-
摘要:
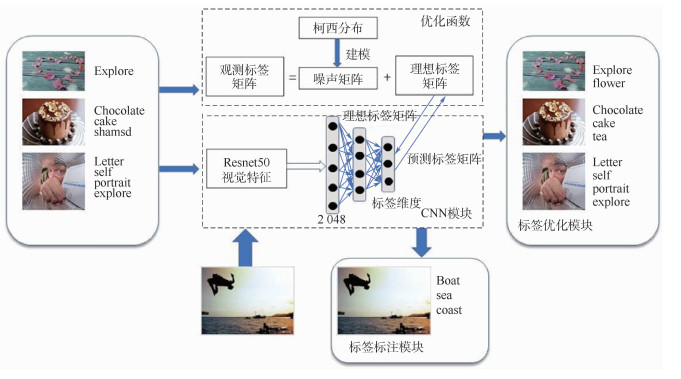
随着社交网络的快速发展,带有用户提供标签的社交网络图像呈现爆炸式增长。但是用户提供的标签是不准确的,存在很多不相关以及错误的标签。这势必会增加相关多媒体任务的困难。针对标签噪声无序性以及常用的高斯分布对标签噪声中大噪声过于敏感的问题,但是高斯分布对大噪声比较敏感。鉴于此,采用对各种噪声都具有鲁棒性的柯西分布拟合噪声,提出了一个基于噪声柯西分布的弱监督非负低秩深度学习(CDNL)模型,通过柯西分布建模标签噪声来获得理想标签,并利用深度神经网络模块学习视觉特征和理想标签之间的内在联系,来得到图像对应的正确标签,从而大幅提高社交网络图像的标签准确率。所提模型不仅可以修正错误标签、补充缺失标签,也可以对新图像进行标注。在2个公开的社交网络图像数据集上进行了验证,并且与一些最新的相关工作进行了对比,证实了所提模型的有效性。
Abstract:With the rapid development of social networks, images with social tags have increased explosively. However, these tags are usually inaccurate and irrelevant which will make it harder for the relevant multimedia tasks. Although label noise is chaotic and disordered, it still conforms to a certain probability distribution. Most of the current methods use Gaussian distribution to fit the noise, but Gaussian distribution is very sensitive to large noise. Thus we use the Cauchy distribution to fit the noise, which is robust to various noises. In this paper, we propose a weakly-supervised Non-negative Low-rank deep learning model based on Cauchy Distribution (CDNL), which builds the noise model by Cauchy distribution to obtain the ideal label and uses deep neural network to reveal the intrinsic connection between the visual features of the image and the ideal labels. The proposed method can not only correct wrong labels and add missing labels, but also tag new images. Experiments are conducted on two public social network image datasets. Compared with some of the latest related work, the results show the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
Key words:
- social tag /
- Cauchy distribution /
- deep neural network /
- image annotation /
- matrix factorization
-
表 1 MIRFlickr和NUS-WIDE实验数据
Table 1. Experimental data of MIRFlickr and NUS-WIDE
参数 MIRFlickr NUS-WIDE 图片数量 25 000 269 627 标签数量 457 1 000 真实标签数量 18 81 每次训练集图片数量 12 500 160 000 表 2 在MIRFlickr和NUS-WIDE数据集进行标签重标注的实验结果(平均MicroAUC/MacroAUC±标准偏差值)
Table 2. Experimental results(mean microauc/macroauc±standard deviation) on the MIRFlickr and NUS-WIDE for image tag refinement
方法 MIRFlickr NUS-WIDE MicroAUC MacroAUC MicroAUC MacroAUC Baseline 0.558 0.587 0.623 0.754 LSCCA 0.594±0.006 0.586±0.004 0.732±0.002 0.632±0.003 CCA-CNN 0.644±0.006 0.631±0.003 0.675±0.005 0.743±0.007 TCCA 0.643±0.006 0.632±0.004 0.768±0.007 0.675±0.008 DMF 0.639±0.002 0.628±0.002 0.751±0.005 0.739±0.004 MPMF 0.634±0.004 0.607±0.002 0.782±0.002 0.681±0.005 DNMF 0.624±0.005 0.621±0.006 0.759±0.009 0.665±0.003 WDMF 0.704±0.005 0.678±0.006 0.805±0.004 0.775±0.006 WDNL 0.685±0.003 0.671±0.003 0.789±0.006 0.762±0.006 DCE 0.732±0.003 0.718±0.004 0.825±0.004 0.797±0.003 本文 0.745±0.004 0.775±0.006 0.774±0.009 0.831±0.005 表 3 在MIRFlickr和NUS-WIDE数据集进行新图像标签标注的实验结果(平均MicroAUC/MacroAUC±标准偏差值)
Table 3. Experimental results(mean microauc/macroauc±standard deviation) on the MIRFlickr and NUS-WIDE for image tag assignment
方法 MIRFlickr NUS-WIDE MicroAUC MacroAUC MicroAUC MacroAUC LSCCA 0.585±0.006 0.562±0.004 0.681±0.002 0.599±0.003 CCA-CNN 0.642±0.005 0.627±0.002 0.617±0.004 0.641±0.003 TCCA 0.610±0.005 0.597±0.006 0.727±0.009 0.625±0.006 DMF 0.635±0.002 0.623±0.003 0.737±0.004 0.632±0.004 MPMF 0.617±0.004 0.596±0.002 0.742±0.002 0.635±0.005 DNMF 0.619±0.005 0.601±0.006 0.699±0.009 0.618±0.003 WDMF 0.661±0.007 0.646±0.004 0.768±0.005 0.675±0.007 WDNL 0.665±0.004 0.652±0.005 0.758±0.004 0.671±0.007 DCE 0.693±0.005 0.667±0.004 0.787±0.006 0.746±0.004 本文 0.715±0.006 0.735±0.005 0.761±0.008 0.794±0.007 表 4 不同尺度参数b对数据集mAP性能的影响
Table 4. Experimental results(mAP) on the MIRFlickr and NUS-WIDE for different scale parameter b
b mAP MIRFlickr NUS-WIDE 0.2 0.417 0.401 0.4 0.423 0.415 0.6 0.425 0.423 0.8 0.452 0.403 -
[1] KENNEDY L S, CHANG S F, KOZINTSEV I V. To search or to label Predicting the performance of search-based automatic image classifiers[C]//Proceedings of the 8th ACM International Conference on Multimedia Information Retrieval. New York: ACM Press, 2006: 249-258. [2] CHEN M, ZHENG A, WEINBERGER K. Fast image tagging[C]//International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ACM Press, 2013: 1274-1282. [3] LI Z, TANG J. Weakly supervised deep matrix factorization for social image understanding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 26(1): 276-288. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7728069/references [4] ZHU G, YAN S, MA Y. Image tag refinement towards low-rank, content-tag prior and error sparsity[C]//Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York: ACM Press, 2010: 461-470. [5] LI Z, TANG J. Weakly-supervised deep nonnegative low-rank model for social image tag refinement and assignment[C]//Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2017: 4154-4160. [6] LI X, SNOEK C G M, WORRING M. Learning social tag relevance by neighbor voting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2009, 11(7): 1310-1322. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2009.2030598 [7] TANG J, SHU X, QI G J, et al. Tri-clustered tensor completion for social-aware image tag refinement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 39(8): 1662-1674. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2608882 [8] MA H C, LIU I, KING I, et al. Probabilistic factor models for web site recommendation[C]//Proceedings of the 34th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. New York: ACM Press, 2011: 265-274. [9] PARK S, SERPEDIN E, QARAQE K. Gaussian assumption: The least favorable but the most useful lecture notes[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2013, 30(3): 183-186. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2013.2238691 [10] ABDI H, WILLIAMS L J. Principal component analysis[J]. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Statistics, 2010, 2(4): 433-459. doi: 10.1002/wics.101 [11] LIU D, HUA X S, WANG M, et al. Image retagging[C]//Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York: ACM Press, 2010: 491-500. [12] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [13] DOLAN-GAVITT B, LEEK T, ZHIVICH M, et al. Virtuoso: Narrowing the semantic gap in virtual machine introspection[C]//2011 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 297-312. [14] BARNARD K, DUYGULU P, FORSYTH D, et al. Matching words and pictures[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2003, 3(2): 1107-1135. [15] MAKADIA A, PAVLOVIC V, KUMAR S. Baselines for image annotation[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2010, 90(1): 88-105. doi: 10.1007/s11263-010-0338-6 [16] WU L, JIN R, JAIN A K. Tag completion for image retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 35(3): 716-727. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/22641703 [17] ZHAO R, GROSKY W I. Narrowing the semantic gap-improved text-based web document retrieval using visual features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2002, 4(2): 189-200. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2002.1017733 [18] FENG Z, FENG S, JIN R, et al. Image tag completion by noisy matrix recovery[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2014: 424-438. [19] BENGIO Y. Learning deep architectures for AI[J]. Foundations and Trends in Machine Learning, 2009, 2(1): 1-127. doi: 10.1561/2200000006 [20] MURTHY V N, MAJI S, MANMATHA R. Automatic image annotation using deep learning representations[C]//Proceedings of the 5th ACM International Conference on Multimedia Information Retrieval. New York: ACM Press, 2015: 603-606. [21] ZHANG J, WU Q, ZHANG J, et al. Kill two birds with one stone: Weakly-supervised neural network for image annotation and tag refinement[C]//Proceedings of the Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2018: 234-257. [22] LI Z, TANG J, ZHANG L, et al. Weakly-supervised semantic guided hashing for social image retrieval[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128: 2265-2278. doi: 10.1007/s11263-020-01331-0 [23] LI Z, TANG J, MEI T. Deep collaborative embedding for social image understanding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(9): 2070-2083. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2852750 [24] BRIAN C, BO W, ALIREZA Z, et al. General partial label learning via dual bipartite graph autoencoder[EB/OL]. [2020-07-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.01290. [25] YOU R, GUO Z, CUI L, et al. Cross-modality attention with semantic graph embedding for multi-label classification[C]//Proceedings of the Thirty-Forth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020: 12709-12716. [26] LI Z, TANG J. Weakly supervised deep metric learning for community-contributed image retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2015, 17(11): 1989-1999. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2015.2477035 [27] DU X, LIU Q, LI Z, et al. Cauchy matrix factorization for tag-based social image retrieval[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 132302-132310. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2940598 [28] LIN Z, CHEN M, MA Y. The augmented Lagrange multiplier method for exact recovery of corrupted low-rank matrices[EB/OL]. [2020-08-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1009.5055. [29] HUISKES M J, LEW M S. The MIR flickr retrieval evaluation[C]//Proceedings of the 1st ACM International Conference on Multimedia Information Retrieval. New York: ACM Press, 2008: 39-43. [30] TANG J, SHU X, LI Z, et al. Generalized deep transfer networks for knowledge propagation in heterogeneous domains[J]. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications (TOMM), 2016, 12(4s): 1-22. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2998574 [31] MURTHY V N, MAJI S, MANMATHA R. Automatic image annotation using deep learning representations[C]//Proceedings of the 5th ACM International Conference on Multimedia Information Retrieval. New York: ACM Press, 2015: 603-606. [32] GONG Y, JIA Y, LEUNG T, et al. Deep convolutional ranking for multi label image annotation[EB/OL]. [2020-08-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.4894 [33] VERMA Y, JAWAHAR C V. Image annotation using metric learning in semantic neighbourhoods[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2012: 836-849. [34] TRIGEORGIS G, BOUSMALIS K, ZAFEIRIOU S, et al. A deep matrix factorization method for learning attribute representations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 39(3): 417-429. http://arxiv.org/abs/1509.03248v1 -







 下载:
下载: