-
摘要:
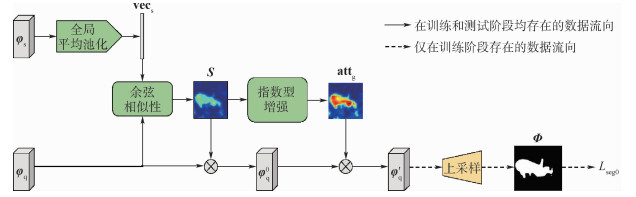
针对小样本分割中如何提取支持图像和查询图像共性信息的问题,提出一种新的小样本分割模型,同时结合了全局相似性和局部相似性,实现了更具泛化能力的小样本分割。具体地,根据支持图像和查询图像全局特征和局部特征之间的相似性,提出了一种新型注意力谱生成器,进而实现查询图像的注意力谱生成和区域分割。所提注意力谱生成器包含2个级联模块:全局引导器和局部引导器。在全局引导器中,提出了一种新的基于指数函数的全局相似性度量,对查询图像特征和支持图像的全局特征进行关系建模,输出前景增强的查询图像特征。在局部引导器中,通过引入局部关系矩阵对支持图像特征和查询图像特征之间的局部相似性进行建模,得到与类别无关的注意力谱。在Pascal-5
i 数据集上做了大量的实验,在1-shot设定下mIoU达到了59.9%,5-shot设定下mIoU达到了61.9%,均优于现有方法。Abstract:Few shot segmentation aims at segmenting objects of novel classes with few annotated images, whose key is to extract the general information between support and query images. The existing methods utilize global features or local features to obtain the general information and validate their effectiveness. However, these two kinds of features' similarity are considered separately in the existing methods, while their mutual effect is ignored. This paper proposes a novel few shot segmentation model using both global and local similarity to achieve more generalizable few shot segmentation. Specifically, an attention generator is proposed to build the attention map of query images based on the relationship between support and query images. The proposed attention generator consists of two cascaded modules: global guider and local guider. In global guider, a novel exponential function based global similarity metric is proposed to model the relationship between query images and support images with respect to global feature, and output foreground-enhanced query image features. As for local guider, a local relationship matrix is introduced to model the local similarity between support and query image features, and obtain the class-agnostic attention map. Comprehensive experiments are performed on Pascal-5
i idataset. The proposed method achieves a mean IoU value of 59.9% under 1-shot setting, and a mean IoU of 61.9% under 5-shot setting, which outperforms many state-of-the-art methods. -
表 1 Pascal-5i四个子集的划分
Table 1. Four subsets setting of Pascal-5i
子集 类别 Fold0 飞机、自行车、鸟、船、瓶子 Fold1 公交车、轿车、猫、椅子、牛 Fold2 餐桌、狗、马、摩托车、人 Fold3 盆栽、山羊、沙发、火车、显示器 表 2 不同主干网络下,本文与现有方法的1-shot对比实验mIoU结果
Table 2. Comparative experimental results (mIoU) of proposed method and existing methods under 1-shot setting using different backbone networks
% 主干网络 方法 mIoU 平均值 F0 F1 F2 F3 VGG16 OSLSM[4] 33.6 55.3 40.9 33.5 40.8 Co-FCN[29] 36.7 50.6 44.9 32.4 41.2 SG-One[1] 40.2 58.4 48.4 38.4 46.4 PANet[6] 42.3 58.0 51.1 41.2 48.2 FWB[8] 47.0 59.6 52.6 48.3 51.9 本文 50.3 65.3 53.0 50.8 54.9 ResNet50 CANet[2] 52.5 65.9 51.3 51.9 55.4 LTM[3] 54.6 65.6 56.6 51.3 57.0 CRNet[30] 55.7 本文 54.6 67.8 57.4 52.1 58.0 ResNet101 FWB[8] 51.3 64.5 56.7 52.2 56.2 本文 57.5 68.7 58.7 54.5 59.9 表 3 不同主干网络下,本文与现有方法的5-shot对比实验mIoU结果
Table 3. Comparative experimental results (mIoU) of proposed method and existing methods under 5-shot setting using different backbone networks
% 主干网络 方法 mIoU 平均值 F0 F1 F2 F3 VGG16 OSLSM[4] 35.9 58.1 42.7 39.1 44.0 Co-FCN[29] 37.5 50.0 44.1 33.9 41.4 SG-One[1] 41.9 58.6 48.6 39.4 47.1 PANet[6] 51.8 64.6 59.8 46.5 55.7 FWB[8] 50.9 62.9 56.5 50.1 55.1 本文 50.3 66.3 54.7 55.3 56.7 ResNet50 CANet[2] 55.5 67.8 51.9 53.2 57.1 LTM[3] 56.4 66.6 56.9 56.8 59.2 CRNet[30] 58.8 本文 54.8 68.1 59.9 56.2 59.8 ResNet101 FWB[8] 54.9 67.4 62.2 55.3 60.0 本文 58.1 69.8 60.8 58.9 61.9 表 4 不同主干网络下,本文与现有方法的1-shot对比实验FB-IoU结果
Table 4. Comparative experimental results (FB-IoU) of proposed method and existing methods under 1-shot setting using different backbone networks
% 表 5 不同主干网络下,本文与现有方法的5-shot对比实验FB-IoU结果
Table 5. Comparative experimental results (FB-IoU) of proposed method and existing methods under 5-shot setting using different backbone networks
% 表 6 全局相似性度量方式的对比实验mIoU结果
Table 6. Comparative experimental results (mIoU) of global similarity metric
% 全局度量方式 mIoU 1-shot 5-shot 余弦距离 51.3 53.2 通道维度拼接 46.5 47.2 所提全局相似性度量 53.8 55.7 表 7 5-shot设定方案对比实验mIoU结果
Table 7. Comparative experimental results (mIoU) under 5-shot setting
% 设定方式 mIoU 平均化注意力谱 59.1 所提k-shot方案 59.7 表 8 全局引导器和局部引导器的消去实验mIoU结果
Table 8. Ablation experimental results (mIoU) of global guider and local guider
% 全局引导器 局部引导器 mIoU 1-shot 5-shot √ 53.8 55.7 √ 56.8 59.0 √ √ 58.0 59.7 表 9 损失函数的消去实验mIoU结果
Table 9. Ablation experimental result (mIoU) of loss function
% Lseg La Lseg0 mIoU 1-shot 5-shot √ 55.4 57.7 √ √ 56.6 58.6 √ √ 55.9 57.9 √ √ √ 58.0 59.7 -
[1] ZHANG X, WEI Y, YANG Y, et al. Sg-One: Similarity guidance network for one-shot semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(9): 3855-3865. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2992433 [2] ZHANG C, LIN G, LIU F, et al. CANet: Class-agnostic segmentation networks with iterative refinement and attentive few-shot learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 5217-5226. [3] YANG Y, MENG F, LI H, et al. A new local transformation module for few-shot segmentation[C]//International Conference on Multimedia Modeling. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 76-87. [4] SHABAN A, BANSAL S, LIU Z, et al. One-shot learning for semantic segmentation[EB/OL]. [2020-07-18]. https: //arxiv.org/abs/1709.03410. [5] TIAN P, WU Z, QI L, et al. Differentiable meta-learning model for few-shot semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. [S. l. ]: AAAI Press, 2020: 12087-12094. [6] WANG K, LIEW J H, ZOU Y, et al. PANet: Few-shot image semantic segmentation with prototype alignment[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 9197-9206. [7] LIU J, QIN Y. Prototype refinement network for few-shot segmentation[EB/OL]. (2020-05-09)[2020-07-18]. [8] NGUYEN K, TODOROVIC S. Feature weighting and boosting for few-shot segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 622-631. [9] FINN C, ABBEEL P, LEVINE S. Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks[J/OL]. (2017-07-18)[2020-07-18]. [10] KIM J, KIM T, KIM S, et al. Edge-labeling graph neural network for few-shot learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 11-20. [11] SNELL J, SWERSKY K, ZEMEL R. Prototypical networks for few-shot learning[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2017: 4077-4087. [12] SUNG F, YANG Y, ZHANG L, et al. Learning to compare: Relation network for few-shot learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1199-1208. [13] LONG J, SHELHAMER E, DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 3431-3440. [14] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, SCHROFF F, et al. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation[EB/OL]. [2020-07-18]. [15] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 40(4): 834-848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184 [16] LIN G, MILAN A, SHEN C, et al. RefineNet: Multi-path refinement networks for high-resolution semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1925-1934. [17] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]//International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted intervention. Berlin: Springer, 2015: 234-241. [18] ZHAO H, SHI J, QI X, et al. Pyramid scene parsing network[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2881-2890. [19] 潘崇煜, 黄健, 郝建国, 等. 融合零样本学习和小样本学习的弱监督学习方法综述[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2020, 42(10): 2246-2256. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.10.13PAN C Y, HUANG J, HAO J G, et al. Survey of weakly supervised learning integrating zero-shot and few-shot learning[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(10): 2246-2256(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.10.13 [20] 孙文赟, 金忠, 赵海涛, 等. 基于深度特征增广的跨域小样本人脸欺诈检测算法[J/OL]. 计算机科学[2020-09-27].SUN W Y, JIN Z, ZHAO H T, et al. Cross-domain few-shot face presentation attack detection method based on deep feature augmentation[J/OL]. Computer Science, 2020[2020-09-27]. (in Chinese). [21] 于重重, 萨良兵, 马先钦, 等. 基于度量学习的小样本零器件表面缺陷检测[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2020(7): 214-223.YU C C, SA L B, MA X Q, et al. Few-shot parts surface defect detection based on the metric learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2020(7): 214-223. [22] 雷相达, 王宏涛, 赵宗泽. 基于迁移学习的小样本机载激光雷达点云分类[J]. 中国激光, 2020, 47(11): 1110002.LEI X D, WANG H T, ZHAO Z Z. Small sample airborne LiDAR point cloud classification based on transfer learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47(11): 1110002. [23] 李文煜, 帅仁俊, 郭汉. 克服小样本学习中灾难性遗忘方法研究[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2020, 37(7): 136-141.LI W Y, SHUAI R J, GUO H. Overcoming catastrophic forgetting in few-shot learning[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2020, 37(7): 136-141(in Chinese). [24] WANG X, GIRSHICK R, GUPTA A, et al. Non-local neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 7794-7803. [25] DENG J, DONG W, SOCHER R, et al. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2009: 248-255. [26] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[EB/OL]. (2014-11-18)[2020-07-18]. [27] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [28] KRÄHENBVHL P, KOLTUN V. Efficient inference in fully connected CRFs with Gaussian edge potentials[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2011: 109-117. [29] RAKELLY K, SHELHAMER E, DARRELL T, et al. Conditional networks for few-shot semantic segmentation[C]. International Conference on Learning Representations, 2018. [30] LIU W, ZHANG C, LIN G, et al. CRNet: Cross-reference networks for few-shot segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 4165-4173. -








 下载:
下载: