-
摘要:
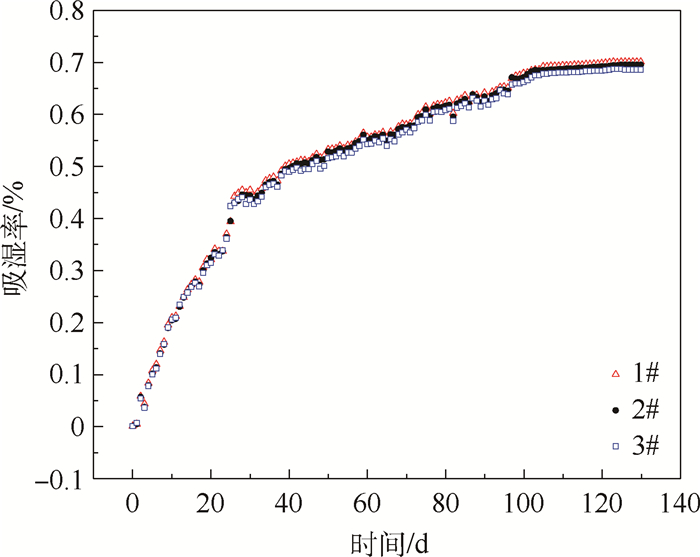
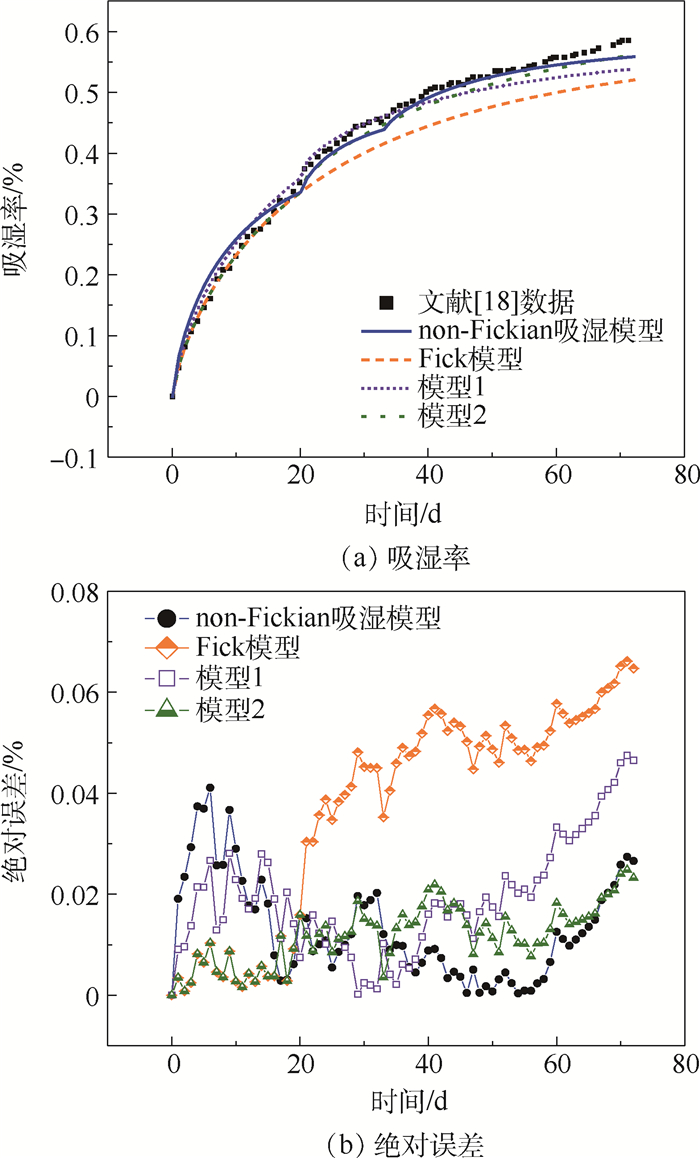
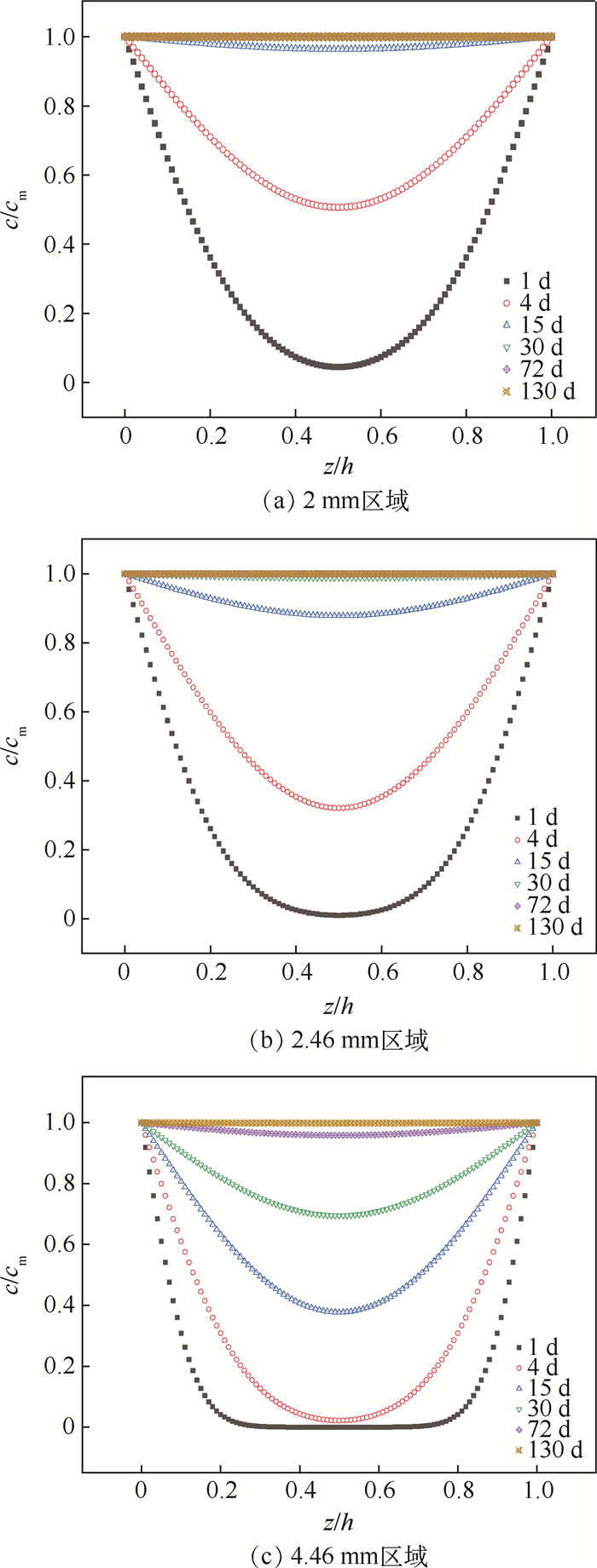
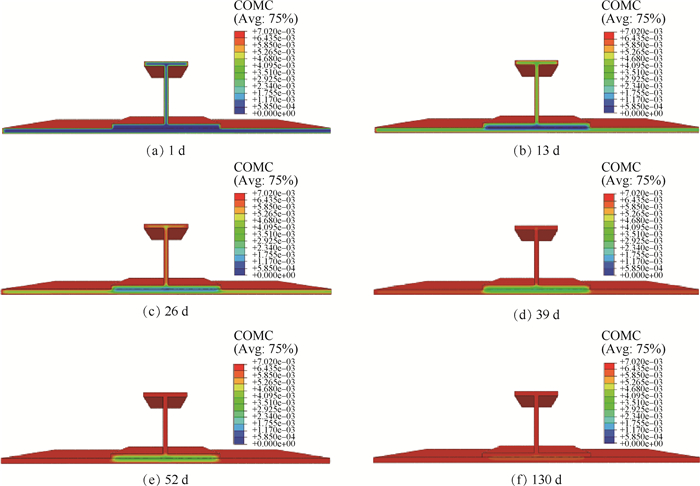
环氧树脂基复合材料的性能对湿热环境敏感,掌握该材料所组成结构的吸湿行为对其实际应用具有重要意义。通过以碳纤维环氧树脂基复合材料层合板的non-Fickian吸湿模型为基础,建立环氧树脂基复合材料加筋板结构的non-Fickian吸湿模型,在70℃/85% RH湿热条件下开展加筋板结构的吸湿实验,对所建立模型进行验证,并与已有的加筋板吸湿模型进行对比,通过所建立模型给出了加筋板沿厚度方向的吸湿量分布规律。结果表明:所建立加筋板non-Fickian吸湿模型的计算结果与实验结果吻合良好,在整个吸湿阶段相对误差小于5%,模型的预测精度高于传统Fick模型。所建立的加筋板non-Fickian吸湿模型可用于环氧树脂基复合材料加筋板层合结构吸湿量的准确预测。
-
关键词:
- 复合材料 /
- 加筋板结构 /
- 吸湿行为 /
- non-Fickian行为 /
- 有限元仿真
Abstract:The properties of epoxy resin matrix composites are sensitive to hygrothermal environment, and it is of great significance to investigate the moisture absorption behavior of epoxy resin matrix composite structures for its practical application. Based on the non-Fickian moisture absorption model of carbon fiber epoxy resin matrix laminates, the non-Fickian moisture absorption model for the epoxy resin matrix stiffened panel was established, the moisture absorption experiments of stiffened panel were conducted under the condition of 70℃/85% RH, and the established model was verified. The proposed model was compared with the existing moisture absorption model further. Finally, the moisture absorption distribution of the typical stiffened panel along the thickness direction was given through the established model. The results show that the calculated results of the established non-Fickian moisture absorption model of the stiffened panel are in good agreement with the experimental results. The relative error of the moisture absorption through the entire moisture absorption stage is less than 5%, and the predictive accuracy of the model is higher than that of the traditional Fick model. The established non-Fickian moisture absorption model of stiffened panel can be used to accurately predict the absorbed moisture content of epoxy resin matrix composite stiffened panels.
-
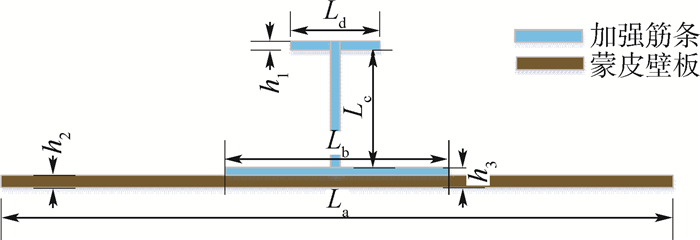
表 1 各区域铺层定义
Table 1. Lay-up definition at each zone
部位 铺层顺序 蒙皮壁板
加强筋条[45*/45/03/-45/90/0/90]s
[0/45/-45/90/45/02/-45]s表 2 mm层合板non-Fickian吸湿模型参数
Table 2. Parameters of non-Fickian moisture absorption model of laminate with 2 mm thickness
参数 Mm/% ϕ hF/mm Dz/(mm2·d-1) α t0/d 数值 0.79 0.8 1 0.003 1 0.4 15 表 3 加筋板non-Fickian吸湿模型参数
Table 3. Parameters of non-Fickian moisture absorption model of stiffened panel
参数 区域1 区域2 区域3 Mmi/% 0.702 0.702 0.702 ϕi 0.8 0.696 0.467 hi/mm 2 2.46 4.46 Dz/(mm2·d-1) 0.004 0.004 0.004 αi 0.4 0.251 5 0.078 4 ti/d 15 20 71 表 4 模型1和模型2参数
Table 4. Parameters of model 1 and model 2
模型1参数 数值 模型2参数 数值 Mn1/% 0.56 MT/% 0.702 Mn2/% 0.142 Dz2/(mm2·d-1) 0.008 6 DzⅠ-1/(mm2·d-1) 0.009 7 ϕT 0.6 DzⅠ-2/(mm2·d-1) 0.014 4 αT 0.001 24 b/mm 2 βT 0.233 tF/d 58 tT/d 20 注:b为板厚度;αT为吸湿系数;βT为吸湿系数;tT为进入non-Fickian时间。 -
[1] 杜善义. 先进复合材料与航空航天[J]. 复合材料学报, 2007, 24(1): 1-12.DU S Y. Advanced composite materials and aerospace engineering[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2007, 24(1): 1-12(in Chinese). [2] 高禹, 李洋洋, 王柏臣, 等. 先进树脂基复合材料在航空发动机上的应用及研究进展[J]. 航空制造技术, 2016, 59(21): 16-21.GAO Y, LI Y Y, WANG B C, et al. Application of advanced resin matrix composites in aeroengine and its research progress[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2016, 59(21): 16-21(in Chinese). [3] 徐伟伟, 文友谊, 顾轶卓, 等. 航空用国产碳纤维/双马树脂复合材料湿热特性[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(1): 86-94. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0155XU W W, WEN Y Y, GU Y Z, et al. Hygrothermal property of domestic carbon fiber/bismaleimide resin composites for aeronautic application[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(1): 86-94(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0155 [4] 吕小军, 张琦, 马兆庆, 等. 湿热老化对碳纤维/环氧树脂基复合材料力学性能影响研究[J]. 材料工程, 2005, 33(11): 50-53.LU X J, ZHANG Q, MA Z Q, et al. Study of hydrothermal aging effect on mechanical properties of carbon fiber/epoxy resin composites[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2005, 33(11): 50-53(in Chinese). [5] 冯青, 李敏, 顾轶卓, 等. 不同湿热条件下碳纤维/环氧复合材料湿热性能实验研究[J]. 复合材料学报, 2010, 27(6): 16-20.FENG Q, LI M, GU Y Z, et al. Experimental research on hygrothermal properties of carbon fiber/epoxy resin composite under different hygrothermal conditions[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2010, 27(6): 16-20(in Chinese). [6] 李静. 纤维增强树脂基复合材料的吸湿性和湿变形[J]. 航天返回与遥感, 2010, 31(2): 69-74.LI J. Moisture absorption and soaking deformation of fiber reinforced resin composites[J]. Spacecraft Recovery & Remote Sensing, 2010, 31(2): 69-74(in Chinese). [7] 张利军, 肇研, 罗云烽, 等. 湿热循环对CCF300/QY8911复合材料界面性能的影响[J]. 材料工程, 2012, 40(2): 25-29.ZHANG L J, ZHAO Y, LUO Y F, et al. On the interfacial properties of CCF300/QY8911 composite with cyclical hygrothermal treatments[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2012, 40(2): 25-29(in Chinese). [8] 张晖, 阳建红, 李海斌, 等. 湿热老化环境对环氧树脂性能影响研究[J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2010, 33(3): 41-43.ZHANG H, YANG J H, LI H B, et al. Effects of hydrothermal aging on properties of epoxy resin[J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2010, 33(3): 41-43(in Chinese). [9] 赵鹏. 纤维增强树脂基复合材料湿热老化性能研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2009: 5-20.ZHAO P. Research on the hygrothermal aging performance of FRP composites[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2009: 5-20(in Chinese). [10] ZHOKH A, STRIZHAK P. Crossover between Fickian and non-Fickian diffusion in a system with hierarchy[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2019, 282: 22-28. [11] PLACETTE M D, FAN X J, ZHAO J H, et al. Dual stage modeling of moisture absorption and desorption in epoxy mold compounds[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2012, 52(7): 1401-1408. [12] CARTER H G, KIBLER K G. Langmuir-type model for anomalous moisture diffusion in composite resins[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 1978, 12(2): 118-131. [13] BARINK M, MAVINKURVE A, JANSSEN J. Predicting non-Fickian moisture diffusion in EMCs for application in micro-electronic devices[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2016, 62(7): 45-49. [14] JACOBS P M, JONES E R. Diffusion of moisture into two-phase polymers[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1989, 24(7): 2343-2347. [15] WONG K J, LOW K O, ISRAR H A, et al. Thickness-dependent non-Fickian moisture absorption in epoxy molding compounds[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2016, 65(10): 160-166. [16] LA SAPONARA V. Environmental and chemical degradation of carbon/epoxy and structural adhesive for aerospace applications: Fickian and anomalous diffusion, Arrhenius kinetics[J]. Composite Structures, 2011, 93(9): 2180-2195. [17] 冯宇, 何宇廷, 安涛, 等. 湿热环境对航空复合材料加筋板压缩屈曲和后屈曲性能的影响[J]. 材料工程, 2015, 43(5): 81-88.FENG Y, HE Y T, AN T, et al. Influence of hygrothermal environment on compressive buckling and post-buckling performance of aero composite stiffened panel[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2015, 43(5): 81-88(in Chinese). [18] 谭翔飞, 谭鹏达, 何宇廷, 等. 航空碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料加筋壁板吸湿行为[J]. 材料工程, 2018, 46(12): 61-69.TAN X F, TAN P D, HE Y T, et al. Moisture behavior of aeronautic carbon fiber reinforced resin composite stiffened panel[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2018, 46(12): 61-69(in Chinese). [19] WONG K J. Moisture absorption characteristics and effects on mechanical behaviour of carbon/epoxy composite: Application to bonded patch repairs of composite structures[D]. Dijon: Université de Bourgogne, 2013: 31-42. [20] ASTM. Standard test method for polymer matrix composite materials: ASTM D5229/D5229M[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 1992: 1-15. [21] ZHANG T J, LI S L, CHANG F, et al. An experimental and numerical analysis for stiffened composite panel subjected to shear loading in hygrothermal environment[J]. Composite Structures, 2016, 138: 107-115. -







 下载:
下载: