Pseudo loosely-integrated navigation of low-cost MEMS-INS/GPS with insufficient observable satellites
-
摘要:
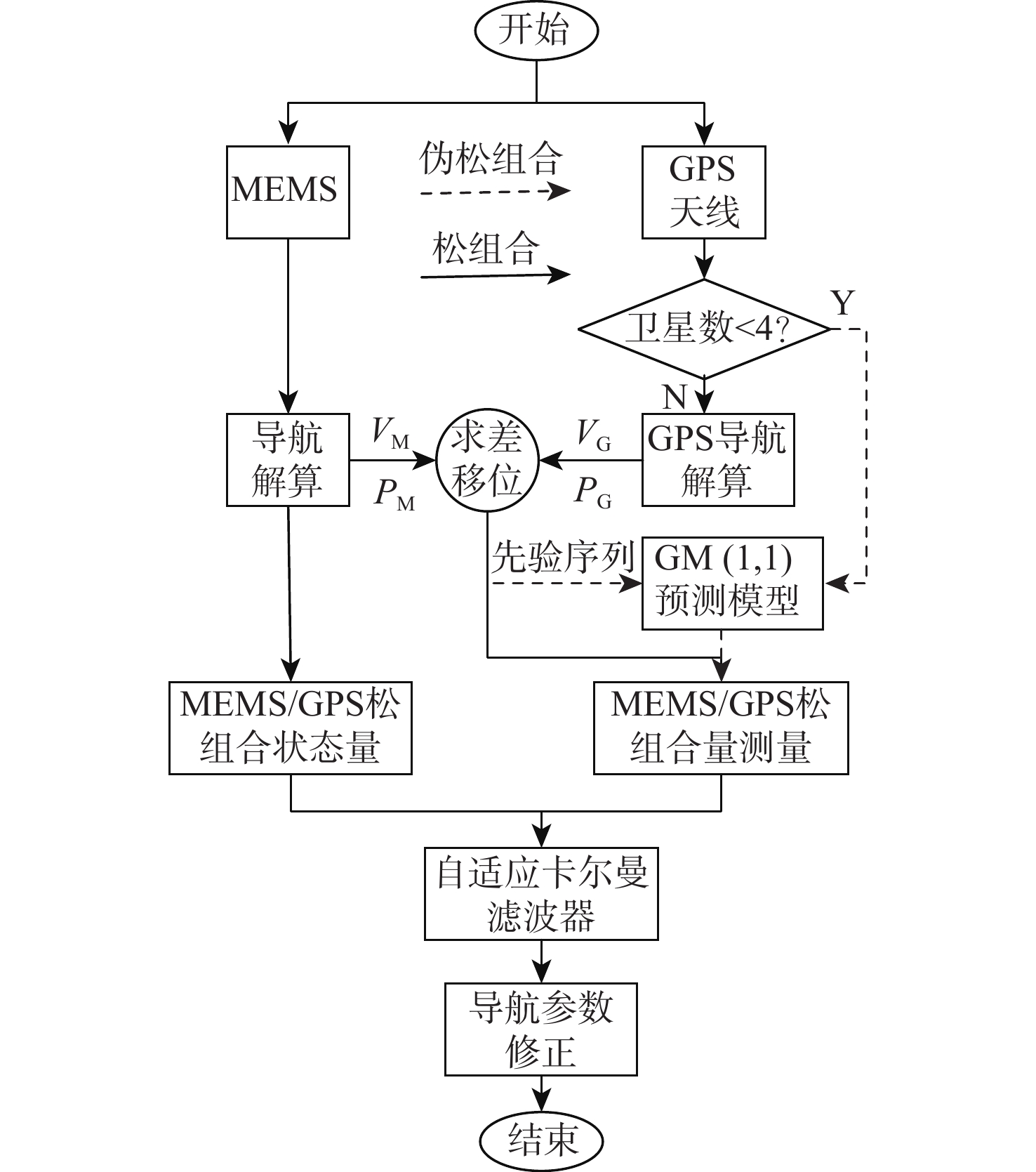
为了解决GPS可观测卫星不足情况下低成本微电子机械-惯性导航系统/全球定位系统(MEMS-INS/GPS)组合导航精度维持问题,提出基于灰色模型和自适应卡尔曼滤波的MEMS-INS/GPS伪松组合导航方法。以MEMS-INS/GPS松组合导航模式为框架,建立了伪松组合导航系统的状态空间模型。基于MEMS-INS/GPS的历史观测数据,使用灰色模型对MEMS-INS/GPS观测差值进行预测,称为系统伪观测量。当GPS可观测卫星充分时,使用噪声自适应估计卡尔曼滤波对MEMS-INS/GPS进行松组合导航;当GPS可观测卫星不足时,使用噪声自适应估计卡尔曼滤波依据系统伪观测量,将MEMS-INS/GPS进行伪松组合导航。以车载低成本MEMS-INS/GPS组合导航系统为例进行仿真和实验验证,结果表明:当GPS可观测卫星不足时,传统的MEMS-INS/GPS松组合导航精度迅速下降并发散,而MEMS-INS/GPS伪松组合导航精度与GPS正常工作时的导航精度相差不大,维持了较高精度的导航状态。
Abstract:To solve the problem of accuracy maintenance of low-cost MEMS-INS/GPS integrated navigation under the condition of insufficient observable GPS satellites, a MEMS-INS/GPS pseudo loosely-integrated navigation method is proposed based on grey model and adaptive Kalman filter. In the framework of the proposed navigation mode, a state space model of integrated navigation system is established. Based on the MEMS-INS/GPS historical observation data, grey model is used to predict the difference between GPS and MEMS-INS, and this prediction is named system pseudo-observation. When the observable GPS satellites are sufficient, noise adaptive estimating Kalman filter is used for MEMS-INS/GPS integrated navigation; otherwise, this filter is used for MEMS-INS/GPS pseudo loosely-integrated navigation based on the system pseudo-observation. An example of low-cost MEMS-INS/GPS integrated vehicle navigation system is used in simulation and experimental verification. The results show that when the observable GPS satellites are insufficient, the traditional MEMS-INS/GPS loosely-integrated navigation decreases in accuracy rapidly and diverges, but the MEMS-INS/GPS pseudo loosely-integrated navigation is not significantly different from the normal GPS navigation in terms of accuracy, maintaining a high precision navigation state.
-
表 1 灰色模型预测精度等级
Table 1. Prediction accuracy grade of grey model
模型精度等级 小误差概率$ p $ 后验差比值$ C $ 1级(好) $ p \geqslant 0.95 $ $ C \leqslant 0.35 $ 2级(合格) $ 0.80 \leqslant p \lt 0.95 $ $ 0.35 \lt C \leqslant 0.5 $ 3级(勉强) $ 0.70 \leqslant p \lt 0.80 $ $ 0.5 \lt C \leqslant 0.65 $ 4级(不合格) $ p \lt 0.70 $ $ C \gt 0.65 $ 表 2 MEMS仪表性能指标参数
Table 2. Property index parameters of MEMS
MEMS陀螺仪 MEMS加速度计 GPS 量程/
((°)·s−1)零偏/
((°)·s−1)零偏稳定性/
((°)·s−1)零偏重复性/
((°)·s−1)量程 零偏 零偏稳定性 零偏重复性 授时精度/
ns位置精度
(CEP DGPS)/m速度精度/
(m·s−1)数据更新率/
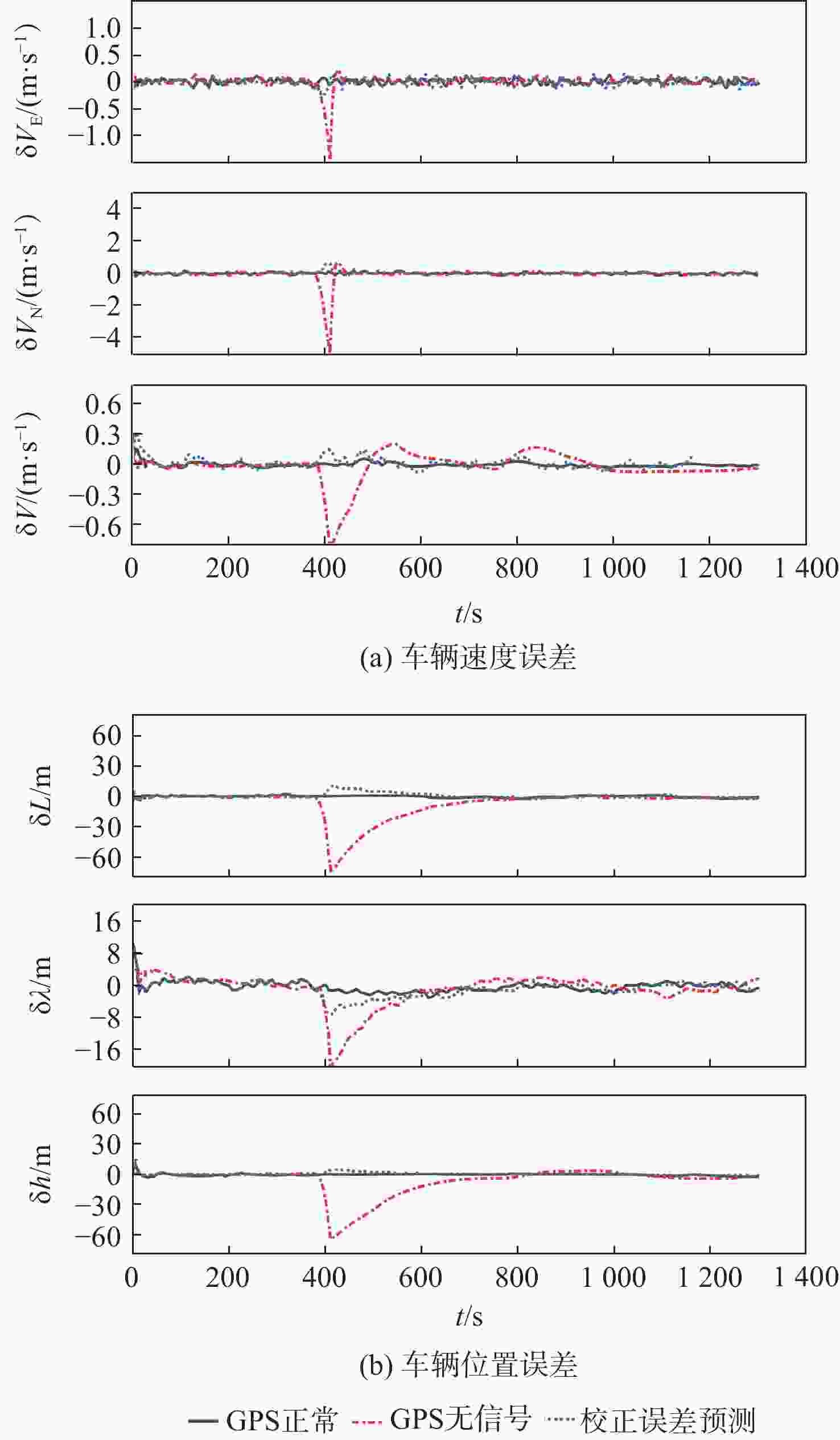
Hz注:CEP为原概率偏差,DGPS是差分GPS工作模式。 表 3 380~410 s位置误差统计
Table 3. Statistics of location error among 380~410 s
m 双测状态 经度 纬度 高度 均值 SD 均值 SD 均值 SD 卫星正常 0.20818 1.0587 −0.25183 1.19667 −0.37409 1.21927 卫星不足 −6.85383 14.33106 −0.98421 4.06205 −6.51393 13.87575 观测量预测 0.81243 2.37502 −0.72929 1.89076 0.25046 1.31343 表 4 380~410 s速度误差统计
Table 4. Statistics of speed error among 380~410 s
m/s 双测状态 ${V_{\rm{E}}}$ ${V_{\rm{N}}}$ ${V_{\rm{U}}}$ 均值 SD 均值 SD 均值 SD 卫星正常 0.01727 0.04224 −0.00426 0.05191 −0.00291 0.02113 卫星不足 0.00796 0.12605 −0.06687 0.44914 −0.02372 0.14846 观测量预测 0.01221 0.06536 0.00564 0.09993 0.00835 0.05092 表 5 伪松组合导航下的最大位置误差
Table 5. Maximum position error under pseudo loosely-integrated navigation
参数 时刻/s 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 最大误差/m 3.6 4.1 5.0 6.2 7.6 9.2 12.2 15.7 19.8 23.9 表 6 卫星失效范围内速度误差统计
Table 6. Statistics of speed error among satellite failure ramge
m/s 实验 ${V_{\rm{E}}}$ ${V_{\rm{N}}}$ 均值 SD 均值 SD 实验2 3.25361 5.78239 2.63561 4.64385 实验3 0.06327 0.09532 0.00863 0.10936 表 7 卫星失效范围内位置误差统计
Table 7. Statistics of location error among satellite failure ramge
m 实验 经度 纬度 均值 SD 均值 SD 实验2 8.06001 18.21367 5.34918 10.40109 实验3 1.01342 2.63926 1.01232 2.20167 -
[1] 宋丽君, 李喆, 付强文, 等. 基于格网框架的极区SINS/GPS组合导航算法研究[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2019, 31(8): 1683-1691. doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.17-0270SONG L J, LI Z, FU Q W, et al. Research on SINS/GPS integrated navigation system based on grid reference frame for transpolar aircraft[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2019, 31(8): 1683-1691(in Chinese). doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.17-0270 [2] 龙腾, 穆荣军, 苏炳志, 等. 双天线GPS/MEMS-INS深组合导航方法研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2021, 42(1): 92-102. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2021.01.010LONG T, MU R J, SU B Z, et al. Research on dual-antenna GPS/MEMS-INS deeply-integrated navigation approach[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2021, 42(1): 92-102(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2021.01.010 [3] HANSEN J M, JOHANSEN T A, SOKOLOVA N, et al. Nonlinear observer for tightly coupled integrated inertial navigation aided by RTK-GNSS measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2018, 27(3): 1084-1099. [4] BITAR N A, GAVRILOV A I. Comparative analysis of fusion algorithms in a loosely-coupled integrated navigation system on the basis of real data processing[J]. Gyroscopy and Navigation, 2019, 10(4): 231-244. doi: 10.1134/S2075108719040023 [5] 张复建, 单斌, 杨波, 等. MIMU/GPS系统在卫星不足时的导航算法研究[J]. 现代防御技术, 2019, 47(2): 30-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2019.02.06ZHANG F J, SHAN B, YANG B, et al. Research on the MIMU/GPS integrated navigation system under the condition of the lack of satellite[J]. Modern Defense Technology, 2019, 47(2): 30-35(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2019.02.06 [6] 刘崇锦. GNSS/INS组合导航定位数据处理算法研究[D]. 西安: 中国科学院国家授时中心, 2020.LIU C J. Research on data processing algorithm for GNSS/INS integrated navigation and positioning [D]. Xi’an: National Time Service Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020 (in Chinese). [7] 李哲, 刘强, 王箫杨. GPS/MEMS-IMU松耦合导航系统的设计[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2018, 38(12): 52-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2018.12.013LI Z, LIU Q, WANG X Y. Design of GPSIMEMS-IMU loosely coupled navigation system[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2018, 38(12): 52-56(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2018.12.013 [8] BALOCHIAN S, BALOOCHIAN H. Improving grey prediction model and its application in predicting the number of users of a public road transportation system[J]. Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2020, 30(1): 104-114. doi: 10.1515/jisys-2019-0082 [9] 陈静, 陈友军. 近似非齐次指数递增序列的IANGM(1, 1, k)模型构造[J]. 统计与决策, 2020, 36(20): 24-27.CHEN J, CHEN Y J. Construction of IANGM(1, 1, k) model with approximate non-homogeneous exponential incremental sequence[J]. Statistics & Decision, 2020, 36(20): 24-27(in Chinese). [10] 梁松, 闫明, 陈卓, 等. 基于灰色估计和多项式变异理论的附件传动系统在随机载荷作用下的疲劳寿命预测[J]. 航空动力学报, 2020, 35(2): 432-439. doi: 10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.2020.02.022LIANG S, YAN M, CHEN Z, et al. Fatigue life prediction under random loading for accessory transmission system based on grey estimation and polynomial mutation theory[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2020, 35(2): 432-439(in Chinese). doi: 10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.2020.02.022 [11] URRUTIA J D, MENESES J L, ANTONIO G V A. Predicting future monthly electricity consumption in the philippines using markov-chain grey model[J]. Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 2019, 12(33): 1-44. [12] 吕明明, 刘荣忠, 侯远龙, 等. 一种光电跟踪平台共轴控制的目标运动滤波方法[J]. 兵工学报, 2019, 40(3): 548-554. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2019.03.013LV M M, LIU R Z, HOU Y L, et al. A target motion filtering method for on-axis control of electro-optical tracking platform[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2019, 40(3): 548-554(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2019.03.013 [13] 吴发友, 王林峰, 翁其能. 灰色预测模型在隧道洞顶楔形体稳定性预测中的应用[J]. 计算机科学, 2019, 46(5): 327-330. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2019.05.051WU F Y, WANG L F, WENG Q N. Application of grey prediction model in prediction of stability of wedge-shaped body of tunnel[J]. Computer Science, 2019, 46(5): 327-330(in Chinese). doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2019.05.051 [14] 郑江涛, 李四海, 刘士明, 等. 基于惯导和激光雷达的采煤机定位方法[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2020, 28(5): 595-602. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2020.05.005ZHENG J T, LI S H, LIU S M, et al. Positioning method of a shearer based on inertial navigation and lidar[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2020, 28(5): 595-602(in Chinese). doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2020.05.005 [15] PANNEKOUCKE O, RICHARD M, AABARIBAOUNE M E, et al. A methodology to obtain model-error covariances due to the discretization scheme from the parametric Kalman filter perspective[J]. Nonlinear Processes in Geophysics, 2021, 28(1): 1-22. doi: 10.5194/npg-28-1-2021 -







 下载:
下载: