-
摘要:
星基增强系统(SBAS)通过GEO卫星转发SBAS电文实现对GNSS服务性能的提升,以满足民航用户不同飞行阶段的导航需求,因此,合理有效的电文内容及播发时序设计是系统实现高质量服务的重要保证。为提高电文编排的灵活性,避免固定时序填补空余电文引起的播发资源浪费,提出了一种SBAS电文时序动态编排算法,在满足国际标准要求的前提下,综合利用SBAS电文龄期和最大播发间隔实现待播发电文的自动选择。利用NTMF实测数据对当前各主要SBAS的电文进行了特性分析,对所提方法的单双频SBAS电文编排效果进行了评估。结果表明:所提算法可保证电文时序符合国际标准要求,实现了重要电文的优先播发,将空余时隙进行动态分配实现了各类型电文播发间隔的近等比例缩短。与固定时序相比,单频SBAS完好性电文播发间隔缩短约15.0%,首次定位时间缩短约8%,双频SBAS电文首次定位时间缩短约6.5%;与固定时序的BDSBAS B1C电文相比,完好性服务能力提升约14.7%,首次定位时间缩短约16.7%。所提算法有效提升了SBAS电文播发的播发效率,实现了SBAS播发资源的100%有效利用。
-
关键词:
- 星基增强系统(SBAS) /
- SBAS电文 /
- 电文时序 /
- 动态时序 /
- 固定时序
Abstract:Satellite Based Augmentation Systems (SBAS) provide SBAS messages through GEO satellites to improve the performance of GNSS in order to meet the navigation needs of civil aviation users, and reasonable and effective message content and broadcast schedule design are important for SBAS to achieve high-quality services. In order to improve the flexibility of message scheduler and avoid the waste of broadcast resources caused by filling the null messages, this paper proposes an automatic scheduler of SBAS message. Under the premise of meeting the requirements of international standards, this scheduler comprehensively uses the age of SBAS message and the maximum broadcast period to realize the automatic selection of the message type to be broadcast. At the same time, this paper uses NTMF data to analyze the characteristics of the current SBAS message, and evaluates the application effect of the proposed scheduler in single- and dual-frequency SBAS message. The results show that this scheduler can ensure that the message schedule meets the requirements of international standards, can achieve the priority broadcast of important messages, and can realize the nearly equal proportion shortening of the broadcast interval of each message type by dynamic allocation of spare time slot. Compared with rigid scheduler, the integrity message broadcast interval is shortened by about 15.0% and the first positioning time is shortened by about 8% for the single-frequency SBAS, and the first positioning time is shortened by about 6.5% for the dual-frequency SBAS message. Compared with BDSBAS B1C rigid scheduler, the integrity message broadcast interval is shortened by about 14.7% and the first positioning time is shortened by about 16.7%. The scheduler can effectively improve the efficiency of SBAS message broadcasting and realize 100% effective use of SBAS broadcast resource.
-
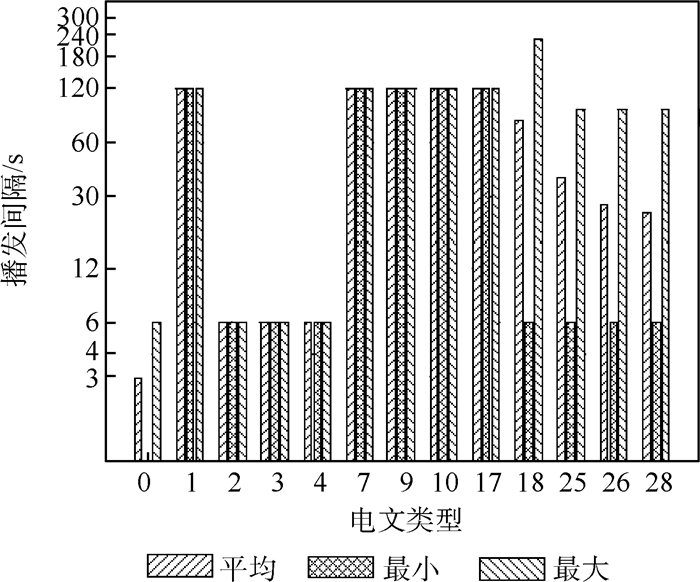
表 1 单频SBAS服务的增强电文类型及最大播发间隔[11]
Table 1. Augmented messages type and maximum update interval of single-frequency SBAS[11]
电文类型 播发内容 最大播发间隔/s 0 系统不可用标识(测试用) 6 1 PRN掩码 120 2~6, 24 UDREI 6 2~5, 24 快速改正数 6~60 24, 25 长期改正数 120 9 GEO导航信息 120 7 快速改正数降效因子 120 10 降效因子 120 18 电离层网格点掩码 300 26 电离层网格点垂直延迟 300 12 系统时间参数 300 17 GEO历书 300 27 服务区域信息 120 28 钟差-轨道协方差阵 120 表 2 SBAS DFMC L5的增强电文类型及最大播发间隔
Table 2. Augmented messages type and maximum update interval of SBAS DFMC L5
电文类型 播发内容 最大播发间隔/s 0 系统不可用标识 6 31 卫星掩码 120 34~36, 32, 40 DFREI信息 6 32 改正数及协方差信息 120 39, 40 SBAS卫星星历及协方差 120 37 OBAD及DFREI量化表 120 37 时间参考标识 120 47 SBAS服务编号 120 47 周翻转计数 120 表 3 固定电文时序与动态电文时序对比
Table 3. Comparison between dynamic and rigid message scheduler
对比项目 固定电文时序 动态电文时序 实现复杂度 简单,只需按设计时序索引待播发电文类型 复杂,需根据电文播发需求等动态确定待播发电文类型 电文灵活性 较差,电文时序确定后,只能按固定策略播发,当信息缺失时,一般用空电文填充 较好,当信息缺失时,可根据优先级确定播发电文,无需空电文填充 播发周期 确定 可根据播发内容动态调整 播发间隔符合性保证 由设计的电文时序保证,需人为或由特定程序对电文播发间隔的标准符合性进行分析 由程序保证,电文时序编排程序在执行过程中使用电文播发间隔对播发电文时序进行约束,保证满足播发要求 表 4 各SBAS增强的卫星数和IGP数
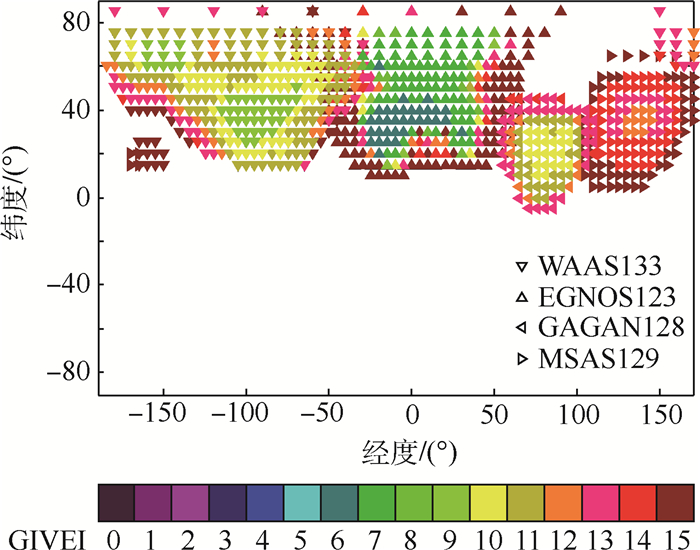
Table 4. Satellite and IGP numbers augmented by each SBAS
系统 播发卫星数均值 播发IGP数均值 WAAS133 15.5 306 EGNOS123 12.0 287 GAGAN128 11.7 102 MSAS129 9.3 143 表 5 单频SBAS动态电文时序各类型电文平均播发间隔对比
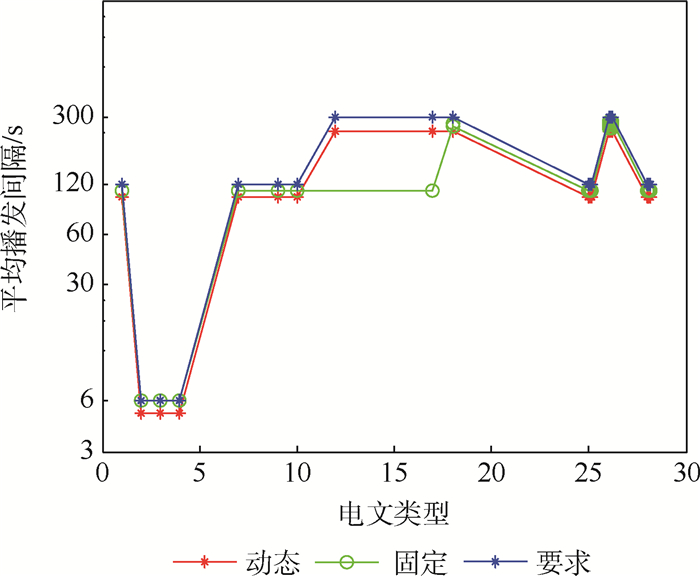
Table 5. Comparison of mean broadcast intervals of different types of single-frequency SBAS message using dynamic message scheduler
电文类型 预设播发间隔/s 平均播发间隔/s 缩短百分比 1 120 100.7 16.1 2/3/4 6 5.1 15.0 7 120 100.7 16.1 9 120 100.7 16.1 10 120 100.7 16.1 12 300 248.2 17.3 17 300 248.2 17.3 18 300 248.3 17.2 25 120 100.7 16.1 26 300 248.3 17.2 28 120 100.7 16.1 表 6 BDSBAS B1C SBAS电文平均播发间隔与时隙占比对比
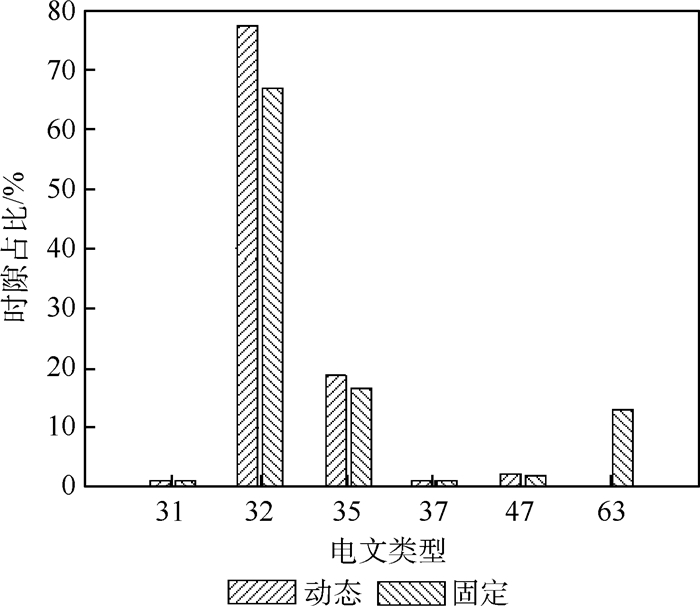
Table 6. Comparison of BDSBAS B1C SBAS message mean broadcast intervals and time slot share
电文变型 平均播发间隔/s 时隙占比/% 设计间隔 BDSBAS播发 动态电文时序 BDSBAS播发 动态电文时序 0 6 2.85 5.12 35.0 19.55 1 120 120 99.96 0.83 1.00 2/3/4 6 6 5.12 16.67 19.55 7 120 120 99.96 0.83 1.0 9 120 120 99.96 0.83 1.0 10 120 120 99.96 0.83 1.0 17 120 120 99.96 0.83 1.0 18 240 240 199.45 1.25 1.5 25 120 120 100.07 2.5 3.96 26 240 240 200.8 3.75 4.42 28 120 120 100.25 3.33 6.94 -
[1] WALTER T, SHALLBERG K, ALTSHULER E, et al. WAAS at 15[J]. Navigation, 2018, 65(4): 581-600. doi: 10.1002/navi.252 [2] SCHEMPP T. WAAS development changes since commissioning[EB/OL]. (2019-06-03)[2020-07-01]. [3] 吴云, 杨鑫春, 陈慧. 多系统多频率的EGNOS系统完备性模拟分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2012, 37(3): 269-273.WU Y, YANG X C, CHEN H. Simulation and analysis of EGNOS system's integrity under multi-system with multi-frequency[J]//Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2012, 37(3): 269-273(in Chinese). [4] SEYNAT C, FLAMENT D. European geostationary navigation overlay service EGNOS status update[C]//The ION 23rd International Technical Meeting, 2010: 1270-1299. [5] RAO S. GAGAN-The Indian satellite based augmentation system[J]. Indian Journal of Radio & Space Physics, 2007, 36: 293-302. [6] SAITO S. MSAS system development[EB/OL]. (2019-06-03)[2020-07-01]. [7] 楼益栋, 郑福, 龚晓鹏. QZSS系统在中国区域增强服务性能评估与分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2016, 41(3): 298-303.LOU Y D, ZHENG F, GONG X P. Evaluation of QZSS system augmentation service performance in China region[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2016, 41(3): 298-303(in Chinese). [8] The development plan of the BeiDou satellite-based augmentation system (BDSBAS)[EB/OL]. (2017-07-17)[2020-07-01]. [9] 陈俊平, 杨赛男, 周建华, 等. 综合伪距相位观测的北斗导航系统广域差分模型[J]. 测绘学报, 2017, 46(5): 537-546.CHEN J P, YANG S N, ZHOU J H, et al. A pseudo range and phase combined SBAS differential correction model[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2017, 46(5): 537-546(in Chinese). [10] ICAO. Annex 10. Vol. I. Radio navigation aids[S]. Montreal: ICAO, 2018. [11] RTCA. Minimum operational performance standards for global positioning system/satellite based augmentation system airborne equipment: RTCA DO-229E[S]. Washington, D.C. : RTCA, 2016. [12] LAWRENCE D, EVANS J, CHAO Y C, et al. Integration of wide area DGPS with local area kinematic DGPS[C]//IEEE Position Location and Navigation Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1996: 524-529. [13] WALTER T, NEISH A, BLANCH J. A rigid message scheduler for SBAS[C]//2020 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 19674219. [14] YUN Y, LEE E, HEO M B, et al. KASS message scheduler design[J]. Journal of Positioning, Navigation, and Timing, 2016, 5(4): 193-202. doi: 10.11003/JPNT.2016.5.4.193 [15] SALOS D, MABILLEAU M, RODRIGUEZ C, et al. SBAS DFMC performance analysis with the SBAS DFMC service volume software prototype (DSVP)[C]//International Technical Symposium on Navigation and Timing, 2017: 1-7. [16] 黄双临, 辛洁, 王冬霞, 等. 星基增强系统电文及播发特性研究[J]. 数字通信世界, 2019(2): 4-6. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1672-7274.2019.02.002HUANG S L, XIN J, WANG D X, et al. Research on propagating message and strategy of satellite-based augmentation system[J]. Digital Communication World, 2019(2): 4-6(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1672-7274.2019.02.002 [17] 梁曦, 陶晓霞, 周昀, 等. 星基增强系统导航电文及完好性信息研究[J]. 空间电子技术, 2016, 13(5): 39-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7135.2016.05.008LIANG X, TAO X X, ZHOU J, et al. Research of SBAS navigation message and integrity message[J]. Space Electronic Technology, 2016, 13(5): 39-47(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7135.2016.05.008 [18] IWG. SBAS DFMC L5 interface control document[R]. [S. l. ]: IWG, 2017. [19] EUROCAE. Minimum operational performance standard for galileo/global positioning system/satellite-based augmentation system airborne equipment: ED-259[S]. Saint-Denis: EUROCAE, 2019. -








 下载:
下载: