-
摘要:
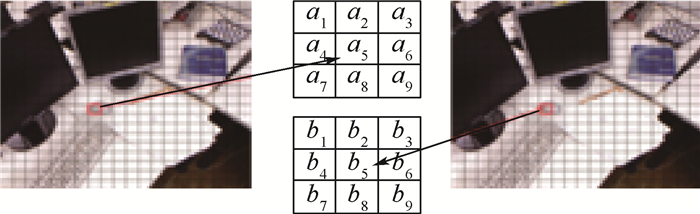
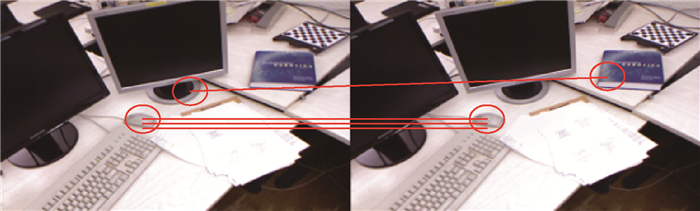
针对现有的ORB特征匹配算法在图像模糊、光照变化、图像压缩、噪声条件下,匹配准确率下降问题,提出了一种改进的ORB特征匹配算法。首先,在提取特征点过程中,对图像进行网格化处理,并引入四叉树结构,使提取的特征点在图像中均匀分布,解决传统的特征提取方法遇到的特征点集中问题。然后,利用暴力匹配进行初步匹配,并采用交叉验证的方式,剔除部分误匹配,改善暴力匹配的结果。最后,利用高斯核对网格运动统计的结果做加权处理,优化统计结果,进一步剔除误匹配,得到准确率更高的匹配集合。实验结果表明:改进后的算法在图像模糊、光照变化、图像压缩和噪声条件下,平均准确率分别提高了3.5%、4.2%、2.2%和6%。
Abstract:An improved ORB feature matching algorithm is proposed to solve the problem of decreasing matching accuracy under the conditions of image blur, light change, image compression and noise. First, in the process of extracting feature points, the image is meshed and quad-tree structure is introduced to make the extracted feature points evenly distributed in the image, thus solving the problem of feature points concentration encountered by traditional feature extraction methods. Then, the brute-force matching is used for preliminary matching, and cross validation is adopted to eliminate some mismatches and improve the result of brute-force matching. Finally, Gaussian kernel is used to weight the results of grid-based motion statistics to optimize the statistical results and further eliminate the mismatches to obtain the matching set with higher accuracy. The experimental results show that this algorithm improves the average accuracy by 3.5%, 4.2%, 1.8% and 6% respectively under the conditions of image blur, light change, image compression and noise.
-
Key words:
- feature matching /
- ORB feature /
- grid-based motion statistics /
- feature extraction /
- Gaussian kernel
-
表 1 实验结果
Table 1. Experimental results
实验图像 最高准确率/% 最低准确率/% 平均准确率/% 准确率标准差/% 原算法 本文算法 原算法 本文算法 原算法 本文算法 原算法 本文算法 图像模糊 95.4 98.3 68.1 79.7 85.8 89.3 7.95 5.37 光照变化 96.8 97.8 87.5 92.7 91.2 95.4 2.48 1.56 图像压缩 99.8 99.7 91.3 94.3 95.7 97.9 2.65 1.72 高斯噪声 96.3 98.3 74 57.1 86.2 92.2 7.21 9.57 -
[1] 王晓华, 方琪, 王文杰. 基于网格运动统计的改进快速鲁棒特征图像匹配算法[J]. 模式识别与人工智能, 2019, 32(12): 1133-1140.WANG X H, FANG Q, WANG W J. Image matching algorithm combining improved SURF algorithm with grid-based motion statistics[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 32(12): 1133-1140(in Chinese). [2] 程向红, 李俊杰. 基于运动平滑性与RANSAC优化的图像特征匹配算法[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2019, 27(6): 765-770.CHENG X H, LI J J. Optimized image feature matching algorithm based on motion smoothness and RANSAC[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2019, 27(6): 765-770(in Chinese). [3] LOWE D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91-110. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 [4] BAY H, TUYTELAARS T, VAN GOOL L. SURF: Speeded up robust features[C]//Computer Vision-ECCV 2006. Berlin: Springer, 2006: 404-417. [5] RUBLEE E, RABAUD V, KONOLIGE K, et al. ORB: An efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF[C]//2011 International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 2564-2571. [6] YI K M, TRULLS E, LEPETIT V, et al. LIFT: Learned invariant feature transform[C]//Computer Vision-ECCV 2016. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 467-483. [7] LAGUNA A B, RIBA E, PONSA D, et al. Key. Net: Keypoint detection by handcrafted and learned CNN filters[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 5835-5843. [8] SHEN X L, WANG C, LI X, et al. RF-NET: An end-to-end image matching network based on receptive field[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 8124-8132. [9] 侯宏录, 李媛, 李光耀. 改进SIFT匹配的动态背景下运动目标检测算法[J]. 自动化仪表, 2019, 40(8): 60-64.HOU H L, LI Y, LI G Y. Moving target detection algorithm under dynamic background with improved SIFT matching[J]. Process Automation Instrumentation, 2019, 40(8): 60-64(in Chinese). [10] 张明浩, 杨耀权, 靳渤文. 基于图像增强技术的SURF特征匹配算法研究[J]. 自动化与仪表, 2019, 34(9): 98-102.ZHANG M H, YANG Y Q, JIN B W. Research on SURF feature matching algorithm based on image enhancement technology[J]. Automation & Instrumentation, 2019, 34(9): 98-102(in Chinese). [11] ROSTEN E, DRUMMOND T. Machine learning for high-speed corner detection[C]//Computer Vision-ECCV 2006. Berlin: Springer, 2006: 430-443. [12] 高翔, 张涛, 刘毅. 视觉SLAM十四讲: 从理论到实践[M]. 2版. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2019.GAO X, ZHANG T, LIU Y. 14 lectures on visual SLAM: From theory to practice[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2019(in Chinese). [13] CALONDER M, LEPETIT V, STRECHA C, et al. BRIEF: Binary robust independent elementary features[C]//ECCV'10: Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision: Part Ⅳ, 2010: 778-792. [14] 杨炳坤, 程树英, 郑茜颖. 改进的ORB特征匹配算法[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2020, 39(2): 136-139.YANG B K, CHENG S Y, ZHENG Q Y. Improved ORB feature matching algorithm[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2020, 39(2): 136-139(in Chinese). [15] 杨弘凡, 李航, 陈凯阳, 等. 基于改进ORB算法的图像特征点提取与匹配方法[J]. 图学学报, 2020, 41(4): 548-555.YANG H F, LI H, CHEN K Y, et al. Image feature points extraction and matching method based on improved ORB algorithm[J]. Journal of Graphics, 2020, 41(4): 548-555(in Chinese). [16] MUJA M, LOWE D G. Fast approximate nearest neighbors with automatic algorithm configuration[C]//Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, 2009: 331-340. [17] MUJA M, LOWE D G. Scalable nearest neighbor algorithms for high dimensional data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(11): 2227-2240. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2321376 [18] FISCHLER M A, BOLLES R C. Random sample consensus[J]. Communications of the ACM, 1981, 24(6): 381-395. doi: 10.1145/358669.358692 [19] SATTLER T, LEIBE B, KOBBELT L. SCRAMSAC: Improving RANSAC's efficiency with a spatial consistency filter[C]//2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2009: 2090-2097. [20] BIAN J W, LIN W Y, MATSUSHITA Y, et al. GMS: Grid-based motion statistics for fast, ultra-robust feature correspondence[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2828-2837. [21] 柳长安, 艾壮, 赵丽娟. 基于网格运动统计的自适应图像特征匹配算法[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 48(1): 37-40.LIU C A, AI Z, ZHAO L J. Self-adaptive image feature matching algorithm based on grid motion statistics[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(1): 37-40(in Chinese). [22] MUR-ARTAL R, TARDÓS J D. ORB-SLAM2: An open-source SLAM system for monocular, stereo, and RGB-D cameras[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2017, 33(5): 1255-1262. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2017.2705103 [23] ALCANTARILLA P F, BARTOLI A, DAVISON A J. KAZE features[C]//Computer Vision-ECCV 2012. Berlin: Springer, 2012: 214-227. -







 下载:
下载: