-
摘要:
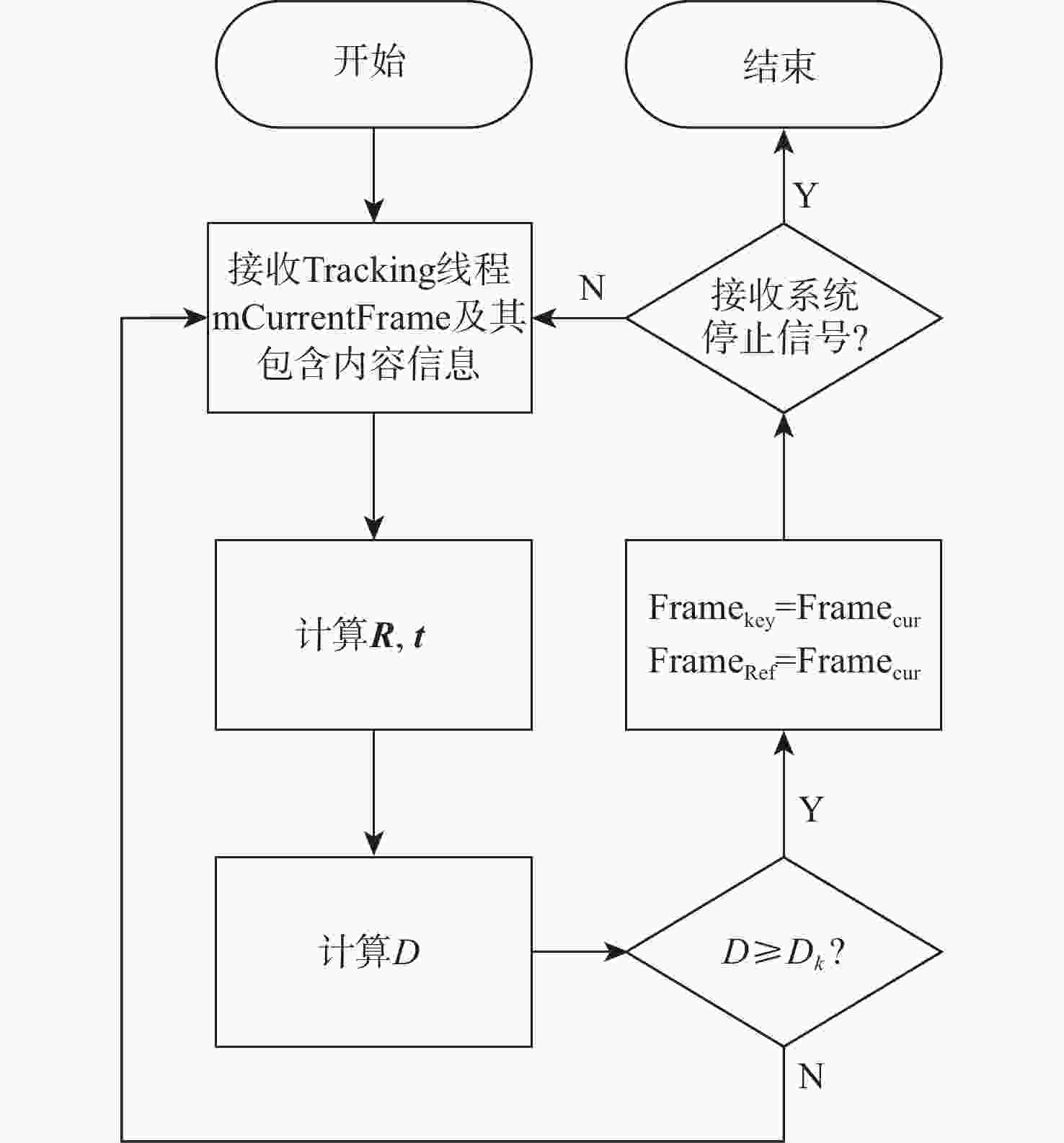
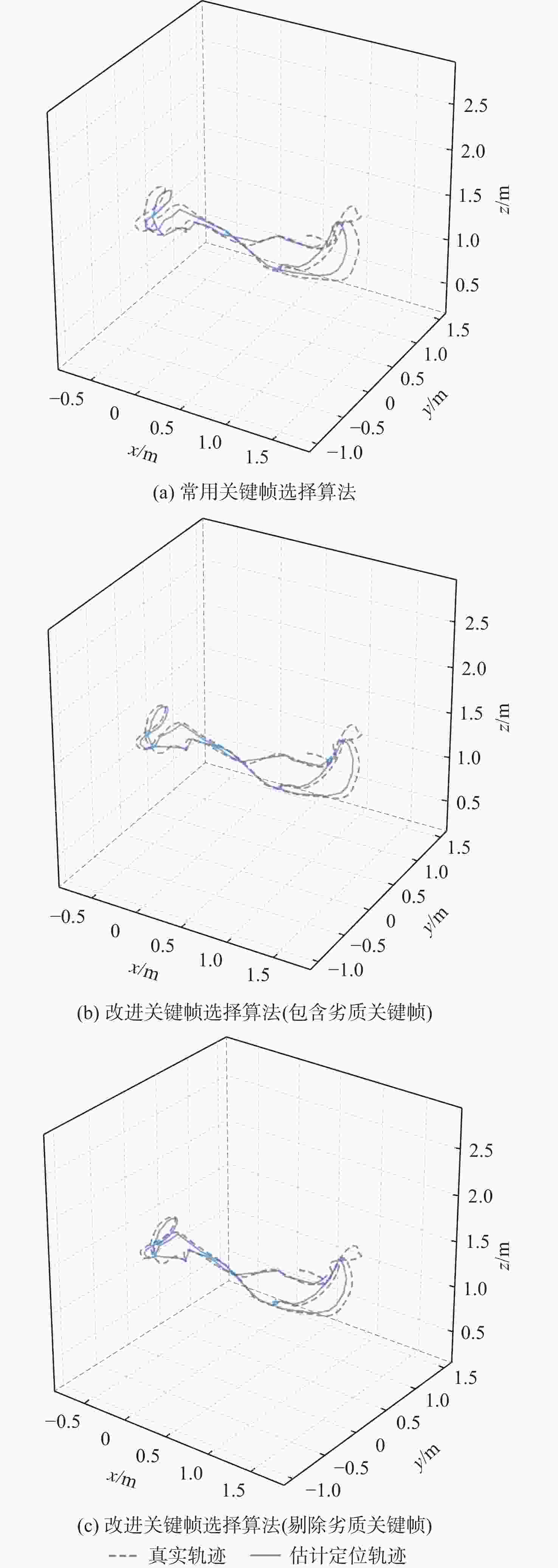
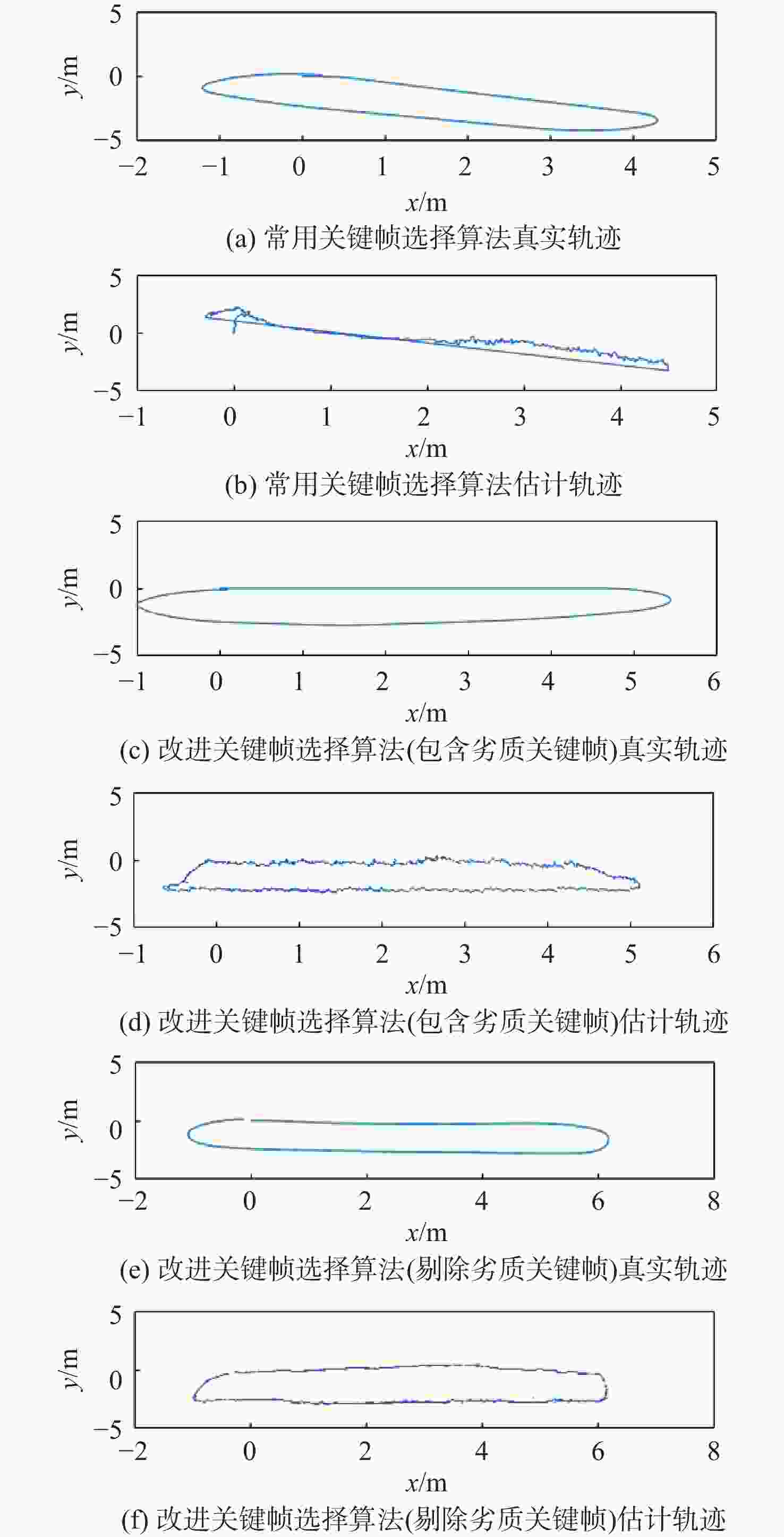
针对同时定位与建图(SLAM)算法精度不高且跟踪易失败的问题,提出了一种改进关键帧选择的ORB-SLAM2算法。通过ORB-SLAM2算法计算帧间相对位姿;在原有算法的基础上,增加旋转与平移量作为判定依据,决定是否创建新关键帧;针对移动机器人所安装的相机与机器人产生相对运动引发误拍摄,导致劣质关键帧生成的问题,设计了劣质关键帧剔除算法;基于RGB-D数据集与自主研发的移动机器人进行了实验验证。实验结果表明:改进的关键帧选择算法能够准确及时地选择关键帧,最优情况下定位误差约为原误差的51.9%,有效消除了相机与机器人之间相对运动产生的影响,直线误差仅为原误差的82.1%。改进算法能够有效提高定位精度,减少跟踪失败。
Abstract:To address the difficulties caused by the low accuracy and poor robustness of simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), an ORB-SLAM2 algorithm is proposed based on key frame selection. First, the relative pose between frames is calculated based on ORB-SLAM2. Second, to determine whether a new key frame should be created, rotation and translation values are added to the original algorithm, functioning as the judgement basis. Then, an inferior key frame removal algorithm is designed to solve the problem of inferior key frame generation which results from incorrect shooting caused by the relative movement between the robot and the camera installed in the self-developed mobile robot. Finally, experiments are carried out based on the RGB-D dataset and the developed mobile robot, verifying the outstanding performance of the proposed algorithm. The results show that the improved key frame selection algorithm can accurately and timely choose the key frame, and reduce tracking failures. In the most optimal case, the positioning error is about 51.9% of that of the original, while the linear error is about 82.1% of that of the original, which effectively eliminates the influence caused by relative motion between the camera and the robot. This research shows that the improved algorithm could effectively promote positioning accuracy and reduce tracking failures.
-
Key words:
- moving robot /
- ORB-SLAM2 /
- key frame selection /
- inferior key frame removal /
- positioning accuracy
-
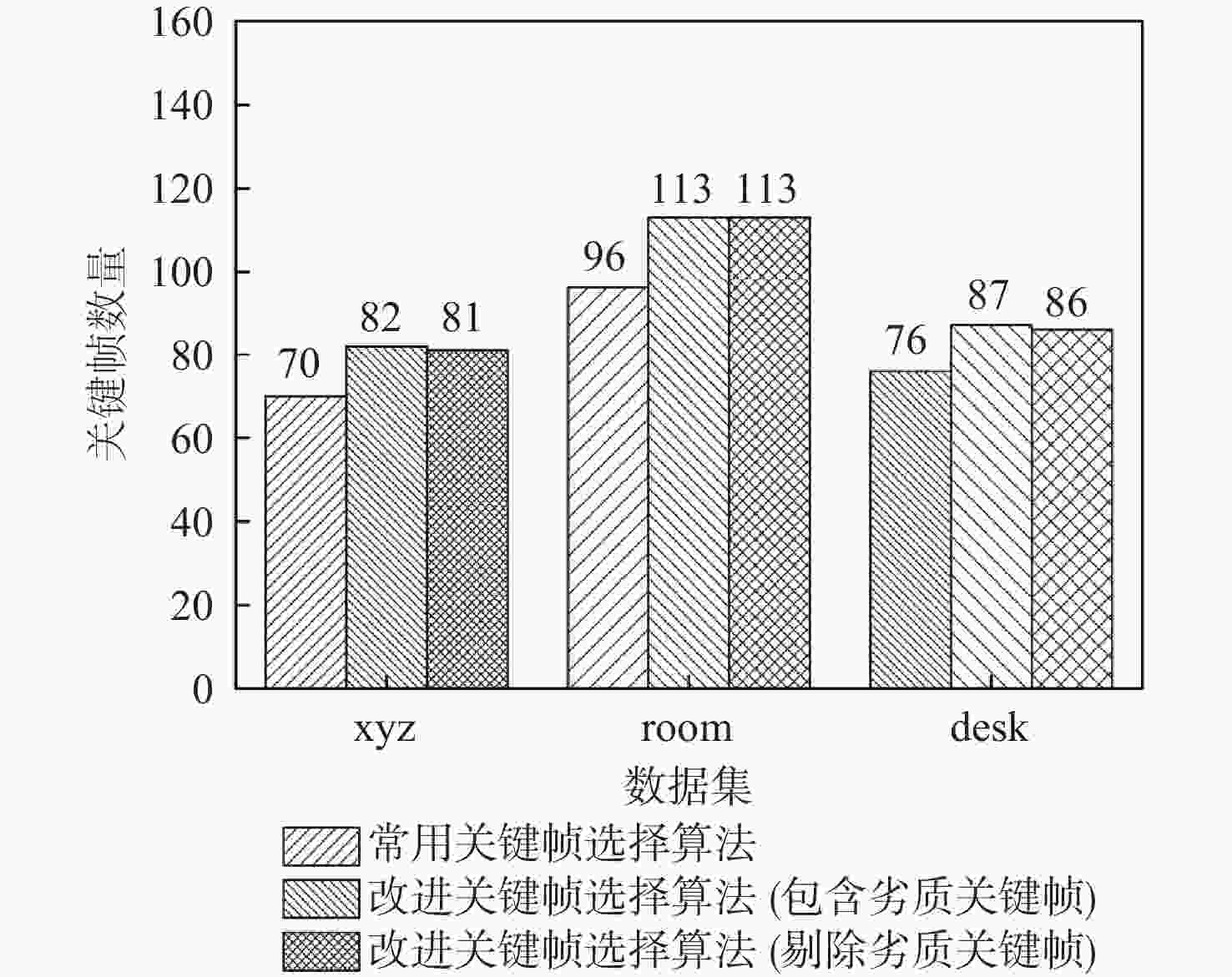
表 1 平均跟踪时间对比结果
Table 1. Comparison of mean tracking time
数据集 平均跟踪时间/ms 常用关键帧
选择算法包含劣质关键
帧的改进算法剔除劣质关键
帧的改进算法desk 39 45 51 xyz 46 51 57 room 30 31 36 表 2 最大绝对轨迹误差对比
Table 2. Maximum absolute trajectory error
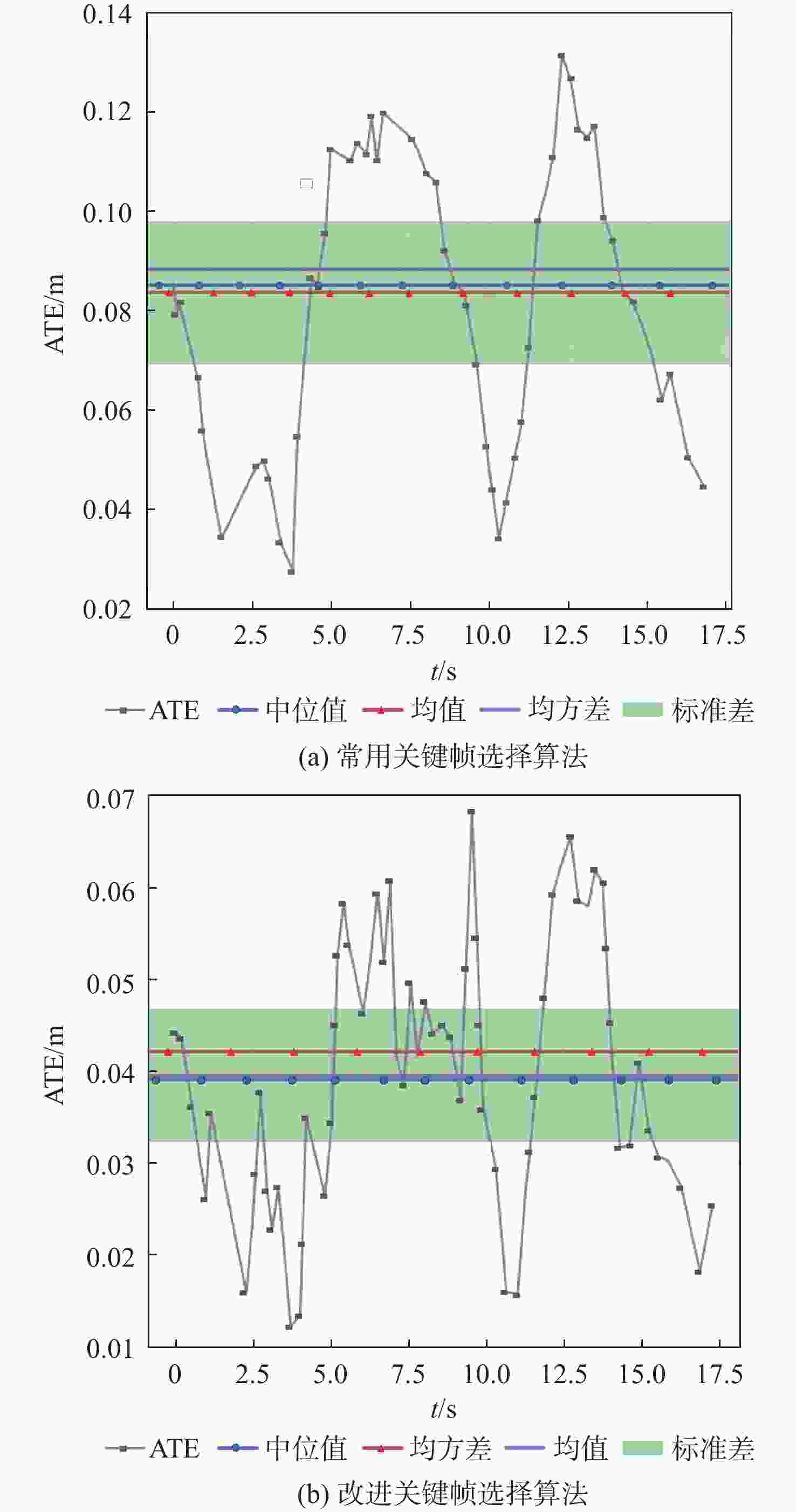
数据集 最大绝对轨迹误差/m 常用关键帧
选择算法包含劣质关键
帧的改进算法剔除劣质关键
帧的改进算法desk 0.131 0.064 0.062 xyz 0.124 0.097 0.097 room 0.202 0.125 0.130 表 3 平均位置误差
Table 3. Average position error
运动方式 平均位置误差/m 常用关键帧
选择算法包含劣质关键
帧的改进算法剔除劣质关键
帧的改进算法直线 0.209 0.202 0.164 转弯 0.964 0.565 0.543 回环 1.236 0.732 0.721 -
[1] JIANG W, YE G C, ZHOU D H. Dynamic model based energy consumption optimal motion planning for high-voltage transmission line mobile robot manipulator[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part K:Journal of Multi-body Dynamics, 2021, 253(1): 93-105. [2] 罗欣, 丁晓军. 地面移动作业机器人运动规划与控制研究综述[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2021, 53(1): 1-15. doi: 10.11918/201910067LUO X, DING X J. Research and prospective on motion planning and control of ground mobile manipulators[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021, 53(1): 1-15(in Chinese). doi: 10.11918/201910067 [3] 魏彤, 龙琛. 基于改进遗传算法的移动机器人路径规划[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(4): 703-711.WEI T, LONG C. Path planning for mobile robot based on improved genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(4): 703-711(in Chinese). [4] 翟敬梅, 刘坤, 徐晓. 室内移动机器人自主导航系统设计与方法[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2020, 26(4): 890-899.ZHAI J M, LIU K, XU X. Autonomous indoor navigation system of mobile robot[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2020, 26(4): 890-899(in Chinese). [5] FUNENTES P, RUIZ A, RENDON M. Visual simultaneous localization and mapping: A survey[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2012, 43(1): 55-81. [6] LI J Q, PEI L, ZHOU D P, et al. Attention-SLAM: A visual monocular SLAM learning from human gaze[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(5): 6408-6420. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3038432 [7] 王晨捷, 罗斌, 李成源, 等. 无人机视觉SLAM协同建图与导航[J]. 测绘学报, 2020, 49(6): 767-776.WANG C J, LUO B, LI C Y, et al. UAV visual SLAM collaborative mapping and navigation[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Crtographica Sinica, 2020, 49(6): 767-776(in Chinese). [8] GARCIA-FIDALGO E, ORTIZ A. Vision-based topological mapping and localization methods: A survey[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2015, 64: 1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2014.11.009 [9] TANG Y C, WANG C, LUO L, et al. Recognition and localization methods for vision-based fruit picking robots: A review[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 510-526. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00510 [10] ENGEL J, SCHOPS T, CREMERS D, et al. LSD-SLAM: Large-scale direct monocular SLAM[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2014, 8690: 834-849. [11] SAKAI T, YOSHIOKA M, INOUE K. Camera tracking improvement for LSD-SLAM system with 360-degree camera[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electronics, Information and Systems, 2020, 140(7): 800-809. doi: 10.1541/ieejeiss.140.800 [12] ENDRES F, HESS J, STURM J, et al. 3D mapping with an RGB-D camera[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2014, 30(1): 177-187. [13] MUR-ARTAL R, MOTIEL J M, TARDOS J D. ORB-SLAM: A versatile and accurate monocular SLAM system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2015, 31(5): 1147-1163. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2015.2463671 [14] MUR-ARTAL R, MOTIEL J M, TARDOS J D. ORB-SLAM2: An open-source slam system for monocular, stereo, and RGB-D cameras[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2017, 33(5): 1255-1262. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2017.2705103 [15] LIU J, SHAHROUDY A, PEREZ M, et al. NTU RGB-D: A large-scale benchmark for 3D human activity understanding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 42(10): 2684-2701. [16] 张括嘉, 张云洲, 吕光浩, 等. 基于局部语义拓扑图的视觉SLAM闭环检测[J]. 机器人, 2019, 41(5): 649-659.ZHANG K J, ZHANG Y Z, LV G H, et al. Loop closure detection based on local semantic topology for visual slam system[J]. Robot, 2019, 41(5): 649-659(in Chinese). [17] GARDENFORS P. Using event representations to generate robot semantics[J]. ACM Transactions on Human-Robot Interaction (THRI), 2019, 8(4): 1-21. [18] YANG G, CHEN Z, LI Y, et al. Rapid relocation method for mobile robot based on improved ORB-SLAM2 algorithm[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(2): 149. doi: 10.3390/rs11020149 [19] XIE P, SU W, LI B, et al. Modified keyframe selection algorithm and map visualization based on ORB-SLAM2[C]//2020 4th International Conference on Robotics and Automation Sciences (ICRAS). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 142-147. [20] CUI L, MA C, WEN F. Direct-ORB-SLAM: Direct monocular ORB-SLAM[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2019, 1345(3): 032016. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1345/3/032016 [21] POMERLEAU F, COLAS F, SIEGWART R. A review of point cloud registration algorithms for mobile robotics[J]. Foundations and Trends in Robotics, 2015, 4(1): 1-104. doi: 10.1561/2300000035 -







 下载:
下载: