Image inpainting method based on incomplete image samples in generative adversarial network
-
摘要:
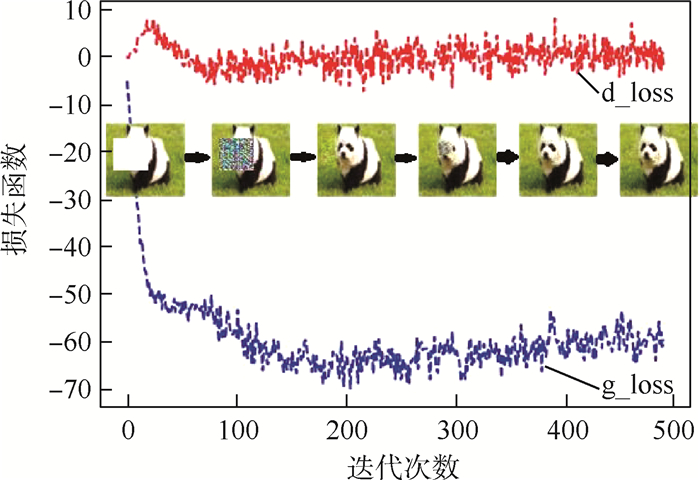
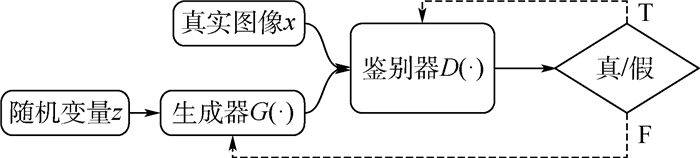
针对大面积图像修复缺失严重时,需要完整且高质量训练样本的问题,提出了一种将残缺或含噪图像样本作为训练集的双生成器深度卷积生成对抗网络(DGDCGAN)模型。构建两个生成器和一个鉴别器以解决单一生成器收敛慢的问题,用残缺图像样本作为训练集,通过交叉计算、搜索损失区域类似的图像信息作为训练生成模型的样本,收敛速度更快。鉴别器损失函数改进为输出的Wasserstein距离,使用自适应估计算法优化生成器损失函数和鉴别器损失函数的模型参数,最小化两两图像之间的总距离差,使用鉴别模型和修复图像总距离变化均方差最小化两个指标优化修复结果。在4个公开数据集上进行主客观实验,结果表明:所提方法能使用残缺图像样本作为训练集,有效实现大面积失真图像的修复,且收敛速度和修复效果优于现有图像修复方法。
-
关键词:
- 图像修复 /
- 残缺图像样本 /
- 深度卷积生成对抗网络 /
- Wasserstein距离 /
- 总距离变化均方差
Abstract:A model of Double Generator Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Network (DGDCGAN), which uses the incomplete or noisy sample image as the training set, is proposed, in order to solve the problem of serious distortion of large area image inpainting, complete and high-quality training samples are frequently required, which is hard to acquire. Furthermore, the convergence of single generator is slow. Therefore, two generators and a discriminator are constructed. The incomplete image training set is used to cross calculate and search the image information similar to the loss area as the sample of training generation model, which achieves faster convergence speed. The loss function of the discriminator is improved to be the Wasserstein distance of the output. The adaptive estimation algorithm is used to optimize the model parameters for generating network loss function and identifying network loss function. Finally, the distance difference between two sets of images is calculated, and the reconstructed image is optimized by discriminating model and minimizing mean square error of the total distance change of a group of repaired images. Experiments are performed on four public dataset, the subjective and objective experimental results show that the proposed method that uses incomplete samples as training data can restore large area of distortion in images with faster convergence speed and better performance compared with the existing methods in image inpainting.
-
表 1 不同方法的PSNR和SSIM对比
Table 1. PSNR/SSIM comparison of different methods
-
[1] BERTALMÍO M, BERTOZZI A L, SAPIRO G. Navier-Stokes, fluid dynamics, and image and video inpainting[C]//2001 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2001: 7176886. [2] LIU D, SUN X, WU F, et al. Image compression with edge-based inpainting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2007, 17(10): 1273-1287. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2007.903663 [3] BUYSSENS P, DAISY M, TSCHUMPERLE D, et al. Exemplar-based inpainting: Technical review and new heuristics for better geometric reconstructions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(6): 1809-1824. [4] DARABI S, SHECHTMAN E, BARNES C, et al. Image melding: Combining inconsistent images using patch-based synthesis[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2012, 31(4): 82. [5] HUANG J B, KANG S B, AHUJA N, et al. Image completion using planar structure guidance[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2014, 33(4): 1-10. [6] BARNES C, SHECHTMAN E, FINKELSTEIN A, et al. PatchMatch: A randomized correspondence algorithm for structural image editing[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2009, 28(3): 24. [7] WEXLER Y, SHECHTMAN E, IRANI M. Space-time completion of video[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2007, 29(3): 463-476. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2007.60 [8] HAYS J, EFROS A A. Scene completion using millions of photographs[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2007, 26(3): 4. doi: 10.1145/1276377.1276382 [9] DEMIR U, UNAL G. Patch-based image inpainting with generative adversarial networks[EB/OL]. (2018-03-20)[2020-07-25]. [10] NAZERI K, NG E, JOSEPH T, et al. EdgeConnect: Generative image inpainting with adversarial edge learning[EB/OL]. (2019-01-11)[2020-07-25]. [11] XIE J, XU L, CHEN E. Image denoising and inpainting with deep neural networks[C]//International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2012, 1: 341-349. [12] YANG C, LU X, LIN Z, et al. High-resolution image inpainting using multi-scale neural patch synthesis[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 17355590. [13] IIZUKA S, SIMO-SERRA E, ISHIKAWA H. Globally and locally consistent image completion[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2017, 36(4): 1-14. [14] LI Y, LIU S, YANG J, et al. Generative face completion[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 17355119. [15] PATHAK D, KRAHENBUHL P, DONAHUE J, et al. Context encoders: Feature learning by inpainting[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 16526723. [16] GOODFELLOW I J, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]//International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2014: 2672-2680. [17] BROCK A, DONAHUE J, SIMONYAN K. Large scale GAN training for high fidelity natural image synthesis[EB/OL]. (2018-09-28)[2020-07-25]. [18] AHMADI M, NEST T, ABDELNAIM M, et al. Reproducing AmbientGAN: Generative models from lossy measurements[EB/OL]. (2018-10-23)[2020-07-25]. [19] SALIMANS T, GOODFELLOW I, ZAREMBA W, et al. Improved techniques for training GANs[C]//International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2016: 2234-2242. [20] ZHU J Y, PARK T, ISOLA P, et al. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 17453078. [21] ARJOVSKY M, CHINTALA S, BOTTOU L. Wasserstein GAN[EB/OL]. (2017-01-26)[2020-07-25]. [22] ARJOVSKY M, BOTTOU L. Towards principled methods for training generative adversarial networks[EB/OL]. (2017-01-17)[2020-07-25]. [23] CHEN Y, HU H. An improved method for semantic image inpainting with GANs: Progressive inpainting[J]. Neural Processing Letters, 2019, 49(3): 1355-1367. doi: 10.1007/s11063-018-9877-6 [24] LIU Z, LUO P, WANG X, et al. Deep learning face attributes in the wild[C]//2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 3730-3738. [25] LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791 [26] 李雪瑾, 李昕, 徐艳杰. 基于生成对抗网络的数字图像修复技术[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2019, 33(1): 40-46.LI X J, LI X, XU Y J. Digital image restoration technology based on generative adversarial networks[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation, 2019, 33(1): 40-46(in Chinese). [27] 李天成, 何嘉. 一种基于生成对抗网络的图像修复算法[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2019, 36(12): 195-200.LI T C, HE J. An image inpainting algorithm based on generative adversarial networks[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2019, 36(12): 195-200(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: