-
摘要:
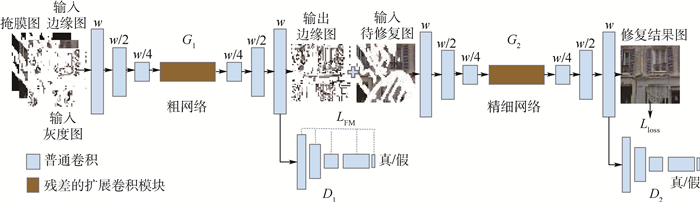
针对粗网络引入先验知识较少使得补全的内容存在明显视觉伪影问题,提出了基于边缘结构生成器的两段式图像修复方法。采用边缘结构生成器对输入的图像边缘和色彩平滑信息进行特征学习,生成缺失区域的结构内容,以引导精细网络重构高质量的语义图像。通过在公开的图像修复基准数据集Paris Street-View上进行实验测试,结果表明,所提模型可对掩膜占比达50%的图像进行补全。在客观的量化评价指标上,峰值信噪比、结构相似度系数、
L 1和L 2均值误差等数值整体优于EC、GC、SF等方法,其中,掩膜占比为0%~20%时,峰值信噪比指数达到33.40 dB,优于其他方法2.37~6.57 dB,结构相似度系数提高了0.006~0.138。同时,补全的图像纹理更清晰,视觉质量更高。Abstract:Aiming at the problem of obvious visual artifacts in the content of rough network with less prior knowledge, a two-stage image inpainting method based on an edge structure generator is proposed. The edge structure generator is used to perform feature learning on the input image edge and color smoothing information, and generate the missing structural contents so as to guide the fine network to reconstruct high-quality semantic images. The mentioned method has been tested on the public benchmark datasets such as Paris Street-View. The experimental results show that the proposed approach can complete the hole images with the mask rate of 50%. The quantitative evaluation indicators: PSNR, SSIM,
L 1 andL 2 errors respectively surpass current images inpainting algorithms with excellent performance, such as EC, GC, SF, etc. Among them, when the mask rate is 0%-20%, the PSNR index reaches 33.40 dB, which is an increase of 2.37-6.57 dB compared to other methods; the SSIM index is increased by 0.006-0.138. Meanwhile, the completed images get clearer texture and higher visual quality.-
Key words:
- image inpainting /
- semantic contents /
- visual artifacts /
- edge structure generator /
- coarse network /
- fine network
-
表 1 不同方法在数据集Paris Street-View上的对比结果
Table 1. Comparison results of different approaches over Paris Street-View dataset
方法 掩膜占比/% PSNR/dB SSIM L1/% L2/% 0~20 28.71 0.953 2.49 2.07 SF 20~40 25.41 0.895 3.96 3.65 40~60 22.32 0.756 5.26 5.03 0~20 31.03 0.963 2.12 1.21 EC 20~40 26.07 0.876 3.43 3.04 40~60 23.45 0.721 6.33 5.89 0~20 28.26 0.932 3.30 2.30 GC 20~40 24.83 0.821 4.21 4.26 40~60 22.61 0.650 7.21 6.13 0~20 26.83 0.831 8.12 3.84 CA 20~40 23.81 0.694 10.2 5.49 40~60 20.26 0.535 11.32 7.81 0~20 33.40 0.969 1.31 1.07 本文方法 20~40 28.65 0.883 3.10 3.01 40~60 24.51 0.762 5.09 4.75 表 2 不同输入信息通过网络测试输出的修复结果
Table 2. Image inpainting results of different input information outputs through network test
结构信息 PSNR/dB SSIM 边缘信息 28.25 0.842 色彩平滑信息 24.637 0.767 两者皆有(本文) 30.23 0.971 -
[1] SHAO H, WANG Y X, FU Y H, et al. Generative image inpainting via edge structure and color aware fusion[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2020, 87: 115929. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2020.115929 [2] LIU H Y, JIANG B, XIAO Y, et al. Coherent semantic attention for image inpainting[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 4169-4178. [3] YU J H, LIN Z, YANG J M, et al. Generative image inpainting with contextual attention[C]//2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 5505-5514. [4] NAZERI K, NG E, JOSEPH T, et al. EdgeConnect: Generative image inpainting with adversarial edge learning[EB/OL]. (2019-01-01)[2020-12-31]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.00212. [5] YU J H, LIN Z, YANG J M, et al. Free-form image inpainting with gated convolution[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 4471-4480. [6] REN Y R, YU X M, ZHANG R N, et al. StructureFlow: Image inpainting via structure-aware appearance flow[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 181-190. [7] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]//International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted Intervention. Berlin: Springer, 2015: 234-241. [8] YU F, KOLTUN V, FUNKHOUSER T. Dilated residual networks[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 472-480. [9] WANG T C, LIU M Y, ZHU J Y, et al. High-resolution image synthesis and semantic manipulation with conditional gans[C]//2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 8798-8807. [10] MIYATO T, KATAOKA T, KOYAMA M, et al. Spectral normalization for generative adversarial networks[EB/OL]. (2018-02-16)[2020-12-31]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.05957. [11] GOODFELLOW I, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]//Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2014: 2672-2680. [12] GATYS L A, ECKER A S, BETHGS M. Image style transfer using convolutional neural networks[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 2414-2423. [13] JOHNSON J, ALAHI A, FEI-FEI L. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 694-711. [14] SONG Y, YANG C, LIN Z X, et al. Contextual-based image inpainting: Infer, match, and translate[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 3-19. [15] XU L, LU C, XU Y, et al. Image smoothing via L0 gradient minimization[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2011, 30(6): 174. [16] XU L, YAN Q, XIA Y, et al. Structure extraction from texture via relative total variation[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2012, 31(6): 139. [17] YU F, KOLTUN V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions[EB/OL]. (2015-11-23)[2020-12-31]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.07122. [18] LIU G, REDA F A, SHIH K J, et al. Image inpainting for irregular holes using partial convolutions[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 85-100. [19] MAO X, LI Q, XIE H, et al. Least squares generative adversarial networks[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2794-2802. [20] LIU Y, CHENG M M, HU X, et al. Richer convolutional features for edge detection[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 5872-5881. [21] CANNY J. A computational approach to edge detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1986, PAMI-8(6): 679-698. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.1986.4767851 [22] DOLLAR P, TU Z, BELONGIE S. Supervised learning of edges and object boundaries[C]//2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2006: 1964-1971. [23] KINGMA D P, BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[EB/OL]. (2014-12-22)[2020-12-31]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980. -







 下载:
下载: