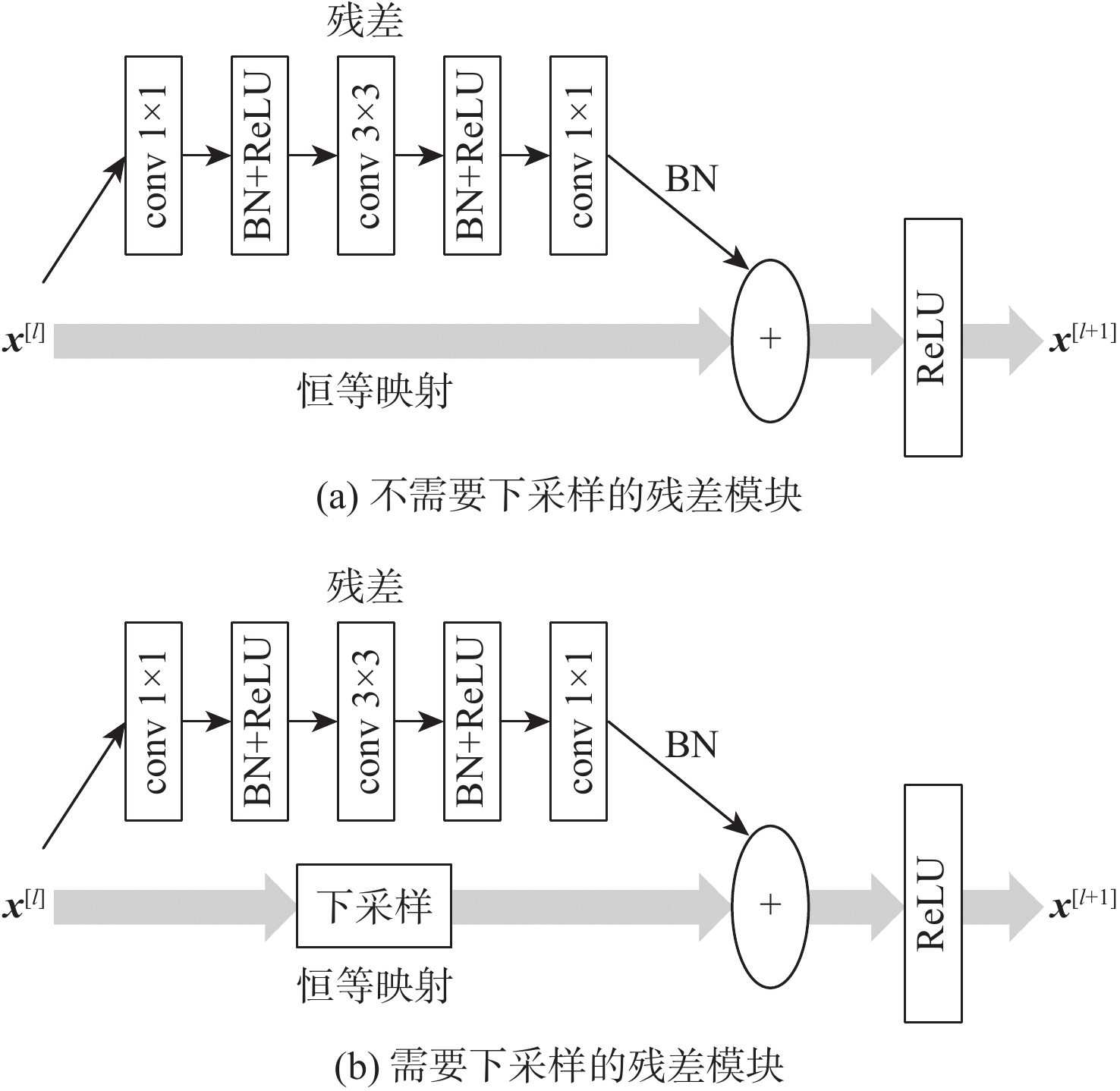
-
摘要:
针对无人机(UAV)跟踪过程中目标经常出现尺寸小、尺度变化大和相似物干扰等问题,提出了一种基于双注意力混洗的多尺度无人机实时跟踪算法。考虑到无人机视角下目标像素点少,构建了双采样融合的深层网络,既提供了语义信息丰富的深度特征,又保留了目标的细节信息;设计了双注意力混洗模块,通道注意力和空间注意力同时分组筛选提取到的特征信息,混洗不同通道间的信息,加强信息交流,提高了算法辨别能力;为利用不同层的特征信息,加入多个区域建议网络完成目标的分类和回归,并针对无人机的目标特点,将结果进行加权融合。实验结果表明:所提算法在数据集上的成功率和准确率分别为60.3%和79.3%,速度为37.5 帧/s。所提算法的辨别能力和多尺度适应能力明显增强,能有效应对无人机跟踪中常见的挑战。
Abstract:A multi-scale real-time tracking algorithm for unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) based on dual-attention shuffling is proposed to solve the problems of small size, large scale variation and similar object interference which often occur during UAV object tracking. First, considering the small number of target pixels in the UAV view, a deep network with double sampling integration is constructed, which provides semantic information-rich depth features and preserves the target’s detailed information. Next, a dual-attention shuffling module is designed. Channel attention and spatial attention are simultaneously grouped to filter the extracted feature information, and then the information between different channels is shuffled to enhance information exchange and improve the discriminative ability of the algorithm. Finally, to utilize the feature information of different layers, multiple region proposal networks are added to complete the target classification and regression, and the results are weighted and fused for the UAV target characteristics. Results show that the success and precision rates of the algorithm are 60.3% and 79.3% on the dataset, respectively, with 37.5 frame/s. The algorithm discrimination ability and multi-scale adaptation are significantly enhanced, which can effectively deal with the common challenges in UAV tracking.
-
Key words:
- unmanned aerial vehicle /
- object tracking /
- attention module /
- shuffle /
- region proposal network
-
-
[1] 孟琭, 杨旭. 目标跟踪算法综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(7): 1244-1260. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180277MENG L, YANG X. A survey of object tracking algorithms[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(7): 1244-1260(in Chinese). doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180277 [2] BERTINETTO L, VALMADRE J, HENRIQUES J F, et al. Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV). Berlin: Springer, 2016, 9914: 850-865. [3] HUANG C, LUCEY S, RAMANAN D. Learning policies for adaptive tracking with deep feature cascades[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 105-114. [4] LI B, YAN J, WU W, et al. High performance visual tracking with Siamese region proposal network[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 8971-8980. [5] REN S, HE K, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [6] LI B, WU W, WANG Q, et al. SiamRPN++: Evolution of Siamese visual tracking with very deep networks[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 4277-4286. [7] FU C, CAO Z, LI Y, et al. Siamese anchor proposal network for high-speed aerial tracking[EB/OL]. (2021-03-26)[2021-04-05]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.10706. [8] 刘芳, 孙亚楠, 王洪娟, 等. 基于残差学习的自适应无人机目标跟踪算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(10): 1874-1882. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0551LIU F, SUN Y N, WANG H J, et al. Adaptive UAV target tracking algorithm based on residual learning[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(10): 1874-1882(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0551 [9] 刘芳, 杨安喆, 吴志威. 基于自适应Siamese网络的无人机目标跟踪算法[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(1): 243-255.LIU F, YANG A Z, WU Z W. Adaptive Siamese network based UAV target tracking algorithm[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(1): 243-255(in Chinese). [10] HE A, LUO C, TIAN X, et al. A twofold Siamese network for real-time object tracking[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 4834-4843. [11] HU J, SHEN L, ALBANIE S, et al. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(8): 2011-2023. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2913372 [12] 钟莎, 黄玉清. 基于孪生区域候选网络的无人机指定目标跟踪[J]. 计算机应用, 2021, 41(2): 523-529. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2020060762ZHONG S, HUANG Y Q. Tracking of specified target of unmanned aerial vehicle based on Siamese region proposal network[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2021, 41(2): 523-529(in Chinese). doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2020060762 [13] HE K M, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [14] MA N, ZHANG X, ZHENG H T, et al. ShuffleNet V2: Practical guidelines for efficient CNN architecture design[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV). Berlin: Springer, 2018, 11218: 122-138. [15] ITTI L, KOCH C, NIEBUR E. A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1998, 20(11): 1254-1259. doi: 10.1109/34.730558 [16] LAROCHELLE H, HINTON G E. Learning to combine foveal glimpses with a third-order Boltzmann machine[C]//Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: Curran Associates Inc, 2010, 1: 1243-1251. [17] ZHANG Q L, YANG Y B. SA-Net: Shuffle attention for deep convolutional neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 2235-2239. [18] MAX J, KAREN S, ANDREW Z, et al. Spatial transformer networks[C]//Proceedings of the 2015 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems(NIPS). New York: Curran Associates Inc, 2015, 28: 2017-2025. [19] WANG Q, WU B, ZHU P, et al. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 11531-11539. [20] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV). Berlin: Springer, 2018, 11211: 3-19. [21] FU J, LIU J, TIAN H, et al. Dual attention network for scene segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 3141-3149. [22] NAM H, HAN B. Learning multi-domain convolutional neural networks for visual tracking[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 4293-4302. [23] KAREN S, ANDREW Z. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[EB/OL]. (2015-04-10)[2021-04-05].https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556. [24] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84-90. doi: 10.1145/3065386 [25] WANG Q, TENG Z, XING J, et al. Learning attentions: Residual attentional Siamese network for high performance online visual tracking[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 4854-4863. [26] WU Y, HE K. Group normalization[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV). Berlin: Springer, 2018: 3-19. [27] RAMPRASAATH R S, MICHAEL C, ABHISHEK D, et al. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision(ICCV). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 618-626. [28] ROMAN P. An in-depth analysis of visual tracking with Siamese neural networks[EB/OL]. (2018-08-02)[2021-04-05]. https://arxiv. org/abs/1707.00569. [29] FAN H, LING H. Siamese cascaded region proposal networks for real-time visual tracking[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 7944-7953. [30] ESTEBAN R, JONATHON S, STEFANO M, et al. YouTube-BoundingBoxes: A large high-precision human-annotated data set for object detection in video[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 7464-7473. [31] OLGA R, JIA D, HAO S, et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 115(3): 211-252. doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y [32] LIN T Y, MAIRE M, BELONGIE S, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context[C]//Proceedings of the 2014 European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV). Berlin: Springer, 2014: 740-755. [33] MATTHIAS M, NEIL S, BERNARD G. A benchmark and simulator for UAV tracking[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV). Berlin: Springer, 2016: 445-461. [34] MARTIN D, GUSTAV H, FAHAD S K. Accurate scale estimation for robust visual tracking[C]//Proceedings of the 2014 British Machine Vision Conference(BMVC). Berlin: Springer, 2014: 1-11. [35] HARE S, GOLODETZ S, SAFFARI A, et al. Struck: Structured output tracking with kernels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(10): 2096-2109. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2509974 [36] ZHANG J, MA S, SCLAROFF S. MEEM: Robust tracking via multiple experts using entropy minimization[C]//Proceedings of the 2014 European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV). Berlin: Springer, 2014: 188-203. [37] LI Y, ZHU J. A scale adaptive kernel correlation filter tracker with feature integration[C]//Proceedings of the 2014 European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV). Berlin: Springer, 2015: 254-265. [38] MARTIN D, GUSTAV H, FAHAD S K, et al. Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking[C]//Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 4310-4318. -







 下载:
下载: