-
摘要:
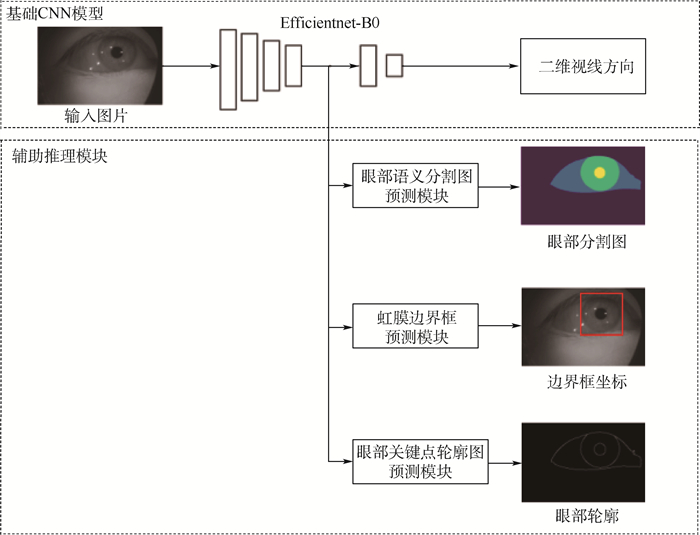
眼动交互是头戴式虚拟现实(VR)/增强现实(AR)设备的关键操控方式, 如何进行高精度、高鲁棒性的非标定视线估计是当前VR/AR眼动交互的核心问题之一, 高效、鲁棒的非标定视线估计需要大量的眼图训练数据和高效的算法结构做支撑。在现有基于深度学习的近眼视线估计方法的基础上, 通过添加多任务辅助推理模块, 增加网络结构的多阶段输出, 进行多任务联合训练, 在不增加视线估计测试耗时的前提下, 有效提升视线估计精度。在模型训练时, 从视线估计网络结构的多个中间阶段引出多个眼部特征的辅助推理并行网络头, 包括眼动图像的语义分割、虹膜边界框及眼部轮廓信息, 为原始视线估计网络提供多阶段中继监控, 在不增加训练数据的基础上, 有效提升视线估计网络的测试精度。在国际公开数据集Acomo-14与OpenEDS2020上的验证实验表明, 与无辅助推理的网络相比, 所提方法精度分别得到了21.74%与18.91%的效果提升, 平均角度误差分别减少到1.38°与2.01°。
Abstract:Eye-tracking interaction is the key control method for head-mounted virtual reality (VR)/augmented reality (AR) devices and non-calibrated gaze estimation is one of the core problem in current VR/AR eye-tracking interactions. Efficient and robust non-calibrated gaze estimation requires a large amount of training data and an efficient network structure. Based on the existing deep-learning-based near-eye gaze estimation method, by adding multitasking auxiliary reasoning and increasing the multi-stage output of the network structure for joint multi-task training, we achieve an effective improvement of gaze estimation accuracy without increasing the refer time compared to the original gaze estimation network. During model training, multiple intermediate stages of the gaze estimation network structure are used to derive multiple parallel network headers for auxiliary reasoning about eye features, including semantic segmentation of eye images, iris border frames, and eye contour information, to provide multi-stage relay monitoring for the original gaze estimation network, which effectively improves the generalization capability of the gaze estimation network without increasing the training data. Experiments on the open datasets Acomo-14 and OpenEDS2020 show that the accuracy of the algorithm is improved by 21.74% and 18.91%, respectively, and the average gaze estimation error is reduced to 1.38 degrees and 2.01 degrees, compared with the network without auxiliary reasoning.
-
表 1 数据集Acomo-14和openEDS2020上跨主体评估的平均角度误差
Table 1. Mean angular error in cross-subjects on Acomo-14 and openEDS2020 datasets
模型 平均角度误差/(°) Acomo-14 openEDS2020 Kim模型[17] 2.51 3.51 不含辅助推理模块的ARGazeNet 1.68 2.39 ARGazeNet 1.38 2.01 使用分割图作为输入的ARGazeNet 5.94 4.95 表 2 测试硬件上的推理性能
Table 2. Inference performance on tested hardware
模型 总耗时/ms Kim模型 2.34 不含辅助推理模块的ARGazeNet 2.47 ARGazeNet 2.47 表 3 辅助推理模块的影响
Table 3. Effectiveness of auxiliary reasoning module
模型 平均角度误差/(°) Acomo-14 openEDS2020 仅使用基础CNN模型 1.68 2.39 添加眼部语义分割图预测模块 1.60 2.20 添加虹膜边界框预测模块 1.46 2.30 添加眼部关键轮廓图预测模块 1.63 2.32 添加眼部语义分割图预测模块与虹膜边界框预测模块 1.41 2.15 添加眼部语义分割图预测模块与眼部关键轮廓图预测模块 1.54 2.18 添加虹膜边界框预测模块与眼部关键轮廓图预测模块 1.43 2.26 ARGazeNet 1.38 2.01 -
[1] KYTÖ M, ENS B, PIUMSOMBOON T, et al. Pinpointing: Precise head-and eye-based target selection for augmented reality[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, 2018: 1-14. [2] SMITH P, SHAH M, DA VITORIA LOBO N. Determining driver visual attention with one camera[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2003, 4(4): 205-218. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2003.821342 [3] ALBERT R, PATNEY A, LUEBKE D, et al. Latency requirements for foveated rendering in virtual reality[J]. ACM Transactions on Applied Perception, 2017, 14(4): 1-13. [4] PATNEY A, SALVI M, KIM J, et al. Towards foveated rendering for gaze-tracked virtual reality[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2016, 35(6): 1-12. [5] ZHANG X, SUGANO Y, BULLING A. Evaluation of appearance-based methods and implications for gaze-based applications[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, 2019: 1-13. [6] ZHANG X, SUGANO Y, FRITZ M, et al. Appearance-based gaze estimation in the wild[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 4511-4520. [7] ZHANG X, SUGANO Y, FRITZ M, et al. MPⅡGaze: Real-world dataset and deep appearance-based gaze estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 41(1): 162-175. [8] CHENG Y, ZHANG X, LU F, et al. Gaze estimation by exploring two-eye ssymmetry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 5259-5272. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2982828 [9] KRAFKA K, KHOSLA A, KELLNHOFER P, et al. Eye tracking for everyone[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 2176-2184. [10] PARK S, SPURR A, HILLIGES O. Deep pictorial gaze estimation[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Berlin: Springer, 2018: 721-738. [11] PARK S, ZHANG X, BULLING A, et al. Learning to find eye region landmarks for remote gaze estimation in unconstrained settings[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 ACM Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications. New York: ACM, 2018: 1-10. [12] YU Y, LIU G, ODOBEZ J M. Deep multitask gaze estimation with a constrained landmark-gaze model[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Berlin: Springer, 2018: 456-474. [13] GARBIN S J, SHEN Y, SCHUETZ I, et al. OpenEDS: Open eye dataset[EB/OL]. (2019-05-17)[2020-12-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.03702. [14] PALMERO C, SHARMA A, BEHRENDT K, et al. OpenEDS2020: Open eyes dataset[EB/OL]. (2020-05-08)[2020-12-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.03876. [15] CHAUDHARY A K, KOTHARI R, ACHARYA M, et al. RITnet: Real-time semantic segmentation of the eye for gaze tracking[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 3698-3702. [16] PALMERO C, KOMOGORTSEV O V, TALATHI S S. Benefits of temporal information for appearance-based gaze estimation[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 ACM Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications. New York: ACM, 2020: 1-5. [17] KIM J, STENGEL M, MAJERCIK A, et al. NVGaze: An anatomically-informed dataset for low-latency, near-eye gaze estimation[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, 2019: 1-12. [18] WU Z, RAJENDRAN S, VAN AS T, et al. EyeNet: A multi-task deep network for off-axis eye gaze estimation[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 3683-3687. [19] TAN M, LE Q. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks[C]//International Conference on Machine Learning, 2019: 6105-6114. [20] QIN X, ZHANG Z, HUANG C, et al. BASNet: Boundary-aware salient object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 7479-7489. [21] CHETLUR S, WOOLLEY C, VANDERMERSCH P, et al. cuDNN: Efficient primitives for deep learning[EB/OL]. (2014-12-18)[2020-12-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1410.0759. -







 下载:
下载: