An underwater coral reef fish detection approach based on aggregation of spatio-temporal features
-
摘要:
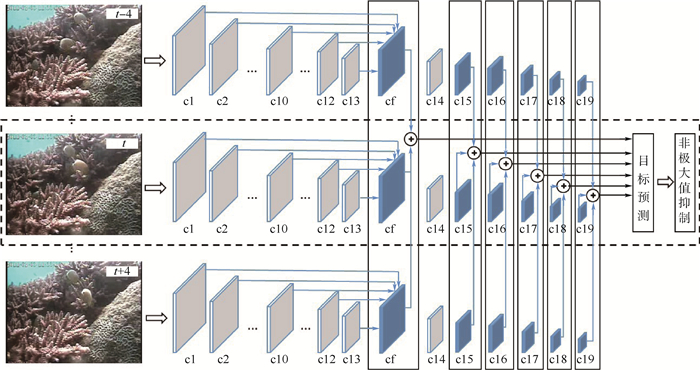
水下监控视频中的珊瑚礁鱼检测面临着视频成像质量不高、水下环境复杂、珊瑚礁鱼视觉多样性高等困难,是一个极具挑战的视觉目标检测问题,如何提取高辨识度的特征成为制约检测精度提升的关键。提出了一种时空特征聚合的水下珊瑚礁鱼检测方法,通过设计视觉特征聚合和时序特征聚合2个模块,融合多个维度的特征以实现这一目标。前者设计了自顶向下的切分和自底向上的归并方案,可实现不同分辨率多层卷积特征图的有效聚合;后者给出了一种帧差引导的相邻帧特征图融合方案,可通过融合多帧特征图强化运动目标及其周边区域的特征表示。公开数据集上的实验表明:基于以上2个模块设计的时空特征聚合网络可以实现对水下珊瑚礁鱼的有效检测,相比于多个主流方法和模型取得了更高的检测精度。
Abstract:It is challenging to detect coral reef fish from underwater surveillance videos, due to issues like poor video imaging quality, complex underwater environment, high visual diversity of coral reef fish, etc. Extracting discriminative features to characterize the fishes has become a crucial issue that dominates the detection accuracy. This paper proposes an underwater coral reef fish detection method based on aggregation of spatio-temporal features. It is achieved by designing two modules for visual and temporal feature aggregation and fusing multi-dimensional features. The former designs a top-down partition and a bottom-up merging, which achieve effective aggregation of feature maps of different convolutional layers with varying resolutions. The latter devises a temporal feature fusion scheme based on the pixel difference between adjacent frames. It enhances the feature representation of moving objects and their surrounding area through the fusion of feature maps coming from adjacent frames. Experiments on a public dataset show that, by employing the spatio-temporal aggregation network built on top of the two proposed modules, we can effectively detect coral reef fishes in the challenging underwater environment. Higher detection accuracy are obtained compared with the existing methods and popular detection models.
-
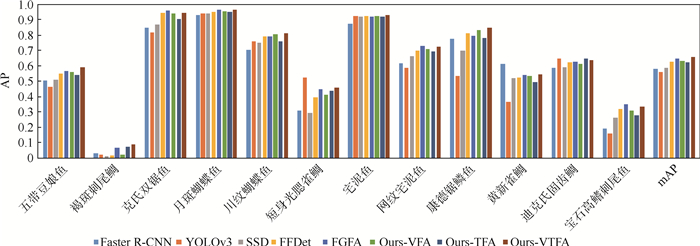
表 1 SeaCLEF数据集中不同类别鱼的数量
Table 1. Numbers of different fish species on SeaCLEF dataset
编号 珊瑚礁鱼名称 训练集样例数 测试集样例数 1 五带豆娘鱼 132 93 2 褐斑刺尾鲷 294 129 3 克氏双锯鱼 363 516 4 月斑蝴蝶鱼 1 217 1 896 5 川纹蝴蝶鱼 335 1 317 6 短身光腮雀鲷 275 24 7 宅泥鱼 894 1 985 8 网纹宅泥鱼 3 165 5 046 9 康德锯鳞鱼 242 118 10 黄新雀鲷 85 1 593 11 迪克氏固齿鲷 737 700 12 宝石高鳍刺尾鱼 72 187 表 2 不同融合方式及性能
Table 2. Different fusion methods and their performance
融合方式 mAP 视觉特征聚合模块 时序特征聚合模块 对应相加 0.634 5 0.600 2 取最大值 0.632 8 0.601 2 取平均值 0.629 6 0.598 6 表 3 输入为3帧图像时不同参数下的网络性能
Table 3. Network performance under different parameters when three-frame images are input
采样邻域及间隔 2 4 6 8 mAP 0.599 0.601 0.602 0.602 表 4 输入为5帧图像时不同参数下的网络性能
Table 4. Network performance under different parameters when five-frame images are input
采样邻域及间隔 24 26 28 46 48 68 mAP 0.612 0.614 0.617 0.618 0.622 0.621 表 5 不同方法的检测性能
Table 5. Detection performance of different methods
-
[1] CINNER J E, HUCHERY C, MACNEIL M A, et al. Bright spots among the world's coral reefs[J]. Nature, 2016, 535(7612): 416-419. doi: 10.1038/nature18607 [2] 赵焕庭, 王丽荣, 袁家义. 南海诸岛珊瑚礁可持续发展[J]. 热带地理, 2016, 36(1): 55-65.ZHAO H T, WANG L R, YUAN J Y. Sustainable development of the coral reefs in the South China Sea Islands[J]. Tropical Geography, 2016, 36(1): 55-65(in Chinese). [3] GRAHAM N A J, EVANS R D, RUSS G R. The effects of marine reserve protection on the trophic relationships of reef fishes on the Great Barrier Reef[J]. Environmental Conservation, 2003, 30(2): 200-208. doi: 10.1017/S0376892903000195 [4] HODGSON G. Reef check: The first step in community-based management[J]. Bulletin of Marine Science, 2001, 69(2): 861-868. [5] 李永振, 史赟荣, 艾红, 等. 南海珊瑚礁海域鱼类分类多样性大尺度分布格局[J]. 中国水产科学, 2011, 18(3): 619-628.LI Y Z, SHI Y R, AI H, et al. Large scale distribution patterns of taxonomic diversity of fish in coral reef waters, South China Sea[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2011, 18(3): 619-628(in Chinese). [6] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2014: 568-576. [7] DONAHUE J, HENDRICKS L A, ROHRBACH M, et al. Long-term recurrent convolutional networks for visual recognition and description[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 2625-2634. [8] CHEN Z, AI S, JIA C. Structure-aware deep learning for product image classification[J]. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications, 2019, 15(1s): 1-20. [9] TRAN D, BOURDEV L, FERGUS R, et al. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 4489-4497. [10] ZHU X, WANG Y, DAI J, et al. Flow-guided feature aggregation for video object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 408-417. [11] ZHAO B, WU X, FENG J, et al. Diversified visual attention networks for fine-grained object classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2017, 19(6): 1245-1256. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2017.2648498 [12] PU J, JIANG Y G, WANG J, et al. Which looks like which: Exploring inter-class relationships in fine-grained visual categorization[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2014: 425-440. [13] LEE D J, SCHOENBERGER R B, SHIOZAWA D, et al. Contour matching for a fish recognition and migration-monitoring system[C]//Two- and Three-Dimensional Vision Systems for Inspection, Control, and Metrology Ⅱ. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2004, 5606: 37-48. [14] FOUAD M M M, ZAWBAA H M, EL-BENDARY N, et al. Automatic nile tilapia fish classification approach using machine learning techniques[C]//13th International Conference on Hybrid Intelligent Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 173-178. [15] LARSEN R, OLAFSDOTTIR H, ERSBØLL B K. Shape and texture based classification of fish species[C]//SCIA 2009: Image Analysis. Berlin: Springer, 2009: 745-749. [16] SPAMPINATO C, GIORDANO D, DI SALVO R, et al. Automatic fish classification for underwater species behavior understanding[C]//Proceedings of the First ACM International Workshop on Analysis and Retrieval of Tracked Events and Motion In Imagery Streams. New York: ACM Press, 2010: 45-50. [17] WEI G, WEI Z, HUANG L, et al. Robust underwater fish classification based on data augmentation by adding noises in random local regions[C]//Pacific Rim Conference on Multimedia. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 509-518. [18] JOLY A, GOËAU H, GLOTIN H, et al. LifeCLEF 2016: Multimedia life species identification challenges[C]//International Conference of the Cross-Language Evaluation Forum for European Languages. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 286-310. [19] CHOI S. Fish identification in underwater video with deep convolutional neural network: SNUMedinfo at LifeCLEF fish task 2015[C]//CLEF (Working Notes), 2015: 1-10. [20] JÄGER J, RODNER E, DENZLER J, et al. SeaCLEF 2016: Object proposal classification for fish detection in underwater videos[C]//CLEF (Working Notes), 2016: 481-489. [21] SHI C, JIA C, CHEN Z. FFDet: A fully convolutional network for coral reef fish detection by layer fusion[C]//2018 IEEE International Conference on Visual Communications and Image Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1-4. [22] ZHUANG P Q, XING L J, LIU Y L, et al. Marine animal detection and recognition with advanced deep learning models[C]//Working Notes of the 8th International Conference of the CLEF Initiative, 2017: 1-9. [23] LIU W, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 21-37. [24] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [25] JAISAKTHI S M, MIRUNALINI P, ARAVINDAN C. Coral reef annotation and localization using faster R-CNNs[C]//Working Notes of the 8th International Conference of the CLEF Initiative, 2019: 1-6. [26] REN S, HE K, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2015: 91-99. [27] BOGOMASOV K, GRAWE P, CONRAD S. A two-staged approach for localization and classification of coral reef structures and compositions[C]//Working Notes of the 8th International Conference of the CLEF Initiative, 2019: 1-11. [28] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 779-788. [29] ZIVKOVIC Z. Improved adaptive Gaussian mixture model for background subtraction[C]//Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Pattern Recognition(ICPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2004, 2: 28-31. [30] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2012: 1097-1105. [31] SZEGEDY C, LIU W, JIA Y, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1-9. [32] CAI Z, VASCONCELOS N. Cascade R-CNN: Delving into high quality object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 6154-6162. [33] REZATOFIGHI H, TSOI N, GWAK J, et al. Generalized intersection over union: A metric and a loss for bounding box regression[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 658-666. [34] LAW H, DENG J. Cornernet: Detecting objects as paired keypoints[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 734-750. [35] LIN T Y, DOLLAR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2117-2125. [36] ZHANG S, WEN L, BIAN X, et al. Single-shot refinement neural network for object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 4203-4212. [37] CORDTS M, OMRAN M, RAMOS S, et al. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 3213-3223. [38] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[EB/OL]. (2015-04-10)[2020-08-01]. -







 下载:
下载: