An infrared small target detection network under various complex backgrounds realized on FPGA
-
摘要:
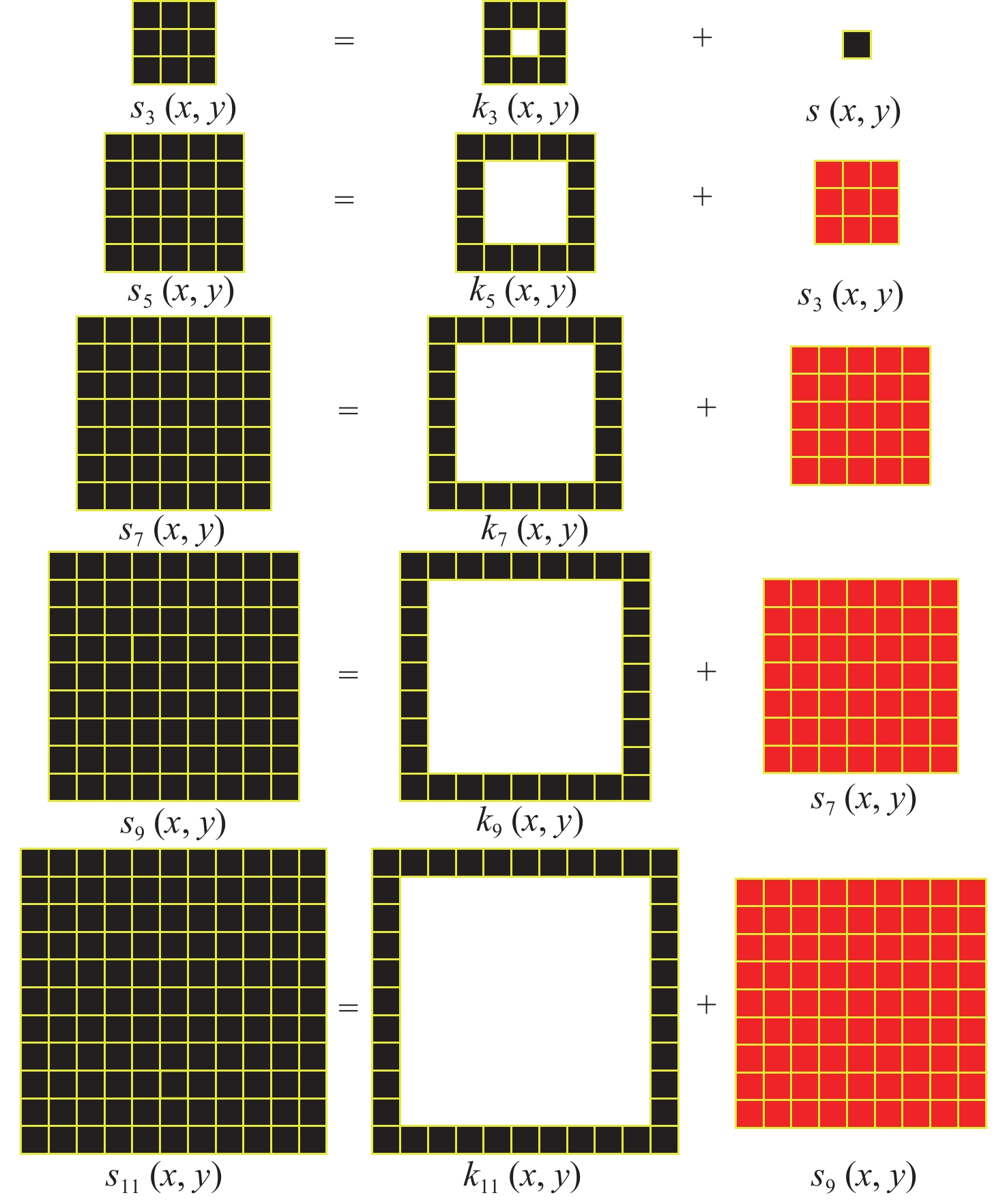
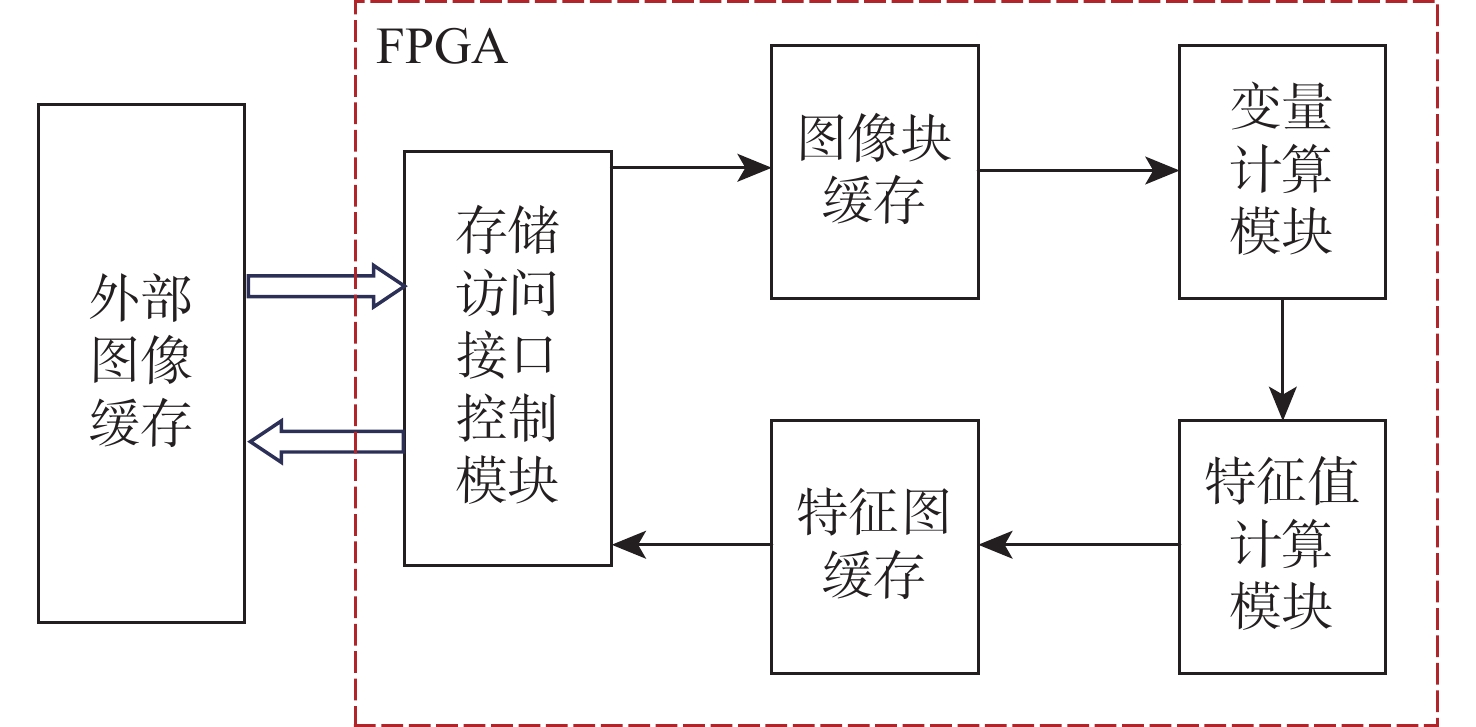
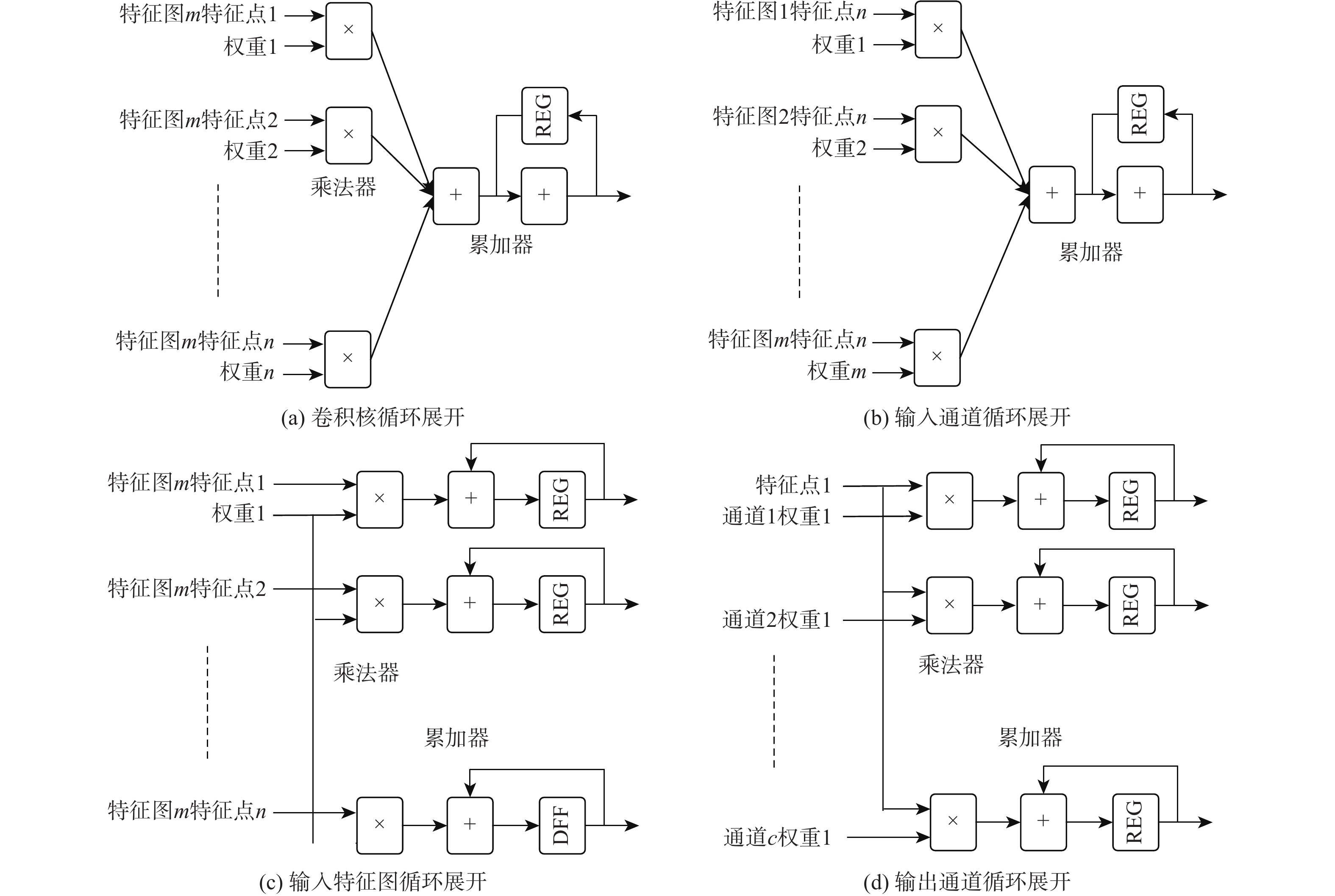
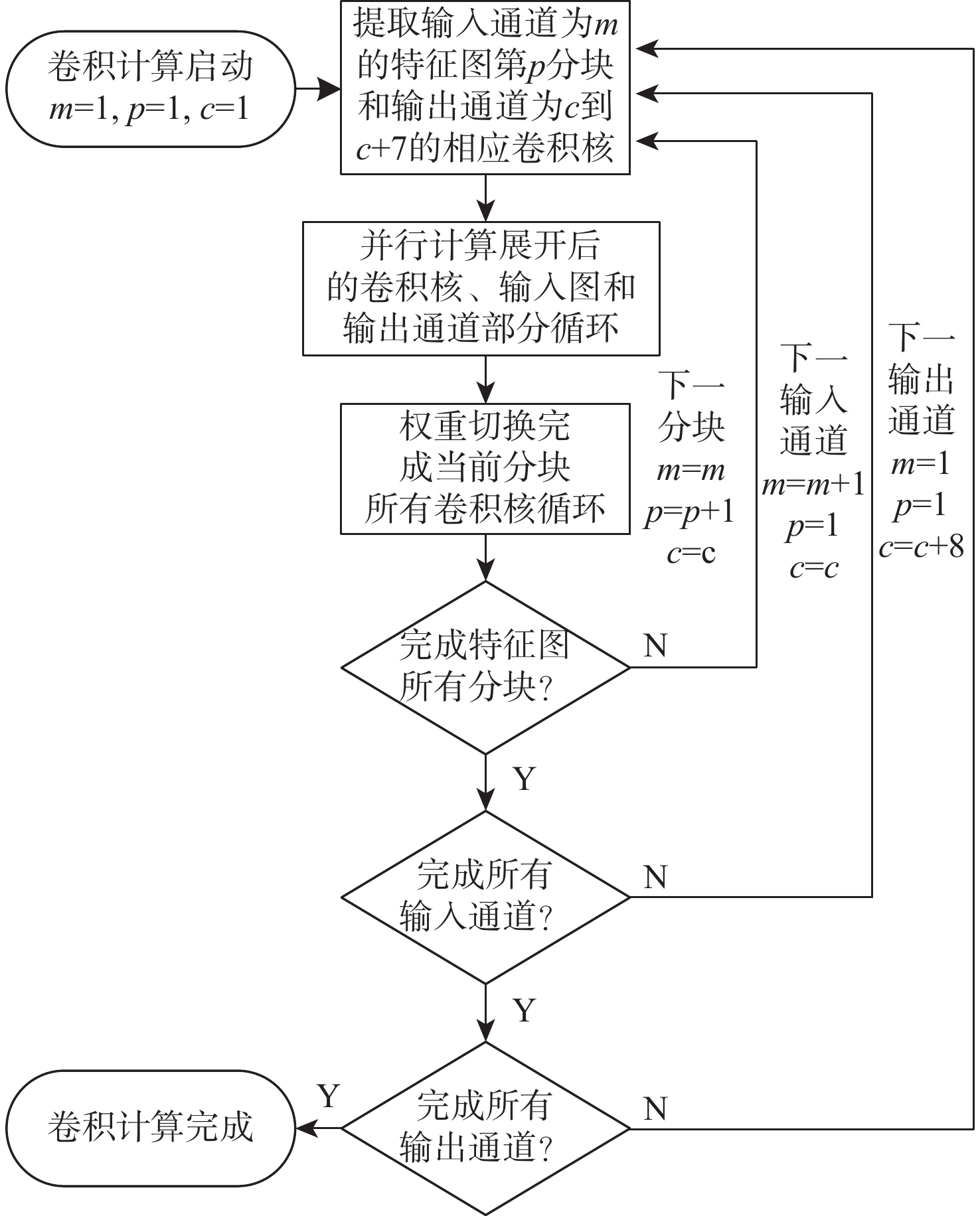
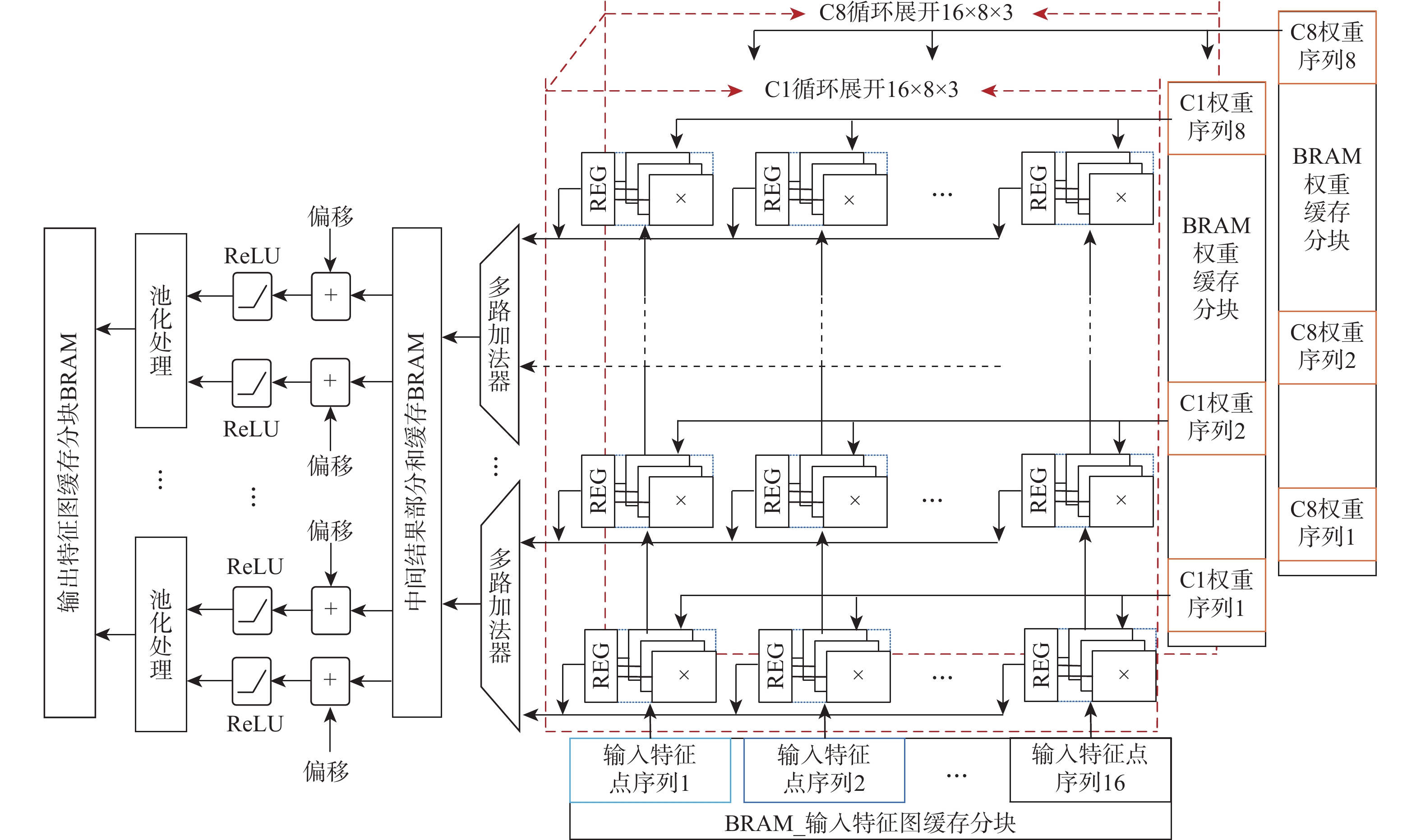
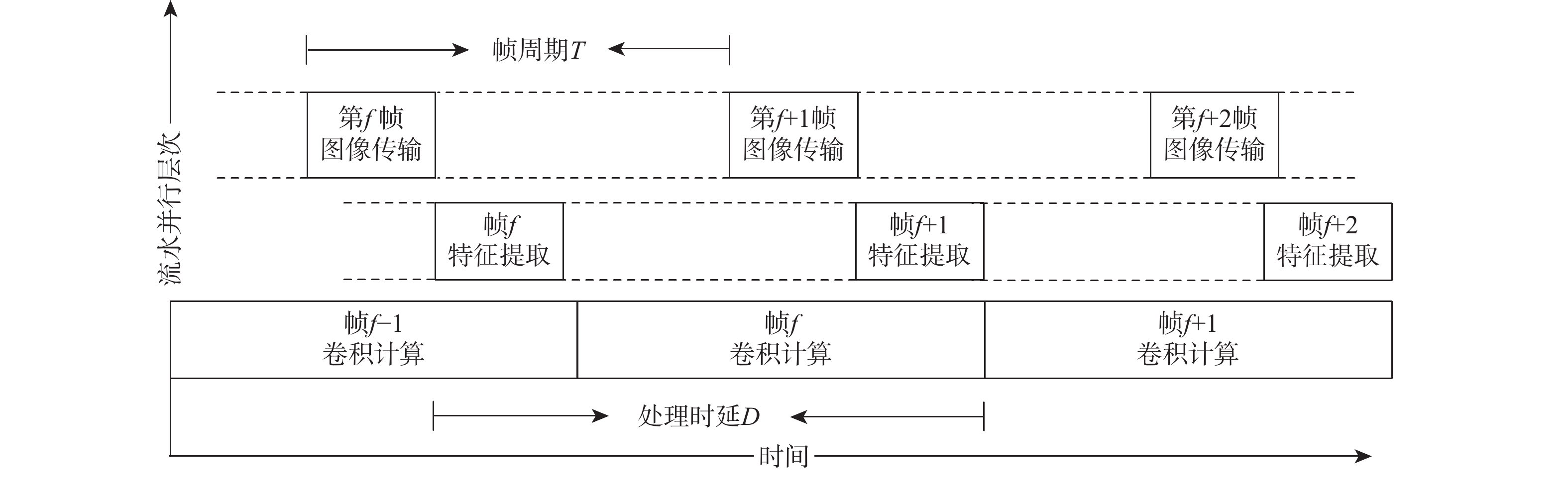
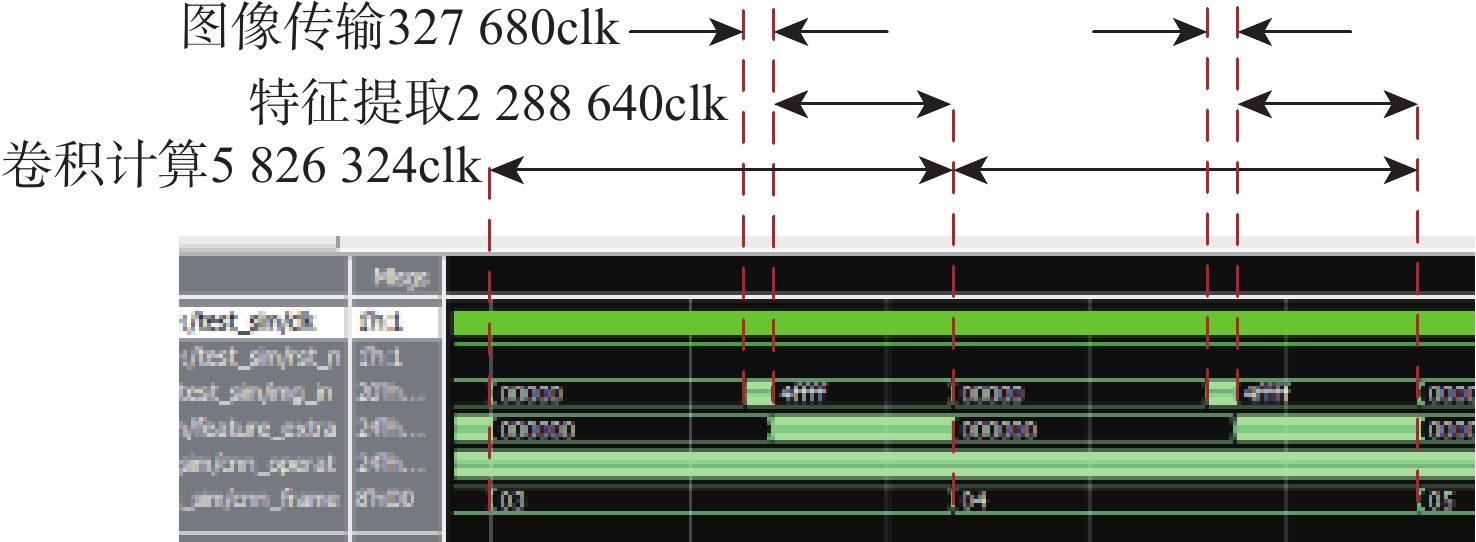
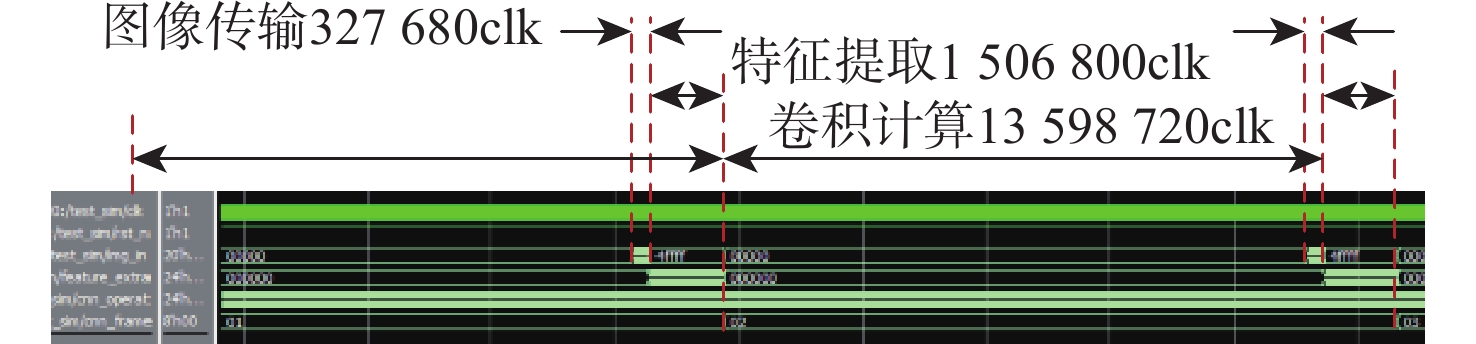
红外(IR)小目标检测算法具有检测率高、虚警率低、实时性好等优点在红外遥感领域有重要的应用价值。由于复杂背景下小目标对比度低和信噪比(SNR)低,传统红外小目标检测算法难以保证检测性能。在强鲁棒性的红外小目标检测网络(RISTDnet)基础上,面向更为多样的目标结构特征和更高的实时处理性能要求,提出一种增强型红外小目标检测网络(EISTDnet)与其基于现场可编程逻辑门阵列(FPGA)高性能并行处理的算法。EISTDnet构造了手工特征算法与卷积神经网络相结合的多尺度小目标特征提取框架,采用多级展开思路对卷积核尺寸进行归一化设计,并通过数据深度复用和多维循环并行展开有效提高推理阶段实时处理性能。实验结果表明:采用单片FPGA实现的EISTDnet能够快速实时检测复杂背景下不同大小、低信噪比的小目标,与现有5种算法相比在10−3低虚警率下平均检测率提升49.5%,与RISTDnet相比,在实时处理速度提高1.33倍的优势下,对低信噪比条状小目标检测率提升29.4%,所提算法具有更好的有效性和鲁棒性。
-
关键词:
- 卷积神经网络 /
- 红外小目标 /
- 目标检测 /
- 现场可编程逻辑门阵列 /
- 实时
Abstract:The infrared (IR) small target detection algorithm with high detection rate, low false alarm rate and good real-time performance has important application value in the field of IR remote sensing. Traditional IR small targets detection algorithms cannot guarantee the detection performance due to the low contrast and low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of small targets under various complex backgrounds. Based on robust infrared small target detection network (RISTDnet) proposed, for more diverse target structure characteristics and higher real-time processing performance requirements, an enhanced infrared small target detection network (EISTDnet) and its field programmable logic gate array (FPGA) based high-performance parallel processing method are proposed. In EISTDnet, a multi-scale small target feature extraction framework that combines manual feature methods and convolutional neural networks is constructed, the size of the convolution kernel is normalized by the idea of multi-level expansion, and real-time processing performance in the inference stage is effectively improved through deep data reuse and multi-dimensional loop parallel unfolding. Experimental results show that the EISTDnet realized on a single FPGA can quickly detect small targets with different sizes and low SNR in various complex backgrounds in real time. Compared with the existing 5 algorithms, the average detection rate is increased by 49.5% with a low false alarm rate of 10−3. Compared with RISTDnet, the real-time processing speed is increased by 1.33 times, and the detection rate of low SNR strip small targets is increased by 29.4%. EISTDnet has better effectiveness and robustness.
-
表 1 EISTDnet网络参数
Table 1. EISTDnet network parameters
层编号 卷积核
数量卷积核
尺寸/步长输出特征图
尺寸特征提取 512×640 Conv1.1 24 3×3/1 512×640 Conv1.2 24 3×3/1 512×640 Conv1.3 24 3×3/1 512×640 Conv1.4 24 3×3/1 512×640 Conv1.5 32 3×3/1 512×640 Pool1 2×2/2 256×320 Conv2.1 32 3×3/1 256×320 Conv2.2 32 3×3/1 256×320 Conv2.3 64 3×3/1 256×320 Pool2 2×2/2 128×160 Conv3.1 64 3×3/1 128×160 Conv3.2 128 3×3/1 128×160 Pool3 2×2/2 64×80 Conv4 256 3×3/1 64×80 Conv5 64 3×3/1 64×80 表 2 EISTDnet与RISTDnet运算操作数比对
Table 2. Comparison of operands between EISTDnet and RISTDnet
网络改进阶段 运算操作数 RISTDnet 69999411200 EISTDnet强化多尺度特征 90460323840 EISTDnet卷积网络轻量化 33919795200 表 3 图像读取与运算操作比对
Table 3. Image reading and operation comparison
算法 像素读取次数 运算操作数 优化前 607846400 629473280 优化后 39649280 97648640 降低比例/% 6.52 15.51 表 4 测试序列典型帧与数量
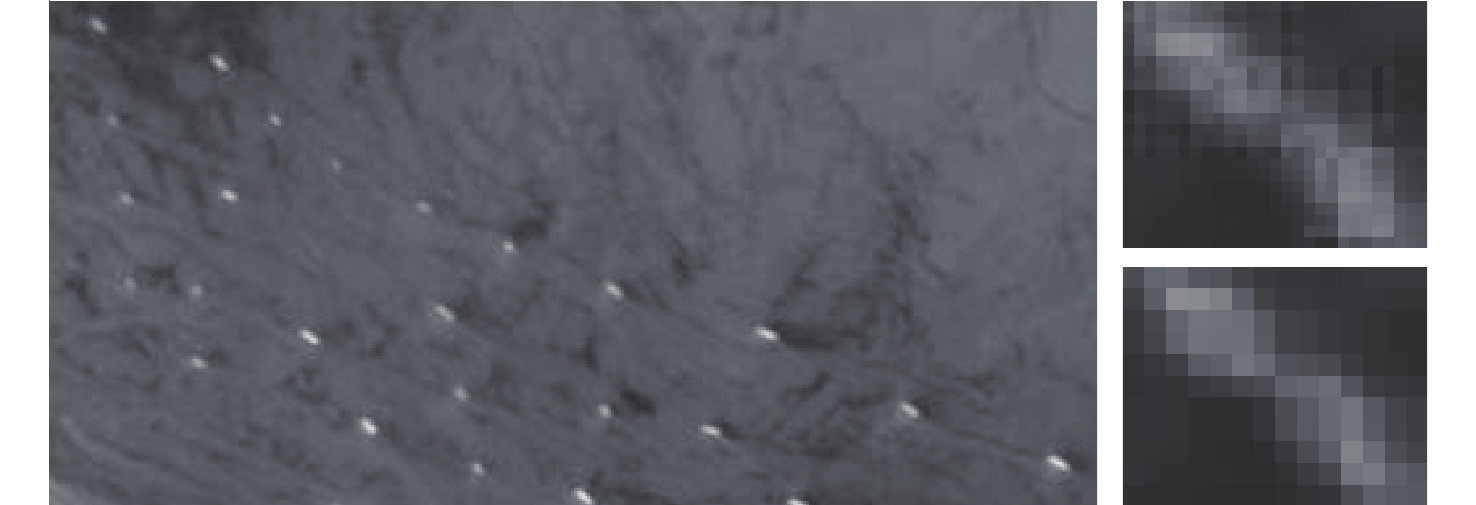
Table 4. Typical frames and number of test sequences
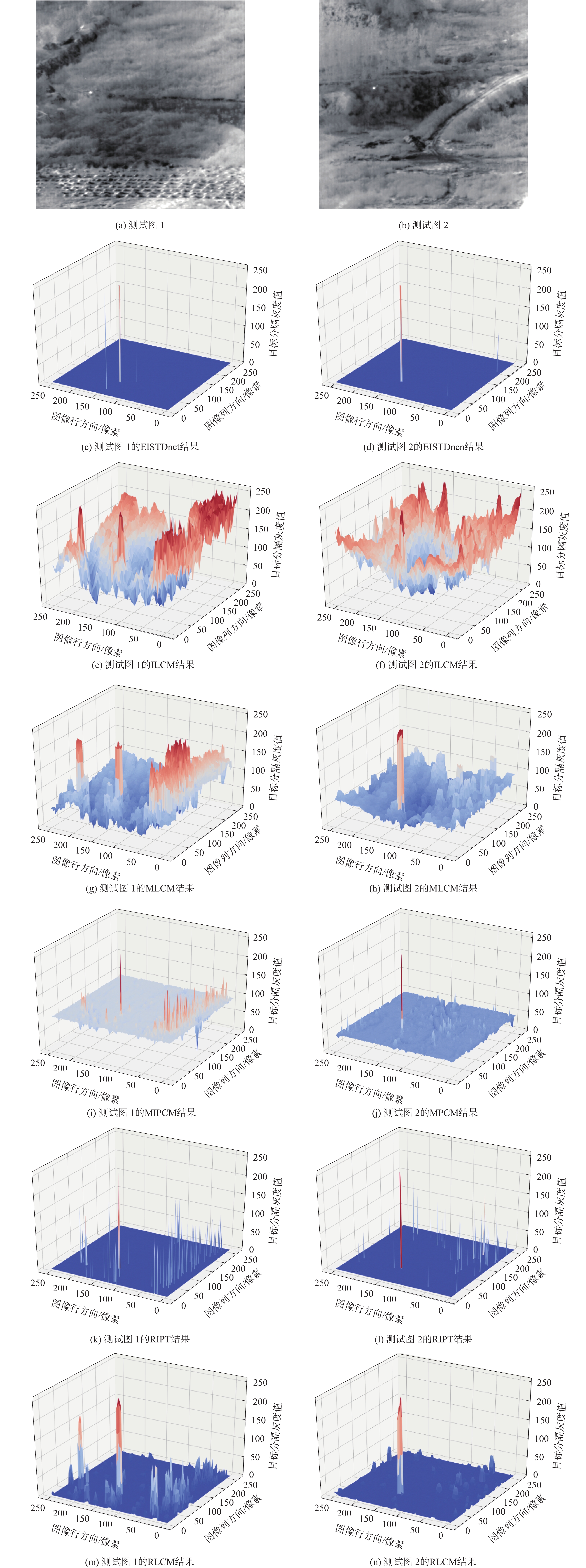
表 5 EISTDnet与RISTDnet目标检测性能对比
Table 5. Comparison of target detection performance between EISTDnet and RISTDnet
% 项目 EISTDnet RISTDnet 测试序列1 66.97 63.81 测试序列2 50.99 48.65 测试序列3 52.76 50.25 表 6 EISTDnet与RISTDnet条状弱小目标检测性能对比
Table 6. Comparison of stripe dim target detection performance between EISTDnet and RISTDnet
项目 EISTDnet
目标数/检出数RISTDnet
目标数/检出数测试序列1 50/31 50/15 测试序列2 50/24 50/12 测试序列3 50/27 50/14 平均检测率/% 56.7 27.3 表 7 FPGA资源利用率
Table 7. FPGA resource utilization
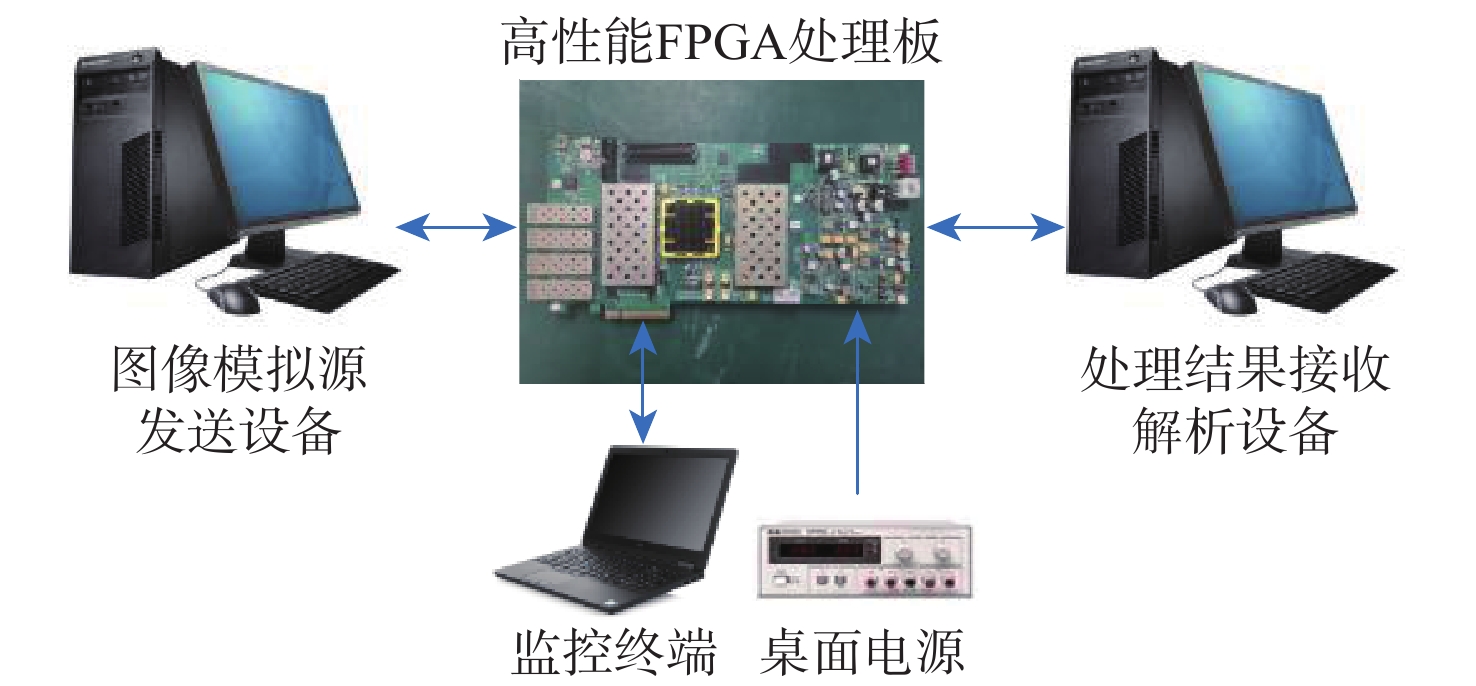
资源 BRAM DSP硬核 触发器 查找表 使用资源 2746 3258 755915 360141 可利用资源 2940 3600 866400 433200 利用率/% 93 91 87 83 -
[1] CHEN C L P, LI H, WEI Y, et al. A local contrast method for small infrared target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(1): 574-581. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2242477 [2] HAN J, MA Y, ZHOU B, et al. A robust infrared small target detection algorithm based on human visual system[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(12): 2168-2172. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2323236 [3] WEI Y, YOU X, LI H. Multiscale patch-based contrast measure for small infrared target detection[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 58: 216-226. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.04.002 [4] HAN J, LIANG K, ZHOU B, et al. Infrared small target detection utilizing the multiscale relative local contrast measure[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(4): 612-616. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2790909 [5] YAO S, CHANG Y, QIN X. A coarse-to-fine method for infrared small target detection[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(2): 256-260. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2872166 [6] HAN J, LIU S, QIN G, et al. A local contrast method combined with adaptive background estimation for infrared small target detection[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(9): 1442-1446. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2898893 [7] GAO C, MENG D, YANG Y, et al. Infrared patch-image model for small target detection in a single image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(12): 4996-5009. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2281420 [8] DAI Y, WU Y, SONG Y, et al. Non-negative infrared patch-image model: Robust target-background separation via partial sum minimization of singular values[J]. Infrared Physics and Technology, 2017, 81: 182-194. doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2017.01.009 [9] DAI Y, WU Y. Reweighted infrared patch-tensor model with both nonlocal and local priors for single-frame small target detection[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(8): 3752-3767. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2700023 [10] ZHANG L, PENG L, ZHANG T, et al. Infrared small target detection via non-convex rank approximation minimization joint l2, 1 norm[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(11): 1821. doi: 10.3390/rs10111821 [11] ZHOU F, WU Y, DAI Y, et al. Detection of small target using schatten 1/2 quasi-norm regularization with reweighted sparse enhancement in complex infrared scenes[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(17): 2058. doi: 10.3390/rs11172058 [12] REN S, HE K, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [13] REDMON J, FARHADI A. Yolo9000: Better, faster, stronger[C]//In 30th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 6517–6525. [14] JOSEPH R, ALI F. Yolov3: An incremental improvement[EB/OL]. (2018-04-08)[2021-04-21]. http: //arxiv. org/abs/1804.02767. [15] LIU W, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector[C]//in 32th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Amsterdam: University of Amsterdam, 2016. [16] HOU Q, WANG Z, TAN F, et al. RISTDnet: Robust infrared small target detection network[EB/OL]. (2020-12-27) [2021-04-20]. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2021.3050828. [17] 李岩. 基于"高分五号"卫星红外影像的舰船尾迹特征分析[J]. 航天返回与遥感, 2020, 41(5): 106-113.LI Y.The ship wake characterization study based on GF-5 infrared images[J]. Spacecraft Recovery & Remote Sensing,2020,41(5):106-113(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: