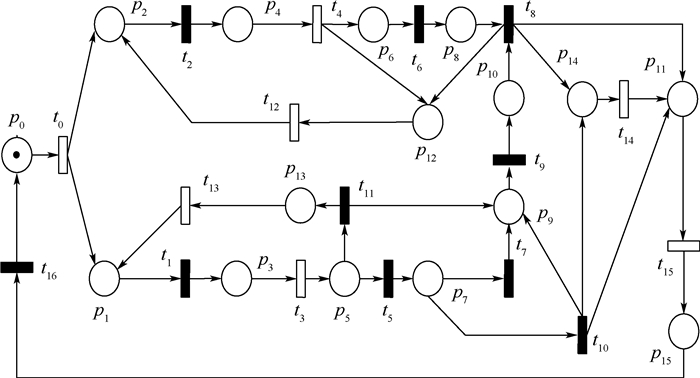
-
摘要:
针对故障本身构建量子贝叶斯Petri网模型算法,并利用该子网模型进行Petri网系统故障分析。对于部分可观Petri网模型中的不可观故障,根据可达标识图分析变迁点火路径不能判断系统状态,建立量子贝叶斯子网模型,通过不确定路径引起的量子干涉重新标定变迁的条件概率表得到量子概率振幅表。根据故障变迁的前置集合并结合量子贝叶斯推理计算变迁触发的先验概率,由后置集合中的可观变迁修正后验概率,由最大后验概率估计系统所处状态,当故障变迁不唯一时,选取最大概率的故障作为故障源。以实际故障系统建立部分可观Petri网模型,结合可观标签概率序列信息和量子贝叶斯概率估计,对系统不可观部分进行故障诊断验证算法的有效性。
Abstract:This paper proposes an algorithm to construct a quantum Bayesian Petri nets model for the fault, and uses the sub net model to analyze the fault of Petri net system. According to the reachability identification diagram, which is the transition firing path can not judge the system state, establish the quantum Bayesian Petri nets subnet model to tackle the unobservable faults in partial observable Petri model. Through the quantum interference caused by the uncertain path, recalibrate the conditional probability table of the transition to obtain the quantum probability amplitude table. According to the pre-set of fault transition and quantum Bayesian reasoning, calculates the firing prior probability of transition. The posterior probability is modified by the observable transition in the post-set, and the state of the system is estimated by the maximum posterior probability. When the fault transition is not unique, the fault with the maximum probability is selected as the fault source. Finally, establishes a partial observable Petri nets model of a real fault system. Combined with the probability sequence information of observable label and quantum Bayesian probability estimation, the fault diagnosis of the unobservable parts of the system is carried out to verify the effectiveness of the algorithm with the data in simulation experiment.
-
Key words:
- fault diagnosis /
- Petri nets /
- partially observed /
- quantum Bayesian /
- quantum interference
-
表 1 总概率情况和量子贝叶斯情况的概率估计比较
Table 1. Comparison of probability estimates between total probability and quantum Bayesian
概率估计 概率值 Pr(t8|t5) 0.81 φ(t8|t5) 
Pr(t10|t5) 0.19 φ(t10|t5) 
Pr(t14|t8) 0.63 φ(t14|t8) 
Pr(t14|t10) 0.43 φ(t14|t10) 
总概率下Pr(t14|t5) 0.592 量子贝叶斯Pr(t14|t5) 0.795 5 总概率下Pr(t14|t5) 0.408 量子贝叶斯Pr(t14|t5) 0.204 5 表 2 基于POPN的量子贝叶斯故障算法故障诊断结果
Table 2. Fault diagnosis results of quantum Bayesian fault algorithm based on POPN
可观概率序列σo 故障变迁Tfi触发概率 干涉角θ/rad QB函数结果 置信度Fb 系统故障概率Pr(σo, ψ, Tfi) 系统状态估计W 系统实际状态 (t0, 1)(t4, 0.883)(t3, 0.926) Pr(tf10|t0, t4, t3) π/2 0 0 0 N 无故障 (t0, 1)(t4, 0.883)
(t3, 0.926)(t15, 0.879)Pr(tf10|t0, t4, t3) π/2 0.162 1 0.4 0.047 1 N 无故障 Pr(tf10|t0, t4, t3, t15) 0 0.047 1 Pr(tf11|t0, t4, t3) π/2 0.158 6 Pr(tf11|t0, t4, t3, t15) 0 0.007 6 (t0, 1)(t4, 0.883)
(t3, 0.926)(t14, 0.851)
(t15, 0.879)(t12, 0.463)Pr(tf10|t0, t4, t3) π/2 0.162 1 0.6 0.966 8 F 故障 Pr(tf10|t0, t4, t3, t14) 0 0.756 9 Pr(tf10|t0, t4, t3, t14, t15) 0 0.926 3 Pr(tf10|t0, t4, t3, t14, t15, t12) 0 0.966 8 Pr(tf11|t0, t4, t3) π/2 0.158 6 Pr(tf11|t0, t4, t3, t14, t15, t12) 0 0.000 6 (t0, 1)(t3, 0.907)
(t13, 0.736)Pr(tf11|t0, t3, t13) π/2 1 1 1 F 故障 表 3 QBPN算法与BPN算法比较
Table 3. Comparison of QBPN algorithm and BPN algorithm
算法 响应时间/ms 诊断正确率/% BPN 300 93.70 QBPN 230 98.74 -
[1] HENRY D, LE PEUVÉDIC C, STRIPPOLI L, et al. Robust model-based fault diagnosis of thruster faults in spacecraft[J]. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2015, 48(21): 1078-1083. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2015.09.670 [2] DJEBKO K, PUPPE F, KAYAL H. Model-based fault detection and diagnosis for spacecraft with an application for the SONATE triple cube nano-satellite[J]. Aerospace, 2019, 6(10): 105. doi: 10.3390/aerospace6100105 [3] 姜连祥, 李华旺, 杨根庆, 等. 航天器自主故障诊断技术研究进展[J]. 宇航学报, 2009, 30(4): 28-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YHXB200904002.htmJIANG L X, LI H W, YANG G Q, et al. Research progress of spacecraft autonomous fault diagnosis technology[J]. Acta astronautics Sinica, 2009, 30(4): 28-34(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YHXB200904002.htm [4] XU B, YIN X, YIN X G, et al. Fault diagnosis of power systems based on temporal constrained fuzzy Petri nets[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 101895-101904. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2930545 [5] LEFEBVRE D. Fault diagnosis and prognosis with partially observed stochastic Petri nets[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers. Part O: Journal of Risk and Reliability, 2014, 228(4): 382-396. doi: 10.1177/1748006X14522221 [6] AN R M, LIANG W. Unobservable fuzzy Petri net diagnosis technique[J]. Aircraft Engineering and Aerospace Technology, 2013, 8(3): 215-221. [7] AMMOUR R, LECLERCQ E, SANLAVILLE E, et al. Faults prognosis using partially observed stochastic Petri-nets: An incremental approach[J]. Discrete Event Dynamic Systems, 2018, 28(2): 247-267. doi: 10.1007/s10626-017-0252-y [8] 郭栋, 熊文真, 徐建新, 等. 基于变精度粗糙集与量子贝叶斯网络的变压器故障诊断研究[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2017, 34(2): 93-99. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYRJ201702016.htmGUO D, XIONG W Z, XU J, et al. Research on transformer fault diagnosis based on variable precision rough set and quantum Bayesian network[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2017, 34(2): 93-99(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYRJ201702016.htm [9] 刘久富, 张治国, 郑锐, 等. 双组元推进系统的部分可观时间Petri网故障诊断[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(6): 1337-1344. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTYD201806021.htmLIU J F, ZHANG Z G, ZHENG R, et al. Fault diagnosis of bipropellant propulsion system using partially observed time Petri nets[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(6): 1337-1344(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTYD201806021.htm [10] LEMM J C. Bayesian approach to inverse time-dependent quantum mechanics[J]. Physics Letters A, 2000, 276(1): 19-24. [11] MOREIRA C, WICHERT A. Exploring the relations between quantum-like Bayesian networks and decision-making tasks with regard to face stimuli[J]. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 2017, 78: 86-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jmp.2016.10.004 [12] YI Y H. Fault diagnosis based on Bayesian Petri nets[J]. Sensors and Transducers, 2014, 179(9): 114-120. [13] CABASINO M P, GIUA A, SEATZU C. Diagnosability of discrete event systems using labeled Petri nets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2014, 11(1): 144-153. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2013.2289360 [14] DON M G, KHAN F. Dynamic process fault detection and diagnosis based on a combined approach of hidden Markov and Bayesian network model[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 201: 82-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2019.01.060 [15] SAHU A R, PALEI S K. Real-time fault diagnosis of HEMM using Bayesian network: A case study on drag system of dragline[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2020, 118: 104917. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2020.104917 [16] DECLERCK P, BONHOMMME P. State estimation of timed labeled Petri nets with unobservable transitions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2014, 11(1): 103-110. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2013.2290314 [17] BASILE F, CORDONE R, PIRODDI L. A branch and bound approach for the design of decentralized supervisors in Petri net models[J]. Automatica, 2015, 52: 322-333. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.12.004 [18] SHEN Q, QIU J, LIU G, et al. Intermittent fault' s parameter framework and stochastic Petri net based formalization model[J]. Eksploatacja I Niezawodnosc-Maintenance and Reliability, 2016, 18(2): 210-217. doi: 10.17531/ein.2016.2.8 [19] WANG L, CHEN Q, GAO Z, et al. Knowledge representation and general Petri net models for power grid fault diagnosis[J]. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2015, 9(9): 866-873. [20] ZHANG Z D, ZHU J L, PAN F. Fault detection and diagnosis for data incomplete industrial systems with new Bayesian network approach[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 24(3): 500-511. doi: 10.1109/JSEE.2013.00058 [21] PENSAR J, NYMAN H, LINTUSAARI J, et al. The role of local partial independence in learning of Bayesian networks[J]. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 2016, 69: 91-105. doi: 10.1016/j.ijar.2015.11.008 [22] YOON S. In-situ sensor calibration in an operational air-handling unit coupling autoencoder and Bayesian inference[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2020, 221: 110026. [23] OMOREGBEE H O, HEYNS P S. Fault detection in roller bearing operating at low speed and varying loads using Bayesian robust new hidden Markov model[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2018, 32(9): 4025-4036. doi: 10.1007/s12206-018-0802-8 [24] 鲁峰, 黄金泉, 吕怡秋, 等. 基于非线性自适应滤波的发动机气路部件健康诊断方法[J]. 航空学报, 2013, 34(11): 2529-2538. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKXB201311011.htmLU F, HUANG J Q, LV Y Q, et al. Aircraft engine gas-path components health diagnosis based on nonlinear adaptive filters[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2013, 34(11): 2529-2538(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKXB201311011.htm [25] 陈金豹, 翟国富, 王淑娟, 等. 航天电子设备多余物检测信号特征的影响因素分析[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2013, 35(4): 889-894. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTYD201304038.htmCHEN J B, ZHAI G F, WANG S J, et al. Factors affecting characteristics of acoustic signals in particle impact noise detection for aerospace devices[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 35(4): 889-894(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTYD201304038.htm [26] SHARDA B, BANERJEE A. Robust manufacturing system design using multi objective genetic algorithms, Petri nets and Bayesian uncertainty representation[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2013, 32(2): 315-324. [27] ZHU M N, HAN G, GUO H. Optimized fault diagnosis based on FMEA-style CBR and BN for embedded software system[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 94(9): 3441-3453. [28] RATH Y, GLIELMO A, BOOTH G H. A Bayesian inference framework for compression and prediction of quantum states[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2020, 153(12): 124108. [29] HUANG Z M, YANG L, JIANG W. Uncertainty measurement with belief entropy on the interference effect in the quantum-like Bayesian networks[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2019, 347: 417-428. [30] PIENAAR J. Quantum causal models via quantum Bayesianism[J]. Physical Review A, 2020, 101(1): 012104. -







 下载:
下载: