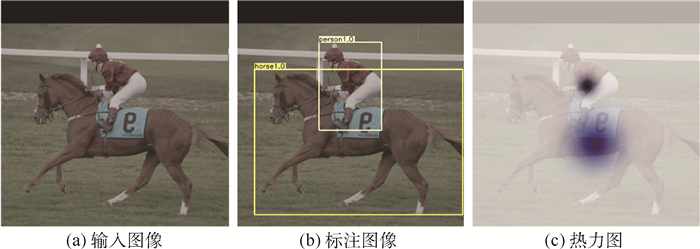
High-resolution network Anchor-free object detection method based on iterative aggregation
-
摘要:
针对目前Anchor-free目标检测方法CenterNet(ObjectsasPoints)生成热力图不准确、检测精度不足的问题,提出了一种基于特征迭代聚合的高分辨率表征网络CenterNet-DHRNet。首先,引入高分辨率表征骨干网络,并用迭代聚合的方式对不同分辨率的特征图进行融合,提高网络的分辨率,有效减少图像在下采样过程中损失的空间语义信息。其次,使用高效通道注意力机制对高分辨率表征骨干网络的输出进行优化。最后,利用结合空洞卷积的空间金字塔池化操作增强网络对不同尺度物体的感受野。实验在PASCALVOC数据集和KITTI数据集上进行,结果表明:CenterNet-DHRNet精度更高,满足实时检测的性能要求,具有良好的鲁棒性。
-
关键词:
- 目标检测 /
- 迭代聚合 /
- Anchor-free /
- CenterNet /
- 注意力机制
Abstract:In order to solve the problems of inaccuracy in heat map generation and insufficient detection accuracy of anchor-free object detection method CenterNet (Objects as Points), a high-resolution representation network CenterNet-DHRNet based on feature iterative aggregation is proposed. First, for the purpose of improving the resolution of the network and reducing the spatial semantic information lost in the image downsampling process, a high-resolution representation backbone network is introduced and low-resolution features are fully fused by iterative deep aggregation. Then, an efficient attention mechanism is used to optimize the output of the high-resolution representation backbone network. Finally, the spatial pyramid pooling with dilated convolution is used to enhance the network's receptive field for objects of different scales. The experiment is carried out on PASCAL VOC dataset and KITTI dataset, and the experimental results show that CenterNet-DHRNet has higher accuracy, meets the performance requirements of real-time detection and has good robustness.
-
Key words:
- object detection /
- iterative aggregation /
- Anchor-free /
- CenterNet /
- attention mechanism
-
表 1 PASCAL VOC数据集测试结果
Table 1. Test results of PASCAL VOC dataset
方法 图像分辨率 mAP/% FPS FasterR-CNN-Res101[5] 600×1 000 76.4 5 FasterR-CNN-Vgg16[5] 600×1 000 73.2 7 R-FCN[23] 600×1 000 80.5 9 Yolov3 544×544 79.3 26 SSD300[7] 300×300 77.2 45 SSD500[7] 513×513 78.9 19 FCOS[9] 800×800 80.2 16 ExtremeNet[10] 512×512 79.5 3.1 DSSD[22] 513×513 81.5 5.5 CenterNet-Res18[11] 512×512 75.7 96* CenterNet-Res101[11] 512×512 78.7 27* CenterNet-DLA[11] 512×512 80.7 30* CenterNet-HRNet 512×512 79.0 21 本文 512×512 81.9 18 注:“*”表示在本机环境下的运行结果。 表 2 PASCAL VOC数据集上训练时间、模型复杂度对比
Table 2. Comparison of training time and model complexity on PASCAL VOC dataset
方法 GPUs 训练时间/h 模型大小/Mbit CenterNet 2×TITAN V 15 80.8 本文 1×1 080TI 55 189.1 表 3 不同方法在PASCAL VOC数据集上每个类别的AP比较
Table 3. AP comparison of different algorithms for each category on PASCAL VOC dataset
类别 本文 CenterNet-DLA[11] CenterNet-HRNet Faster R-CNN[5] Mask R-CNN R-FCN[23] SSD300[7] mAP 81.9 80.7 79.0 73.2 78.2 80.5 77.2 飞机 86.2 85.0 86.1 76.5 80.3 79.9 77.7 自行车 88.6 86.0 83.9 79.0 84.1 87.2 84.0 鸟 82.4 81.4 77.1 70.9 78.5 81.5 76.3 船 72.8 72.8 70.2 65.5 70.8 72.0 71.3 杯子 73.4 68.4 71.0 52.1 68.5 69.8 48.6 公共汽车 86.6 86.0 84.6 83.1 88.0 86.8 85.3 小轿车 88.8 88.4 88.1 84.7 85.9 88.5 86.3 猫 87.3 86.5 84.6 86.4 87.8 89.8 87.3 椅子 68.1 65.0 65.63 52.0 60.3 67.0 59.3 牛 86.9 86.3 84.9 81.9 85.2 88.1 81.8 餐桌 78.4 77.6 74.3 65.7 73.7 74.5 77.2 狗 84.6 85.2 82.6 84.8 87.2 89.8 85.2 马 88.5 87.0 86.0 84.6 86.5 90.6 87.0 摩托车 86.5 86.1 82.6 77.5 85.0 79.9 83.7 人 86.0 85.0 84.3 76.7 76.4 81.2 79.2 盆栽植物 59.0 58.1 55.4 38.8 48.5 53.7 53.0 羊 85.3 83.4 82.3 73.6 76.3 81.8 76.3 沙发 81.5 79.6 73.1 73.9 75.5 81.5 79.8 火车 87.5 85.0 84.0 83.0 85.0 85.9 88.3 电视 80.2 80.3 79.4 72.6 81.0 79.9 76.2 表 4 在PASCAL VOC数据集上的消融实验
Table 4. Ablation experiment on PASCAL VOC dataset
HRNet 迭代聚合 ECANet Espp mAP/% √ 79.0 √ √ 80.9 √ √ √ 81.6 √ √ √ √ 81.9 表 5 KITTI数据集上不同目标检测方法对比
Table 5. Comparison of different object detection algorithms on KITTI dataset
方法 输入 FPS mAP% Yolov3 544 26 84.9 CenterNet 512 30 86.1 本文 512 18 87.1 表 6 KITTI数据集上3类目标AP对比
Table 6. Comparison of three types of object AP on KITTI dataset
方法 AP/% mAP/% Car Pedestrian Cyclist CenterNet 95.4 78.3 84.6 86.1 本文 96.7 79.1 85.5 87.1 -
[1] LOWE D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91-110. doi: 10.1023%2FB%3AVISI.0000029664.99615.94.pdf [2] 蒋弘毅, 王永娟. 目标检测模型及其优化方法综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(6): 1232-1255. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO202106004.htmJIANG H Y, WANG Y J. A survey of object detection models and its optimization methods[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(6): 1232-1255(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO202106004.htm [3] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]//2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 580-587. [4] GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]//International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1440-1448. [5] REN S, HE K, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017(6): 1137-1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [6] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 779-788. [7] LIU W, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 21-37. [8] LAW H, DENG J. CornerNet: Detecting objects as paired keypoints[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 765-781. [9] TIAN Z, SHEN C, CHEN H, et al. FCOS: Fully convolutional one-stage object detection[C]//International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 9626-9635. [10] ZHOU X, ZHUO J, KRAHENBUHL P, et al. Bottom-up object detection by grouping extreme and center points[EB/OL]. (2019-04-25)[2020-08-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.08043. [11] ZHOU X, WANG D, KRAHENBUHL P, et al. Objects as points[EB/OL]. (2019-04-25)[2020-08-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.07850. [12] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [13] XIAO B, WU H, WEI Y, et al. Simple baselines for human pose estimation and tracking[EB/OL]. (2018-08-21)[2020-08-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.06208v2. [14] YU F, WANG D, SHELHAMER E, et al. Deep layer aggregation[EB/OL]. (2019-01-04)[2020-08-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.06484. [15] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[EB/OL]. (2015-04-10)[2020-08-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556. [16] SUN K, XIAO B, LIU D, et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation[EB/OL]. [2020-08-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.09212. [17] WANG Q, WU B, ZHU P, et al. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks[C]//IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 11534-11542. [18] HU J, SHEN L, ALBANIE S, et al. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]//IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 7132-7141. [19] CHEN L, ZHU Y, PAPANDREOU G, et al. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation[EB/OL]. (2018-03-08)[2020-08-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.02611v2. [20] YU F, KOLTUN V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions[EB/OL]. (2016-04-30)[2020-08-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.07122. [21] LIN T, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[EB/OL]. (2018-03-07)[2020-08-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.02002. [22] FU C, LIU W, RANGA A, et al. DSSD: Deconvolutional single shot detector[EB/OL]. [2020-08-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1701.06659. [23] DAI J, LI Y, HE K, et al. R-FCN: Object detection via region-based fully convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems December. New York: ACM, 2016: 379-387. -







 下载:
下载: