-
摘要:
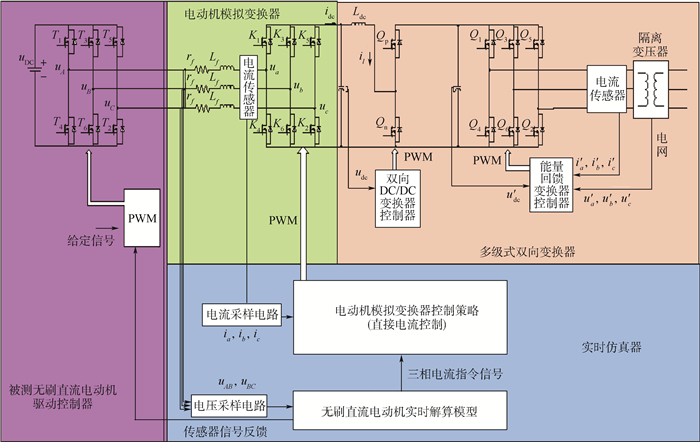
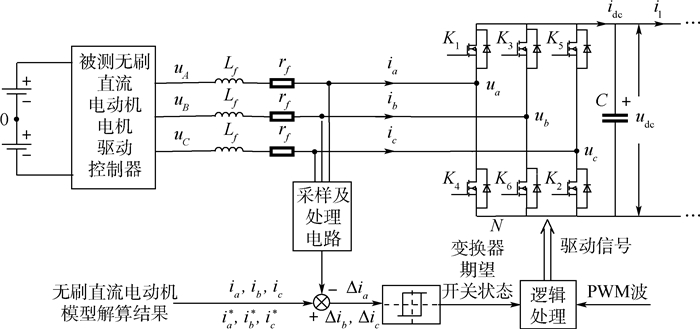
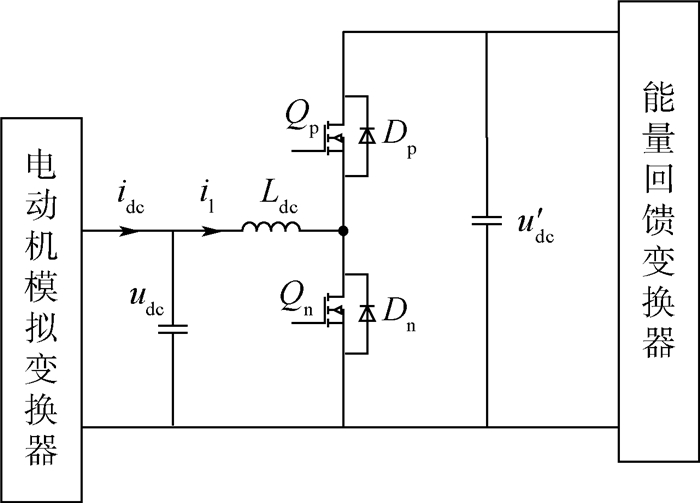
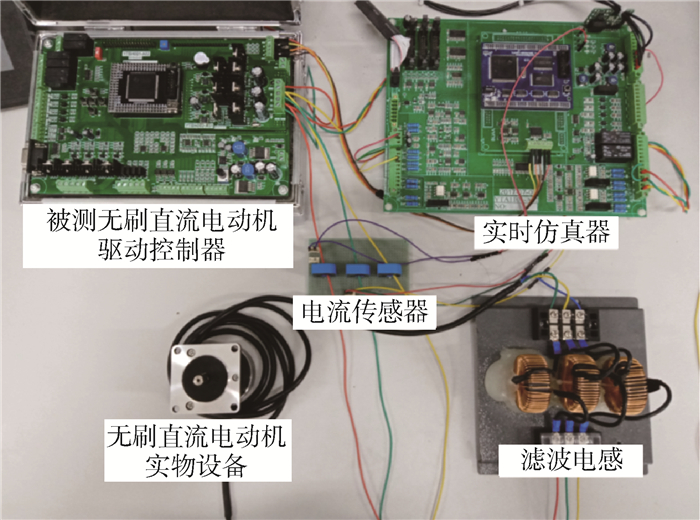
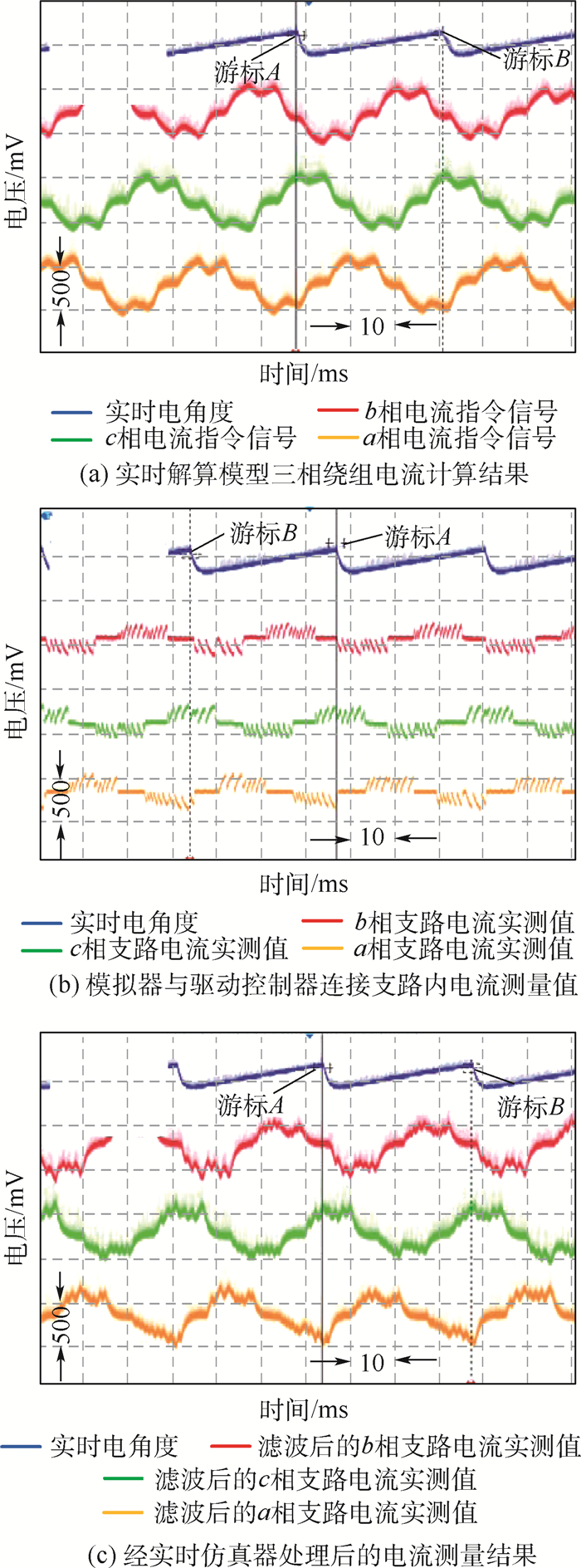
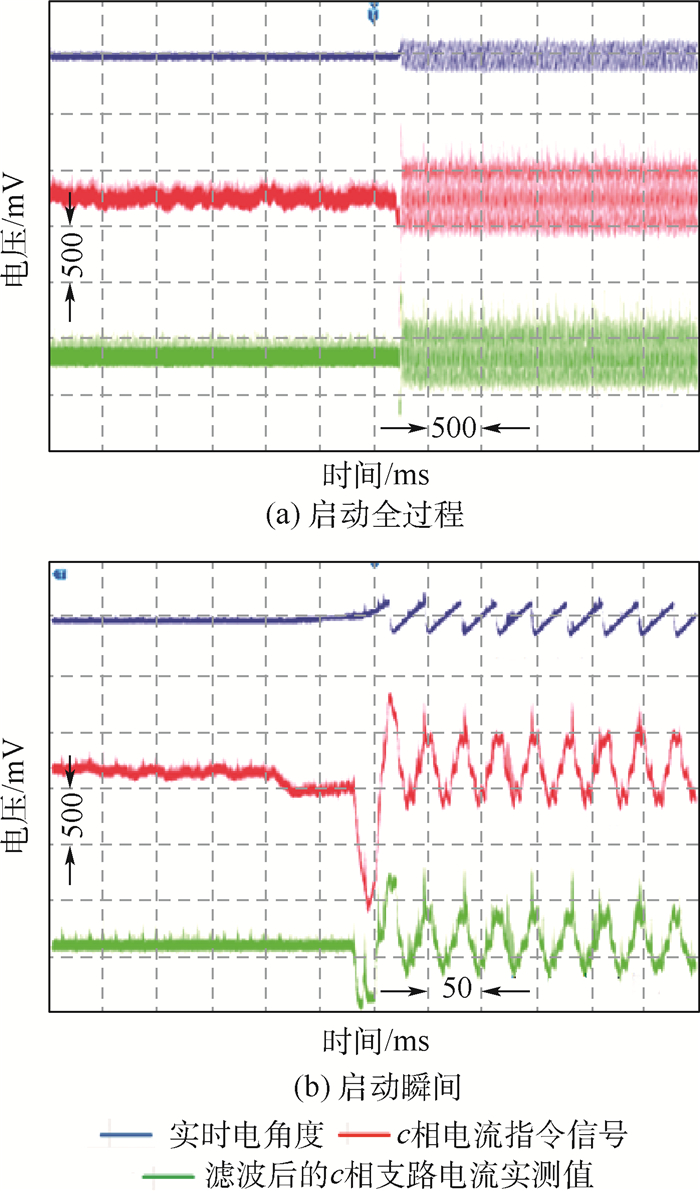
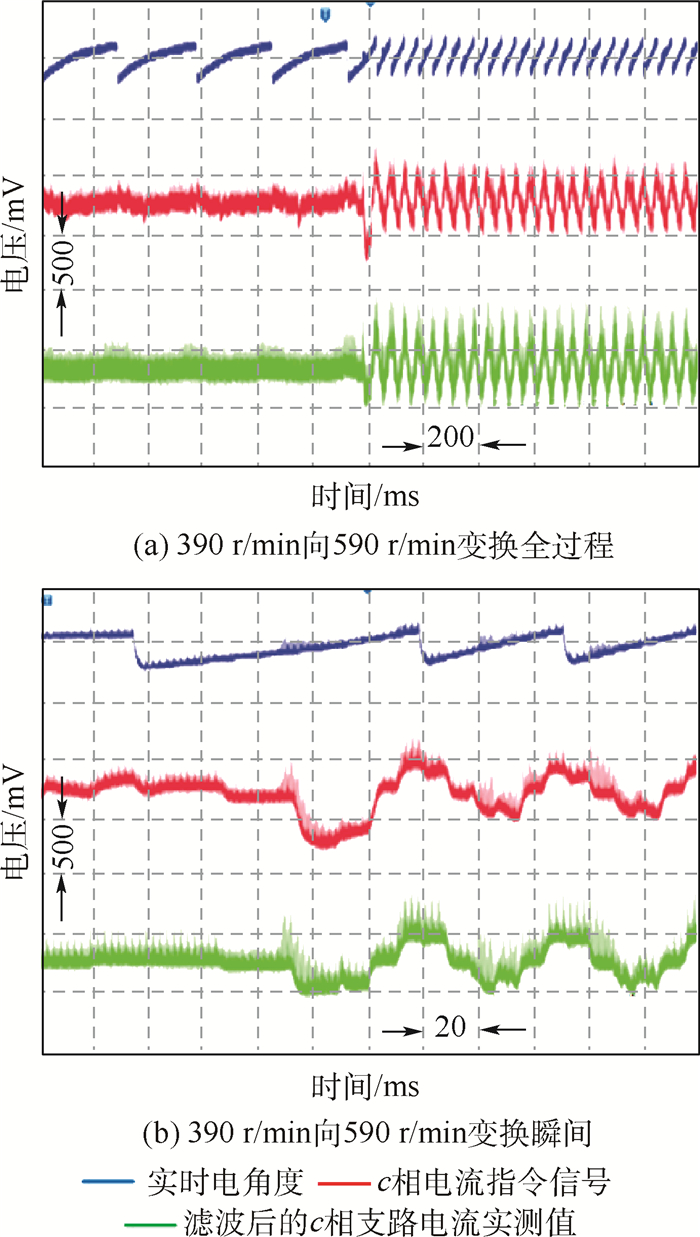
针对无刷直流电动机(BLDCM)驱动控制器在研发过程中全工况测试困难、测试成本高和研发周期长的问题,提出了一种采用分区间采样和解算方法的、具有四象限运行能力的功率级(PHIL)无刷直流电动机模拟器,替代实物电动机和机械负载装置完成对两两导通控制方式下无刷直流电动机驱动控制器的各项性能测试与可靠性试验。该模拟器由实时仿真器、电动机模拟变换器和多级式双向变换器3部分组成,实时仿真器负责采集被测电动机驱动控制器输出的PWM电压,实时解算电动机模型得到三相电流指令,控制电动机模拟变换器生成三相电流,多级式双向变换器负责维持模拟器输入、输出间的能量平衡关系,从而实现对四象限运行时无刷直流电动机的功率级模拟。实验结果表明:所提出的功率级无刷直流电动机模拟器模拟精度高、实时性好、测试灵活,能够有效替代实物电动机和机械负载装置,满足电动机驱动控制器的测试需求。
-
关键词:
- 功率级(PHIL)电动机模拟器 /
- 四象限运行 /
- 无刷直流电动机(BLDCM) /
- 实时仿真器 /
- 电动机模拟变换器
Abstract:Since it is difficult, costly, and time-consuming to test the power electronic converter of Brushless DC Motor (BLDCM) in all operating conditions with a motor-load test bench, this paper proposes a four-quadrant Power Hardware-In-the-Loop (PHIL) BLDCM emulator, which submits a methods of sampling and calculation based on the different operating regions. it can replace the motor-load test bench in the performance test and the reliability test of the BLDCM controller under a two-phase conduction control mode. Meanwhile, the paper employs a piecewise method to optimize the sampling and model calculation processes of the emulator. This PHIL BLDCM emulator comprises a real-time simulator, a motor simulation converter, and a multi-stage bidirectional converter. The real-time simulator measures the output PWM voltages of the power electronic converter and calculates the behavior of the electric motor by the real-time calculation model. The motor simulation converter receives the calculated currents as the control instruction and generates the currents of the emulator. In the meantime, the multi-stage bidirectional converter maintains the energy balance between the input and output of the emulator and realizes the PHIL simulation to the BLDCM operating in different states. The experimental results show that the proposed PHIL BLDCM emulator has many benefits, such as high simulation precision, good real-time performance, and flexible operation, it can achieve the PHIL simulation to the real BLDCM and the mechanical-load in the test of the BLDCM controller.
-
表 1 无刷直流电动机驱动控制器两两导通控制方式下主电路开关管的6种组合状态
Table 1. Six combination states of switches in power electronic converter of BLDCM under two-phase conduction control mode
组合状态 开关组合 导通相 有效线电压 Ⅰ T5T6 C+B- uCBuBC Ⅱ T1T6 A+B- uABuBA Ⅲ T1T2 A+C- uACuCA Ⅳ T3T2 B+C- uBCuCB Ⅴ T3T4 B+A- uBAuAB Ⅵ T5T4 C+A- uCAuAC 表 2 不同开关组合状态下的三相绕组电流解算公式
Table 2. Three-phase winding current calculation equations in different combination states of switches
开关组合 dia(k+1) dib(k+1) dic(k+1) T5T6 0 

T1T6 

0 T1T2 
0 
T3T2 0 

T3T4 

0 T5T4 
0 
表 3 转换过程中各相支路电流实时解算公式
Table 3. Real-time calculation equations of each phase branch current during switching process
支路状态 电流方向 电流解算公式 初始值 持续导通 正向 
in(0)=I 反向 
in(0)=-I 续流导通 正向 
in(0)=I 反向 
in(0)=-I 开通 正向 
in(0)=0 反向 
in(0)=0 注:n代表a、b、c。 表 4 实物电动机主要参数
Table 4. Main parameters of real BLDCM
参数 数值 电枢电阻/Ω 0.42 转动惯量/(kg·m2) 0.000 33 反电势系数/(V·(r·min-1)-1) 0.012 电枢电感/H 0.001 2 极对数 2 额定转速/(r·min-1) 2 000 -
[1] 匡晓霖, 徐金全, 黄春蓉, 等. 六相永磁同步电动机驱动控制方式[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(7): 1361-1369. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0695KUANG X L, XU J Q, HUANG C R, et al. Drive-control modes of six-phase PMSM[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(7): 1361-1369(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0695 [2] 刘勇智, 李杰, 鄯成龙. 基于最优角度自适应TSF的SRM直接瞬时转矩控制[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(11): 2152-2159. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0101LIU Y Z, LI J, SHAN C L. Direct instantaneous torque control of switched reluctance motor based on optimal angle adaptive TSF[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(11): 2152-2159(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0101 [3] JACK A G, ATKINSON D J, SLATER H J. Real-time emulation for power equipment development. Part 1: Real-time simulation[J]. IEE Proceedings-Electric Power Applications, 1998, 145(2): 92-97. doi: 10.1049/ip-epa:19981753 [4] SLATER H J, ATKINSON D J, JACK A G. Real-time emulation for power equipment development. Part 2: The virtual machine[J]. IEE Proceedings-Electric Power Applications, 1998, 145(3): 153-158. doi: 10.1049/ip-epa:19981849 [5] DUFOUR C, LAPOINTE V, BELANGER J. Hardware-in-the-loop closed-loop control of virtual FPGA-coded permanent magnet synchronous motor drives using a rapidly prototyped controller[C]//International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2008: 2152-2158. [6] SCHMITT A, RICHTER J, GOMMERINGER M, et al. A novel 100 kW power hardware-in-the-loop emulation test bench for permanent magnet synchronous machines with nonlinear magnetics[C]//International Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives. Stevenage: IET, 2016: 1-6. [7] LENTIJO S, ARCO S D, MONTI A. Comparing the dynamic performances of power hardware-in-the-loop interfaces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2010, 57(4): 1195-1207. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2009.2027246 [8] MOJLISH S, ERDOGAN N, LEVINE D, et al. Review of hardware platforms for real-time simulation of electric machines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2017, 3(1): 130-146. doi: 10.1109/TTE.2017.2656141 [9] RALPH M K, TILL B, JOACHIM H. Replacement of electrical (load) drives by a hardware-in-the-loop system[C]//International Aegean Conference on Electrical Machines and Power Electronics and Electro-motion, Joint Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 17-25. [10] GAO J, SONG S, HUANG Y, et al. Implementation and test for the semi-physical real-time simulation of IPMSM based on 3-D inductance table[C]//IEEE Conference and Expo Transportation Electrification Asia-Pacific. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 1-5. [11] SARIKHANI A, MOHAMMED O A. HIL-based finite-element design optimization process for the computational prototyping of electric motor drives[C]//IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 737-746. [12] TAVANA N R, DINAVAHI V. Real-time FPGA-based analytical space harmonic model of permanent magnet machines for hardware-in-the-loop simulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2015, 51(8): 1-9. [13] TAVANA N R, DINAVAHI V. Real-time nonlinear magnetic equivalent circuit model of induction machine on FPGA for hardware-in-the-loop simulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2016, 31(2): 520-530. doi: 10.1109/TEC.2015.2514099 [14] KRAUSE P C, WASYNCZUK O, SUDHOFF S D, et al. Analysis of electric machinery and drive systems[M]. New York: Wiley-IEEE Press, 2013: 121-141. [15] YANG F, TAYLOR A R, BAI H, et al. Using d-q transformation to vary the switching frequency for interior permanent magnet synchronous motor drive systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2015, 1(3): 277-286. doi: 10.1109/TTE.2015.2443788 [16] LOK-FU P, VENKATA D. Real-time simulation of a wind energy system based on the doubly-fed induction generator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2009, 24(3): 1301-1309. doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2009.2021200 [17] 夏长亮. 无刷直流电动机控制系统[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 31-56.XIA C L. Control system of brushless DC machine[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009: 31-56(in Chinese). [18] RAO Y S, MUKUL C. Real-time electrical load emulator using optimal feedback control technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2010, 57(4): 1217-1225. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2009.2037657 [19] 张崇巍, 张兴. PWM整流器及其控制[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2003: 154-186.ZHANG C W, ZHANG X. PWM rectifier and its control[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2003: 154-186(in Chinese). [20] 王雷. 能量回馈型交流电子负载变换器研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2008: 16-22.WANG L. Study of AC electronic load converter with energy feedback[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2008: 16-22(in Chinese). 期刊类型引用(4)
1. 赵勇,丁锐,张静,李吉德. 基于Levy-AVOA优化模糊PID的动力定位船舶循迹控制研究. 舰船科学技术. 2024(06): 73-80 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 杜文芒,曹建国,朱继友. 基于智能控制的船舶电力系统优化研究. 船舶物资与市场. 2024(04): 90-92 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 陈玲萍,张振华. 多船并行航行轨迹精准控制算法研究. 舰船科学技术. 2023(12): 128-131 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 孟祥飞,张强,胡宴才,张燕,杨仁明. 欠驱动船舶自适应神经网络有限时间跟踪控制. 山东大学学报(工学版). 2022(04): 214-226 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(3)
-







 下载:
下载:










 百度学术
百度学术

