marked the structural importance of nodes based on distance, and obtained nodes hierarchical attributes through factor analysis and hierarchical clustering. Then the two types of features of subgraph structure and nodes attributes were fused, and the Deep Graph Convolutional Neural Network (DGCNN) was used to perform link prediction to discover the future new air routes. The experimental results on the actual operation data of Chinese air transport network show that, compared with the benchmark algorithm, the prediction accuracy rate of NARP model is improved by 9.28% at most. When the network is extremely incomplete, the prediction accuracy rate can remain around 80%. The predicted results are in line with the actual evolution of air transport network.
-
表 1 DGCNN的主要参数设置
Table 1. Main parameter setting in DGCNN
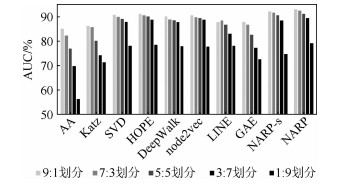
参数 数值 迭代数num_epochs 30 批大小batch_size 30 学习率learning_rate 0.000 4 子图数占比p 0.6 优化器optimizer RMS prop 丢弃函数droupout Yes 表 2 数据集7∶3划分下各模型的AUC值
Table 2. AUC value of each model under dataset 7∶3 partition
模型 AUC/% AA 82.37±0.62 Katz 85.78±0.93 SVD 89.88±0.70 HOPE 90.59±0.79 DeepWalk 89.04±2.03 node2vec 89.83±1.28 LINE 88.42±3.14 GAE 86.84±1.12 NARP-s 91.65±0.95 NARP 92.47±0.67 表 3 NARP预测的TOP-15新增航线
Table 3. Top-15 new air routes predicted by NARP
序号 新增航线 1 TAO-SYX 2 WUH-SJW 3 TAO-URC 4 HET-WNZ 5 KWL-CGQ 6 HAK-LJG 7 TAO-ZUH 8 HGH-DSN 9 CTU-YNZ 10 HAK-YNZ 11 TNA-HFE 12 SHA-LXA 13 HAK-CZX 14 CKG-ACX 15 INC-NGB -
[1] KASTURI E, DEVI S P, KIRAN S V, et al. Airline route profitability analysis and optimization using BIG DATA analytics on aviation data sets under heuristic techniques[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2016, 87: 86-92. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2016.05.131 [2] 葛伟, 朱金福, 吴薇薇. 蛛网式航线网络模型设计[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2012, 12(4): 172-177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2012.04.025GE W, ZHU J F, WU W W. Design of cobweb air route network model[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2012, 12(4): 172-177(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2012.04.025 [3] MARTINEZ V, BERZAL F, CUBERO J C. A survey of link prediction in complex networks[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2017, 49(4): 1-33. [4] LIBEN-NOWELL D, KLEINBERG J. The link-prediction problem for social networks[J]. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 2007, 58(7): 1019-1031. [5] LEI C, RUAN J. A novel link prediction algorithm for reconstructing protein-protein interaction networks by topological similarity[J]. Bioinformatics, 2013, 29(3): 355-364. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts688 [6] YUE X, WANG Z, HUANG J, et al. Graph embedding on biomedical networks: Methods, applications and evaluations[J]. Bioinformatics, 2020, 36(4): 1241-1251. [7] TAKAHASHI Y, OSAWA R, SHIRAYAMA S. A basic study of the forecast of air transportation networks using different forecasting methods[J]. Journal of Data Analysis and Information Processing, 2017, 5(2): 49-66. doi: 10.4236/jdaip.2017.52004 [8] NAJARI S, SALEHI M, RANJBAR V, et al. Link prediction in multiplex networks based on interlayer similarity[J]. Physica A-Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2019, 536: 120-978. [9] 刘宏鲲, 吕琳媛, 周涛. 利用链路预测推断网络演化机制[J]. 中国科学: 物理学力学天文学, 2011, 41(7): 816-823.LIU H K, LV L Y, ZHOU T. Uncovering the network evolution mechanism by link prediction[J]. Scientia Sinica Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica, 2011, 41(7): 816-823(in Chinese). [10] ZHENG Y, LI W, CAO X, et al. Optimization of air transportation network using link prediction methods[C]//Proceedings of the 17th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals, 2018: 991-1000. [11] ZHANG M, CHEN Y. Link prediction based on graph neural networks[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2018, 31: 5171-5181. [12] ZHANG M, CUI Z, NEUMANN M, et al. An end-to-end deep learning architecture for graph classification[C]//Proceedings of 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2018: 4438-4445. [13] 中国民用航空局发展计划司. 中国民航统计年鉴2016[M]. 北京: 中国民航出版社, 2016: 52-140.PL CAAC. China civil aviation statistical yearbook 2016[M]. Beijing: China Civil Aviation Publishing House, 2016: 52-140(in Chinese). [14] 中国民用航空局发展计划司. 从统计看民航2017[M]. 北京: 中国民航出版社, 2017: 53-137.PL CAAC. Statistical data on civil aviation of China[M]. Beijing: China Civil Aviation Publishing House, 2017: 53-137(in Chinese). [15] ZHOU T, LV L Y, ZHANG Y C. Predicting missing links via local information[J]. The European Physical Journal B, 2009, 71(4): 623-630. doi: 10.1140/epjb/e2009-00335-8 [16] GOYAL P, FERRARA E. Graph embedding techniques, applications, and performance: A survey[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2018, 151: 78-94. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2018.03.022 [17] MUTLU E C, OGHAZ T A. Review on graph feature learning and feature extraction techniques for link prediction[EB/OL]. (2019-01-10)[2020-06-27]. [18] ADAMIC L A, ADAR E. Friends and neighbors on the Web[J]. Social Networks, 2003, 25(3): 211-230. doi: 10.1016/S0378-8733(03)00009-1 [19] DAI W, LIU X, CAO Y B, et al. Matrix factorization-based prediction of novel drug indications by integrating genomic space[J]. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2015, 2015: 1-9. [20] OU M D, CUI P, PEI J, et al. Asymmetric transitivity preserving graph embedding[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM Press, 2016: 1105-1114. [21] PEROZZI B, AI-RFOU R, SKIENA S. DeepWalk: Online learning of social representations[C]//Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM Press, 2014: 701-710. [22] GROVER A, LESKOVEC J. node2vec: Scalable feature learning for networks[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM Press, 2016: 855-864. [23] TANG J, QU M, WANG M, et al. LINE: Large-scale information network embedding[C]//Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on World Wide Web, 2015: 1067-1077. [24] KIPF T N, MAX W. Variational graph auto-encoders[EB/OL]. (2016-11-21)[2020-07-01]. -








 下载:
下载: