-
摘要:
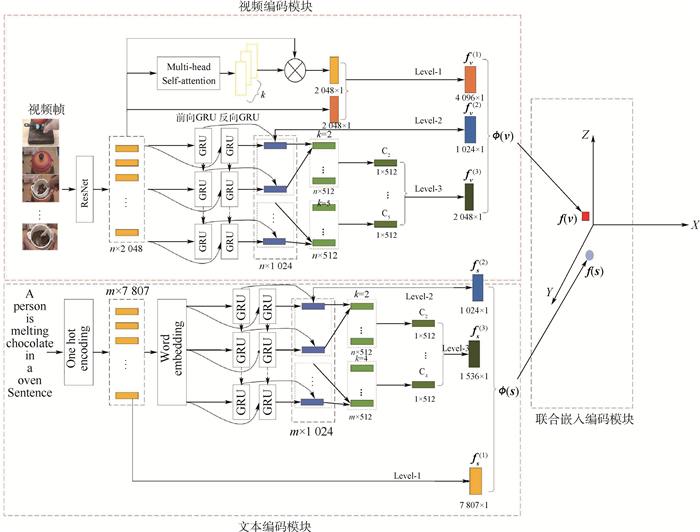
针对现有的大多数跨模态视频检索算法忽略了数据中丰富的语义线索,使得生成特征的表现能力较差的问题,设计了一种基于多语义线索的跨模态视频检索模型,该模型通过多头目自注意力机制捕捉视频模态内部对语义起到重要作用的数据帧,有选择性地关注视频数据的重要信息,获取数据的全局特征;采用双向门控循环单元(GRU)捕捉多模态数据内部上下文之间的交互特征;通过对局部数据之间的细微差别进行联合编码挖掘出视频和文本数据中的局部信息。通过数据的全局特征、上下文交互特征和局部特征构成多模态数据的多语义线索,更好地挖掘数据中的语义信息,进而提高检索效果。在此基础上,提出了一种改进的三元组距离度量损失函数,采用了基于相似性排序的困难负样本挖掘方法,提升了跨模态特征的学习效果。在MSR-VTT数据集上的实验表明:与当前最先进的方法比较,所提算法在文本检索视频任务上提高了11.1%;在MSVD数据集上的实验表明:与当前先进的方法比较,所提算法在文本检索视频任务上总召回率提高了5.0%。
Abstract:Most of the existing cross-modal video retrieval algorithms map heterogeneous data to a space, so that semantically similar data are close to each other and semantically dissimilar data are far from each other, that is, the global similarity relationship of different modal data is established. However, these methods ignore the rich semantic clues in the data, which makes the performance of feature generation poor. To solve this problem, we propose a cross-modal retrieval model based on multi-semantic clues. This model captures the data frames that play an important role in semantics within video model through multi-head self-attention mechanism, and pays attention to the important information of video data to obtain the global characteristics of the data. Bidirectional Gate Recurrent Unit (GRU) is used to capture the interaction characteristics between contexts within multimodal data. Our method can also mine the local information in video and text data through the joint coding of the slight differences between the local data. Through the global features, context interaction features and local features of the data, the multi-semantic clues of the multi-modal data are formed to better mine the semantic information in the data and improve the retrieval effect. Besides this, an improved triplet distance measurement loss function is proposed, which adopts the difficult negative sample mining method based on similarity sorting and improves the learning effect of cross-modal characteristics. Experiments on MSR-VTT dataset show that the proposed method improves the text retrieval video task by 11.1% compared with the state-of-the-art methods. Experiments on MSVD dataset show that the proposed method improves the text retrieval video task by 5.0% compared with the state-of-the-art methods.
-
表 1 在MSR-VTT数据集上的结果
Table 1. Results on MSR-VTT dataset
算法 文本检索视频 视频检索文件 Recall Sum R@1 R@5 R@10 MedR R@1 R@5 R@10 MedR VSE++ 5.0 16.4 24.6 47 7.7 20.3 31.2 28 105.2 W2VV 5.5 17.6 25.9 51 9.1 24.6 36.0 23 118.7 Fusion 7.0 20.9 29.7 38 12.5 31.3 42.4 14 143.8 本文(VSE++) 7.6 21.7 31.2 31 12.2 29.4 42.4 18 144.5 本文 7.8 23.0 33.1 29 13.1 30.7 43.1 15 150.8 表 2 在MSVD数据集上的结果
Table 2. Results on MSVD dataset
算法 文本检索视频 视频检索文本 Recall Sum R@1 R@5 R@10 MedR R@1 R@5 R@10 MedR VSE++ 15.4 39.6 53.3 9 21.2 43.4 52.2 9 225.1 W2VV 15.4 39.2 51.4 10 16.3 33.4 44.8 14 200.5 Fusion 18.9 46.1 60.9 6 30.6 49.1 61.5 6 267.1 本文(VSE++) 19.7 48.2 61.0 6 31.7 50.7 61.8 6 272.5 本文 20.9 49.0 62.6 5 32.2 51.1 62.2 5 278.0 表 3 在MSR-VTT数据集上的消融分析结果
Table 3. Ablation analysis results on MSR-VTT dataset
方法 文本检索视频 视频检索文本 Recall Sum R@1 R@5 R@10 MedR R@1 R@5 R@10 MedR Level-1 6.4 18.9 27.1 46 11.9 28.3 39.2 22 131.8 Level-2 6.3 19.7 28.8 38 10.0 26.2 38.3 20 128.8 Level-3 7.3 21.5 31.2 32 10.6 27.3 38.5 20 136.4 Level-(1+2) 7.2 21.3 29.6 37 12.1 30.5 40.9 17 141.6 Level-(1+3) 7.4 21.2 32.3 30 12.4 29.9 42.5 16 147.1 Level-(2+3) 7.6 22.4 32.2 31 11.9 30.6 42.4 16 147.2 Level-(1+2+3) 7.8 23.0 33.1 29 13.1 30.7 43.1 15 150.8 -
[1] 张鸿, 吴飞, 庄越挺. 跨媒体相关性推理与检索研究[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2008, 45(5): 869.ZHANG H, WU F, ZHUANG Y T. Research on cross-media correlation inference and retrieval[J]. Computer Research and Development, 2008, 45(5): 869(in Chinese). [2] DONG J, LI X, SNOEK C G M. Predicting visual features from text for image and video caption retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2018, 20(12): 3377-3388. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2018.2832602 [3] MITHUN N C, LI J, METZE F, et al. Learning joint embedding with multimodal cues for cross-modal video-text retrieval[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 ACM on International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval. New York: ACM Press, 2018: 19-27. [4] DONG J, LI X, SNOEK C G M. Word2VisualVec: Image and video to sentence matching by visual feature prediction[EB/OL]. (2016-04-23)[2020-08-01]. [5] TORABI A, TANDON N, SIGAL L. Learning language-visual embedding for movie understanding with natural-language[EB/OL]. (2016-08-26)[2020-08-01]. [6] RASIWASIA N, COSTA P J, COVIELLO E, et al. A new approach to cross-modal multimedia retrieval[C]//Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York: ACM Press, 2010: 251-260. [7] FAGHRI F, FLEET D J, KIROS J R, et al. VSE++: Improving visual-semantic embeddings with hard negatives[EB/OL]. (2017-07-18)[2020-08-01]. [8] GONG Y, KE Q, ISARD M, et al. A multi-view embedding space for modeling internet images, tags, and their semantics[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2014, 106(2): 210-233. doi: 10.1007/s11263-013-0658-4 [9] HODOSH M, YOUNG P, HOCKENMAIER J. Framing image description as a ranking task: Data, models and evaluation metrics[J]. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2013, 47(24): 853-899. doi: 10.5555/2832747.2832838 [10] 李志欣, 施智平, 陈宏朝, 等. 基于语义学习的图像多模态检索[J]. 计算机工程, 2013, 39(3): 258-263.LI Z X, SHI Z P, CHEN H C, et al. Multi-modal image retrieval based on semantic learning[J]. Computer Engineering, 2013, 39(3): 258-263(in Chinese). [11] WANG L, LI Y, HUANG J, et al. Learning two-branch neural networks for image-text matching tasks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 41(2): 394-407. [12] FROME A, CORRADO G S, SHLENS J, et al. Devise: A deep visual-semantic embedding model[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: ACM Press, 2013: 2121-2129. [13] KIROS R, SALAKHUTDINOV R, ZEMEL R S. Unifying visual-semantic embeddings with multimodal neural language models[EB/OL]. (2014-11-10)[2020-08-01]. [14] XU R, XIONG C, CHEN W, et al. Jointly modeling deep video and compositional text to bridge vision and language in a unified framework[C]//Proceedings of the 29th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2015: 6. [15] MIKOLOV T, CHEN K, CORRADO G, et al. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space[EB/OL]. (2013-01-16)[2020-08-03]. https: //arxiv.org/abs/1301.3781. [16] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [17] SONG Y, SOLEYMANI M. Polysemous visual-semantic embedding for cross-modal retrieval[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1979-1988. [18] CHO K, VAN MERRIËNBOER B, GULCEHRE C, et al. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation[EB/OL]. (2014-01-03)[2020-08-01]. [19] KIM Y. Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification[EB/OL]. (2014-08-25)[2020-08-01]. [20] YOUNG P, LAI A, HODOSH M, et al. From image descriptions to visual denotations: New similarity metrics for semantic inference over event descriptions[J]. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2014, 2(1): 67-78. [21] XU J, MEI T, YAO T, et al. MSR-VTT: A large video description dataset for bridging video and language[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 5288-5296. [22] CHEN D, DOLAN W B. Collecting highly parallel data for paraphrase evaluation[C]//Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, 2011: 190-200. 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 刘涛,杨子渊,蒋燕妮,高贵. 极化SAR图像舰船目标检测研究综述. 雷达学报. 2021(01): 1-19 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(1)
-







 下载:
下载:



 百度学术
百度学术

