-
摘要:
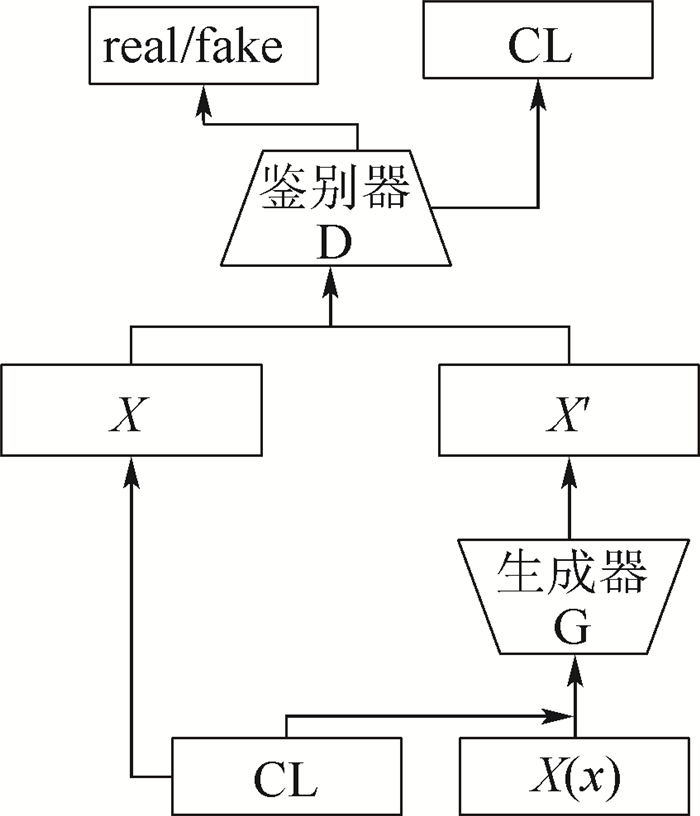
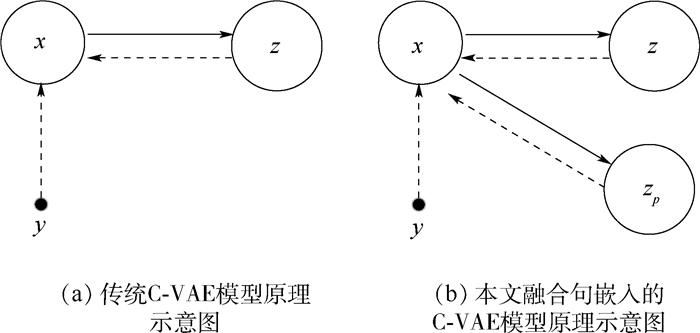
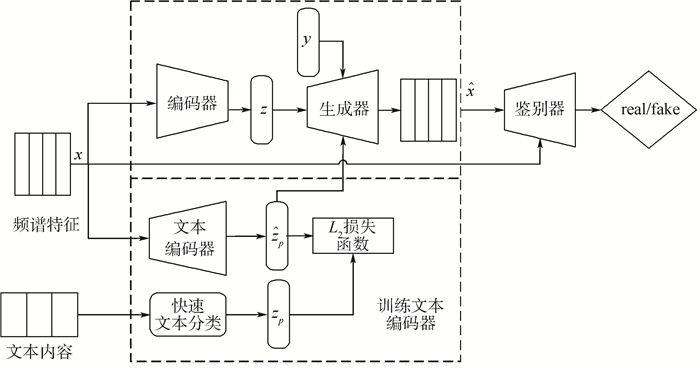
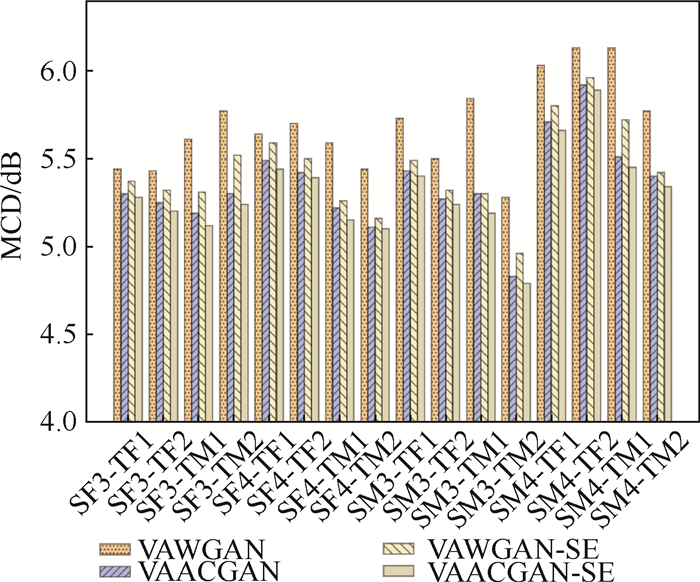
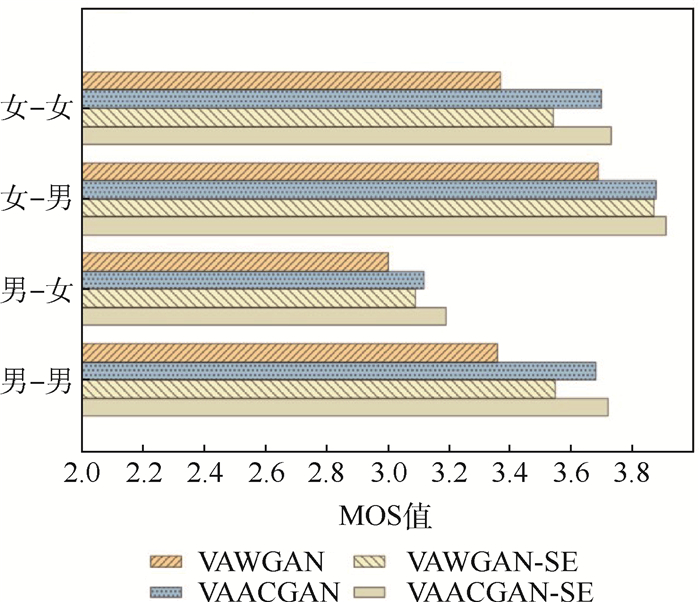
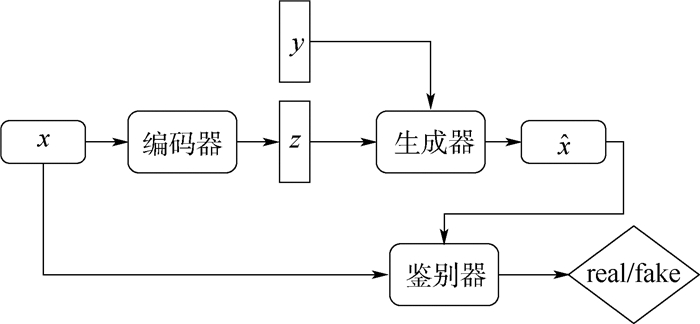
针对非平行文本条件下语音转换质量不理想、说话人个性相似度不高的问题,提出一种融合句嵌入的变分自编码辅助分类器生成对抗网络(VAACGAN)语音转换方法,在非平行文本条件下,有效实现了高质量的多对多语音转换。辅助分类器生成对抗网络的鉴别器中包含辅助解码器网络,能够在预测频谱特征真假的同时输出训练数据所属的说话人类别,使得生成对抗网络的训练更为稳定且加快其收敛速度。通过训练文本编码器获得句嵌入,将其作为一种语义内容约束融合到模型中,利用句嵌入包含的语义信息增强隐变量表征语音内容的能力,解决隐变量存在的过度正则化效应的问题,有效改善语音合成质量。实验结果表明:所提方法的转换语音平均MCD值较基准模型降低6.67%,平均MOS值提升8.33%,平均ABX值提升11.56%,证明该方法在语音音质和说话人个性相似度方面均有显著提升,实现了高质量的语音转换。
Abstract:To solve the problems of poor speech quality and unsatisfactory speaker similarity for converted speech in existing non-parallel VC methods, this paper presents a novel voice conversion model based on Variational Autoencoding Auxiliary Classifier Generative Adversarial Network (VAACGAN) with sentence embedding, which achieves high-quality many-to-many voice conversion for non-parallel corpora. First, in the ACGAN, the discriminator contains an auxiliary decoder network that predicts the true or false of the spectral feature meanwhile the speaker category to which the training data belongs, thus achieving a more stable training process and a faster iterative convergence. Furthermore, sentence embedding is obtained by training the text encoder, which is introduced into the model as semantic content constraint, can enhance the ability of latent variables to characterize the speech content, effectively solve the over-regularization effect of latent variables and improve the quality of converted speech significantly. Experimental results show that the average value of MCD of the converted speech is decreased by 6.67%, MOS is increased by 8.33%, and ABX is increased by 11.56% compared with baseline method, which demonstrate that the proposed method significantly outperforms the baseline method in both speech quality and speaker similarity and achieves high-quality voice conversion.
-
-
[1] GODOY E, ROSEC O, CHONAVEL T. Voice conversion using dynamic frequency warping with amplitude scaling, for parallel or nonparallel corpora[J]. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2012, 20(4): 1313-1323. doi: 10.1109/TASL.2011.2177820 [2] TODA T, CHEN L H, SAITO D, et al. The voice conversion challenge 2016[C]//Interspeech, 2016: 1632-1636. [3] 李燕萍, 曹盼, 石杨, 等. 非平行文本下基于变分自编码器和辅助分类器生成对抗网络的语音转换[J]. 复旦学报(自然科学版), 2020, 59(3): 322-329.LI Y P, CAO P, SHI Y, et al. Voice conversion based on variational autoencoder and auxiliary classifier generative adversarial network in non-parallel corpora[J]. Journal of Fudan University(Natural Science), 2020, 59(3): 322-329(in Chinese). [4] DONG M, YANG C, LU Y, et al. Mapping frames with DNN-HMM recognizer for non-parallel voice conversion[C]//2015 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference(APSIPA). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 488-494. [5] ZHANG M, TAO J, TIAN J, et al. Text-independent voice conversion based on state mapped codebook[C]//2008 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2008: 4605-4608. [6] NAKASHIKA T, TAKIGUCHI T, MINAMI Y. Non-parallel training in voice conversion using an adaptive restricted Boltzmann machine[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2016, 24(11): 2032-2045. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2016.2593263 [7] MOUCHTARIS A, VAN DER SPIEGEL J, MUELLER P. Nonparallel training for voice conversion based on a parameter adaptation approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2006, 14(3): 952-963. doi: 10.1109/TSA.2005.857790 [8] HSU C C, HWANG H T, WU Y C, et al. Voice conversion from non-parallel corpora using variational auto-encoder[C]//2016 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference(APSIPA). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1-6. [9] HSU C, HWANG H, WU Y, et al. Voice conversion from unaligned corpora using variational autoencoding Wasserstein generative adversarial networks[C]//Interspeech, 2017: 3364-3368. [10] ZHANG J, LING Z, DAI L R. Non-parallel sequence-to-sequence voice conversion with disentangled linguistic and speaker representations[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2019, 28(1): 540-552. [11] ARJOVSKY M, CHINTALA S, BOTTOU L. Wasserstein generative adversarial networks[C]//Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). New York: ACM Press, 2017: 214-223. [12] SAITO Y, IJIMA Y, NISHIDA K, et al. Non-parallel voice conversion using variational autoencoders conditioned by phonetic posteriorgrams and d-vectors[C]//2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 5274-5278. [13] 石杨. 非平行文本条件下基于文本编码器, VAE和ACGAN的多对多语音转换研究[D]. 南京: 南京邮电大学, 2019: 34-69.SHI Y. Non-parallel voice conversion using ACGAN and variational autoencoders conditioned by sentence embedding[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2019: 34-69(in Chinese). [14] ODENA A, OLAH C, SHLENS J. Conditional image synthesis with auxiliary classifier GANs[C]//Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2017: 2642-2651. [15] LORENZO-TRUEBA J, YAMAGISHI J, TODA T, et al. The voice conversion challenge 2018: Promoting development of parallel and nonparallel methods[C]//The Speaker and Language Recognition Workshop, 2018: 195-202. [16] ARORA S, LIANG Y Y, MA T Y. A simple but tough-to-beat baseline for sentence embeddings[C]//ICLR, 2017: 1-16. [17] MORISE M, YOKOMORI F, OZAWA K. WORLD: A vocoder-based high-quality speech synthesis system for real-time applications[J]. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems, 2016, 99(7): 1877-1884. [18] MAAS A L, HANNUN A Y, NG A Y. Rectifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models[J]. Computer Science, 2013, 30(1): 1152-1160. [19] 左宇涛. 非平行文本条件下基于i-vector, VAE和GAN的多对多语音转换算法研究[D]. 南京: 南京邮电大学, 2019: 35-64.ZUO Y T. Research on many-to-many voice conversion based on i-vector, variational auto-encoder and generative adversarial networks for non-parallel corpora[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2019: 35-64(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: