-
摘要:
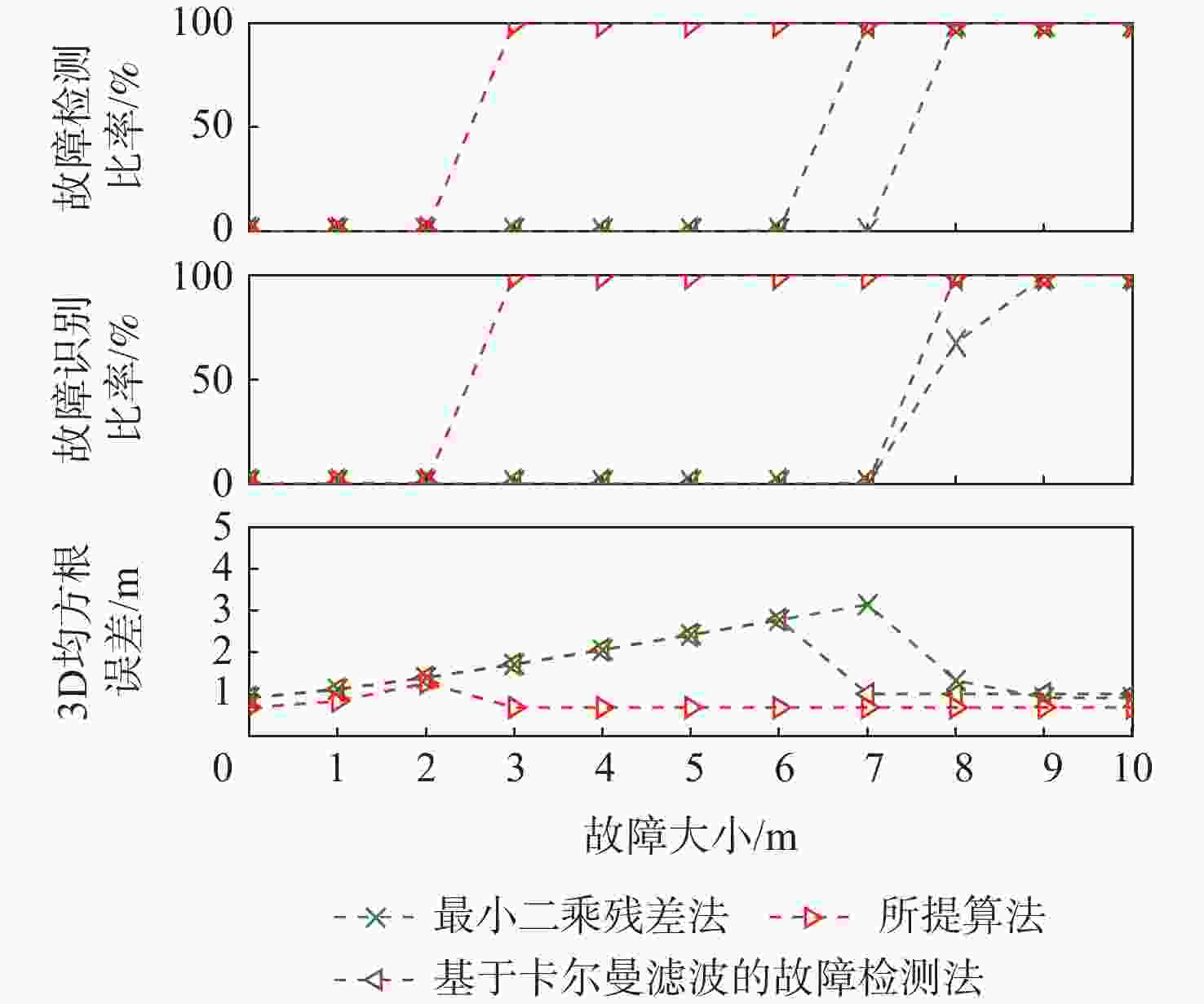
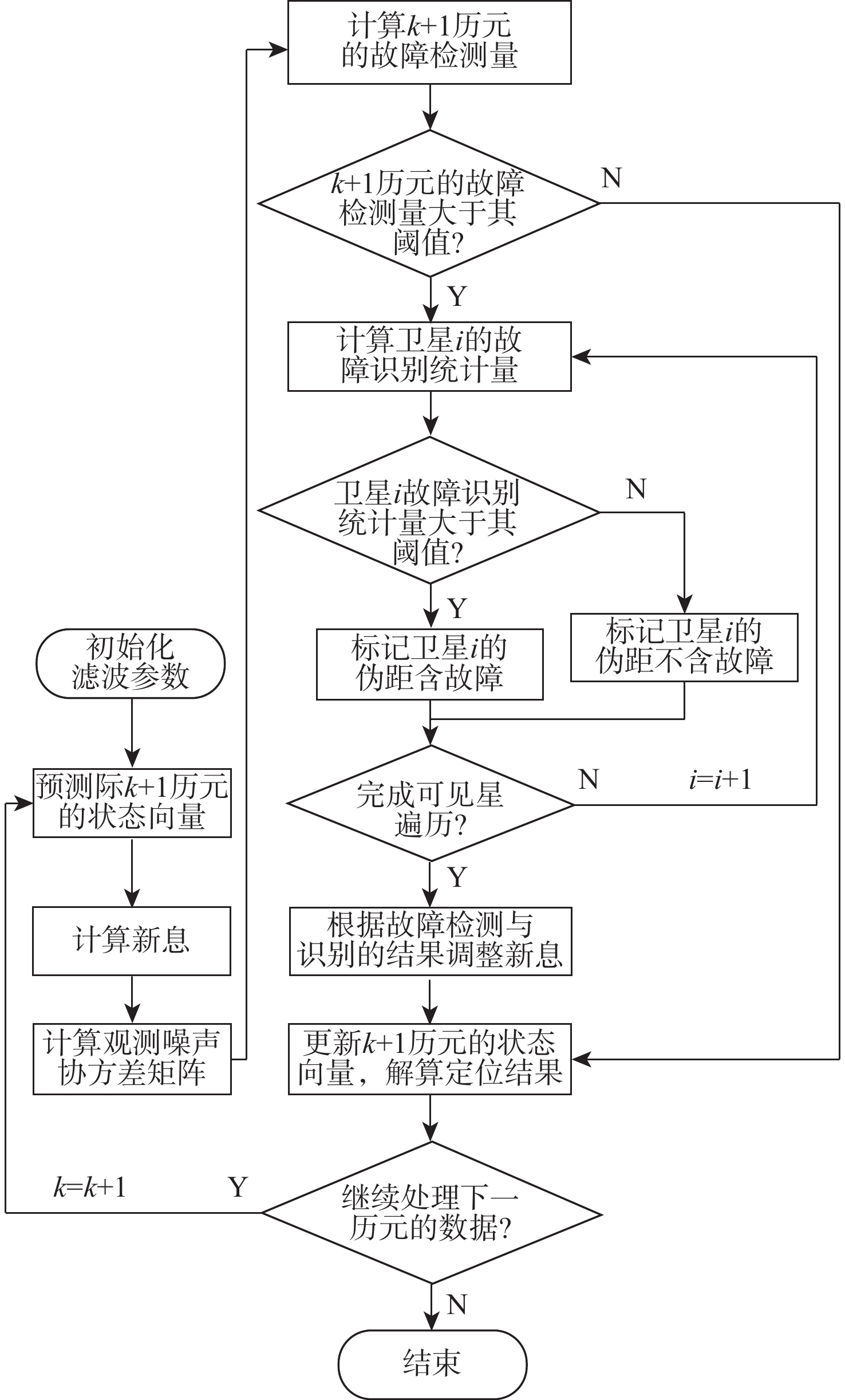
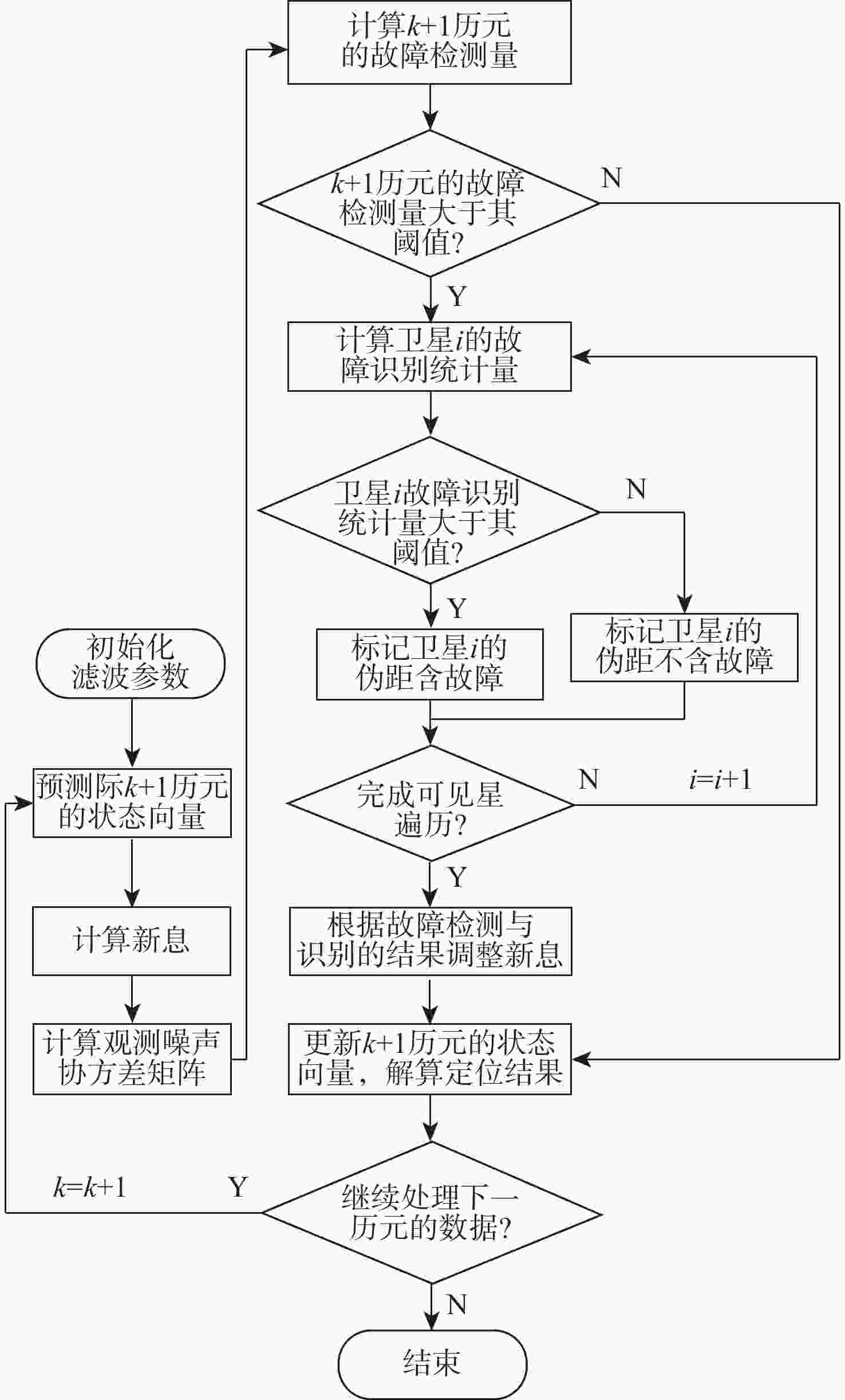
不同观测环境的实际观测噪声可能存在较大差别,因此,固定的噪声方差矩阵可能使基于卡尔曼滤波故障检测法的故障检测效果下降。对此,提出自适应噪声方差的卫星定位故障检测算法,利用滑动窗内的历史新息实时估计观测噪声方差矩阵,在此基础上构建故障检测量与识别量对故障进行检测与识别,利用不含故障的新息更新状态向量并解算出定位结果。实验结果表明:所提算法在静态模式下,可100%检测和识别的最小单阶跃故障为3 m,对持续时间为100 s、斜坡故障增长速率为0.2 m/s的斜坡故障识别比率为51.4%,可100%检测和识别的最小多故障为4 m;在动态模式下,可100%检测和识别的最小单阶跃故障为10 m,对持续时间为200 s、斜坡故障增长速率为0.2 m/s的斜坡故障识别比率为66.25%,可100%检测和识别的最小多故障为12 m。所提算法性能优于基于最小二乘和卡尔曼滤波的故障检测法。
-
关键词:
- 全球卫星导航系统 /
- 全球卫星导航系统质量控制 /
- 故障检测 /
- 卡尔曼滤波 /
- 自适应滤波
Abstract:As actual observation noises vary in different environments, the fixed noise variance matrix may degrade the performance of the Kalman filter (KF)-based fault detection method. To deal with this issue, we proposed an adaptive noise variance-based fault detection algorithm. Its fault detection and identification statistics are generated based on the real-time observation noise variance matrix estimated from historical innovations with a sliding window. The innovation without faults will then be used to update the state vector for positioning solutions. Both static and dynamic modes have been tested in the experiment. In the static mode, the proposed algorithm can provide a 100% fault detection rate (FDR) and fault identification rate (FIR) of the minimum single-step error of 3 m, and the FIR for the 0.2 m/s ramp error of 100 s is 51.4%. In addition, it can provide a 100% FDR and FIR of the minimum multiple error of 4 m. In the dynamic mode, the suggested algorithm can deliver a 100% FDR and FIR of the minimum single-step error of 10 m, and a 66.25% FIR for the 0.2 m/s ramp error of 200 s. In addition, it can provide a 100% FDR and FIR of the minimum multiple-error of 12 m. Its performance is superior to the least square residual-based method and the KF-based fault detection method.
-
表 1 本文的实验场景
Table 1. The designed scenarios
实验章节 数据类型 故障类型 具体描述 2.1.1节 静态数据
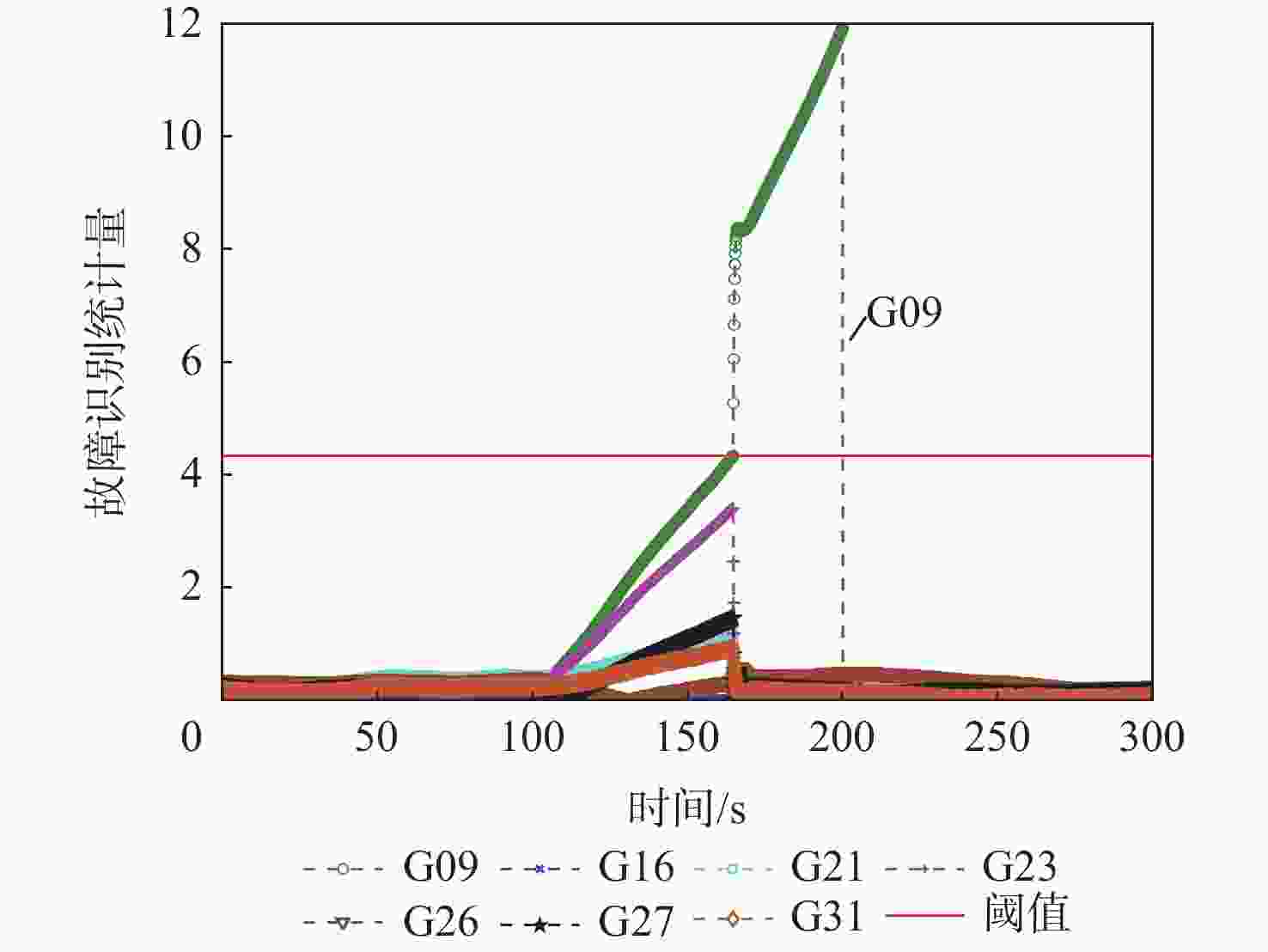
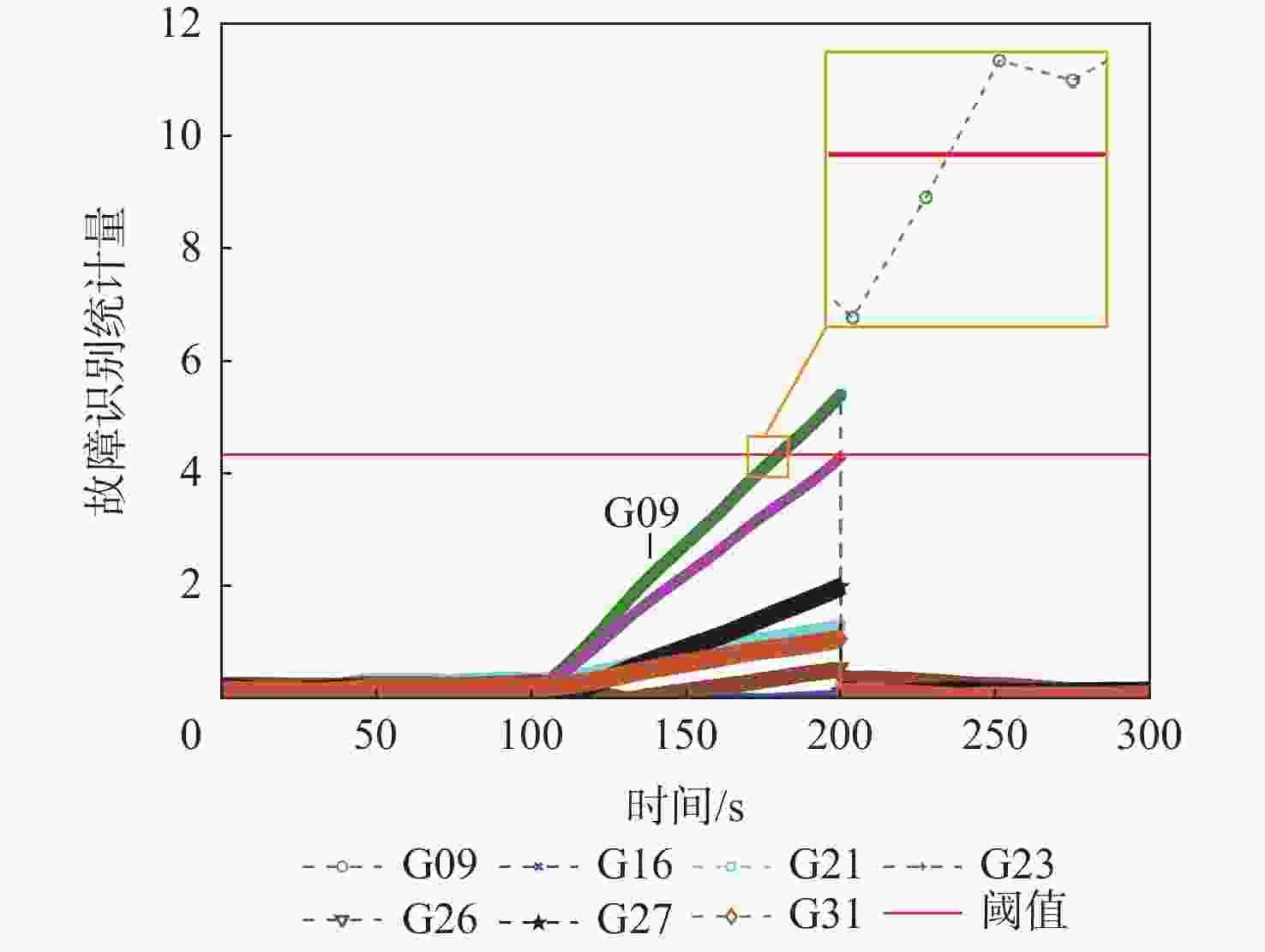
(采样率10 Hz)无故障 原始的静态观测数据。 2.1.2节 单阶跃故障 往卫星G09在观测时刻150~200 s(含150 s和200 s,共501个历元)内的伪距中添加阶跃故障 2.1.3节 单斜坡故障 往卫星G09在观测时刻100~200 s(不含100 s,含200 s,共1 000个历元)内的伪距中添加斜坡故障 2.1.4节 多故障 往卫星G09和G16在观测时刻150~200 s(含150 s和200 s,共501个历元)内的伪距中添加阶跃故障 2.2.1节 动态数据
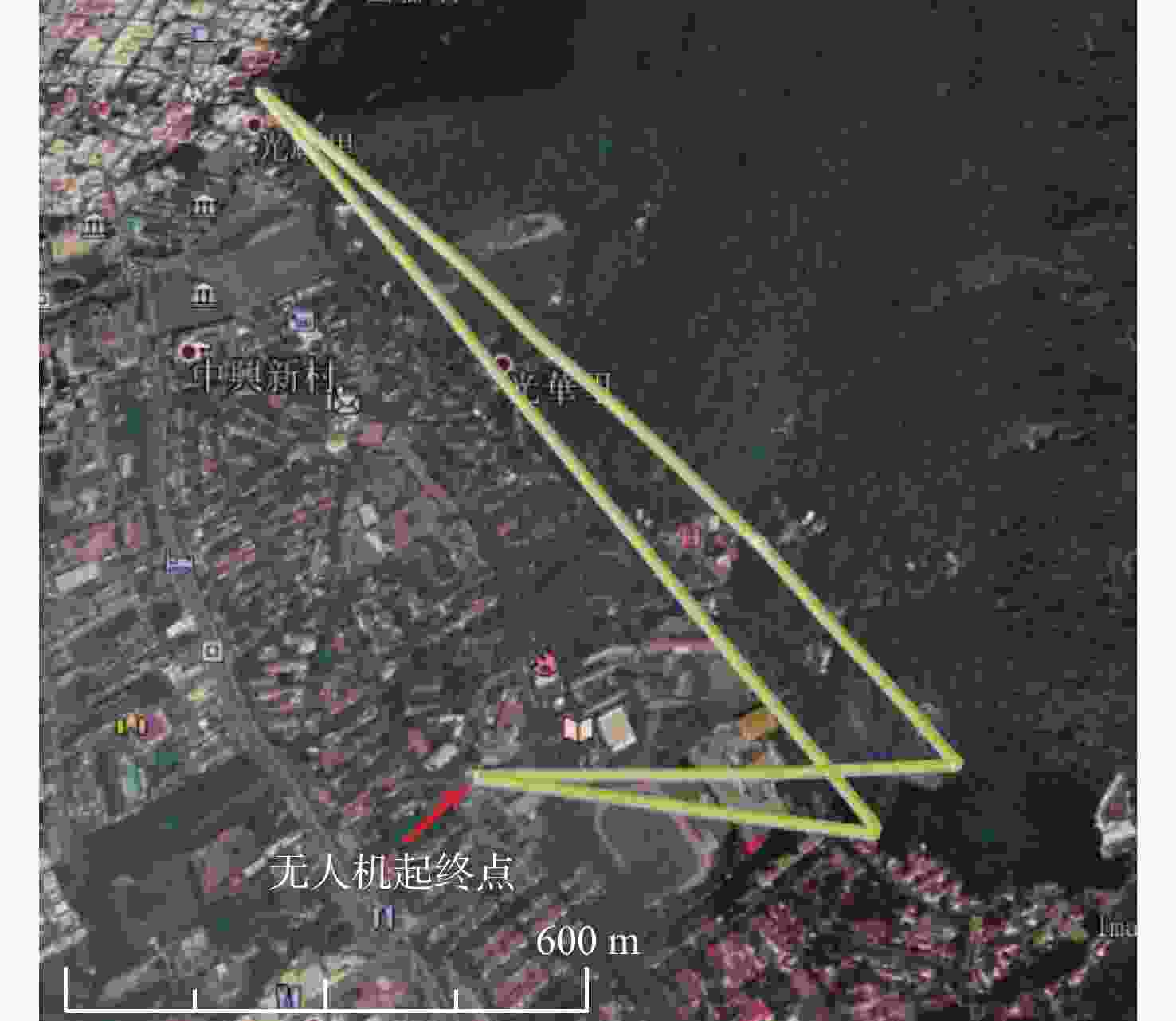
(采样率10 Hz)无故障 原始的动态观测数据 2.2.2节 单阶跃故障 往卫星G10在观测时刻300~400 s(含300 s和400 s,共1001个历元)内的伪距添加阶跃故障 2.2.3节 单斜坡故障 往卫星G10在观测时刻400~600 s(不含400 s,含600 s,共2 000个历元)内的伪距添加斜坡故障 2.2.4节 多故障 往卫星G10和G12在观测时刻400~500 s(含400 s和500 s,共1 001个历元)内的伪距中添加阶跃故障 表 2 原始静态数据的定位精度指标
Table 2. The positioning accuracy for the candidate algorithms based on the original static data
m 故障检测算法 方向 误差
最大值95%分位误差 均方根误差 最小二乘残差法 竖直 1.467 1.294 0.900 水平 0.422 0.395 0.222 3D 1.467 1.297 0.927 基于卡尔曼滤波
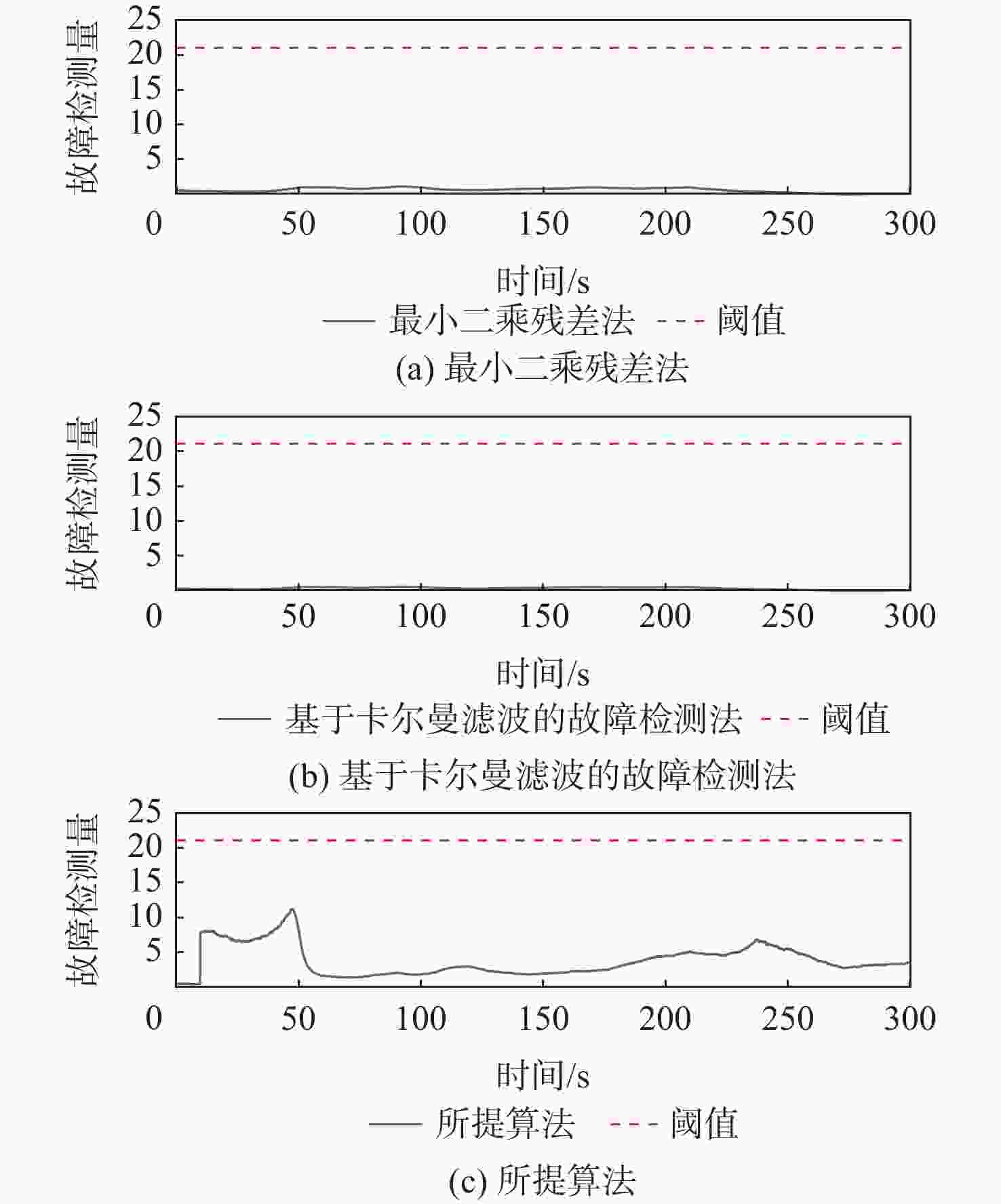
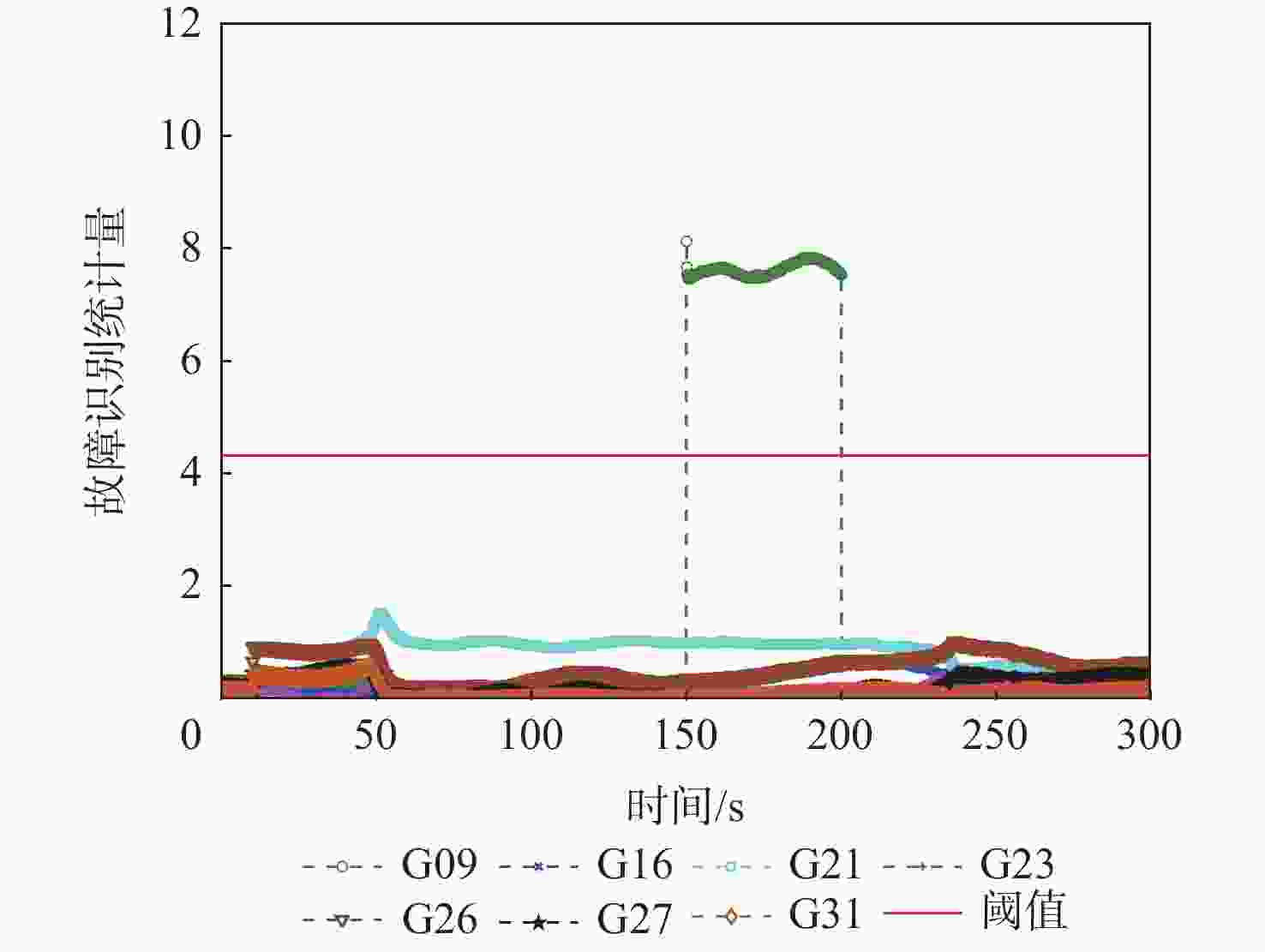
的故障检测法竖直 1.433 1.297 0.892 水平 0.420 0.396 0.222 3D 1.434 1.298 0.919 所提算法 竖直 1.418 1.126 0.657 水平 0.335 0.292 0.191 3D 1.420 1.131 0.685 表 3 静态数据含5 m阶跃故障下的故障检测指标
Table 3. Fault detection performance for a 5 m step error added on the static data
% 故障检测
算法FDR FIR FAR MDR 最小二乘残差法 0 0 0 100 基于卡尔曼滤波的
故障检测法0 0 0 100 所提算法 100 100 0 0 表 4 静态数据含5 m阶跃故障下的定位精度指标
Table 4. The positioning accuracy for the candidate algorithms based on the static data with a 5 m step error
m 故障检测算法 方向 误差
最大值95%分位误差 均方根误差 最小二乘残差法 竖直 5.122 5.008 2.174 水平 2.794 2.711 1.075 3D 5.741 5.664 2.425 基于卡尔曼滤波
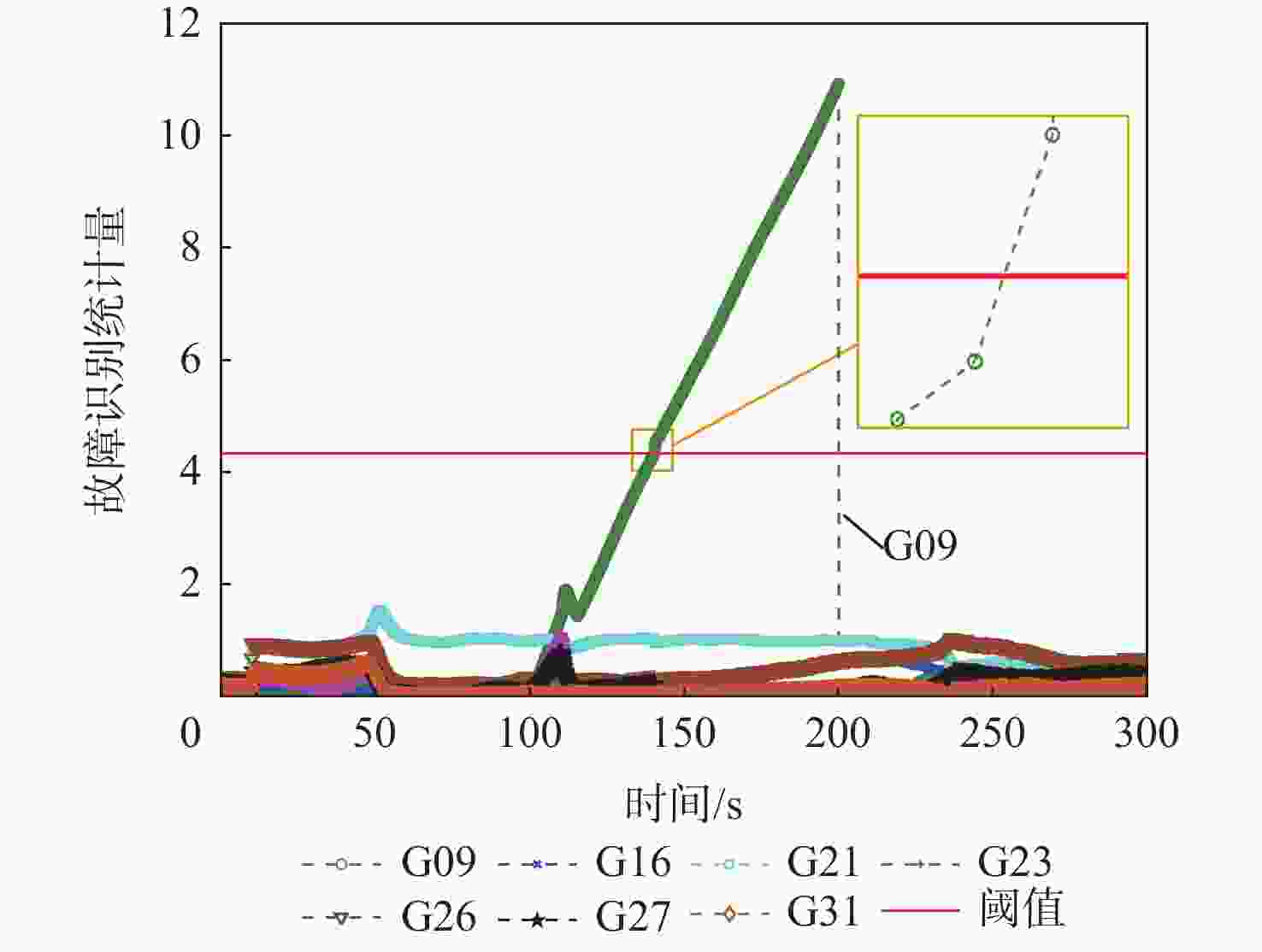
的故障检测法竖直 5.556 5.025 2.174 水平 2.925 2.704 1.077 3D 6.270 5.657 2.426 所提算法 竖直 1.418 1.126 0.659 水平 0.335 0.286 0.192 3D 1.420 1.131 0.687 表 5 静态数据在TSE = 100 s,VSE = 0.2 m/s故障下的故障检测指标
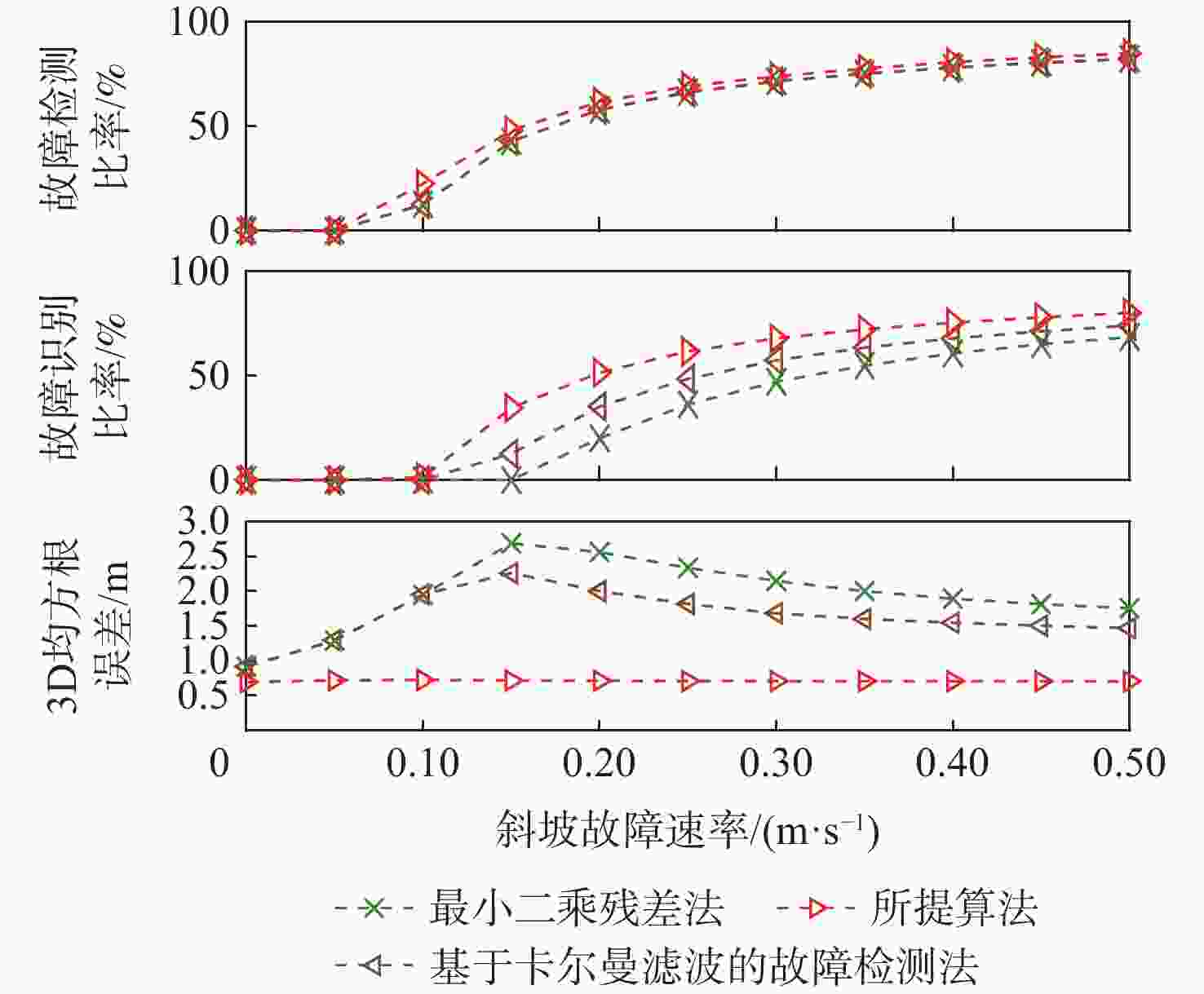
Table 5. Fault detection performance for the candidate algorithms with a 0.2 m/s ramp error added for 100 s in the static mode
% 故障检测
算法FDR FIR FAR MDR 最小二乘残差法 57.8 20 0 42.2 基于卡尔曼滤波的
故障检测法57.8 35.2 0 42.2 所提算法 61.6 51.4 0 38.4 表 6 静态数据在TSE = 100 s,VSE = 0.2 m/s故障下的定位精度指标
Table 6. The positioning accuracy for the candidate algorithms with a 0.2 m/s ramp error added for 100 s in the static mode
m 故障检测算法 方向 误差最
大值95%分位点定
位误差均方根
误差最小二乘残差法 竖直 4.198 3.595 1.595 水平 6.719 5.471 2.006 3D 7.923 6.548 2.563 基于卡尔曼滤波
的故障检测法竖直 3.670 2.997 1.357 水平 5.444 4.219 1.472 3D 6.517 5.161 2.002 所提算法 竖直 1.418 1.125 0.657 水平 1.150 0.424 0.275 3D 1.420 1.134 0.712 表 7 静态数据中卫星G09和G16的伪距同时有5 m的阶跃故障下的故障检测指标
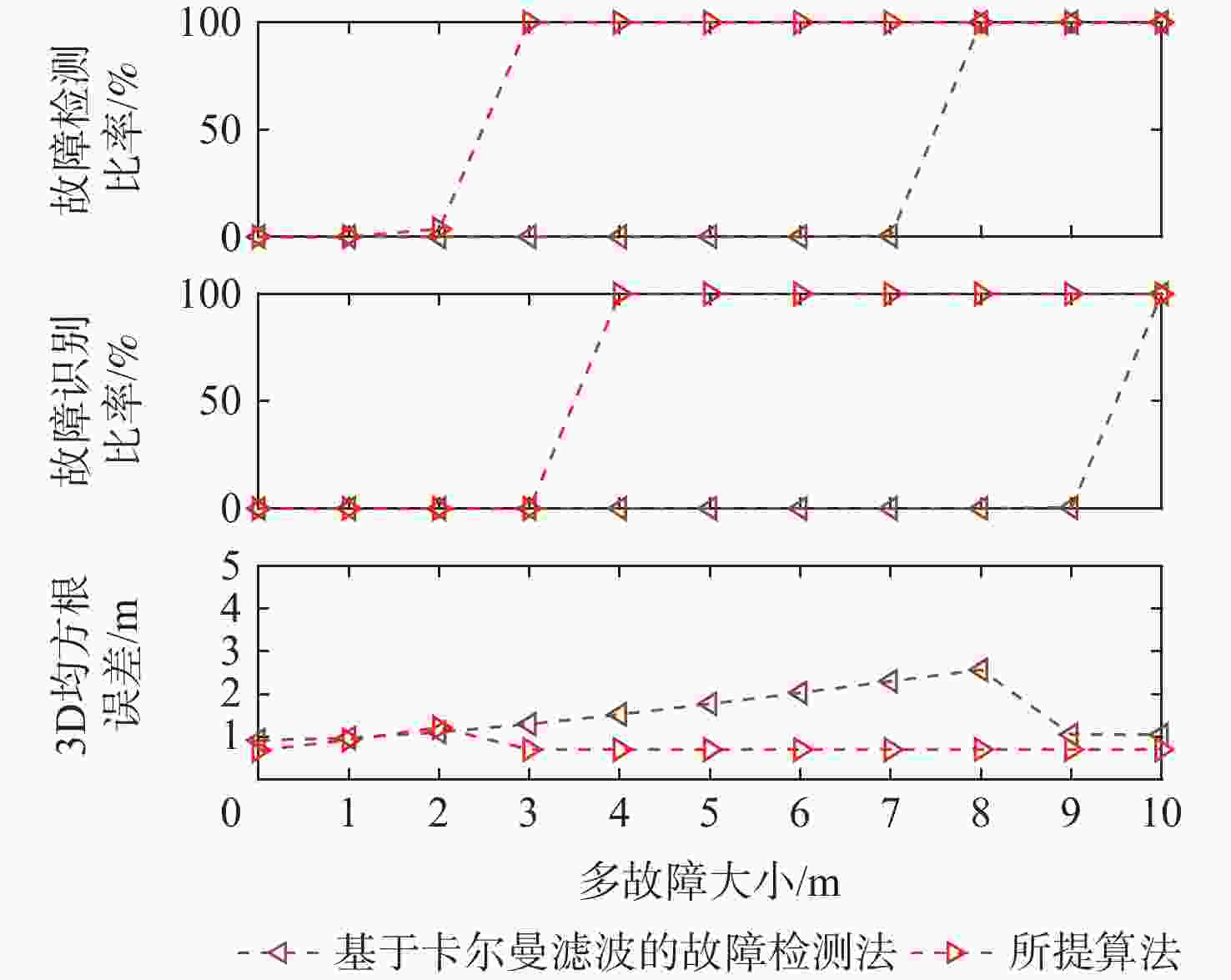
Table 7. Fault detection performance for candidate algorithms with 5 m step errors added on pseudorange of G09 and G16 in static mode
% 故障检测算法 FDR FIR FAR MDR 基于卡尔曼滤波的故障检测法 0 0 0 100 所提算法 100 100 0 0 表 8 静态数据中卫星G09和G16的伪距同时含有5 m的阶跃故障下的定位精度指标
Table 8. Positioning accuracy performance for candidate algorithms with 5 m step errors added on pseudorange of G09 and G16 in static mode
m 故障检测算法 方向 误差
最大值95%分位点定位误差 均方根误差 基于卡尔曼滤波
的故障检测法竖直 1.432 1.301 0.813 水平 4.316 3.957 1.576 3D 4.328 3.965 1.773 所提算法 竖直 1.418 1.125 0.655 水平 0.687 0.553 0.260 3D 1.420 1.131 0.704 表 9 原始动态数据的定位精度指标
Table 9. Positioning accuracy performance for candidate algorithms based on original dynamic data
m 故障检测算法 方向 误差
最大值95%分位误差 均方根误差 最小二乘残差法 竖直 6.481 4.765 2.955 水平 4.590 2.881 1.585 3D 7.289 5.069 3.353 基于卡尔曼滤波
的故障检测法竖直 9.920 4.466 2.891 水平 5.976 2.933 1.558 3D 11.267 4.743 3.284 所提算法 竖直 9.920 3.007 1.591 水平 5.976 3.242 1.567 3D 11.267 4.052 2.233 表 10 动态数据含10 m阶跃故障下的故障检测指标
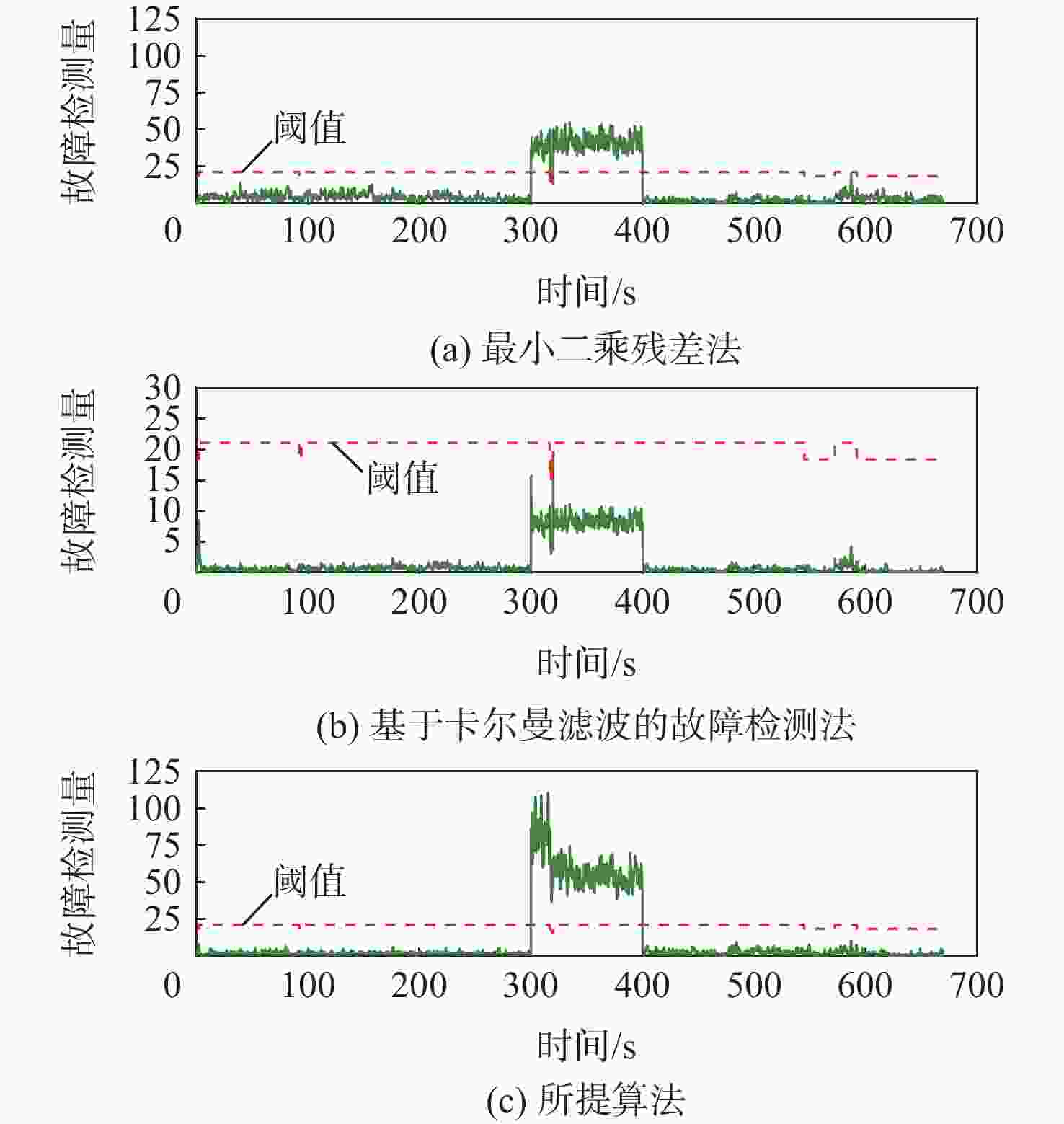
Table 10. Fault detection performance for candidate algorithms with a 10 m step error added on the observations in the dynamic mode
% 故障检测
算法FDR FIR FAR MDR 最小二乘残差法 98.7 56.4 0 1.3 基于卡尔曼滤波的
故障检测法0 0 0 100 所提算法 100 100 0 0 表 11 动态数据含10 m阶跃故障下的定位精度指标
Table 11. Positioning accuracy performance for candidate algorithms with a 10 m step error added on observations in dynamic mode
m 故障检测算法 方向 误差
最大值95%分位误差 均方根误差 最小二乘残差法 竖直 22.460 14.069 4.800 水平 4.590 2.947 1.635 3D 22.668 14.401 5.071 基于卡尔曼滤波
的故障检测法竖直 18.823 14.622 6.180 水平 5.976 3.020 1.646 3D 19.239 14.854 6.396 所提算法 竖直 9.920 4.858 2.600 水平 5.976 5.239 1.592 3D 11.267 3.208 3.049 表 12 动态数据在
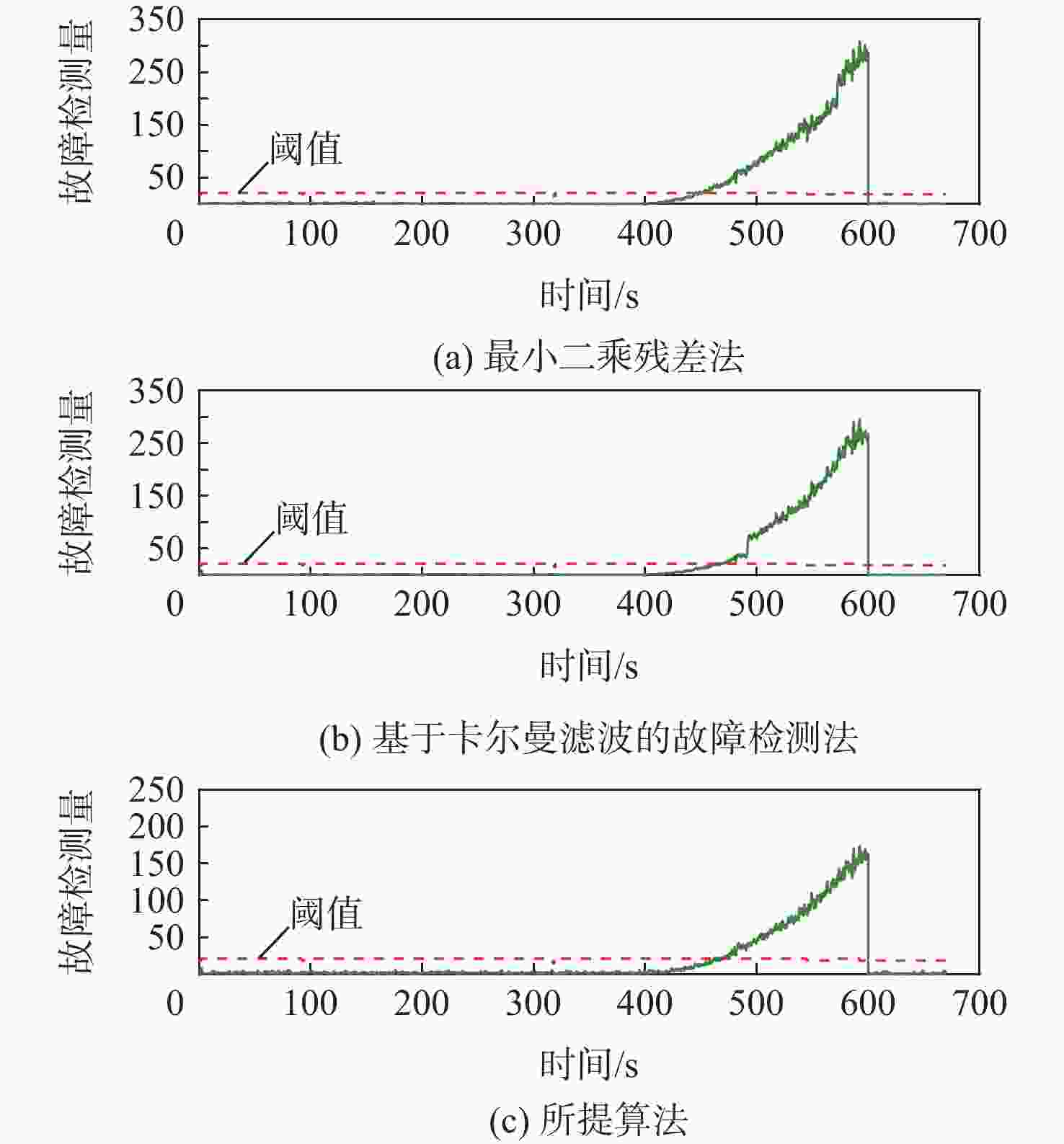
${{\boldsymbol{T}}_{{\bf{SE}}}} $ = 200 s,${{\boldsymbol{V}}_{{\bf{SE}}}} $ = 0.2 m/s故障下的故障检测指标Table 12. Fault detection performance for candidate algorithm with a 0.2 m/s ramp error added for 200 s in dynamic mode
% 故障检测
算法FDR FIR FAR MDR 最小二乘残差法 75.1 38.2 0 24.9 基于卡尔曼滤波的
故障检测法66.75 54.3 0 33.25 所提算法 66.25 66.25 0 33.75 表 13 动态数据在
${{\boldsymbol{T}}_{{\bf{SE}}}} $ = 200 s,${{\boldsymbol{V}}_{{\bf{SE}}}}$ = 0.2 m/s故障下定位精度指标Table 13. Positioning accuracy for candidate algorithms with a 0.2 m/s ramp error added for 200 s indynamic mode
m 故障检测算法 方向 误差最大值 95%分位误差 均方根误差 最小二乘残差法 竖直 18.743 4.570 2.575 水平 11.845 8.743 3.385 3D 20.681 8.814 4.253 基于卡尔曼滤波
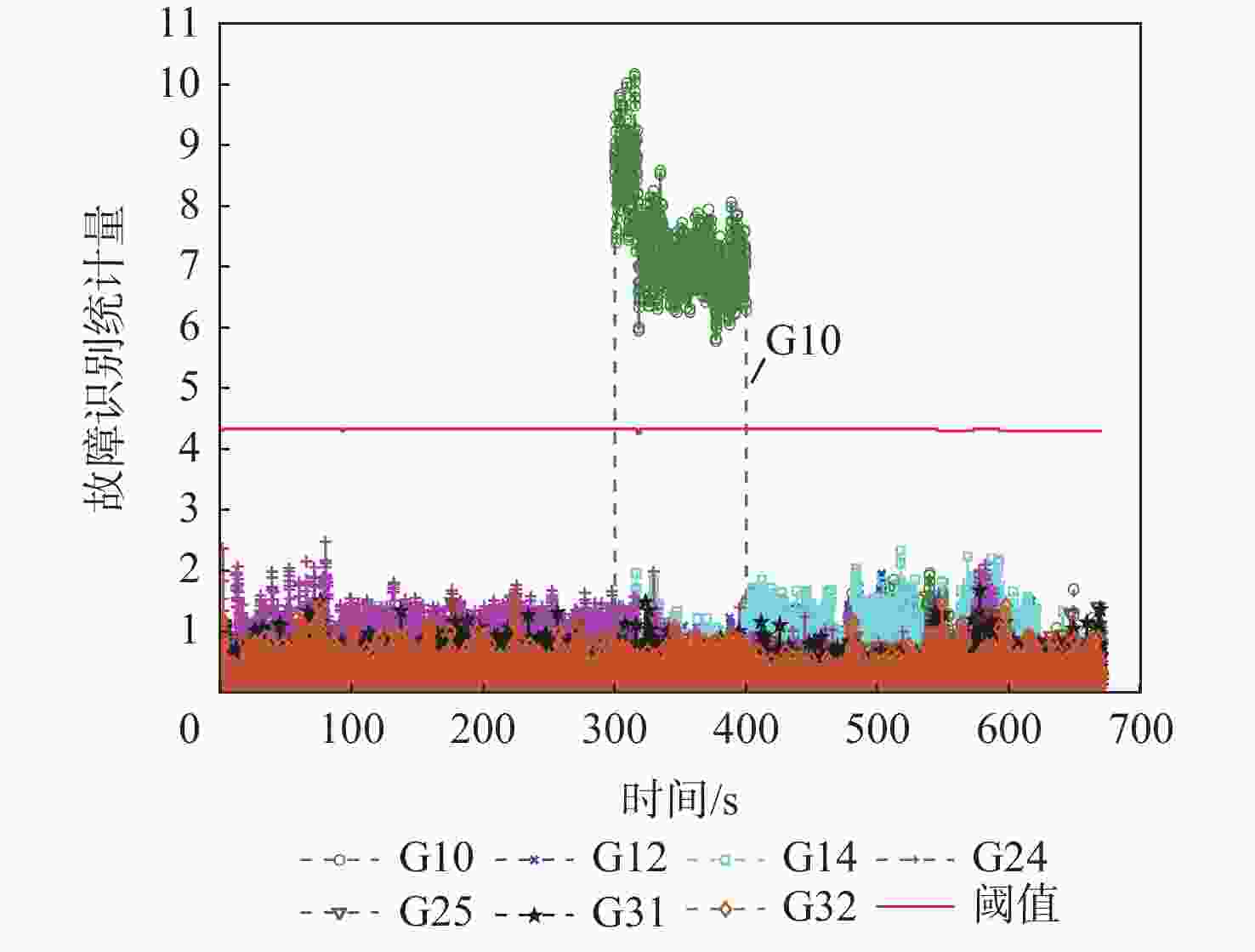
的故障检测法竖直 9.920 4.453 2.776 水平 8.845 5.956 2.429 3D 11.267 6.124 3.689 所提算法 竖直 9.920 3.942 1.975 水平 5.976 3.347 1.616 3D 11.267 4.629 2.552 表 14 动态数据中卫星G10和G12的伪距同时含有10 m阶跃故障下的故障检测指标
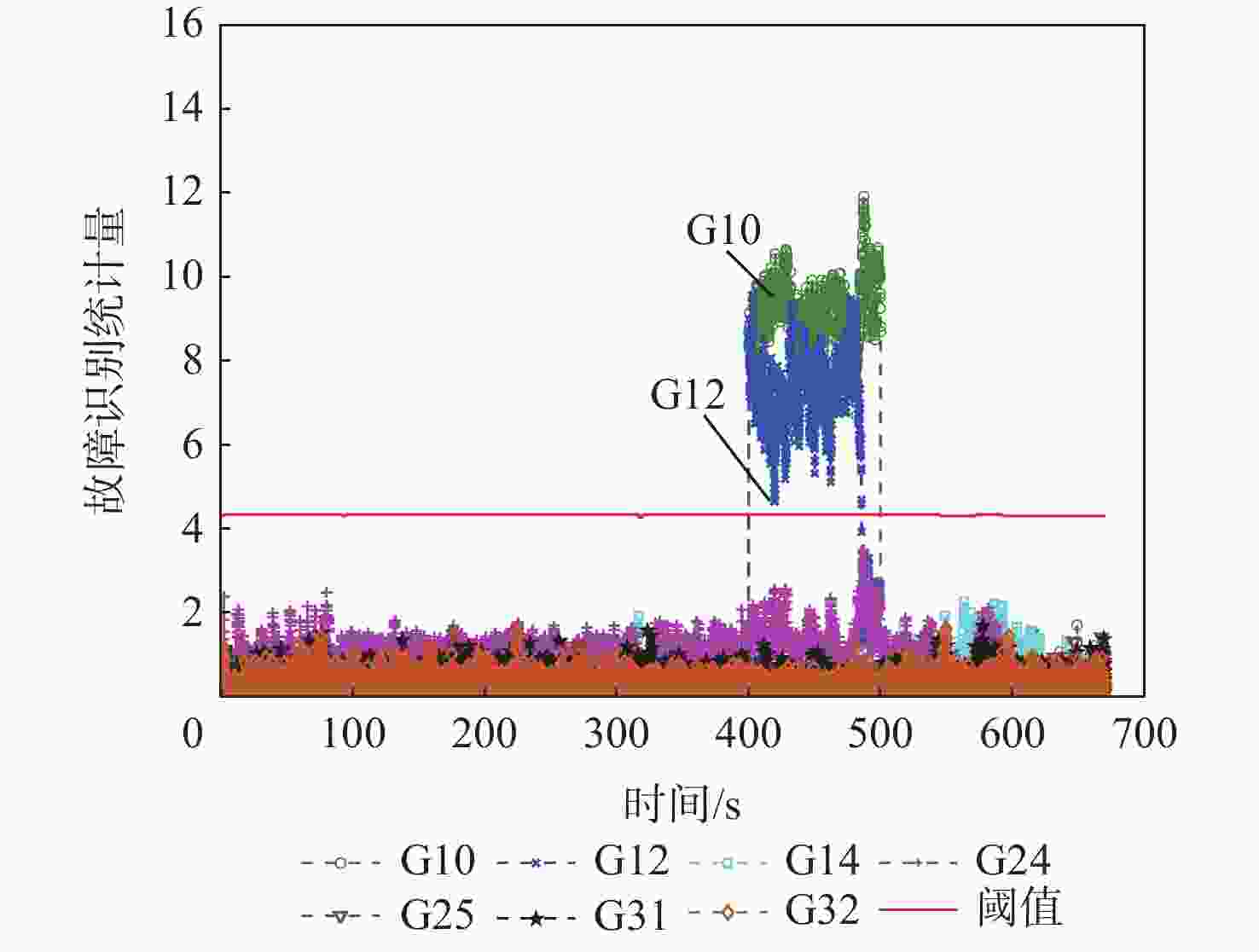
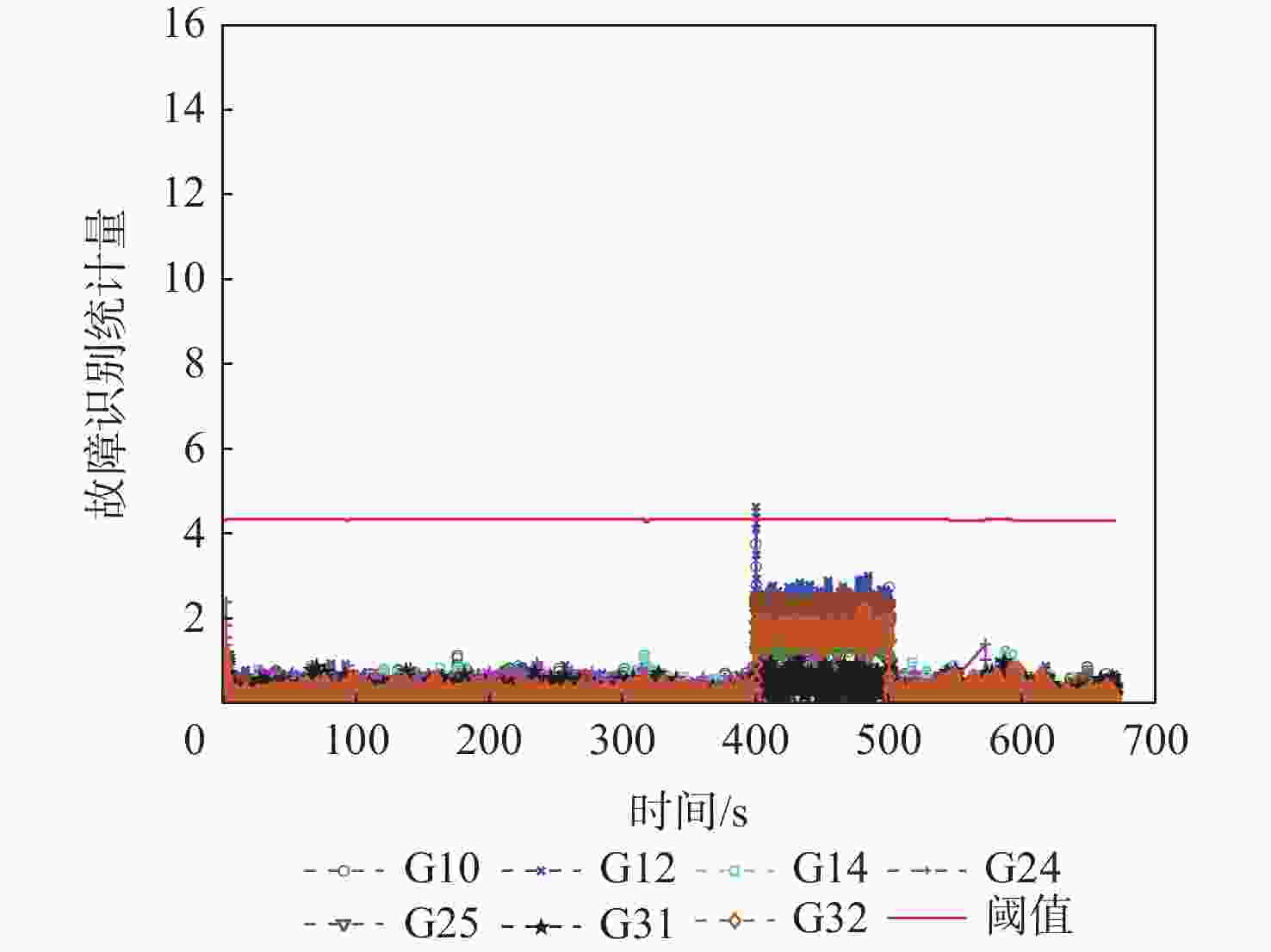
Table 14. Fault detection performance for candidate algorithms with 10 m step errors added on pseudorange of G10 and G12 in dynamic mode
% 故障检测
算法FDR FIR FAR MDR 基于卡尔曼滤波的
故障检测法3.7 0 0 96.3 所提算法 100 85.6 0 0 表 15 动态数据中卫星G10和G12的伪距同时含有10 m的故障下的定位精度指标
Table 15. Positioning accuracy performance for candidate algorithms with 10 m step errors added on pseudorange of G10 and G12 in dynamic mode
m 故障检测算法 方向 误差
最大值95%分位误差 均方根误差 基于卡尔曼滤波
的故障检测法竖直 17.316 15.237 6.382 水平 5.976 3.018 1.756 3D 17.476 15.496 6.618 所提算法 竖直 11.851 4.118 2.064 水平 5.976 3.340 1.654 3D 12.572 5.102 2.645 -
[1] MENG Q, HSU L T. Integrity for autonomous vehicles and towards a novel alert limit determination method[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D:Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2021, 235(4): 996-1006. doi: 10.1177/0954407020965760 [2] HSU L T. GNSS multipath detection using a machine learning approach[C]//2017 IEEE 20th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1-6. [3] LEE Y. Analysis of range and position comparison methods as a means to provide GPS integrity in the user receiver[J]. Navigation Journal of the Institute of Navigation, 1986: 1-17. [4] PARKINSON B W, AXELRAD P. Autonomous GPS integrity monitoring using the pseudorange residual[J]. Navigation, 1988, 35(2): 255-274. doi: 10.1002/j.2161-4296.1988.tb00955.x [5] STURZA M A. Navigation system integrity monitoring using redundant measurements[J]. Navigation, 1988, 35(4): 483-501. doi: 10.1002/j.2161-4296.1988.tb00975.x [6] BROWN R G. A baseline GPS RAIM scheme and a note on the equivalence of three RAIM methods[J]. Navigation, 1992, 39(3): 301-316. doi: 10.1002/j.2161-4296.1992.tb02278.x [7] 沙海, 黄新明, 刘文祥, 等. 基于非相干积累的微小伪距偏差RAIM方法研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2014, 35(6): 708-712.SHA H, HUANG X M, LIU W X, et al. Research on the RAIM method based on non-coherent accumulation for tiny pseudo-range bias[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2014, 35(6): 708-712(in Chinese). [8] 沙海, 田丰, 王东会, 等. 用于消除缓变伪距偏差的抗差扩展卡尔曼滤波方法[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2014, 36(5): 131-135. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201405022SHA H, TIAN F, WANG D H, et al. A new robust extended Kalman filter method for eliminating the slowly growing pseudo-range error[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2014, 36(5): 131-135(in Chinese). doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201405022 [9] BHATTACHARYYA S, GEBRE-EGZIABHER D. Kalman filter–based RAIM for GNSS receivers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(3): 2444-2459. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2015.130585 [10] 黄小平, 王岩. 卡尔曼滤波原理及应用: MATLAB仿真[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2015: 77-79.HUANG X P, WANG Y. Principle and application of Kalman filter: MATLAB simulation [M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2015: 77-79 (in Chinese). [11] 王尔申, 庞涛, 曲萍萍, 等. 基于粒子滤波和似然比的接收机自主完好性监测算法[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2015, 47(1): 46-51. doi: 10.16356/j.1005-2615.2015.01.006WANG E S, PANG T, QU P P, et al. RAIM algorithm based on particle filter and likelihood ratio method[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2015, 47(1): 46-51(in Chinese). doi: 10.16356/j.1005-2615.2015.01.006 [12] 王尔申, 曲萍萍, 庞涛, 等. 粒子群优化粒子滤波的接收机自主完好性监测[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(12): 2572-2578. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0362WANG E S, QU P P, PANG T, et al. Receiver autonomous integrity monitoring based on particle swarm optimization particle filter[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42(12): 2572-2578(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0362 [13] 刘江, 蔡伯根, 王剑, 等. 专用短程通信辅助的车辆卫星定位故障检测方法[J]. 中国公路学报, 2021, 34(11): 265-281. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2021.11.022LIU J, CAI B G, WANG J, et al. Dedicated short-range-communication-aided fault detection method for satellite-based vehicle positioning[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2021, 34(11): 265-281(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2021.11.022 [14] 吴云. GNSS粗差检测的“快照”法与“滤波”法的比较研究[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 2010, 35(6): 649-652. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis2010.06.024WU Y. GNSS fault detection and identification performance comparison of snapshot and filtering[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2010, 35(6): 649-652(in Chinese). doi: 10.13203/j.whugis2010.06.024 [15] 许明, 刘建业, 袁信. 自适应卡尔曼滤波在惯导初始对准中的应用研究[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 1999, 7(3): 15-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6734.1999.03.003XU M, LIU J Y, YUAN X. The application of adaptive Kalman filter technique in initial alignment of inertial navigation system[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 1999, 7(3): 15-17(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6734.1999.03.003 [16] MOHAMED A H, SCHWARZ K P. Adaptive Kalman filtering for INS/GPS[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 1999, 73(4): 193-203. doi: 10.1007/s001900050236 -






 下载:
下载: