-
摘要:
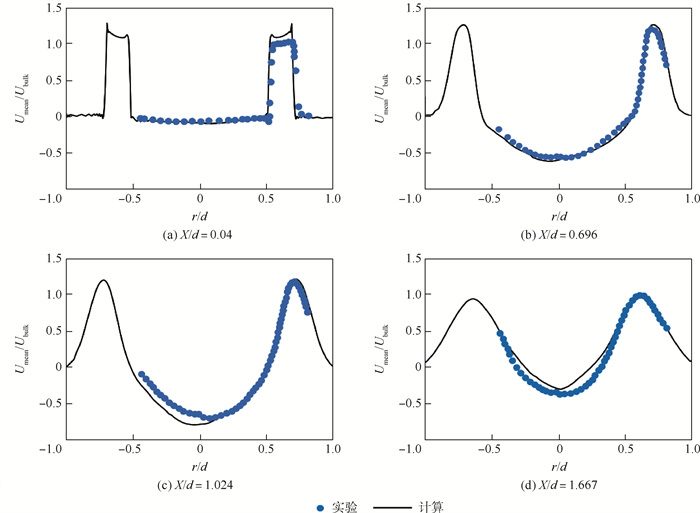
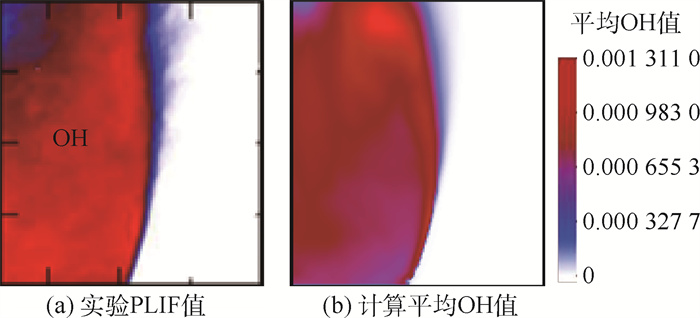
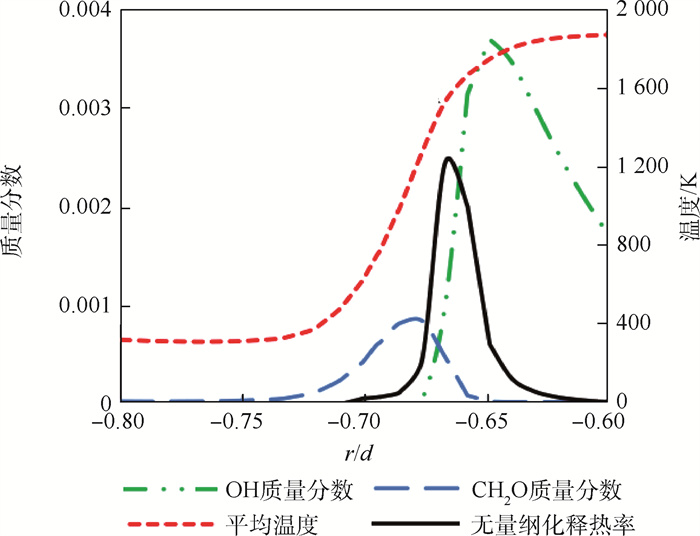
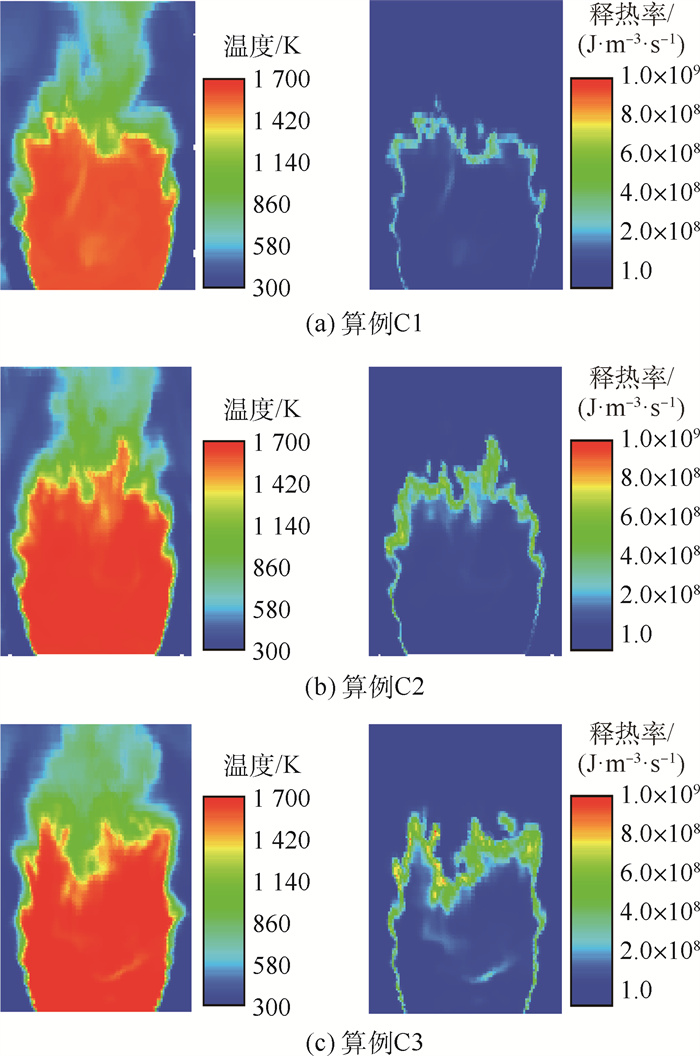
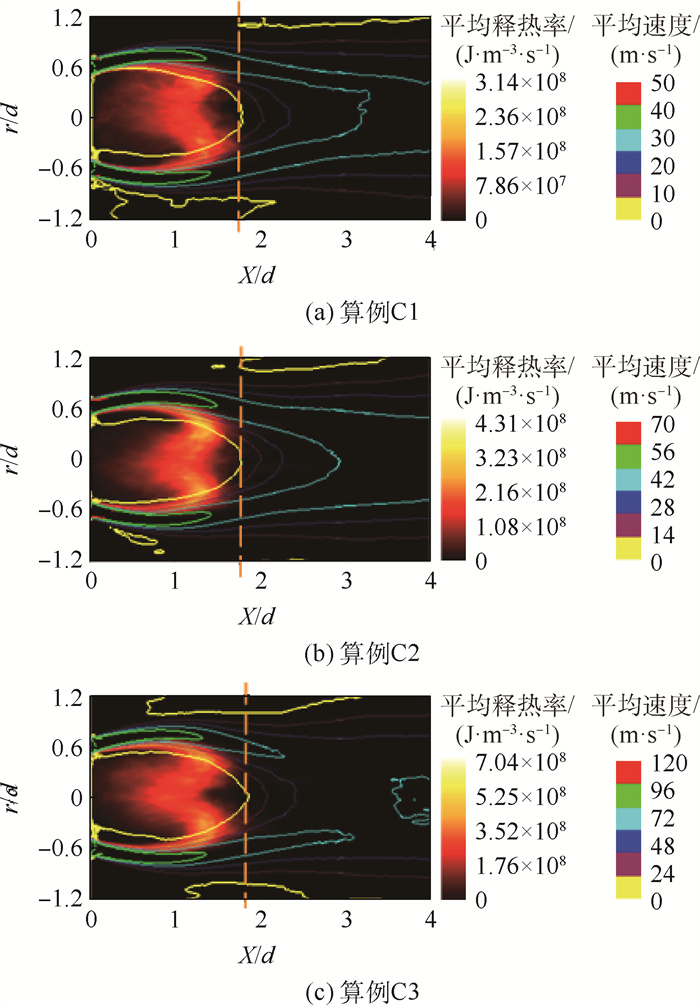
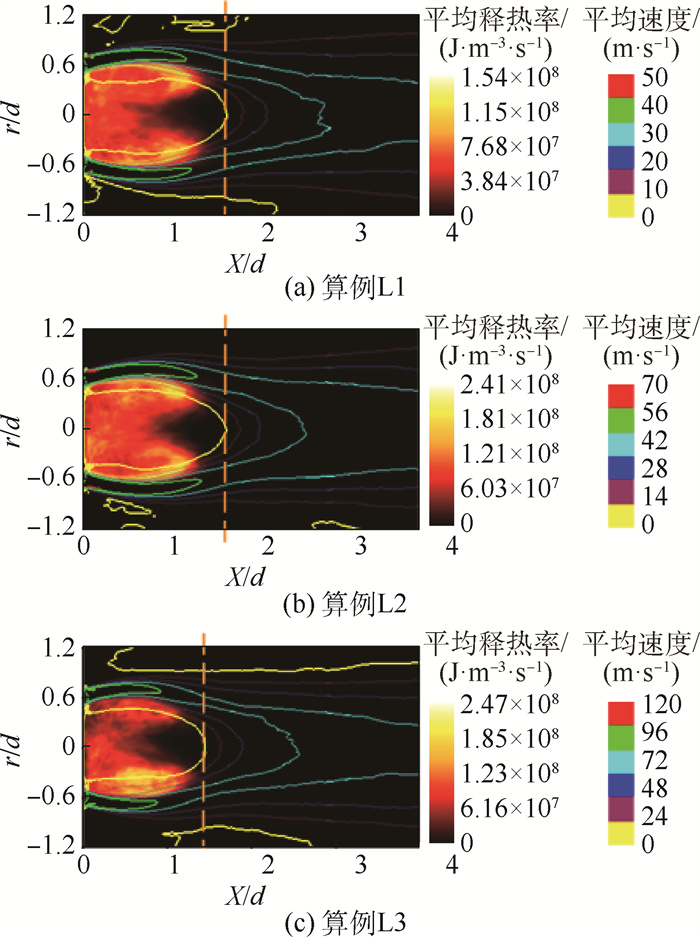
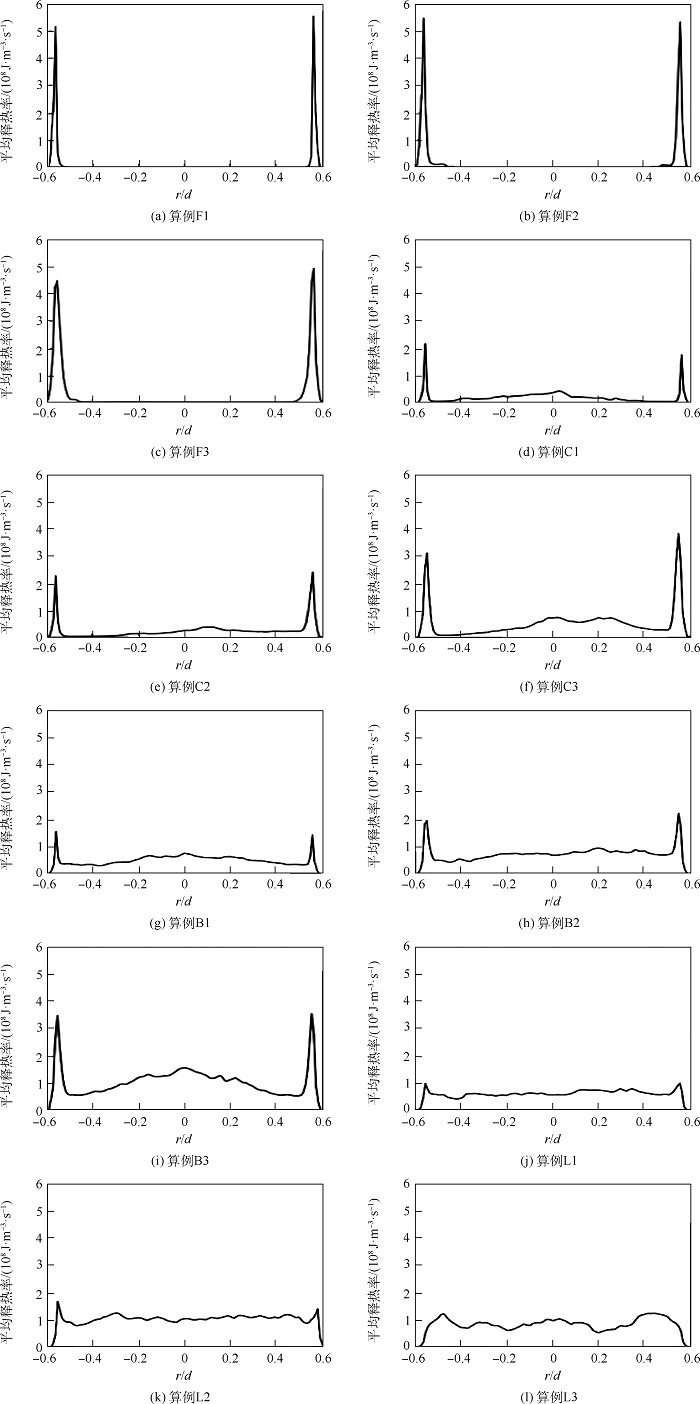
针对锥形钝体稳定的甲烷-空气预混湍流火焰复杂的熄火过程,采用大涡模拟(LES)与输运方程概率密度函数(TPDF)湍流燃烧模型相结合的模拟方法,研究远离熄火、近熄火及熄火点的火焰和释热率(HRR)数值变化情况,定量分析熄火判据。结果表明:冷态速度模拟结果和实验的相对均方根误差在10%以内,热态误差在20%以内;释热率是否出现在OH和CH2O重叠的区域,是判断熄火的一个重要参数;远离熄火时,释热率高的区域主要沿内侧剪切层出现;近熄火工况下,释热率在流向轴上闭合,回流区下游也出现较大的释热率;熄火点工况下,较大释热率的区域在回流区下游和上游均有出现;模拟预测的熄火情况和实验PLIF结果一致;平均释热率可作为判断熄火的定量依据,即当钝体后方0.2
d 处内侧剪切层平均释热率与回流区平均释热率的比值小于4时,发生熄火。-
关键词:
- 释热率(HRR) /
- 贫油熄火边界预测 /
- 大涡模拟(LES) /
- 输运方程概率密度函数(TPDF) /
- 湍流燃烧
Abstract:To understand the complicated blowoff process of premixed turbulence methane-air flame after a conical bluff body, the numerical simulation method based on large eddy simulation (LES) and transport equation probability density function (TPDF) turbulence combustion model was adopted to simulate the flame situations, i.e. far away from blowoff, close to blowoff and blowoff conditions. The flame and the heat release rate (HRR) value under these different conditions were studied, and the criterion for lean blowoff judgement was analyzed quantitatively. The results show that the average relative error between velocity simulation results and experimental results is under 10% in cold situation and under 20% in hot situation. HRR appears in the region where OH and CH2O overlap, and is an important blowoff judgment parameter. When the flame is far away from blowoff conditions, HRR mainly appears at the inner shear layer; when close to blowoff conditions, HRR closes on the flow axis and also appears downstream of the recirculation zone; under blowoff conditions, higher HRR regions spread from downstream to upstream of the recirculation zone. The simulation blowoff predictions are consistent with the experimental PLIF results. In this study, the average HRR can be quantitatively used as a criterion for lean blowoff judgment. At 0.2
d section behind the bluff body, blowoff will occur when the ratio of the average HRR for inner shear layer to the average HRR of the recirculation zone is less than 4. -
表 1 算例编号及边界条件
Table 1. Number of cases and conditions of boundary
算例工况 算例编号 进口平均速度/ (m·s-1) 当量比φ 冷态验证算例 A1 10.94 0 热态验证算例 A2 10.94 0.64 远离熄火工况 F1 19.00 0.80 φ高于熄火工况B1 2.5% C1 19.00 0.615 实验熄火工况 B1 19.00 0.60 φ低于熄火工况B1 3.3% L1 19.00 0.58 远离熄火工况 F2 27.50 0.80 φ高于熄火工况B2 2.5% C2 27.50 0.645 实验熄火工况 B2 27.50 0.629 φ低于熄火工况B2 3.3% L2 27.50 0.608 远离熄火工况 F3 44.10 0.80 φ高于熄火工况B3 2.5% C3 44.10 0.697 实验熄火工况 B3 44.10 0.68 φ低于熄火工况B3 3.3% L3 44.10 0.657 表 2 其他边界条件
Table 2. Other boundary conditions
边界 边界条件 入口边界 温度T=300 K 压力P=101 325 Pa 甲烷-空气预混燃气 出口边界 压力出口边界 钝体及其他边界 绝热固壁无滑移边界 表 3 12个算例的ΔH值
Table 3. Value of ΔH for twelve cases
算例编号 ΔH F1 1 720 F2 227 F3 96.3 C1 10.9 C2 13.1 C3 7.72 B1 3.36 B2 3.38 B3 3.73 L1 1.73 L2 1.67 L3 1.05 -
[1] LEFEBVRE A H, BALLAL D R. Gas turbine combustion[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1983: 5-10. [2] DAWSON J R, GORDON R L, KARIUKI J, et al. Visualization of blow-off events in bluff-body stabilized turbulent premixed flames[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2011, 33(1): 1559-1566. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2010.05.044 [3] 陶焰明, 肖为, 江立军. 基于半经验耦合的贫熄边界预测方法[J]. 航空动力学报, 2019, 34(5): 1111-1118.TAO Y M, XIAO W, JIANG L J. Prediction method of lean blow-out limit based on a hybrid semi-empirical model[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2019, 34(5): 1111-1118(in Chinese). [4] HODIZC E, DUWIG C, SZASZ R, et al. Large eddy simulation of lean blow off[C]//21st AIAA Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2013. [5] LEE H, LEE B K. Stability limit of a bluff-body-stabilized lean premixed turbulent flame[C]//AIAA Scitech 2019 Forum. Reston: AIAA, 2019. [6] FOALE M J, GIUSTI A, MASTORAKOS E. Numerical investigation of lean blow-out of kerosene spray flames with detailed chemical models[C]//AIAA Scitech 2019 Forum. Reston: AIAA, 2019. [7] PAUL P H, NAJM H N. Planar laser-induced fluorescence imaging of flame heat release rate[J]. Symposium (International) on Combustion, 1998, 27(1): 43-50. doi: 10.1016/S0082-0784(98)80388-3 [8] KARIUKI J, DOWLUT A, YUAN R, et al. Heat release imaging in turbulent premixed methane-air flames close to blow-off[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2015, 35(2): 1443-1450. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2014.05.144 [9] HODZIC E, JANGI M, SZASZ R Z, et al. Large eddy simulation of bluff body flames close to blow-off using an Eulerian stochastic field method[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2017, 181: 1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2017.03.010 [10] JONES W P, KAKHI M. PDF modeling of finite-rate chemistry effects in turbulent nonpremixed jet flames[J]. Combustion and Flame, 1998, 115(1-2): 210-229. doi: 10.1016/S0010-2180(98)00002-9 [11] CLAYTON D J, JONES W P. Large eddy simulation of a methane-air diffusion flame[J]. Flow, Turbulence and Combustion, 2008, 81(4): 497-521. doi: 10.1007/s10494-008-9143-5 [12] JONES W P, LETTIERI C. Large eddy simulation of spray atomization with stochastic modeling of breakup[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2010, 22(11): 115-106. [13] 曾家, 金捷, 张晟, 等. 基于LES-PDF方法的双旋流模型燃烧室数值模拟[J]. 气体物理, 2019, 4(5): 52-64.ZENG J, JIN J, ZHANG S, et al. Numerical simulation of double swirl model combustor based on LES-PDF method[J]. Physics of Gases, 2019, 4(5): 52-64(in Chinese). [14] 金捷, 刘邓欢. 航空发动机燃烧室湍流两相燃烧模型发展现状[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 48(3): 303-309.JIN J, LIU D H. Development status of turbulent two-phase combustion model in aero-engine combustion chamber[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 48(3): 303-309(in Chinese). [15] JONES W P, NAVARRO-MARTINEZ S. Large eddy simulation of auto-ignition with a subgrid probability density function method[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2007, 150(3): 170-187. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2007.04.003 [16] JONES W P, PRASAD V N. Large eddy simulation of the S andia flame series (D-F) using the Eulerian stochastic field method[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2010, 157(9): 1621-1636. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2010.05.010 [17] JONES W P, MARQUIS A J, PRASAD V N. LES of a turbulent premixed swirl burner using the Eulerian stochastic field method[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2012, 159(10): 3079-3095. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2012.04.008 [18] JABERI F A, COLUCCI P J, JAMES S, et al. Filtered mass density function for large eddy simulation of turbulent reacting flows[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1999, 401(2): 85-121. [19] BALACHANDRAN R, AYOOLA B O, KAMINSKI C F, et al. Experimental investigation of the nonlinear response of turbulent premixed flames to imposed inlet velocity oscillations[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2005, 143(1-2): 37-55. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2005.04.009 [20] KARIUKI J, DAWSON J R, MASTORAKOS E. Measurements in turbulent premixed bluff body flames close to blow-off[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2012, 159(8): 2589-2607. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2012.01.005 [21] SUNG C J, LAW C K, CHEN J Y. Augmented reduced mechanisms for NO emission in methane oxidation[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2001, 125(1-2): 906-919. doi: 10.1016/S0010-2180(00)00248-0 -








 下载:
下载: