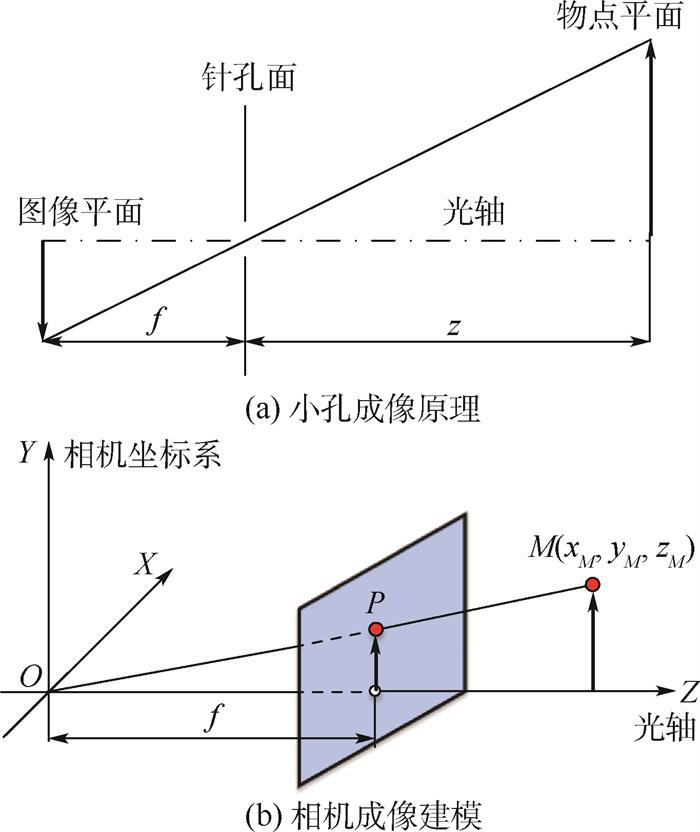
-
摘要:
现有图像配准算法中,借助图像采集设备参数的方法存在硬件内参难以获得或精度不够的问题,采用匹配图像特征计算图像单应性的方法存在对场景深度信息利用不全的问题。针对这一现象,提出了结合可见光图像与其深度信息来生成更具有真实性的配准图像对数据,用以训练得到一个可以进行像素级别图像配准的深度神经网络PIR-Net。建立了一个大规模、多视角、超仿真的图像配准数据集:多视角配准(MVR)数据集,该数据集包含7 240对含有深度信息的待配准图像及其像素级别的坐标对准真值;基于编码器-解码器的深度神经网络结构,训练得到一个能以全分辨率形式对2幅输入图像之间的坐标变化矩阵进行重建的PIR-Net。通过实验验证了PIR-Net能够在未知相机内参的情况下实现不同视角的可见光图像配准,并比传统算法具有更高的配准精度。在MVR数据集上,PIR-Net的配准误差仅为通用的特征匹配对准算法(SIFT+RANSAC)的18%,同时减少了30%的时间消耗。
Abstract:Current image registration algorithms relying on the internal parameters of sensing devices for image alignment face the difficulty of acquiring precise device parameters and reaching high mapping precision; while the ones using matched image features to calculate image homography matric for registration have the problem of insufficient utilization of scene depth information. Based on this observation, we propose a method which can generate more authentic image registration data from monocular images and their depth-maps, and use the data to train a pixel-wise image registration network, the PIR-Net, for fast, accurate and practical image registration. We construct a large-scale, multi-view, realistic image registration database with pixel-wise depth information that imitates real-world situations, the multi-view image registration (MVR) dataset. The MVR dataset contains 7 240 pairs of RGB images and their corresponding registraton labels. With the dataset, we train an encoder-decoder structure based, fully convolutional image registration network, the PIR-Net, extensive experiments on the MVR dataset demonstrate that the PIR-Net can predict pixel-wise image alignment matrix for multi-view RGB images without accessing the camera internal parameters, and that the PIR-Net out-performs traditional image registration methods. On the MVR dataset, the registration error of PIR-Net is only 18% of the general feature matching method (SIFT+RANSAC), and its time cost is 30% less.
-
Key words:
- deep learning /
- image registration /
- coordinate transformation /
- homography estimation /
- depth-map
-
表 1 HomographyNet的图像配准算法精度评估
Table 1. Image registration algorithm accuracy estimation of HomographyNet
数据集 ACE EPE COCO2014-homo 6.67 MVR-homo(不含深度信息) 5.81 MVR(含深度信息) 109.14 8.89 表 2 MVR数据集上的图像配准算法评估
Table 2. Image registration algorithm estimation on MVR dataset
-
[1] BALAKRISHNAN G, ZHAO A, SABUNCU M R, et al. VoxelMorph: A learning framework for deformable medical image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2019, 38(8): 1788-1800. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2897538 [2] FAN J, CAO X, YAP P T, et al. BIRNet: Brain image registration using dual-supervised fully convolutional networks[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2019, 54: 193-206. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2019.03.006 [3] BALAKRISHNAN G, ZHAO A, SABUNCU M R, et al. An unsupervised learning model for deformable medical image registration[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 9252-9260. [4] CHENG X, ZHANG L, ZHENG Y. Deep similarity learning for multimodal medical images[J]. Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering: Imaging & Visualization, 2018, 6(3): 248-252. [5] 梁怀丹. 空间遥感红外与可见光图像快速配准算法研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学, 2019: 18-25.LIANG H D. Research on fast registration of spatial remote sensing infrared and visible light images[D]. Changchun: Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019: 18-25(in Chinese). [6] MA J, JIANG J, ZHOU H, et al. Guided locality preserving feature matching for remote sensing image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(8): 4435-4447. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2820040 [7] XIANG Y, WANG F, YOU H. OS-SIFT: A robust SIFT-like algorithm for high-resolution optical-to-SAR image registration in suburban areas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(6): 3078-3090. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2790483 [8] WANG J, SUENAGA H, HOSHI K, et al. Augmented reality navigation with automatic marker-free image registration using 3-D image overlay for dental surgery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2014, 61(4): 1295-1304. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2014.2301191 [9] ARSLAN S, YAZICI A, SACAN A, et al. Comparison of feature-based and image registration-based retrieval of image data using multidimensional data access methods[J]. Data & Knowledge Engineering, 2013, 86: 124-145. [10] WOLF Y A, GOREN G, VITITZRABIN E, et al. Method and device for stereoscopic vision: US10567732B2[P]. 2020-02-18. [11] BELLO G A, DAWES T J W, DUAN J, et al. Deep-learning cardiac motion analysis for human survival prediction[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2019, 1(2): 95-104. doi: 10.1038/s42256-019-0019-2 [12] BENHIMANEB S, MALIS E. Homography-based 2D visual tracking and servoing[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2007, 26(7): 661-676. doi: 10.1177/0278364907080252 [13] LI J, WANG Z, LAI S, et al. Parallax-tolerant image stitching based on robust elastic warping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2017, 20(7): 1672-1687. [14] HWANG S, PARK J, KIM N, et al. Multispectral pedestrian detection: Benchmark dataset and baseline[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1037-1045. [15] NEWCOMBE R A, IZADI S, HILLIGES O, et al. KinectFusion: Real-time dense surface mapping and tracking[C]//IEEE International Symposium on Mixed & Augmented Reality. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 127-136. [16] LOWE D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91-110. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 [17] WANG B, WU D, LU Q, et al. A new image registration method for infrared images and visible images[C]//2010 3rd International Congress on Image and Signal Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010, 4: 1745-1749. [18] 贾雯晓, 张贵仓, 汪亮亮, 等. 基于SIFT和改进的RANSAC图像配准算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2018, 54(2): 203-207. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSGG201802033.htmJIA W X, ZHANG G C, WANG L L, et al. Image registration algorithm based on SIFT and improved RANSAC[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2018, 54(2): 203-207(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSGG201802033.htm [19] 许佳佳. 结合Harris与SIFT算子的图像快速配准算法[J]. 中国光学, 2015, 8(4): 62-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGA201504007.htmXU J J. Fast image registration method based on Harris and SIFT algorithm[J]. Chinese Optics, 2015, 8(4): 62-69(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGA201504007.htm [20] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [21] XIE S, GIRSHICK R, DOLLAR P, et al. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1492-1500. [22] SUN K, XIAO B, LIU D, et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 5693-5703. [23] DOSOVITSKIY A, FISCHER P, SPRINGENBERG J T, et al. Discriminative unsupervised feature learning with exemplar convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(9): 1734-1747. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2496141 [24] YANG Z, DAN T, YANG Y. Multi-temporal remote sensing image registration using deep convolutional features[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 38544-38555. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2853100 [25] DETONE D, MALISIEWICZ T, RABINOVICH A. Deep image homography estimation[EB/OL]. (2016-06-13)[2020-11-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.03798v1. [26] NGUYEN T, CHEN S W, SHIVAKUMAR S S, et al. Unsupervised deep homography: A fast and robust homography estimation model[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2018, 3(3): 2346-2353. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2018.2809549 [27] ZHANG J, WANG C, LIU S, et al. Content-aware unsupervised deep homography estimation[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV). Berlin: Springer, 2020: 653-669. [28] YE N, WANG C, LIU S, et al. DeepMeshFlow: Content adaptive mesh deformation for robust image registration[EB/OL]. (2019-12-11)[2020-11-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.05131. [29] ZHAO C, CAO Z, LI C, et al. NM-Net: Mining reliable neighbors for robust feature correspondences[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 215-224. [30] ZEINIK L, IRANI M. Multiview constraints on homographies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2002, 24(2): 214-223. doi: 10.1109/34.982901 [31] DOSOVITSKIY A, FISCHER P, ILG E, et al. FlowNet: Learning optical flow with convolutional networks[C]//IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision(ICCV). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 2758-2766. [32] SILBERMAN N, HOIEM D, KOHLI P, et al. Indoor segmentation and support inference from RGBD images[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV). Berlin: Springer, 2012: 746-760. [33] LIN T Y, MAIRE M, BELONGIE S, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV). Berlin: Springer, 2014: 740-755. -







 下载:
下载: