-
摘要:
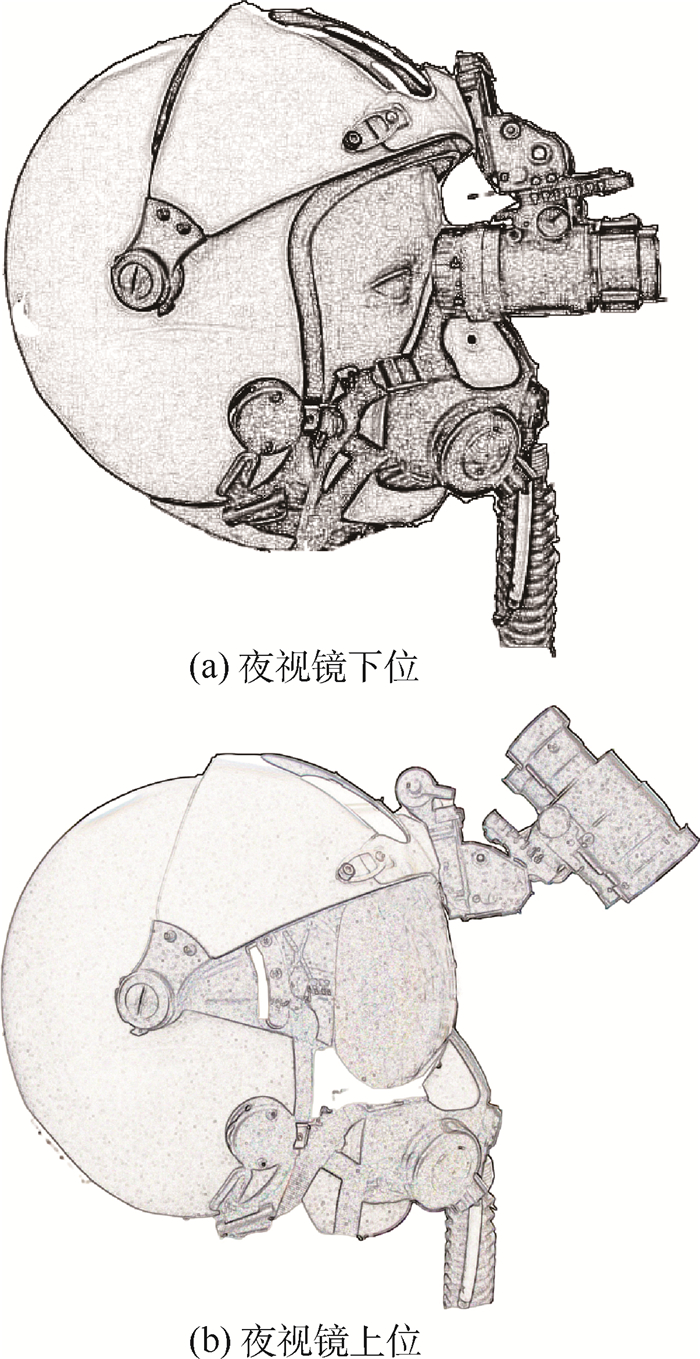
开展飞行员头盔夜视镜系统的高速气流吹袭试验,研究其气动特性和作用在人体颈椎上的力,评价其对弹射救生安全性的影响,为头盔夜视镜系统的设计和使用提供依据。采用高速气流吹袭台(敞开式风洞)吹袭的试验方法,将弹射座椅固定在吹袭台喷口前的台架上,试验假人(HYBRID Ⅱ型假人)端正地放置在弹射座椅上,试验假人穿抗荷服,佩戴头盔、夜视镜、供氧面罩。以850 km/h的吹袭速度作为试验的起点,按照试验设计确定的原则依次调整吹袭速度。夜视镜分下位(工作)和上位(非工作)2个状态进行试验,用高速摄像机记录头盔夜视镜在吹袭时的佩戴状态,测量试验假人颈椎下端的力和力矩。高速摄像机、力和力矩测量系统用高速气流吹袭台设定的时间基准同步测量。共进行了10发试验,其中5发试验夜视镜从头盔上吹脱,5发未吹脱;获得了各次试验中假人颈椎的受力曲线及夜视镜吹脱的时刻和轨迹。按照试验合格判据,吹袭速度均未超过850 km/h。头盔加装夜视镜后,相比头盔不加装夜视镜,气流吹袭性能下降,吹袭速度800 km/h以上颈椎力矩超标,700 km/h为临界点,600 km/h合格。建议将头盔夜视镜系统的气流吹袭性能包线限制在600 km/h以内。
Abstract:High-speed windblast experiments of pilot helmet-mounted night vision goggle system were carried out to study its aerodynamic characteristics and the forces on human cervical vertebra, and to evaluate the influence on the safety of ejection life-saving, so as to provide a basis for the design and use of helmet-mounted night vision goggle system. The test was carried out by an open wind tunnel called high-speed windblast test platform. The ejection seat was fixed in front of the tunnel nozzle, and the HYBRID Ⅱ dummy was fastened on the ejection seat with anti-gravity suit, helmet with night vision goggles and oxygen mask. Taking 850 km/h as the starting speed, we adjusted the speed in turn according to the principle determined by the experimental design. The night vision goggles had lower and upper state, which corresponded to working and non-working state respectively. The helmet-mounted night vision goggles wearing state during the windblast was recorded by a high-speed camera, and the force and torque of the lower cervical vertebra of the test dummy were measured. The high-speed camera and force and torque measuring system used the time benchmark set by the windblast test system to achieve synchronous measurement. A total of ten tests were carried out, in five of which the night vision goggles were blown off the helmet, and in another five of which they were not. The force and torque curves of the cervical vertebra, and the time and trajectory of the goggles blown off were obtained in each test. According to the test criterion, the blowing speeds do not exceed 850 km/h. Compared with the helmet without night vision goggles, the windblast performance of helmet-mounted night vision goggles is relatively reduced. The cervical torque exceeds the standard when the speed is more than 800 km/h, 700 km/h is the critical point and 600 km/h is qualified. It is recommended to limit the windblast performance envelope of helmet-mounted night vision goggle system to 600 km/h.
-
Key words:
- pilot /
- helmet /
- night vision goggles /
- windblast /
- ejection life-saving /
- physiological tolerance
-
表 1 基本试验结果
Table 1. Essential test results
序号 夜视镜编号 夜视镜/护目镜位置 吹袭速度/
(km·h-1)试验件状态 升力Fz/N 侧力Fy/N 阻力Fx/N 俯仰力矩My/
(N·m)1 1# U/L 850 A; C 1 083.8 288.5 1 143.7 219.0 2 2# L/U 700 A; C 880.3 261.3 916.8 172.4 3 3# L/U 600 A; B;D 340.9 95.5 357.8 75.5 4 3# L/U 700 A; B;D 1 098.8 270.2 966.2 201.2 5 3# U/L 600 A; C 550.9 276.8 677.2 130.7 6 4# L/U 700 A; B;D 918.3 212.8 929.0 158.5 7 4# U/L 600 A; C 789.5 349.5 971.1 154.5 8 5# L/U 800 A; B;D 932.1 250.0 983.8 199.5 9 5# U/L 700 A; C 703.8 265.3 838.6 154.6 10 6# L/U 850 A; B;D 1 221.9 294.4 1 028.4 232.6 表 2 力和力矩的峰值时刻与夜视镜吹脱时刻
Table 2. Moment of force and torque peak and blow-off of night vision goggles
s 序号 T t1 T+t1 tmax tmax Fx Fy Fz Mx My Mz 1 162.166 1.066 163.232 162.602 162.688 162.651 162.685 162.547 162.766 2 161.688 1.280 162.968 162.152 162.406 162.235 162.406 161.961 162.234 5 189.200 1.280 190.480 189.712 189.646 189.852 189.646 189.780 189.872 7 176.006 1.314 177.320 176.324 176.481 176.522 176.480 176.304 176.476 9 163.889 1.258 165.147 164.397 164.275 164.433 164.198 164.336 164.402 -
[1] 孙喜庆, 姜世忠. 航空航天生物动力学[M]. 西安: 第四军医大学出版社, 2013: 132-133.SUN X Q, JIANG S Z. Aerospace biodynamics[M]. Xi'an: The Fourth Military Medical University Press, 2013: 132-133(in Chinese). [2] 中国人民解放军总装备部. 弹射座椅型乘员应急离机救生系统通用规范: GJB 1800A—2007[S]. 北京: 总装备部军标出版发行部出版, 2007. .The General Equipment Department, PLA. General specification for ejection seat type of aircrew emergency escape system: GJB 1800A—2007[S]. Beijing: The Circulation Department of the General Equipment Department, PLA, 2007(in Chinese). [3] 孙立华. 军用夜视镜[J]. 百科知识, 2015(8): 25-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BKZS201516013.htmSUN L H. Military night vision goggles[J]. Encyclopedia Knowledge, 2015(8): 25-26(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BKZS201516013.htm [4] 刘何庆, 邓略, 吴明磊, 等. 飞行员夜视头盔过载稳定性研究[J]. 中华航空航天医学杂志, 2016, 27(4): 274-279. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-6239.2016.04.009LIU H Q, DENG L, WU M L, et al. Study on the stability of pilot's night vision goggles mounted helmet under G loads[J]. Chinese Journal of Aerospace Medicine, 2016, 27(4): 274-279(in Chinese). doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-6239.2016.04.009 [5] KEDEM S. Expanding the use of HMD for night missions using a modular design[C]//Proceedings of the International Society for Optical Engineering, 1999, 3689: 90-97. [6] 陈航辉, 刘俊彪. "天价头盔"开启空战新时代[N/OL]. 解放军报, 2015-04-25(05)[2017-03-20]. http://www.81.cn/jfjbmap/content/1/2015-04/25/05/2015042505-pdf.CHEN H H, LIU J B. "Sky-high helmet"-Opens a new era of air combat[N/OL]. China's PLA Daily, 2015-04-25(05)[2017-03-20]. http://www.81.cn/jfjbmap/content/1/2015-04/25/05/2015042505-pdf (in Chinese). [7] 红漫, 郭涛. 具有夜视功能的头盔显示器[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2007, 36(增刊): 583-588. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYJ2007S2149.htmHONG M, GUO T. Helmet mounted display with night vision[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2007, 36(Supplementary): 583-588(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYJ2007S2149.htm [8] 吴明磊, 马春生, 刘威, 等. 弹射时装显示器头盔对人体的生物力学效应[J]. 中华航空航天医学杂志, 2005, 16(4): 267-271. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-6239.2005.04.007WU M L, MA C S, LIU W, et al. Biodynamic effect of helmet with mounted display system on human during ejection[J]. Chinese Journal of Aerospace Medicine, 2005, 16(4): 267-271(in Chinese). doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-6239.2005.04.007 [9] SELF B P, ISDAHL W. Performance of the ITT night vision system auto-release mechanism during sustained acceleration[J]. Safe Journal, 1998, 28(2): 101-105. [10] JACKSON T W, CRAIG J L. Design, development, fabrication, and safety-of-flight testing of a panoramic night vision goggle[C]//Proceedings of SPIE, 1999: 98-109. [11] Inspector General. AD-A616902 evaluation of aircraft ejection seat safety when using advanced helmet sensors[R]. Washington, D.C. : U.S. Department of Defense, 2015: 1-34. [12] 吴明磊. 飞行员使用综合显示/夜视头盔安全策略分析[J]. 中华航空航天医学杂志, 2018, 29(1): 1-7. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-6239.2018.01.001WU M L. Analysis on safety strategy for the pilots with integrated helmet display/night vision goggles[J]. Chinese Journal of Aerospace Medicine, 2018, 29(1): 1-7(in Chinese). doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-6239.2018.01.001 [13] 吴铨. 从飞行事故看战斗机飞行员夜视飞行中的航空医学问题[J]. 航空军医, 2015, 43(5): 183-185.WU Q. Aviation medicine issues reflected from the accidents of fighter pilot's night vision flight[J]. Flight Surgeon, 2015, 43(5): 183-185(in Chinese). [14] BRIAN E. F-16 investigation: Pilot killed while ejecting[EB/OL]. [2015-07-06]. http://archive.airforcetimes.com/article/20131106/NEWS/311060011/F-16-investigation-Pilot-killed-while-ejecting. [15] 罗永昌. 军事航空医学概论[M]. 北京: 人民军医出版社, 2014: 69-70.LUO Y C. Introduction to military aviation medicine[M]. Beijing: People's Military Medical Publishing House, 2014: 69-70(in Chinese). [16] 张云然, 吴桂荣. 高速气流吹袭问题[J]. 航空学报, 1994, 15(7): 826-832. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.1994.07.010ZHANG Y R, WU G R. The problems of windblast[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 1994, 15(7): 826-832(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.1994.07.010 [17] 中国人民解放军总装备部. 人耐受高速气流吹袭限值: GJB 6751—2009[S]. 北京: 中国人民解放军总装备部, 2009.The General Equipment Department, PLA. Tolerance limit of crewman to high speed windblast: GJB 6751—2009[S]. Beijing: The General Equipment Department, PLA, 2009(in Chinese). [18] PERRY C E, BUHRMAN J R. Effect of helmet inertial properties on the biodynamics of the head and neck during +Gz impact acceleration[J]. Safe Journal, 1996, 26(2): 34-41. [19] 孙晓艳, 吴明磊, 刘何庆, 等. 佩戴头盔时头颈对-Gx加速度的动力学响应[J]. 中华航空航天医学杂志, 2018, 29(2): 99-104. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-6239.2018.02.005Sun X Y, WU M L, LIU H Q, et al. Dynamics response of head and neck to-Gx acceleration when wearing helmet[J]. Chinese Journal of Aerospace Medicine, 2018, 29(2): 99-104(in Chinese). doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-6239.2018.02.005 [20] BOSTROM O, BOHMARIN K, HALAND Y, et al. New ASI-1 long-term neck injury criteria canditates based on rear frontal crash analysis[C]//Proceedings of the IRCOBIC, 2000: 249-264. [21] KLEINBERGER M, EPPINGER R, KUPPA S, et al. Development of improved injury criteria for the assessment of advanced automotive restraint system: NHTSA Docket 98-4405-9[R]. Washington, D.C. : U.S. Department of Transportation, 1998. [22] PANJABI M M, WANG J L, DELSON N. Neck injury criterion based on intervertebral motions and its evaluation using an instrumented neck dummy[C]//Proceedings of IRCOBI, 2005: 179-190. [23] 熊端琴, 郭小朝. 航空夜视镜人机工效研究进展[J]. 中华航空航天医学杂志, 2005, 16(4): 312-315. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-6239.2005.04.025XIONG D Q, GUO X C. The man-machine ergonomics problems of aviator's night vision goggles (NVGs)-A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Aerospace Medicine, 2005, 16(4): 312-315(in Chinese). doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-6239.2005.04.025 [24] PARR J C, MILLER M E, PELLETTIERE J A. Neck injury criteria formulation and injury risk curves for the ejection environment: A pilot study[J]. Aviation Space Environment Medicine, 2013, 84(12): 1240-1248. doi: 10.3357/ASEM.3722.2013 -







 下载:
下载: