-
摘要:
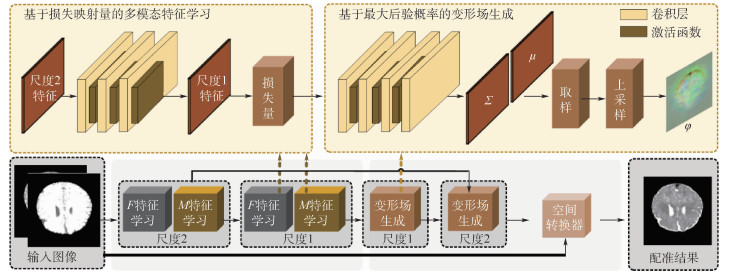
针对医学图像配准问题,传统方法提出通过解决优化问题进行配准,但计算成本高、运行时间长。深度学习方法提出使用网络学习配准参数,从而进行配准并在单模态图像上取得高效性能。但在多模态图像配准时,不同模态图像的强度分布未知且复杂,大多已有方法严重依赖标签数据,现有方法不能完全解决此问题。提出一种基于无监督学习的深度多模态可变形图像配准框架。该框架由基于损失映射量的特征学习和基于最大后验概率的变形场学习组成,借助空间转换函数和可微分的互信息损失函数实现无监督训练。在MRI T1、MRI T2以及CT的3D多模态图像配准任务上,将所提方法与现有先进的多模态配准方法进行比较。此外,还在最新的COVID-19的CT数据上展示了所提方法的配准性能。大量结果表明:所提方法与其他方法相比,在配准精度上具有竞争优势,并且大大减少了计算时间。
Abstract:Multimodal deformable registration is designed to solve dense spatial transformations and is used to align images of two different modalities. It is a key issue in many medical image analysis applications. Multimodal image registration based on traditional methods aims to solve the optimization problem of each pair of images, and usually achieves excellent registration performance, but the calculation cost is high and the running time is long. The deep learning method greatly reduces the running time by learning the network used to perform registration. These learning-based methods are very effective for single-modality registration. However, the intensity distribution of different modal images is unknown and complex. Most existing methods rely heavily on label data. Faced with these challenges, this paper proposes a deep multimodal registration framework based on unsupervised learning. Specifically, the framework consists of feature learning based on matching amount and deformation field learning based on maximum posterior probability, and realizes unsupervised training by means of spatial conversion function and differentiable mutual information loss function. In the 3D image registration tasks of MRI T1, MRI T2 and CT, the proposed method is compared with the existing advanced multi-modal registration methods. In addition, the registration performance of the proposed method is demonstrated on the latest COVID-19 CT data. A large number of results show that the proposed method has a competitive advantage in registration accuracy compared with other methods, and greatly reduces the calculation time.
-
Key words:
- deep learning /
- unsupervised /
- medical image registration /
- multimodal /
- computer vision
-
表 1 MRI T1-MRI T2 RMSE配准结果
Table 1. MRI T1-MRI T2 RMSE registration results
方法 配准方向 MRI T2->MRI T1 MRI T1->MRI T2 affined 17.549(3.116) 17.549(3.116) VoxelMorph 16.844(3.276) 17.545(2.982) Elastix 17.731(3.140) 17.717(3.111) ANTs (SyN) 16.932(3.141) 17.206(3.078) 本文 16.725(3.303) 16.915(3.223) 表 2 CT-MRI配准结果
Table 2. CT-MRI registration results
方法 RMSE affined 29.932(0.819) VoxelMorph 28.196(4.374) Elastix 27.252(0.961) ANTs (SyN) 29.401(1.021) 本文 25.886(0.374) 表 3 CT-CT配准结果
Table 3. CT-CT registration results
方法 Dice RMSE NCC Grad Det-Jac/10-3 affined 0.464(0.091) 32.714(1.694) 0.180(0.008) VoxelMorph 0.636(0.109) 21.086(2.313) 0.224(0.016) 4.497(1.058) Elastix 0.522(0.123) 33.874(2.191) 0.112(0.021) ANTs (SyN) 0.611(0.233) 31.382(4.169) 0.133(0.063) 本文-L1_cost 0.654(0.077) 30.135(3.336) 0.285(0.014) 0.866(0.004) 本文-Prob 0.678(0.094) 28.617(3.232) 0.283(0.012) 0.812(0.005) 本文 0.708(0.086) 27.461(3.162) 0.287(0.014) 0.812(0.004) 表 4 MRI T2->MRI T1配准运行时间
Table 4. MRI T2->MRI T1 registration running time
方法 时间/s VoxelMorph 0.406 Elastix 6.595 SyN 20.038 本文 0.281 -
[1] MAINTZ J B A, VIERGEVER M A. A survey of medical image registration[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 1998, 2(1): 1-36. doi: 10.1016/S1361-8415(98)80001-7 [2] ASHBURNER J. A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm[J]. NeuroImage, 2007, 38(1): 95-113. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.07.007 [3] GUIZAR-SICAIROS M, THURMAN S T, FIENUP J R. Efficient subpixel image registration algorithms[J]. Optics Letters, 2008, 33(2): 156-158. doi: 10.1364/OL.33.000156 [4] MAES F, VANDERMEULEN D, SUETENS P. Medical image registration using mutual information[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2003, 10(91): 1699-1722. [5] D'AGOSTINO E, MAES F, VANDERMEULEN D, et al. A viscous fluid model for multimodal non-rigid image registration using mutual information[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2003, 7(4): 565-575. doi: 10.1016/S1361-8415(03)00039-2 [6] BALAKRISHNAN G, ZHAO A, SABUNCU M R, et al. An unsupervised learning model for deformable medical image registration[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 9252-9260. [7] HU Y, MODAT M, GIBSON E, et al. Weakly-supervised convolutional neural networks for multimodal image registration[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2018, 49: 1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2018.07.002 [8] QIN C, SHI B, LIAO R, et al. Unsupervised deformable registration for multi-modal images via disentangled representations[C]//International Conference on Information Processing in Medical Imaging. Berlin: Springer, 2019: 249-261. [9] MAHAPATRA D, GE Z. Training data independent image registration using generative adversarial networks and domain adaptation[EB/OL]. [2020-07-21]. https://doi.org/10./olb/j.patcog.2019.107109. [10] ZHANG Y X, LIU R S, LI Z, et al. Coupling principled refinement with bi-directional deep estimation for robust deformable 3D medical image registration[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 86-90. [11] LIU R S, LI Z, ZHANG Y X, et al. Bi-level probabilistic feature learning for deformable image registration[C]//International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020: 723-730. [12] JADERBERG M, SIMONYAN K, KAVUKCUOGLU K, et al. Spatial transformer networks[C]//Conference and Workshop on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: Curran Associates, 2015: 2017-2025. [13] SUN D, YANG X, LIU M, et al. PWC-NET: CNNs for optical flow using pyramid, warping, and cost volume[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 8934-8943. [14] ZACH C, POCK T, BISCHOF H. A duality based approach for real TV-L1 optical flow[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2007, 4713: 214-223. [15] 徐峻岭, 周毓明, 陈林, 等. 基于互信息的无监督特征选择[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2012, 49(2): 158-168.XU J L, ZHOU Y M, CHEN L, et al. An unsupervised feature selection approach based on mutual information[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2012, 49(2): 158-168(in Chinese). [16] MAHAPATRA D, ANTONY B, SEDAI S. Deformable medical image registration using generative adversarial networks[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1449-1453. [17] MUELLER S G, WEINER M W, THAL L J, et al. Ways toward an early diagnosis in Alzheimer's disease: The Alzheimer's disease neuroimaging initiative(ADNI)[J]. Alzheimer's & Dementia, 2005, 1(1): 55-66. [18] KISER K J, AHMED S, STIEB S M, et al. Data from the thoracic volume and pleural effusion segmentations in diseased lungs for benchmarking chest ct processing pipelines[EB/OL]. [2020-08-22]. https://doi.org/10.7937/tcia.2020.6c7y-gq39. [19] AERTS H J W L, WEE L, VELAZQUEZ E R, et al. Data from NSCLC-radiomics[EB/OL]. [2020-08-22]. https://doi.org/10.7937/K9/TCIA.2015.PF0M9REI. [20] CHILAMKURTHY S, GHOSH R, TANAMALA S, et al. Deep learning algorithms for detection of critical findings in head CT scans: A retrospective study[J]. Lancet, 2018, 392(10162): 2388-2396. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31645-3 [21] MA J, GE C, WANG Y, et al. COVID-19 CT lung and infection segmentation dataset(Version1.0)[EB/OL]. [2020-08-22]. [22] AVANTS B B, TUSTISON N, GANG S. Advanced normalization tools (ANTs)[J]. Insight, 2009, 2(365): 1-35. [23] AVANTS B B, EPSTEIN C L, GROSSMAN M, et al. Symmetric diffeomorphic image registration with cross-correlation: Evaluating automated labeling of elderly and neurodegenerative brain[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2008, 12(1): 26-41. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2007.06.004 [24] KLEIN S, STARING M, MURPHY K, et al. Elastix: A toolbox for intensity based medical image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2010, 29(1): 196-205. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2009.2035616 -







 下载:
下载:



