-
摘要:
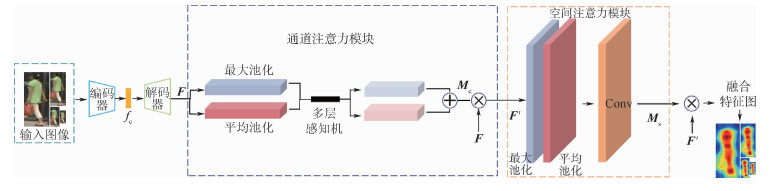
行人图像分辨率的变化对现有的行人重识别方法带来了很大的挑战。针对这一问题,提出了一种新的跨分辨率行人重识别方法。该方法从两方面解决分辨率变化带来的识别困难:一方面通过通道注意力机制和空间注意力机制捕捉人物特征获取局部区域;另一方面通过核动态上采样模块恢复任意分辨率图像的局部区域信息。为了验证所提方法的有效性,在Market1501、CUHK03和CAVIAR三个公开数据集上开展了对比实验,实验结果表明:所提方法取得了最佳性能。
Abstract:The resolution variation of person images poses great challenges to current person re-identification methods. To address this problem, this paper presents a cross-resolution person re-identification method. This method solves the resolution variation from two aspects. On the one hand, the spatial and channel attention mechanisms are utilized to capture person features and obtain local region; On the other hand, local information of any resolution image is recovered by the nuclear dynamic upsampling module. Comparative experiments have been conducted to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method against state-of-the-art methods on Market1501, CUHK03, and CAVIAR person re-identification datasets. The experimental results show that the proposed method has the best performance.
-
表 1 现有方法在Market1501和CUHK03数据集上的定量结果对比
Table 1. Quantitative result comparison of existing methods on Market1501和CUHK03 datasets
% 表 2 现有方法在CAVIAR数据集上的定量结果对比
Table 2. Quantitative result comparison of existing methods on CAVIAR dataset
% 表 3 各模块消融实验结果
Table 3. Ablation experimental results of each module
% 模块 MLRCUHK03 Rank1 Rank5 ResNet50 58.1 79.3 ResNet50+CAM 63.2 85.0 ResNet50+SAM 65.0 87.1 ResNet50+NonLocal 70.7 87.7 ResNet50+SENet 71.3 89.1 ResNet50+CAM+SAM 78.9 90.3 ResNet50+MASR+ID 83.3 93.1 本文 89.2 97.5 -
[1] ZAJDEL W, ZIVKOVIC Z, KROSE B J A. Keeping track of humans: Have I seen this person before[C]//Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2005: 2081-2086. [2] JING X Y, ZHU X K, FEI W, et al. Super-resolution person re-identification with semi-coupled low-rank discriminant dictionary learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 695-704. [3] LI X, ZHENG W S, WANG X J, et al. Multi-scale learning for low-resolution person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 3765-3773. [4] JIAO J N, ZHENG W S, WU A C, et al. Deep low-resolution person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2018: 6967-6974. [5] WANG Z, YE M, YANG F, et al. Cascaded SR-GAN for scale-adaptive low resolution person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2018: 3891-3897. [6] WANG Z, HU R M, YU Y, et al. Scale-adaptive low-resolution person re-identification via learning a discriminating surface[C]//Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2016: 2669-2675. [7] CHEN Y C, LI Y J, DU X F, et al. Learning resolution-invariant deep representations for person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2019: 8215-8222. [8] LI Y J, CHEN Y C, LIN Y Y, et al. Recover and identify: A generative dual model for cross-resolution person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 8090-8099. [9] CHENG Z Y, ZHU X T, GONG S G. Low-resolution face recognition[C]//Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, 2018: 605-621. [10] LU Z, JIANG X D, ALEX K. Deep coupled resnet for low-resolution face recognition[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2018, 25(4): 526-530. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2018.2810121 [11] CHENG Z Y, DONG Q, GONG S G, et al. Inter-task association critic for cross-resolution person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 2605-2615. [12] MAO S N, ZHANG S L, YANG M. Resolution-invariant person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2019: 883-889. [13] ZHAO R, OUYANG W L, WANG X G. Person re-identification by salience matching[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 2528-2535. [14] HU X K, MU H Y, ZHANG X Y, et al. Meta-SR: A magnification-arbitrary network for super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1575-1584. [15] WANG Z, JIANG J, WU Y, et al. Learning sparse and identity-preserved hidden attributes for person re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 29(1): 2013-2025. [16] ZENG Z, WANG Z, WANG Z, et al. Illumination-adaptive person re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2020, 22(12): 3064-3074. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2020.2969782 [17] WANG Z, WANG Z, ZHENG Y, et al. Beyond intra-modality: A survey of heterogeneous person re-identification[EB/OL]. (2020-04-21)[2020-07-14]. [18] SARATH C, CHINNNADHURAI S, EUGENE V, et al. Towards non-saturating recurrent units for modelling long-term dependencies[EB/OL]. (2020-07-14)[2020-08-01]. [19] SANGHYUN W, JONGCHAN P, JOONYOUNG L, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 3-19. [20] HU J, SHEN L, SUN G. Squeeze and excitation networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 7132-7141. [21] KOMODAKIS N, ZAGORUYKO S. Paying more attention to attention: Improving the performance of convolutional neural networks via attention transfer[EB/OL]. (2011-02-12)[2020-07-12]. [22] IAN G, JEAN P A, MEHDI M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]//Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2014: 2672-2680. [23] CHRISTIAN L, LUCAS T, FERENC H, et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 4681-4690. [24] ZHANG Y L, LI K P, LI K, et al. Image super-resolution using very deep residual channel attention networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 286-301. [25] ZHANG Y, TIAN Y, KONG Y, et al. Residual dense network for image super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 2472-2481. [26] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [27] ZHENG L, SHEN L Y, TIAN L, et al. Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1116-1124. [28] LI W, ZHAO R, XIAO T, et al. DeepReID: Deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 152-159. [29] ZHONG Z, ZHENG L, CAO D, et al. Re-ranking person re-identification with k-reciprocal encoding[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 3652-3661. [30] CHENG D S, CRISTANI M, STOPPA M, et al. Custom pictorial structures for re-identification[C]//British Machine Vision Conference, 2011: 6. [31] GE Y X, LI Z W, ZHAO H Y, et al. FD-GAN: Pose-guided feature distilling gan for robust person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2018: 1222-1233. [32] WANG X S, GIRSHICK R, GUPTA A, et al. Non-local neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 7794-7803. -








 下载:
下载: