Causal classification method of transmission lines fitting defect combined with deep features
-
摘要:
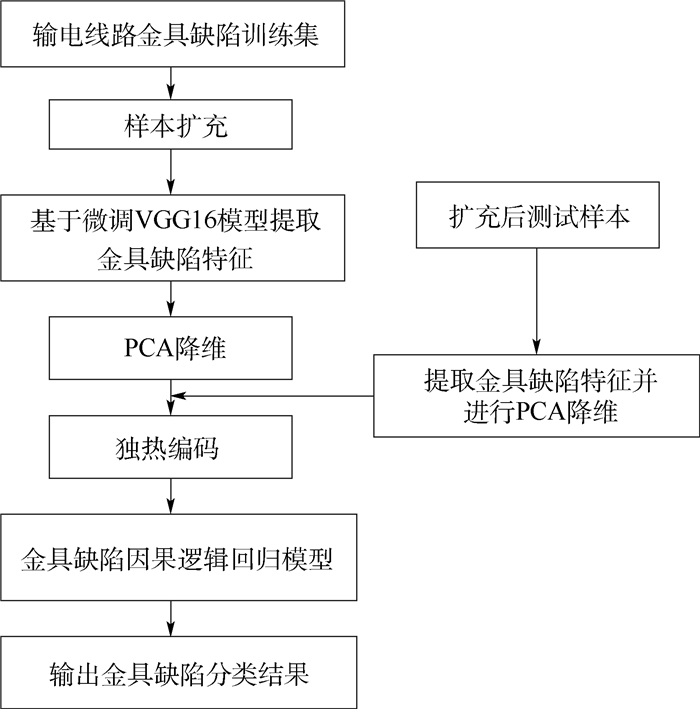
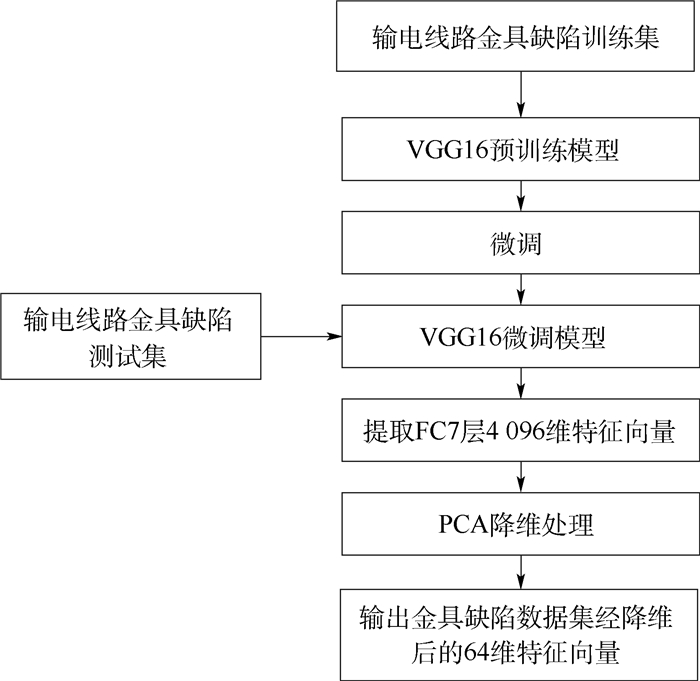
针对输电线路金具缺陷样本不足和缺陷目标形态多样化,仅仅利用深度学习模型导致金具缺陷分类准确率较低的问题,提出了一种结合深度网络和逻辑回归模型的因果分类方法。首先,通过样本扩充方法获得数量丰富化和角度多样化的数据集;然后,基于微调后的VGG16模型提取深度特征并进行特征处理,以构建符合因果关系学习的输入特征集;最后,通过全局混杂平衡进行金具缺陷特征与标签之间的因果关系学习,构建符合金具特点的因果逻辑回归模型,完成金具缺陷分类。为了证明所提方法的有效性,利用无人机实际采集的4类金具缺陷图片分别进行了实验,所使用的训练样本和测试样本数量较原始数据集提升了5倍左右。实验结果表明:所提方法可以实现对输电线路金具缺陷的精准分类,其中,防震锤相交和变形分类准确率分别达到了0.929 9和0.911 8,屏蔽环锈蚀和均压环损坏分类准确率分别达到了0.956 7和0.966 9。
Abstract:Aimed at the insufficient transmission lines fitting defect samples and diverse defect target shapes, a causal classification method combining deep network and logistic regression model is proposed to solve low defect classification accuracy when only using deep learning models. Firstly, rich and diverse datasets are obtained through the sample expansion method. Secondly, deep features are extracted based on the fine-tuned VGG16 model, and processed to construct an input feature set that conforms to causality learning. Finally, the causal relationship between fitting defect feature and label is learned through the global balance, and a causal logistic regression model is constructed to complete the classification of the fitting defects. Four types of fitting defect images collected by UAV are used respectively in the experiments to prove the effectiveness of the proposed method. The number of training and testing samples used is about 5 times higher than the original dataset. The experimental results show the proposed method can realize the accurate classification of the fitting defects, the classification accuracy of the shockproof hammer intersection and deformation reach 0.929 9 and 0.911 8 respectively, and the classification accuracy of the shielding ring corrosion and the grading ring damage reach 0.956 7 and 0.966 9 respectively.
-
Key words:
- transmission line fitting defect /
- causality learning /
- deep features /
- logistic regression model /
- VGG
-
表 1 防震锤相交分类实验结果
Table 1. Classification experimental results of shockproof hammer intersection
方案 准确率 召回率 F1分数 方案1 0.803 7 0.763 2 0.805 6 方案2 0.887 8 0.807 1 0.884 6 方案3 0.929 9 0.894 7 0.891 4 表 2 防震锤变形分类实验结果
Table 2. Classification experimental results of shockproof hammer deformation
方案 准确率 召回率 F1分数 方案1 0.808 8 0.388 9 0.518 5 方案2 0.860 3 0.472 2 0.641 5 方案3 0.911 8 0.666 7 0.800 1 表 3 屏蔽环锈蚀分类实验结果
Table 3. Classification experimental results of shielding ring corrosion
方案 准确率 召回率 F1分数 方案1 0.839 5 0.861 1 0.826 7 方案2 0.882 7 0.847 2 0.865 2 方案3 0.956 7 0.902 7 0.948 9 表 4 均压环损坏分类实验结果
Table 4. Classification experimental results of grading ring damage
方案 准确率 召回率 F1分数 方案1 0.842 5 0.834 2 0.843 3 方案2 0.914 4 0.887 6 0.914 5 方案3 0.966 9 0.956 5 0.972 3 表 5 样本扩充前后本文方法实验结果
Table 5. Experimental results by proposed method before and after sample expansion
金具缺陷类别 扩充前准确率 扩充前召回率 扩充后准确率 扩充后召回率 防震锤相交 0.906 7 0.555 6 0.929 9 0.894 7 防震锤变形 0.901 5 0.333 4 0.911 8 0.666 7 屏蔽环锈蚀 0.927 5 0.833 4 0.956 7 0.902 7 均压环损坏 0.933 0 0.647 1 0.966 9 0.956 5 表 6 不同分类器的实验结果
Table 6. Experimental results of different classifiers
方案 准确率 召回率 F1分数 方案1 0.552 5 0.515 0 0.571 9 方案2 0.702 5 0.725 0 0.700 5 方案3 0.762 5 0.711 1 0.780 4 -
[1] 赵强. 输电线路金具理论与应用[M]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2013: 2-12.ZHAO Q. Theory and application of transmission line fittings[M]. Beijing: China Electric Power Press, 2013: 2-12(in Chinese). [2] DENG C, WANG S, HUANG Z, et al. Unmanned aerial vehicles for power line inspection: A cooperative way in platforms and communications[J]. Journal of Communications, 2014, 9(9): 687-692. doi: 10.12720/jcm.9.9.687-692 [3] TONG W, YUAN J, LI B. Application of image processing in patrol inspection of overhead transmission line by helicopter[J]. Power System Technology, 2010, 34(12): 204-208. [4] 金哲, 尹洪, 吴启进. 典型500 kV输电线路地线金具腐蚀及磨损事件机理分析[J]. 电工技术, 2017(8): 66-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1388.2017.08.026JIN Z, YIN H, WU Q J. Analysis on the corrosion and wear event mechanism of the ground wire of typical 500 kV transmission line[J]. Electric Engineering, 2017(8): 66-69(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1388.2017.08.026 [5] 陆旭, 罗汉武, 李文震, 等. 电力金具图像故障状态评估[J]. 红外技术, 2020, 42(7): 632-636.LU X, LUO H W, LI W Z, et al. Evaluation of image failure state of power fittings[J]. Infrared Technology, 2020, 42(7): 632-636(in Chinese). [6] 吴坤祥, 朱迪锋, 许杨勇, 等. ±800 kV特高压输电线路耐张线夹未压区鼓胀缺陷分析[J]. 浙江电力, 2017, 36(7): 11-13.WU K X, ZHU D F, XU Y Y, et al. Analysis of bulging defects in uncompressed zone of tension clamp in ±800 kV UHV transmission line[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2017, 36(7): 11-13(in Chinese). [7] 金立军, 胡娟, 闫书佳. 基于图像的高压输电线间隔棒故障诊断方法[J]. 高电压技术, 2013, 39(5): 1040-1045. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6520.2013.05.003JIN L J, HU J, YAN S J. Image-based fault diagnosis method for spacers of high-voltage transmission lines[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2013, 39(5): 1040-1045(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6520.2013.05.003 [8] 胡彩石, 吴功平, 曹珩, 等. 高压输电线路巡线机器人障碍物视觉检测识别研究[J]. 传感技术学报, 2008, 21(12): 2092-2096. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2008.12.028HU C S, WU G P, CAO H, et al. Research on visual inspection and recognition of obstacles for high-voltage transmission line patrol robot[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 2008, 21(12): 2092-2096(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2008.12.028 [9] 宋伟, 左丹, 邓邦飞, 等. 高压输电线防震锤锈蚀缺陷检测[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2016, 37(S1): 113-117.SONG W, ZUO D, DENG B F, et al. Corrosion defect detection of earthquake hammer for high voltage transmission line[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2016, 37(S1): 113-117(in Chinese). [10] 付晶, 邵瑰玮, 吴亮, 等. 利用层次模型进行训练学习的线路设备缺陷检测方法[J]. 高电压技术, 2017, 43(1): 266-275.FU J, SHAO G W, WU L, et al. Line equipment defect detection method using hierarchical model for training and learning[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2017, 43(1): 266-275(in Chinese). [11] 李辉, 钟平, 戴玉静, 等. 基于深度学习的输电线路锈蚀检测方法的研究[J]. 电子测量技术, 2018, 41(22): 54-59.LI H, ZHONG P, DAI Y J, et al. Research on transmission line corrosion detection method based on deep learning[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2018, 41(22): 54-59(in Chinese). [12] 汤踊, 韩军, 魏文力, 等. 深度学习在输电线路中部件识别与缺陷检测的研究[J]. 电子测量技术, 2018, 41(6): 60-65.TANG Y, HAN J, WEI W L, et al. Research on deep learning in component identification and defect detection in transmission lines[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2018, 41(6): 60-65(in Chinese). [13] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 1-14. [14] MARCUS G. Deep leaening: A critical appraisal[EB/OL]. (2018-01-02)[2020-08-01]. [15] GHOSH J, JUDEA P. Causality: Models, reasoning and inference[J]. International Statistical Review, 2011, 79(2): 289-290. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-5823.2011.00149_16.x [16] LOPEZPAZ D, NISHIHARA R, CHINTALA S, et al. Discovering causal signals in images[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 58-66. [17] ZHONG J, SUN Y, YU Y, et al. Attribute-guided network for cross-modal zero-shot hashing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 31(1): 321-330. [18] 郭琳, 秦世引. 遥感图像飞机目标高效搜检深度学习优化算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(1): 159-173. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0239GUO L, QIN S Y. Deep learning and optimization algorithm for high efficient searching and detection of aircraft targets in remote sensing images[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(1): 159-173(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0239 [19] 杨博雄, 杨雨绮. 利用PCA进行深度学习图像特征提取后的降维研究[J]. 计算机系统应用, 2019, 28(1): 279-283.YANG B X, YANG Y Q. Research on dimensionality reduction after deep learning image feature extraction using PCA[J]. Computer Systems & Applications, 2019, 28(1): 279-283(in Chinese). [20] JOSE C. A fast on-line algorithm for PCA and its convergence characteristics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Network, 2000, 4(2): 299-305. [21] 李航. 统计学习方法[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2012: 77-87.LI H. Statistical learning method[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2012: 77-87(in Chinese). [22] SHEN Z, CUI P, KUANG K, et al. Causally regularized learning with agnostic data selection bias[C]//ACM Multimedia. New York: ACM Press, 2018: 411-419. [23] 梁杰, 陈嘉豪, 张雪芹, 等. 基于独热编码和卷积神经网络的异常检测[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 59(7): 523-529.LIANG J, CHEN J H, ZHANG X Q, et al. One-hot encoding and convolutional neural network based anomaly detection[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University(Science and Technology), 2019, 59(7): 523-529(in Chinese). [24] KUANG K, CUI P, LI B, et al. Estimating treatment effect in the wild via differentiated confounder balancing[C]//ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM Press, 2017: 265-274. [25] NEAL P, STEPHEN B. Proximal algorithms[J]. Foundations and Trends in Optimization, 2014, 1(3): 127-239. 期刊类型引用(3)
1. 艾梦琪,郭保,赵彦. 双机身布局验证机气动特性及横航向飞行品质分析. 飞行力学. 2023(06): 10-15 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 陈奎,闫稳,王凌伟,王建生. 一种新型高隐身低阻尼控制系统设计与仿真. 计算机仿真. 2020(06): 30-35 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 陈俊平,王立新. 低能量状态对飞行安全的危害及改出方法. 航空学报. 2017(08): 66-76 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(2)
-







 下载:
下载:



 百度学术
百度学术

