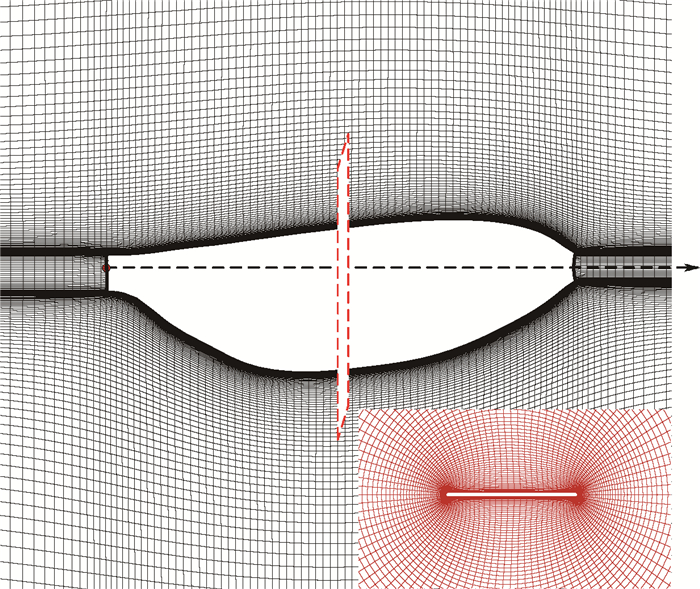
-
摘要:
抬升角的存在对昆虫飞行时的气动力会产生不同程度的影响,其对昆虫飞行动稳定性的影响也非常值得探索。首先,求解Navier-Stokes方程得到了有抬升角时食蚜蝇的纵向与横向稳定性导数;然后,用特征模态分析法研究其动稳定性。结果表明:有抬升角时,在侧向来流作用下食蚜蝇的滚转力矩对应的导数比无抬升角时明显减小,而其余导数无明显变化,导数减小是由于抬升角的存在使得有侧向来流时因左右翅举力不同产生的正向滚转力矩数值明显减小,而由侧向力产生的负向滚转力矩数值略有增大,从而使得其总的负向滚转力矩数值增大;但有侧向来流时滚转力矩所对应导数的减小并未引起食蚜蝇飞行动稳定性的改变,其纵向和横向的特征模态仍与无抬升角时相同。
-
关键词:
- 抬升角 /
- 食蚜蝇 /
- 飞行动稳定性 /
- Navier-Stokes方程 /
- 运动模态
Abstract:The aerodynamic performance of insect can be affected by wing stroke deviation, which may also influence the flight stability. The longitudinal and lateral non-dimensional stability derivatives of hoverfly with stroke deviation are obtained by solving Navier-Stokes equation, and then the natural modes of motion analysis method is used to analyze the flight stability. The results show that, when stroke deviation exists, the stability derivative of the rolling moment induced by the side motion velocity decreases significantly, while the other derivatives have little difference by comparing the situation with no stroke deviation. The reason why the existence of stroke deviation causes the decrease of the derivative is that the positive rolling moment of the left and right wings declines obviously under lateral wind circumstance, while the negative rolling moment caused by the lateral force increases slightly, which makes the total negative rolling moment increase. However, the decrease of the derivative of the rolling moment caused by the lateral flow does not alter the flight stability of hoverfly, and the longitudinal and lateral characteristic modes of motion are still the same as those without stroke deviation.
-
Key words:
- stroke deviation /
- true hoverfly /
- flight stability /
- Navier-Stokes equation /
- natural mode of motion
-
表 1 纵向无量纲稳定性导数
Table 1. Longitudinal non-dimensional stability derivatives
有/无抬升角 Xu+ Zu+ Mu+ Xw+ Zw+ Mw+ Xq+ Zq+ Mq+ 无抬升角 -1.998 -0.087 2.378 0.146 -1.777 0.475 -0.206 -0.220 -0.128 有抬升角 -1.519 -0.136 2.449 0.112 -1.829 0.630 -0.155 -0.188 -0.174 表 2 横向无量纲稳定性导数
Table 2. Lateral non-dimensional stability derivatives
有/无抬升角 Yv+ Lv+ Nv+ Yp+ Lp+ Np+ Yr+ Lr+ Nr+ 无抬升角 -0.700 -0.530 0.473 -0.341 -3.727 0.249 0.066 0.805 -3.156 有抬升角 -0.759 -1.100 0.303 -0.495 -3.891 0.204 0.066 0.768 -3.155 表 3 v+=0.15时有无抬升角2种情形下左右两翅的侧向力系数、举力系数和滚转力矩系数
Table 3. Coefficients of lateral force, vertical force and rolling moment of left and right wing at v+=0.15 with and without stroke deviation
有/无抬升角 YL+ YR+ ΔY+ ZL+ ZR+ ΔZ+ LL+ LR+ ΔL+ 无抬升角 0.093 -0.303 -0.210 1.773 1.690 0.083 2.843 -2.922 -0.079 有抬升角 0.326 -0.554 -0.228 1.780 1.749 0.031 2.961 -3.125 -0.164 表 4 纵向稳定性矩阵A1+的特征值
Table 4. Eigenvalues of longitudinal system matrix A1+
有/无抬升角 模态1λ1 模态2λ2 模态3λ3, 4 无抬升角 -0.169 -0.028 0.065±0.136i 有抬升角 -0.169 -0.028 0.067±0.138i 表 5 横向稳定性矩阵A2+的特征值
Table 5. Eigenvalues of lateral system matrix A2+
有/无抬升角 模态1λ1 模态2λ2 模态3λ3, 4 无抬升角 -1.269 -0.153 -0.006±0.058i 有抬升角 -1.330 -0.157 -0.003±0.089i -
[1] ELLINGTON C. The aerodynamics of hovering insect flight. III. Kinematics[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 1984, 305(1122): 41-78. [2] LIU Y, SUN M. Wing kinematics measurement and aerodynamics of hovering droneflies[J]. Journal of Experimental Biology, 2008, 211(13): 2014-2025. doi: 10.1242/jeb.016931 [3] MOU X L, LIU Y P, SUN M. Wing motion measurement and aerodynamics of hovering true hoverflies[J]. Journal of Experimental Biology, 2011, 214(17): 2832-2844. doi: 10.1242/jeb.054874 [4] ENNOS A R. The kinematics and aerodynamics of the free flight of some diptera[J]. Journal of Experimental Biology, 1989, 142(1): 49-85. doi: 10.1242/jeb.142.1.49 [5] WILLMOTT A P, ELLINGTON C P. The mechanics of flight in the hawkmoth Manduca sexta. I. Kinematics of hovering and forward flight[J]. Journal of Experimental Biology, 1997, 200(21): 2705-2722. doi: 10.1242/jeb.200.21.2705 [6] FRY S N, SAYAMAN R, DICKINSON M H. The aerodynamics of free-flight maneuvers in Drosophila[J]. Science, 2003, 300(5618): 495-498. doi: 10.1126/science.1081944 [7] FRY S N, SAYAMAN R, DICKINSON M H. The aerodynamics of hovering flight in Drosophila[J]. Journal of Experimental Biology, 2005, 208(12): 2303-2318. doi: 10.1242/jeb.01612 [8] WANG C, ZHOU C Y, XIE P. Numerical investigation into the effects of stroke trajectory on the aerodynamic performance of insect hovering flight[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2016, 30(4): 1659-1669. doi: 10.1007/s12206-016-0322-3 [9] LUO G Y, DU G, SUN M. Effects of stroke deviation on aerodynamic force production of a flapping wing[J]. AIAA Journal, 2018, 56(1): 25-35. doi: 10.2514/1.J055739 [10] HU F J, LIU X M. Effects of stroke deviation on hovering aerodynamic performance of flapping wings[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2019, 31(11): 111901. doi: 10.1063/1.5124916 [11] LEI M L, LI C Y. The aerodynamic performance of passive wing pitch in hovering flight[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2020, 32(5): 051902. doi: 10.1063/5.0006902 [12] 牟晓蕾, 许娜. 翅尖轨迹对食蚜蝇悬停时气动特性的影响[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(12): 2603-2609. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2015.0843MOU X L, XU N. Effect of wing-tip trajectory on aerodynamics of hovering true hoverfly[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42(12): 2603-2609(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2015.0843 [13] JANKAUSKI M, DANIEL T L, SHEN I Y. Asymmetries in wing inertial and aerodynamic torques contribute to steering in flying insects[J]. Bioinspiration & Biomimetics, 2017, 12(4): 046001. [14] SUN M, XIONG Y. Dynamic flight stability of a hovering bumblebee[J]. Journal of Experimental Biology, 2005, 208(3): 447-59. doi: 10.1242/jeb.01407 [15] SUN M, WANG J K, XIONG Y. Dynamic flight stability of hovering insects[J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2007, 23(3): 231-246. doi: 10.1007/s10409-007-0068-3 [16] ZHANG Y, SUN M. Dynamic flight stability of a hovering model insect: Lateral motion[J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2010, 26(2): 175-190. doi: 10.1007/s10409-009-0303-1 [17] MOU X L, SUN M. Dynamic flight stability of a model hoverfly in inclined-stroke-plane hovering[J]. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2012, 9(3): 294-303. doi: 10.1016/S1672-6529(11)60123-6 [18] XU N, SUN M. Lateral dynamic flight stability of a model bumblebee in hovering and forward flight[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2013, 319: 102-115. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2012.11.033 [19] XU N, SUN M. Lateral dynamic flight stability of a model hoverfly in normal and inclined stroke-plane hovering[J]. Bioinspiration & Biomimetics, 2014, 9(3): 036019. [20] ETKIN B, REID L D. Dynamics of flight: Stability and control[M]. New York: John Wiley and Sons, Inc, 1996. [21] TAYLOR G K, THOMAS A L R. Animal flight dynamics. II. Longitudinal stability in flapping flight[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2002, 214(3): 351-370. doi: 10.1006/jtbi.2001.2470 [22] ROGERS S E, KWAK D, KIRIS C. Numerical solution of the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations for steady-state and time-dependent problems[C]//27th Aerospace Sciences Meeting, 1989: 0463. [23] SUN M, TANG J. Lift and power requirements of hovering flight in Drosophila virilis[J]. Journal of Experimental Biology, 2002, 205(16): 2413-2427. doi: 10.1242/jeb.205.16.2413 [24] ZHU H J, MENG X G, SUN M. Forward flight stability in a drone-fly[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 12. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55410-5 [25] CHENG B, DENG X. Translational and rotational damping of flapping flight and its dynamics and stability at hovering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2011, 27(5): 849-864. 期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)
-







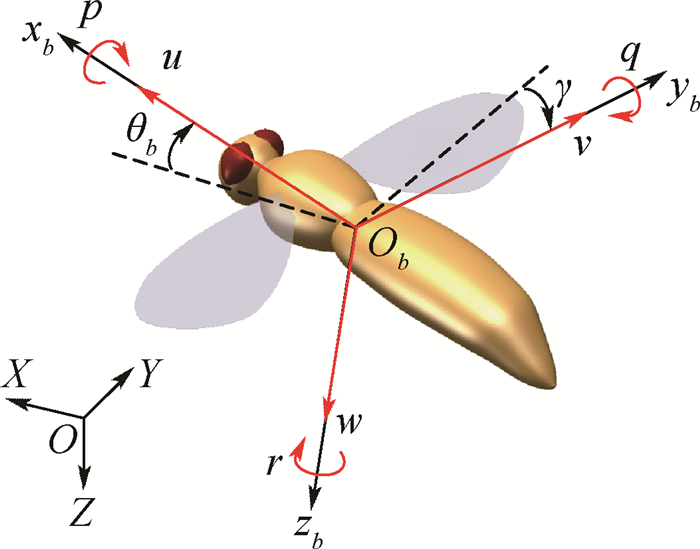
 下载:
下载: