-
摘要:
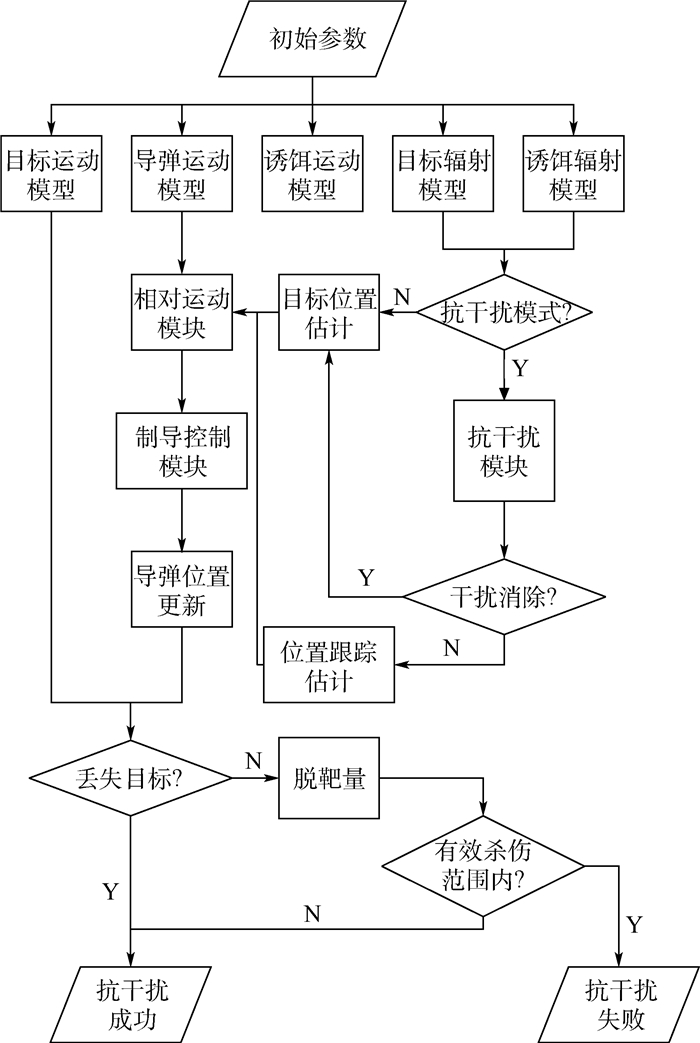
为了分析空空导弹在红外抗干扰过程中, 各干扰量与脱靶量之间的耦合关系, 利用红外抗干扰试验仿真平台, 通过设置干扰量获得海量数据, 构建数据立方体对海量数据进行数据预处理, 同时统计出数据集中各事务的支持度计数, 将处理后的数据利用FP-Growth关联规则算法挖掘干扰量与脱靶量之间的关联规则。通过对关联规则的分析得到:导弹进入角与弹目距离是影响导弹脱靶量大小的主要因素, 各个干扰量之间不能随意组合, 应该根据导弹来袭方向、目标机动方式选择诱饵投掷策略, 否则干扰效果会大大下降。同时设置一组对比试验, 验证基于数据立方体的FP-Growth算法处理高维数的脱靶量数据, 拥有较高的挖掘效率。
-
关键词:
- 数据立方体 /
- 数据处理 /
- FP-Growth算法 /
- 关联规则 /
- 红外抗干扰
Abstract:This study aims at analyzing the coupling relationship between disturbance variables and miss distance of air-to-air missiles in infrared anti-jamming. Massive data are obtained by setting disturbance variables through an experimental simulation platform. The data cube is then constructed to preprocess the massive data and compute the support count of each transaction. The processed data are used to mine the association rules between disturbance variables and miss distance by FP-Growth algorithm. Analysis of the association rules show that the entry angle of the missile and the distance between the missile and the target are the main factors for miss distance. The disturbance variables cannot be combined freely, but should be selected according to the attack direction of the missile and the target maneuver mode. Otherwise, the jamming effect will be greatly reduced. A group of comparative experiments is also set up to verify the high efficiency of FP-Growth algorithm based on the data cube in processing the miss distance data with a high dimension.
-
Key words:
- data cube /
- data processing /
- FP-Growth algorithm /
- association rule /
- infrared anti-jamming
-
表 1 干扰量参数设定范围
Table 1. Range of disturbance variable parameters
干扰量 参数 取值设定 诱饵投掷参数 投掷总数Ns/个 12, 24, 36, 48 每次投掷个数Ne/个 1, 2 每组投掷个数Nf/个 4, 6, 12 投掷时机Tl/s 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5 投掷组内间隔Ti/s 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5 投掷组间间隔Te/s 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0 投掷速度Vf/(m·s-1) 10, 20, 30, 40 水平投掷角度θl/(°) 0, 30, 60, 90, 120, 150 垂直投掷角度θv/(°) -90, -60, 0,30,60, 90 弹目相对态势 进入角θm/(°) 10, 20, 30, 70, 80, 90, 130, 140, 150 弹目距离Dr/km (0, 3], (3, 4], (4, 5], (5, 6], (6, 7], (7, 8], (8, 9], (9, 10] 表 2 MD1立方体的1-D关系
Table 2. 1-D relation table of MD1 cube
PIB MTRP TMM 数目 Ns1 * * 10 656 ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ * θm1 * 5 556 ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ * * 1 9 878 注:*代表可取任意参数。 表 3 MD1立方体的2-D关系
Table 3. 2-D relation table of MD1 cube
PIB MTRP TMM 数目 Ns1 θm1 * 3 078 ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ * θm1 1 2 043 ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ Ns1 * 1 4 028 ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ 注:*代表可取任意参数。 表 4 MD1立方体的3-D关系
Table 4. 3-D relation table of MD1 cube
PIB MTRP TMM 数目 Ns1 θm1 1 1 059 ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ 注:*代表可取任意参数。 表 5 干扰量参量编号
Table 5. Disturbance variable numbering
干扰量 参数 取值设定 诱饵投掷参量 Ns/个 12(4), 24(5), 36(6), 48(7) Ne/个 1(8), 2(9) Nf/个 4(10), 6(11), 12(12) Tl/s 0.5(13), 1(14), 1.5(15), 2(16), 2.5(17) Ti/s 0.1(18), 0.2(19), 0.3(20), 0.4(21), 0.5(28.2) Te/s 0.2(23), 0.4(24), 0.6(25), 0.8(26), 1(27) Vf/(m·s-1) 10(28), 20(29), 30(30), 40(31) θl/(°) 0(32), 30(33), 60(34), 90(35), 120(36), 150(37) θv/(°) -90(38), -60(39), 0(40), 30(41), 60(42), 90(43) 弹目相对态势 θm/(°) 10(44), 20(45), 30(46), 70(47), 80(48), 90(49), 130(50), 140(51), 150(52) Dr/km (0, 3](53), (3, 4](54), (4, 5](55), (5, 6](56), (6, 7](57), (7, 8](58), (8, 9](59), (9, 10](60) 目标机动 TMM 无机动(61), 左转弯(62), 右转弯(63), 跃升(64) 脱靶量 MD/m MD1(1), MD1(2), MD1(3) 注: 括号内数字为编号。 表 6 MD1部分内部关联规则(MD1 < 12 m)
Table 6. Inner association rules of MD1 (MD1 < 12 m)
序号 Conf Sup Kulc IR 规则 1 0.989 0.011 0.571 0.968 13, 52, 59→23, 1 2 0.976 0.006 0.538 0.925 37, 47, 53→17, 1 3 0.972 0.007 0.549 0.901 21, 37, 53→17, 1 4 0.966 0.005 0.533 0.935 5, 43, 53→17, 1 5 0.961 0.009 0.559 0.933 9, 36, 53→17, 1 表 7 MD2部分内部关联规则(12 m≤MD2 < 16 m)
Table 7. Inner association rules of MD2 (12 m≤MD2 < 16 m)
序号 Conf Sup Kulc IR 规则 1 0.996 0.005 0.513 0.975 34, 53→61, 2 2 0.988 0.006 0.512 0.975 44, 56→8, 2 3 0.975 0.008 0.517 0.967 6, 32→8, 2 表 8 MD3部分内部关联规则(MD3≥16 m)
Table 8. Inner association rules of MD3 (MD3≥16 m)
序号 Conf Sup Kulc IR 规则 1 0.986 0.006 0.555 0.918 17, 60, 62→27, 3 2 0.977 0.006 0.706 0.588 17, 60, 62→22, 3 3 0.984 0.006 0.511 0.978 10, 13, 53→9, 3 4 0.965 0.005 0.543 0.988 13, 24, 53→10, 3 表 9 部分方体间外联关联规则
Table 9. Part of outer association rules
序号 Conf Sup Kulc IR 规则 1 0.986 0.010 0.508 0.984 17, 26, 53→1 2 0.983 0.006 0.505 0.990 52, 53, 63→1 3 0.980 0.006 0.505 0.991 32, 44, 64→1 4 0.973 0.006 0.505 0.990 11, 52, 64→1 5 0.972 0.007 0.506 0.988 37, 49, 59, 64→1 6 0.992 0.005 0.510 0.979 17, 34, 63→2 7 0.987 0.005 0.511 0.978 52, 55, 61→2 8 0.977 0.006 0.512 0.977 35, 52, 61→2 9 0.975 0.007 0.514 0.973 44, 58, 64→2 10 0.971 0.006 0.513 0.974 33, 48, 63→2 11 0.996 0.009 0.537 0.927 50, 58, 61→3 12 0.987 0.008 0.531 0.937 9, 52, 58, 62→3 13 0.978 0.009 0.537 0.927 8, 51, 58→3 14 0.974 0.009 0.534 0.932 35, 51, 58→3 15 0.972 0.007 0.527 0.946 52, 60, 63→3 16 0.967 0.009 0.537 0.927 49, 54, 64→3 表 10 不同数据量下算法效率对比
Table 10. Comparison of algorithm efficiency with different data volumes
数据量 TFP/s TDC_FP/s 1 000 56.4 55.9 5 000 534.6 108.7 10 000 5 063.7 305.3 15 000 9 886.2 502.9 20 000 20 043.2 745.8 50 000 * 1 034.9 注:*代表数据量过大,结果未获得。 -
[1] 李立坤. 精确制导技术现状及发展方向[J]. 航空兵器, 2004(1): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5048.2004.01.001LI L K. Present situation and development direction of precision guidance technology[J]. Aero Weaponry, 2004(1): 1-4(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5048.2004.01.001 [2] 王晓铭, 王玫. 防空导弹武器抗干扰试验技术[J]. 上海航天, 2013, 30(2): 34-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1630.2013.02.008WANG X M, WANG M. ECCM test technology for antiaircraft missile weapon system[J]. Aerospace Shanghai, 2013, 30(2): 34-38(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1630.2013.02.008 [3] 胡朝晖, 闫杰. 红外空空导弹抗干扰性能评估方法研究[J]. 空军工程大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 25(3): 45-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJGC200804012.htmHU Z H, YAN J. An evaluation method of infrared missile countermeasures performance[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University(Natural Science Edition), 2008, 25(3): 45-52(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJGC200804012.htm [4] 王涛, 王祥. 红外导弹抗干扰能力多维度评估方法[J]. 红外技术, 2014, 36(7): 573-576. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWJS201407011.htmWANG T, WANG X. An evaluation method with five dimensions for infrared missile anti-jamming[J]. Infrared Technology, 2014, 36(7): 573-576(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWJS201407011.htm [5] 李慎波, 李韬锐, 童中翔, 等. 导弹战术参数对面源红外诱饵干扰效能影响[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2018, 47(7): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYJ201807019.htmLI S B, LI T R, TONG Z X, et al. Influence of tactical parameters of missile on jamming effectiveness of surface source infrared decoy[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2018, 47(7): 1-10(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYJ201807019.htm [6] 牛得清, 伍友利, 徐洋, 等. 点源红外诱饵干扰下环境复杂度量化建模[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2020, 49(2): 211-219. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYJ202002028.htmNIU D Q, WU Y L, XU Y, et al. Quantification modeling for environmental complexity under point source infrared decoy interference[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(2): 211-219(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYJ202002028.htm [7] 马潮, 陆志沣, 余海鸣, 等. 红外成像导引头抗干扰性能评估方法研究[J]. 空天防御, 2018, 1(4): 44-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTFY201804007.htmMA C, LU Z F, YU H M, et al. Research on evaluation method of anti-interference performance of infrared seeker[J]. Air & Space Defense, 2018, 1(4): 44-47(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTFY201804007.htm [8] 葛辰杰, 陆志沣, 洪泽华, 等. 基于支持向量回归与多核集成的红外成像导引头抗干扰性能评估方法[J]. 上海航天, 2019, 36(5): 94-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHHT201905011.htmGE C J, LU Z F, HONG Z H, et al. Anti-interference capability evaluation based on SVM regression and multi-kernel boosting[J]. Aerospace Shanghai, 2019, 36(5): 94-98(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHHT201905011.htm [9] 杨开, 李少毅, 张凯, 等. 基于朴素贝叶斯分类器的空中红外目标抗干扰识别方法研究[J]. 飞控与探测, 2019, 2(4): 62-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FKTC201904007.htmYANG K, LI S Y, ZHANG K, et al. Research on anti-jamming recognition method of aerial infrared target based on naive Bayes classifier[J]. Flight Control & Detection, 2019, 2(4): 62-70(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FKTC201904007.htm [10] 周卫文, 康美玲, 周泽强. 红外诱饵对成像制导导弹影响规律研究[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2019, 48(12): 118-124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYJ201912015.htmZHOU W W, KANG M L, ZHOU Z Q. Research of infrared flares influence mechanism on the imaging guidance missile[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2019, 48(12): 118-124(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYJ201912015.htm [11] 张志波, 童中翔, 王超哲, 等. 视线方向飞机红外辐射特性建模与仿真[J]. 激光与红外, 2013, 43(8): 890-895. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGHW201308011.htmZHANG Z B, TONG Z X, WANG C Z, et al. Modeling and simulation of airplane infrared characteristic along the sightline[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2013, 43(8): 890-895(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGHW201308011.htm [12] LI S, ZHANG K, YIN J, et al. A study on IR target recognition approach in aerial jamming environment based on Bayesian probabilistic model[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 50300-50316. [13] XU Y, FANG Y W, WU Y L, et al. Association rule mining for the infrared countermeasure by the PF-Growth algorithm[C]//Proceedings of the 37th China Control Conference, 2018: 8043-8048. [14] FREDERIC G, LAKSHMANAN L V S. nD-SQL: A multi-dimensional language for interoperability and OLAP[C]//International Conference on VLDB, 1998: 134-145. [15] 冯玉才, 向隆刚. 维上带层次数据立方的自底向上计算[J]. 小型微型计算机系统, 2004(8): 1477-1481. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXWX200408015.htmFENG Y C, XIANG L G. Bottom-up computation of data cube with hierarchy along dimension[J]. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems, 2004(8): 1477-1481(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXWX200408015.htm [16] TAN P N, STEINBACH M, KUMAR V. Association analysis: Basic concepts and algorithms[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Posts and Telecom Press, 2011: 200-240. -







 下载:
下载: