Multi-objective optimization of a high alcohol/expanded graphite composite PCM based heat sink
-
摘要:
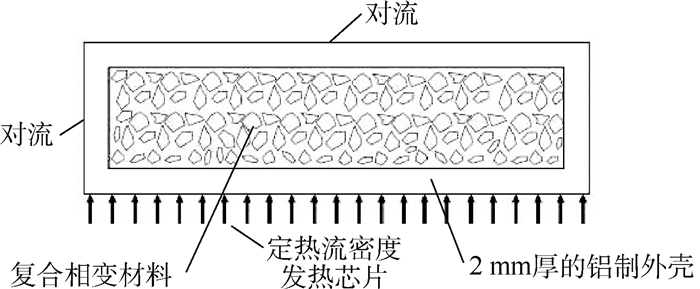
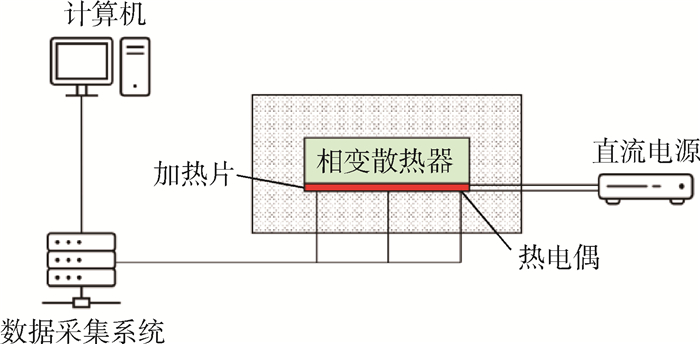
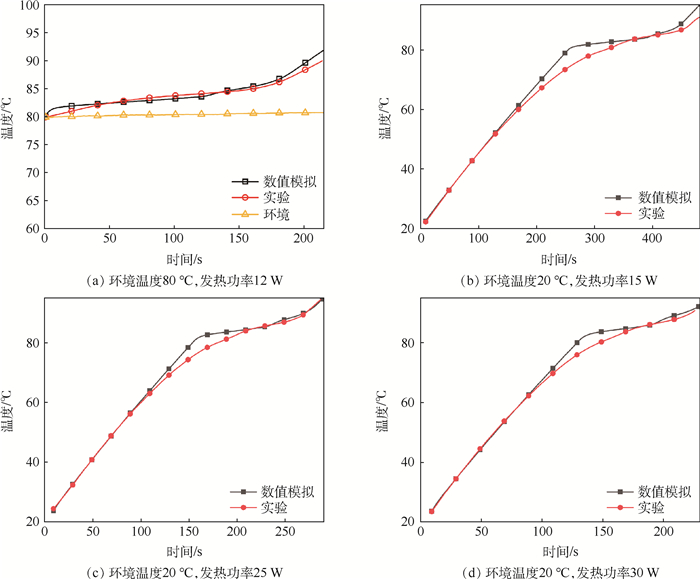
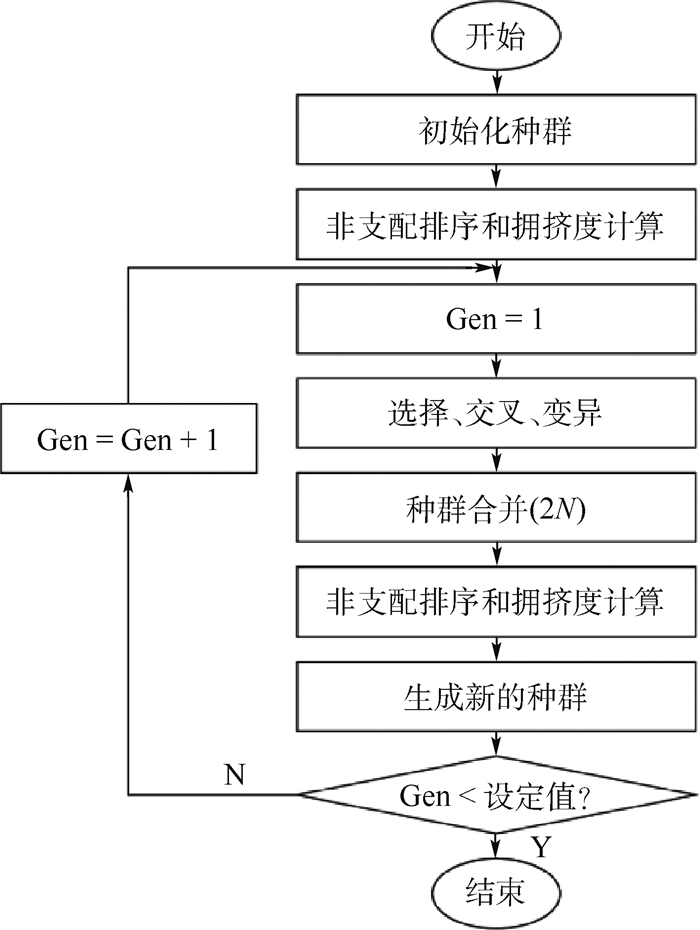
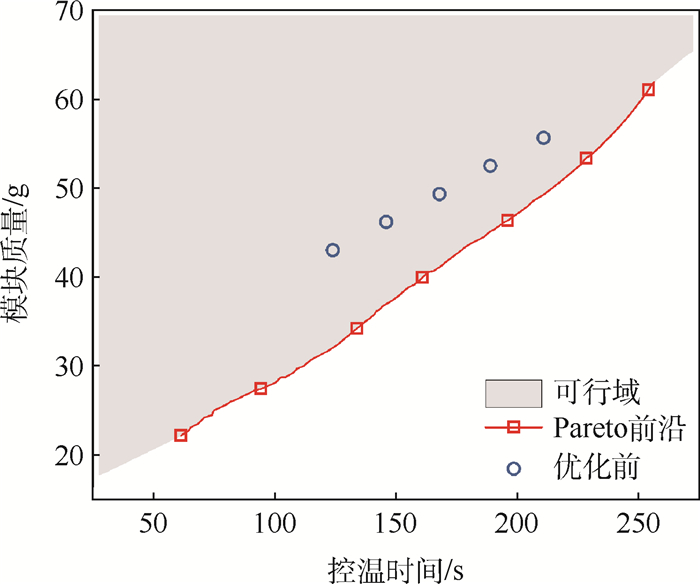
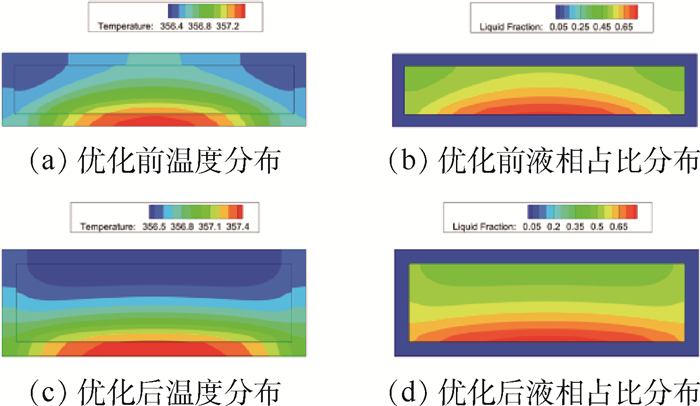
为解决高温工作环境下电子芯片的发热问题,设计采用相变材料(PCM)的控温模块,建立相变材料的控温模块模型。相变材料选择高碳醇/膨胀石墨复合材料。借助FLUENT软件进行数值模拟,探究在相同加热功率下,加热面积对控温时间的影响。对控温模块的几何尺寸进行参数分析,将数值模拟结果用于训练人工神经网络,实现对控温时间的预测。根据芯片发热功耗、芯片尺寸,通过NGSA-Ⅱ多目标优化算法优化控温模块几何尺寸,延长控温时间,降低模块质量。最终得到一系列非支配解集,可根据控温时间需求选择合适的模块尺寸设计。针对长宽为35.4 mm、发热功率为15 W的芯片进行控温模块优化设计。环境温度为80℃,温控目标小于90℃,控温时间180 s,优化后模块减重13.0%,模块内温度与液相分布也更均匀。
Abstract:A novel composite Phase Change Material (PCM) based heat sink is proposed to cool chips under high ambient temperature. Physical and numerical model is proposed for the heat sink. High alcohol/expanded graphite composite material is chosen as PCM in the heat sink. Numerical model is obtained with the help of FLUENT software for three-dimensional simulation. The effect of heated area on the chip's operation time under same thermal output is investigated. Parameter analysis is performed on the geometric dimensions of the heat sink. Artificial neural network is trained with numerical results to predict the operation time of a given heat sink/chip configuration. NGSA-Ⅱ multi-objective optimization algorithm is employed to optimize the geometric shape of heat sink based on chip size and power output. The main objective is to stretch operation time while reducing the total weight of the heat sink. A series of non-dominate solution is obtained so that optimal geometric design can be chosen based on operation time needs. The optimization process is carried out to obtain the optimal heat sink design to cool a chip, whose side length is 35.4 mm with constant power output of 15 W. The ambient temperature is 80℃ while the chip needs to be kept under 90℃ for a sustained operation time of at least 180 s. After optimization, the weight of heat sink is reduced by 13.0%. The temperature and the liquid fraction distribution are more uniform.
-
表 1 数值模拟芯片-控温模块组合的几何尺寸
Table 1. Geometric dimension for chip-heat sink configuration for numerical simulation
芯片边长c/mm 模块边长l/mm 厚度H/mm 50 50 9~13 35.4 50 9~13 35.4 35.4 9~13 28.9 50 9~13 28.9 28.9 9~13 表 2 物性参数
Table 2. Parameters of physical properties
材料 高碳醇 膨胀石墨 铝 密度/(kg·m-3) 920 比热/(J·(kg·K)-1) 3 000 620 2 719 导热系数/(W·(m·K)-1) 0.3 698 871 潜热/(kJ·kg-1) 200 229.52 202.4 相变温度/K 358 表 3 优化前后的模块几何尺寸对比
Table 3. Comparison of heat sink dimension before and after optimization
参数 优化后 优化前 c/mm 35.4 35.4 P/W 15 15 l/mm 42.5 50 H/mm 15 12 m/g 45.64 52.47 -
[1] 胡锦炎. 固液相变储能热沉的理论与实验研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2017.HU J Y. Theoretical and experimental research on thermal storage heat sink based on solid-liquid phasechange[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2017(in Chinese). [2] ARSHAD A, ALI H M, YAN W M, et al. An experimental study of enhanced heat sinks for thermal management using n-eicosane as phase change material[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2018, 132: 52-66. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.12.066 [3] SRIKANTH R, NEMANI P, BALAJI C. Multi-objective geometric optimization of a PCM based matrix type composite heat sink[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 156: 703-714. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.07.046 [4] WANG S P, QIN P, FANG X M, et al. A novel sebacic acid/expanded graphite composite phase change material for solar thermal medium-temperature applications[J]. Solar Energy, 2014, 99: 283-290. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2013.11.018 [5] QU Y, WANG S, ZHOU D, et al. Experimental study on thermal conductivity of paraffin-based shape-stabilized phase change material with hybrid carbon nano-additives[J]. Renewable Energy, 2020, 146: 2637-2645. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2019.08.098 [6] 车海山. 赤藓糖醇基相变储热材料的制备及性能研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2018.CHE H S. Preparation and performance study of erythritol-based phase change energy storage composites[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2018(in Chinese). [7] GHARBI S, HARMAND S, JABRALLAH S B. Experimental comparison between different configurations of PCM based heat sinks for cooling electronic components[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2015, 87: 454-462. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.05.024 [8] ARSHAD A, ALI H M, KHUSHNOOD S, et al. Experimental investigation of PCM based round pin-fin heat sinks for thermal management of electronics: Effect of pin-fin diameter[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 117: 861-872. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.10.008 [9] 周慧琳, 邱燕. 矩形单元蓄热特性及结构优化[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9(4): 1082-1090.ZHOU H L, QIU Y. Heat storage characteristic and structure optimum in rectangular unit[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(4): 1082-1090(in Chinese). [10] LIU H L, LI B T, ZHANG L K, et al. Optimizing heat-absorption efficiency of phase change materials by mimicking leaf vein morphology[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 269: 114982. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.114982 [11] VOLLER V R. Implicit finite-Difference solutions of the enthalpy formulation of Stefan problems[J]. IMA Journal of Numerical Analysis, 1985, 5(2): 201-214. doi: 10.1093/imanum/5.2.201 [12] SARI A, BICER A, LAFCI O, et al. Galactitol hexa stearate and galactitol hexa palmitate as novel solid-liquid phase change materials for thermal energy storage[J]. Solar Energy, 2011, 85(9): 2061-2071. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2011.05.014 [13] YANG M Z, WANG H, SHUAI W Q, et al. Thermal optimization of a kirigami-patterned wearable lithium-ion battery based on a novel design of composite phase change material[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2019, 161: 114141. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.114141 [14] DEB K, PRATAP A, AGARWAL S, et al. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-Ⅱ[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2002, 6(2): 182-197. doi: 10.1109/4235.996017 [15] SRIKANTH R, BALAJI C. Experimental investigation on the heat transfer performance of a PCM based pin fin heat sink with discrete heating[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2017, 111: 188-203. doi: 10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2016.08.018 -








 下载:
下载: