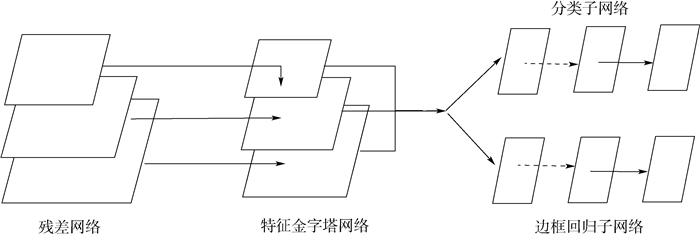
-
摘要:
针对卷积神经网络难以对低光照环境拍摄的图像进行人脸检测的问题。提出了一种将图像显著性检测算法和深度学习相结合的算法,并应用于低光照人脸检测。所提算法将图像的显著性信息与图像原始RGB通道融合,用于神经网络训练。在低光照人脸数据集DARK FACE上进行了充分的实验,结果表明:所提方法在DARK FACE数据集上获得了比当前主流人脸检测算法更好的检测精度,进而验证了所提算法的有效性。
Abstract:To deal with the problem that it is hard for convolution neural network to do face detection in low light environment, we propose a method combining image saliency and deep learning and apply it to low-light face detection, which integrates saliency and the original RGB channels of the image into neural network training. Sufficient experiments are implemented on DARK FACE, a low-light face dataset, and the results show that the proposed low-light face detection method achieves better detection accuracy than the existing mainstream face detection algorithms on DARK FACE, thus confirming the validity of the proposed method.
-
Key words:
- face detection /
- saliency guided /
- deep neural network /
- low light /
- computer vision
-
表 1 DARK FACE数据集发布的检测精度(使用图像增强算法)
Table 1. Detection accuracies published from DARK FACE dataset (with image enhancement)
检测算法 精度 DSFD+MF 0.414 DSFD+MSRCR 0.413 DSFD+LIME 0.403 DSFD+BIMEF 0.402 DSFD+Dehazing 0.365 DSFD+RetinexNet 0.332 DSFD+JED 0.179 PyramidBox+MF 0.263 PyramidBox+Dehazing 0.249 PyramidBox+LIME 0.248 PyramidBox+MSRCR 0.246 PyramidBox+BIMEF 0.245 PyramidBox+RetinexNet 0.207 PyramidBox+JED 0.146 表 2 DARK FACE数据集发布的检测精度(未使用图像增强算法)
Table 2. Detection accuracies published from DARK FACE dataset (without image enhancement)
检测算法 精度 DSFD 0.153 Faster R-CNN 0.017 PyramidBox 0.132 SSH 0.076 表 3 CVPR 2019 UG2+国际竞赛发布的基准检测精度(使用图像增强算法)
Table 3. Benchmark accuracies published from CVPR 2019 UG2+ competition (with image enhancement)
检测算法 精度 DSFD+MF 0.393 DSFD+MSRCR 0.393 DSFD+BIMEF 0.383 DSFD+LIME 0.383 DSFD+Dehazing 0.348 DSFD+RetinexNet 0.316 DSFD+JED 0.170 PyramidBox+MF 0.251 PyramidBox+Dehazing 0.237 PyramidBox+LIME 0.237 PyramidBox+MSRCR 0.235 PyramidBox+BIMEF 0.234 PyramidBox+RetinexNet 0.199 PyramidBox+JED 0.138 表 4 CVPR 2019 UG2+国际竞赛发布的基准检测精度(未使用图像增强算法)
Table 4. Benchmark accuracies published from CVPR 2019 UG2+ competition (without image enhancement)
检测算法 精度 DSFD 0.136 Faster R-CNN 0.125 PyramidBox 0.069 SSH 0.017 表 5 本文实验模型检测精度
Table 5. Detection accuracy of experimental models from this paper
训练方法 精度 DARK FACE数据集原图训练 0.504 MSRCR增强DARK FACE训练 0.522 显著性引导增强DARK FACE训练(r=0.1) 0.540 显著性引导增强DARK FACE训练(r=0.2) 0.533 DARK FACE原图融合显著图四通道训练 0.560 -
[1] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Reocgnition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 580-587. [2] GIRSHICK R. Fast RCNN[C]//Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 10-15. [3] REN S, HE K, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1147. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [4] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unifified, real-time object detection[C]. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 779-788. [5] LI J, WANG Y, WANG C, et al. DSFD: Dual shot face detector[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 5060-5069. [6] TANG X, DU D K, HE Z Q, et al. PyramidBox: A context-assisted single shot face detector[EB/OL]. (2018-08-17)[2020-09-12]. https: arxiv.orglabs/1803.07737 context=cs. [7] JAIN V, LEARNED-MILLER E G. FDDB: A benchmark for face detection in unconstrained settings[EB/OL]. [2020-09-12]. [8] YANG S, LUO P, LOY C C, et al. WIDER FACE: A face detection benchmark[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Version and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 5525-5533. [9] YE Y, YANG W H, REN W Q, et al. UG2+ Track 2: A collective benchmark effort for evaluating and advancing[EB/OL]. [2020-03-31]. [10] JOBSON D J, RAHMAN Z, WOODELL G. A multiscale retinex for bridging the gap between color images and the human observation of scenes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(7): 965-976. doi: 10.1109/83.597272 [11] LIU W, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector[C]//European Conference on Computer Version. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 21-37. [12] LI Z H, TANG X, HAN J Y, et al. PyramidBox++: High performance detector for finding tiny face[EB/OL]. [2020-09-12]. [13] LIU S, HUANG D, WANG Y H. Receptive field block net for accurate and fast object detection[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 404-419. [14] LAND E H. The Retinex theory of color vision[J]. Scientific American, 1977, 237(6): 108. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican1277-108 [15] JOBSON D J, RAHMAN Z, WOODELL G A. Properties and performance of a center/surround Retinex[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(3): 451-462. doi: 10.1109/83.557356 [16] RAHMAN Z U, JOBSON D J, WOODELL G A. Multi-scale Retinex for color image enhancement[C]//Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Image Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1996: 1003-1006. [17] GUO X J, LI Y, LING H B. LIME: Low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(2): 982-993. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2639450 [18] YUN Z, MUBARAK S. Visual attention detection in video sequences using spatiotemporal cues[C]//Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York: ACM Press, 2006: 815-824. [19] CHENG M M, ZHANG G X, MITRA N J. Global contrast based salient region detection[C]//Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on omputer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 569-582. [20] ACHANTA R, ESTRADA F, WILS P, et al. Salient region detection and segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computer Version Systems. Berlin: Springer, 2008. [21] 张冬明, 靳国庆, 代锋, 等. 基于深度融合的显著性目标检测算法[J]. 计算机学报, 2019, 42(9): 2076-2086.ZHANG D M, JIN G Q, DAI F, et al. Salient object detection based on deep fusion of hand-crafted features[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2019, 42(9): 2076-2086(in Chinese). [22] JIAN M W, LAM K M, DONG J Y, et al. Visual-patch-attention-aware saliency detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2015, 45(8): 1575-1586. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2014.2356200 [23] TSUNG-YI L, PRIYA G, ROSS B G, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Version. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2999-3007. [24] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Version and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [25] LIN T Y, DOLLA P, CIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Version and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 936-944. [26] LIN T Y, MAIRE M, BELONGIE S, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context[C]//European Conference on Computer Version. Berlin: Springer, 2014: 740-755. [27] REDMON J, FARHADI A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 6517-6525. [28] FU C Y, LIU W A, RANGA A. et al. DSSD: Deconvolutional single shot detector[EB/OL]. [2019-09-12]. [29] FAEN Z, FAN X Y, AI G, et al. Accurate face detection for high performance[EB/OL]. (2019-05-24)[2020-09-12]. [30] HOU X D, HAREL J, KOCH C. Image signature: Highlighting sparse salient regions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(1): 194-201. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.146 [31] NAJIBI M, SAMANGOUEI P, CHELLAPPA R, et al. SSH: Single stage headless face detector[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 4875-4884. [32] YING Z Q, LI G, GAO W. A bio-inspired multi-exposure fusion framework for low-light image enhancement[EB/OL]. [2020-09-12]. [33] DONG X, WANG G, PANG Y, et al. Fast efficient algorithm for enhancement of low lighting video[C]//Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 1-6. [34] FU X Y, ZENG D, HUANG Y H, et al. A fusion-based enhancing method for weakly illuminated images[J]. Signal Processing, 2016, 129: 82-96. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.05.031 [35] REN X D, LI M D, CHENG W H, et al. Joint enhancement and denoising method via sequential decomposition[C]//2018 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1-5. [36] WEI C, WANG W, YANG W, et al. Deep Retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement[C]//Proceedings of British Machine Vision Conference, 2018: 155. [37] YANG W H, YUAN Y, REN W Q, et al. Advancing image understanding in poor visibility environments: A collective benchmark study[J]. IEEE Transanctions on Processing, 2020, 29: 5737-5752. -








 下载:
下载: