-
摘要:
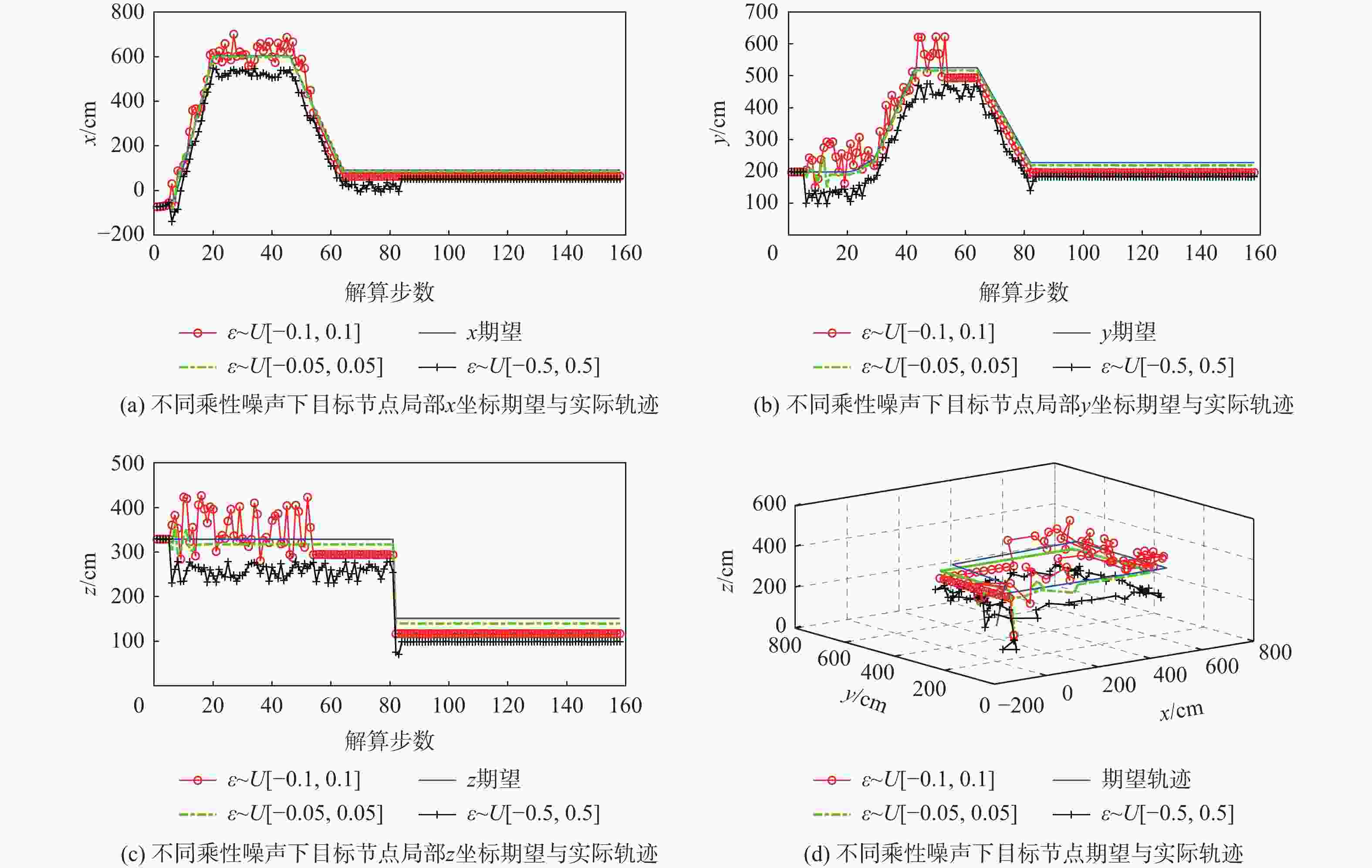
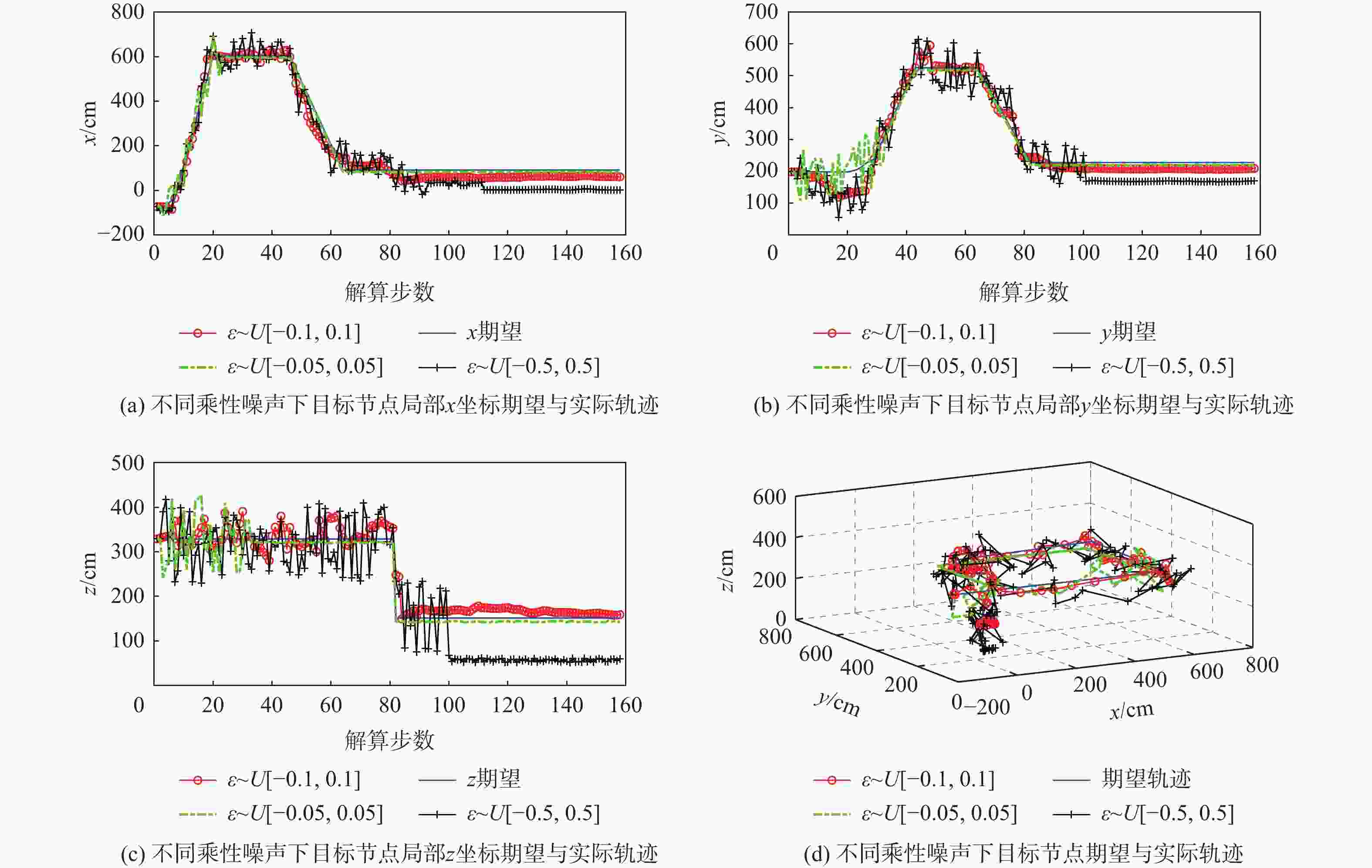
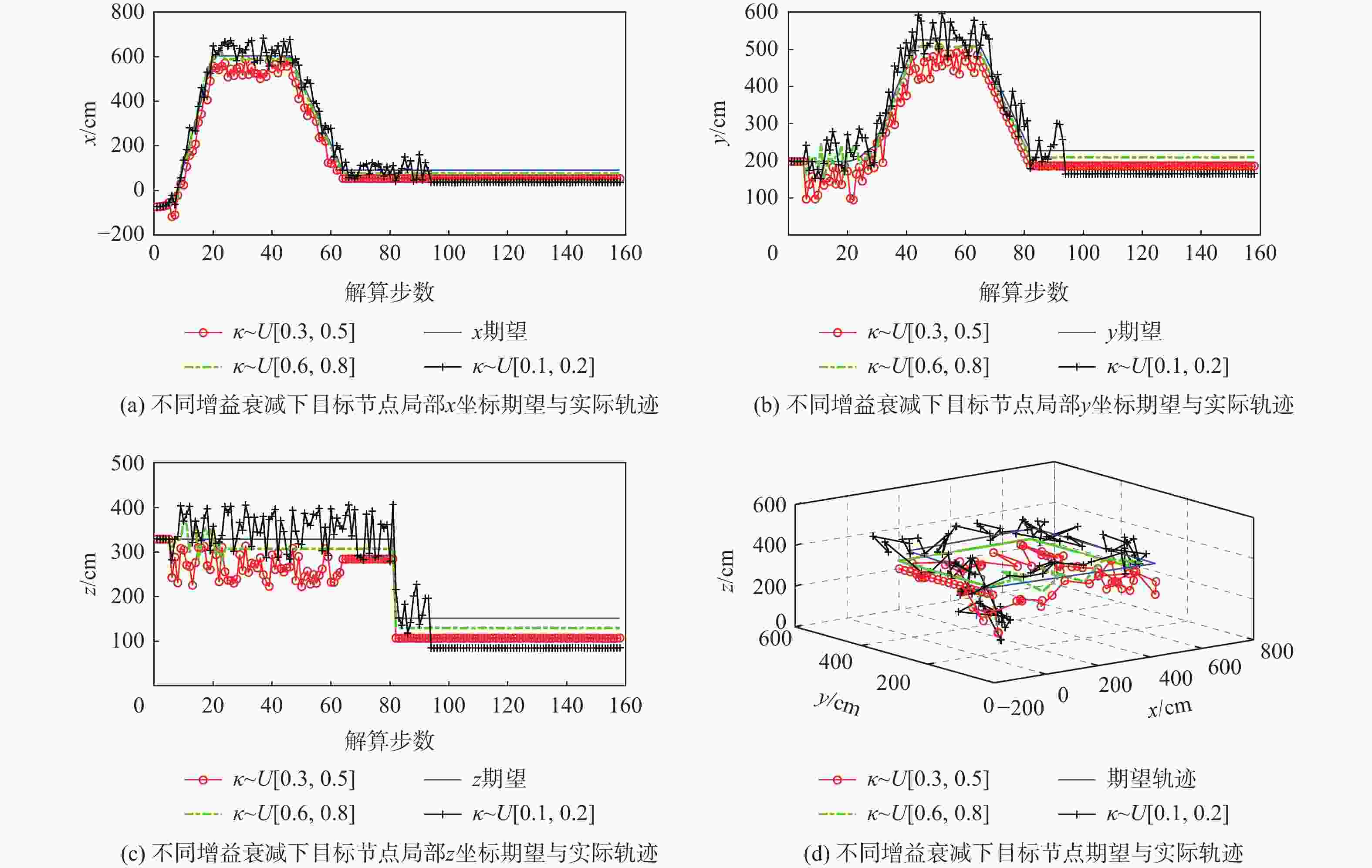
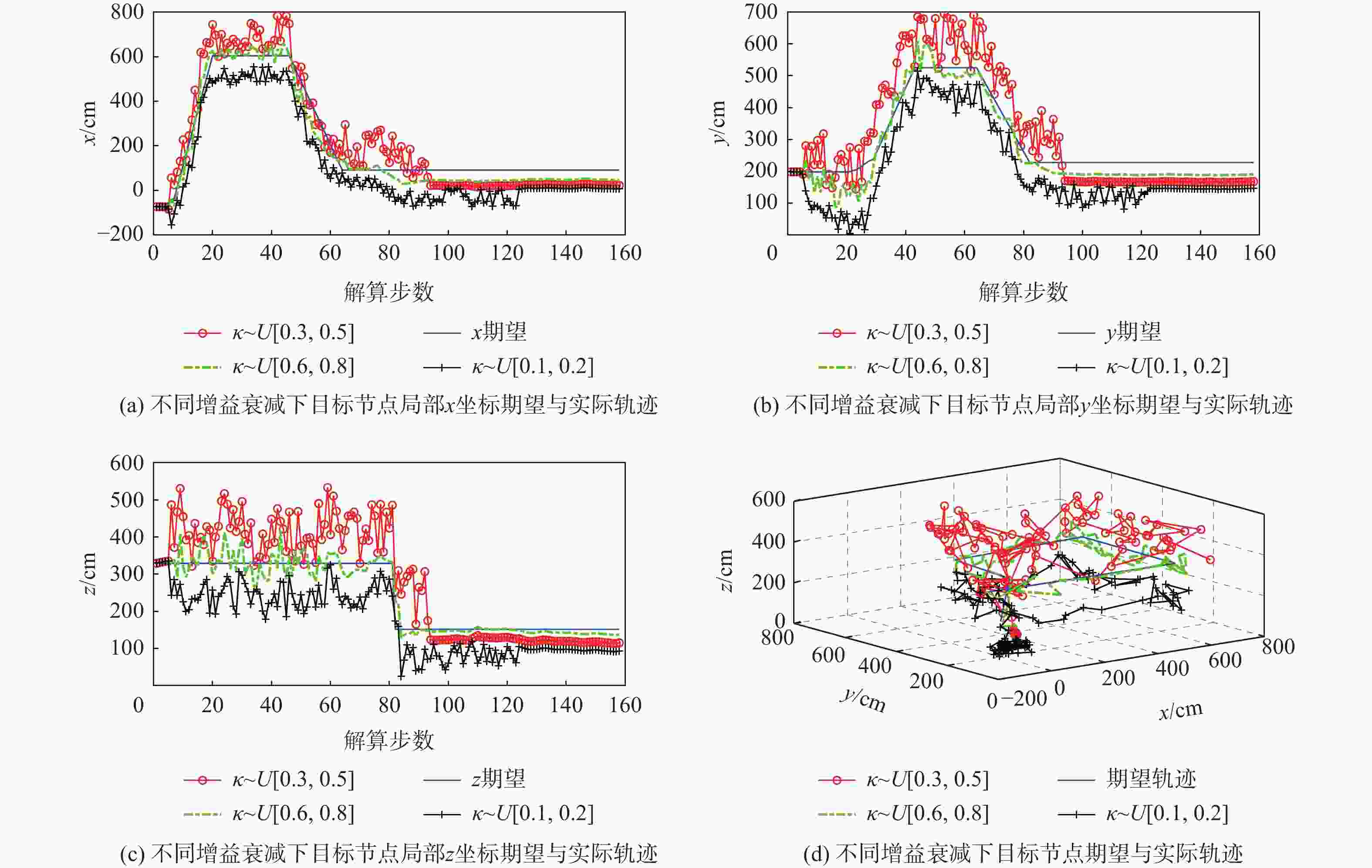
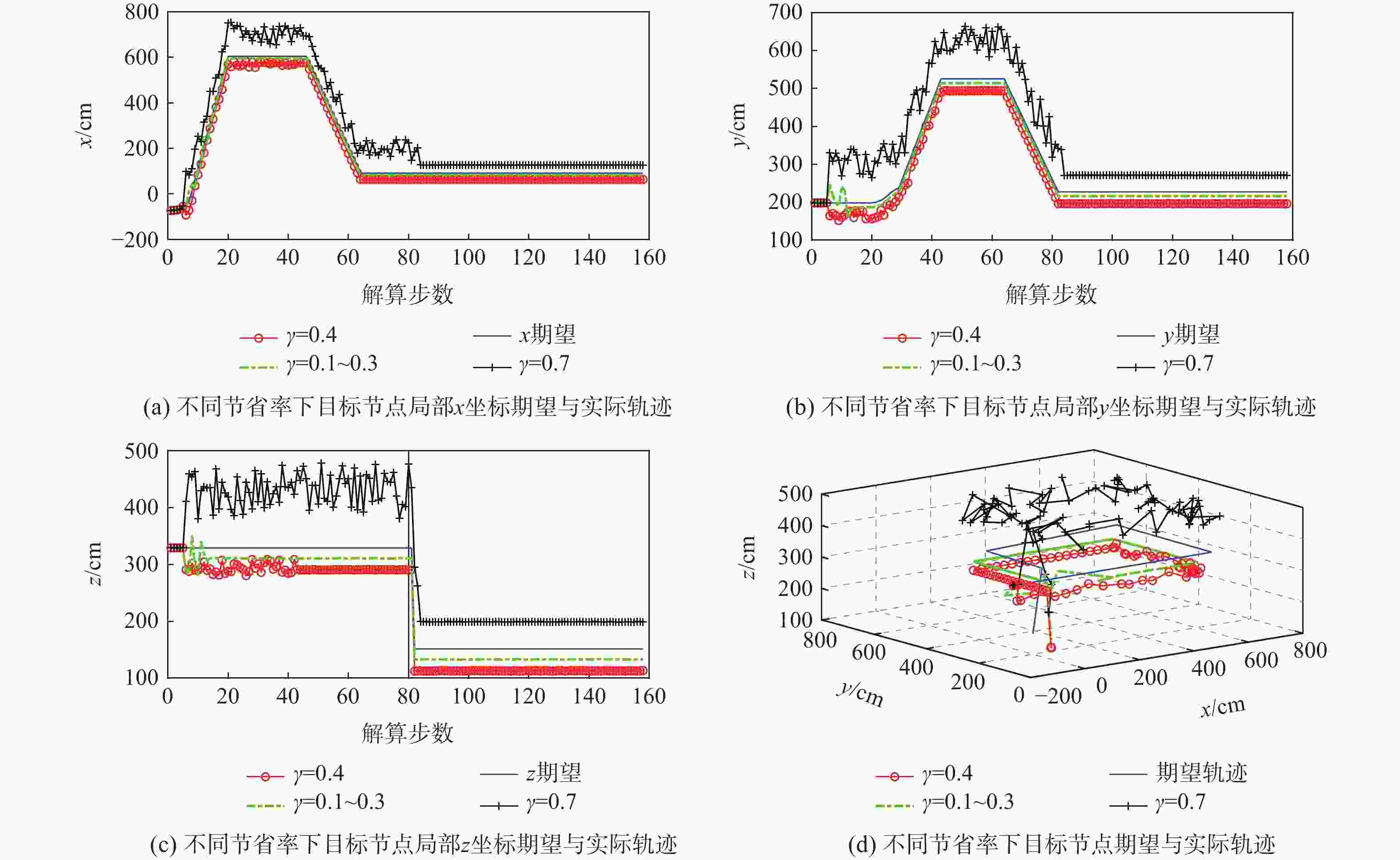
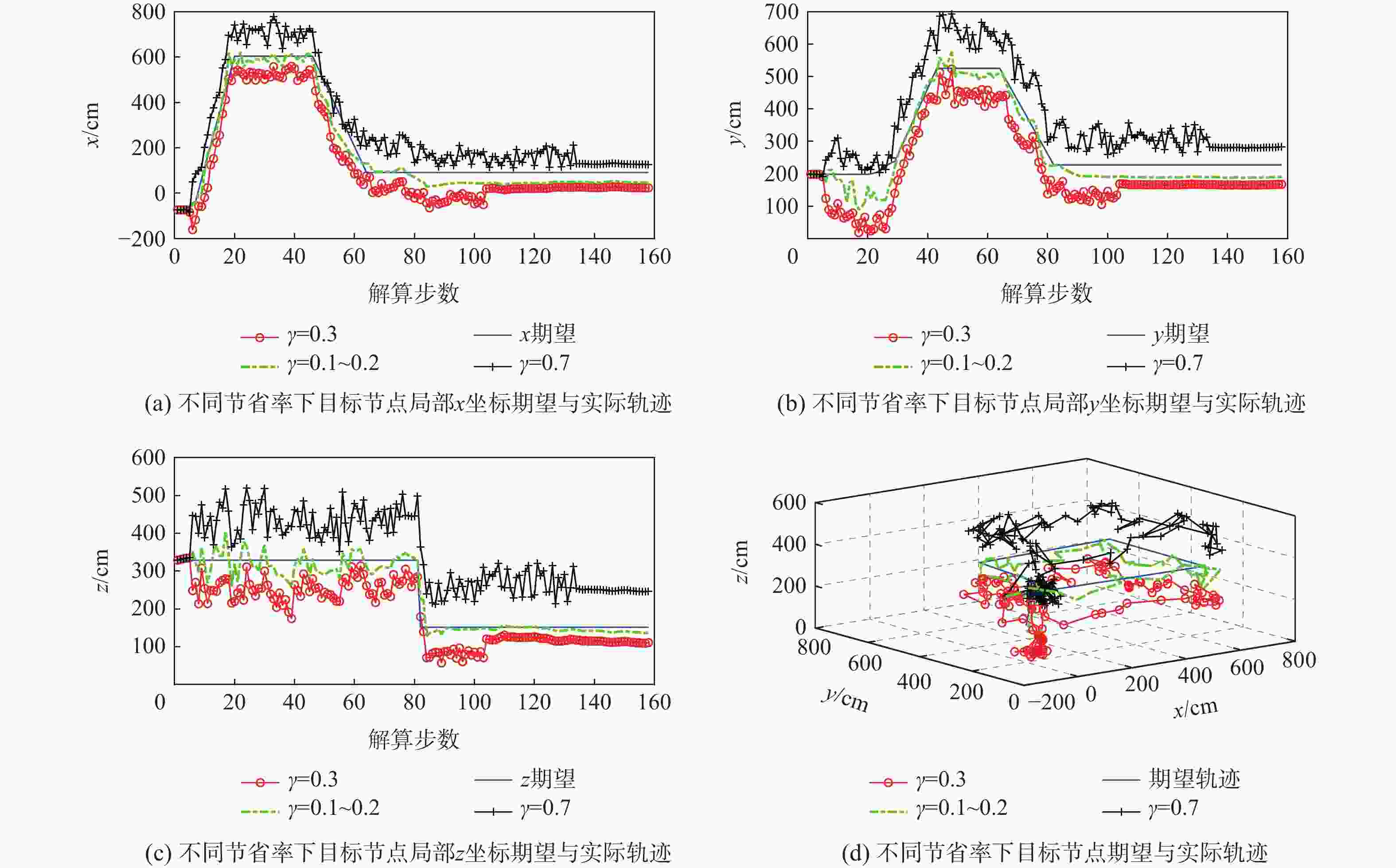
针对节点量测增益衰减、节点能量受限与系统模型不确定3种网络约束下具有随机通信时滞和非固定丢包率的组网导航系统(NNS)分布式状态融合估计问题,将增益衰减程度描述为统计特性已知的随机变量,将模型不确定描述为系统矩阵中的乘性有色噪声,将减小能耗描述为降低节点数据传输率。分别在邻节点端和目标节点端引入2种不同的线性编码器以解决丢包与时滞问题。建立丢包率与同时传输信息的节点数目之间的函数关系,将邻节点在过去有限个时刻的量测值进行线性编码后再传输,以补偿丢包与降低传输率导致的信息损失。目标节点把在同一采样周期内获取的来自同一邻节点的多个量测值按时间戳进行线性编码,以解决通信时滞导致的信息多余。基于2次线性编码建立增广系统模型,设计最小方差意义下局部无偏估计器,利用最优矩阵加权融合法得到全局融合估计器,推导得到融合估计误差协方差收敛的充分条件及次优传输率。通过算例仿真验证所提算法的有效性。
Abstract:For the distributed state fusion estimation problem of networked navigation system (NNS) with random communication delay and non-fixed packet loss rate under three network constraints, namely, node measurement gain attenuation, node energy limitation and system model uncertainty, the degree of node gain attenuation is described as a random variable with known statistical characteristics, and the system model uncertainty is described as a multiplicative colored color in the system matrix noise, the reduction of energy consumption of small cell network node is described as the reduction of the data transmission rate. To address the packet loss and delay issues, two distinct linear encoders are introduced at the target node and the adjacent node, respectively. In order to compensate the information loss caused by packet loss and transmission rate reduction, a function relationship between the non-fixed packet loss rate and the number of nodes transmitting information simultaneously is established. In order to solve the problem of information redundancy caused by communication delay, the target node linearly encodes multiple measurements from the same neighbor node in the same sampling period according to the time stamp. An augmented system model is established based on the new measurements added linearly at the end of the target node. The global fusion estimator form is obtained by utilizing the optimal matrix weighting approach, and the recursive form of the local unbiased estimation is generated by employing minimal variance. The sufficient conditions for the bounded covariance of the fusion estimation error and the suboptimal transmission rate are derived. Finally, an example is given to verify the effectiveness of the algorithm.
-
-
[1] GAO C, LU J H, ZHAO G R, et al. Adaptive finite-horizon group estimation for networked navigation systems with remote sensing complementary observations under mixed LOS/NLOS environments[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2016, 2016: 6489165. [2] HELEN B, ELIANE S, HARRY K, et al. Comprehension and navigation of networked hypertexts[J]. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 2018, 34(3): 306-314. doi: 10.1111/jcal.12243 [3] 赵国荣, 韩旭, 王康. 具有传感器增益退化、传输时延和丢包的离线状态估计器[J]. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(3): 540-548.ZHAO G R, HAN X, WANG K. Off line state estimator with sensor gain degradation, transmission delay and packet loss[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(3): 540-548(in Chinese). [4] SONG H Y, YU L, ZHANG D. Distributed set-valued estimation in sensor networks with limited communication data rate[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2013, 350(5): 1264-1283. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2013.02.024 [5] SHI Z C, YANG Y Q, CHANG Q, et al. The optimal state estimation for competitive neural network with time-varying delay using local search algorithm[J]. Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2020, 540: 123102. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2019.123102 [6] WANG X, SUN S L. Optimal recursive estimation for networked descriptor systems with packet dropouts, multiplicative noises and correlated noises[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2017, 63: 41-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2016.11.025 [7] GABRIEL A, ABDOLLAH H. A reliability-based multi-sensor data fusion with application in target classification[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(8): 69-79. [8] XIA Y Q, SHANG J Z, CHEN J, et al. Networked data fusion with packet losses and variable delays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 2009, 39(5): 37-48. [9] ÁGUILA R, CARAZO A. Networked distributed fusion estimation under uncertain outputs with random transmission delays, packet losses and multi-packet processing[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 156: 71-83. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2018.10.012 [10] HE L D, HAN D F, WANG X F, et al. Optimal linear state estimation over a packet-dropping network using linear temporal coding[J]. Automatica, 2013, 49(4): 1075-1082. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2013.01.043 [11] SUI T J, YOU K Y, FU M Y, et al. Stability of MMSE state estimators over lossy networks using linear coding[J]. Automatica, 2015, 51: 167-174. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.10.086 [12] MA J, SUN S L. Linear estimators for networked systems with one-step random delay and multiple packet dropouts based on prediction compensation[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2017, 11(2): 197-204. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2016.0260 [13] STEFANO B, ANGELO M. Stochastic output delay identification of discrete-time Gaussian systems[J]. Automatica, 2019, 109: 108499. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.108499 [14] GAO C, ZHAO G R, LU J H, et al. Decentralised moving-horizon state estimation for a class of networked spatial-navigation systems with random parametric uncertainties and communication link failures[J]. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2015, 9(18): 2666-2677. doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2015.0323 [15] LIU W, SHI P. Optimal linear filtering for networked control systems with time-correlated fading channels[J]. Automatica, 2019, 101: 345-353. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2018.11.042 [16] LIN H L, SUN S L. Globally optimal sequential and distributed fusion state estimation for multi-sensory systems with cross-correlated noises[J]. Automatica, 2019, 101: 128-137. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2018.11.043 [17] HABTI A, DELMAS J. Efficiency of subspace-based estimators for elliptical symmetric distributions[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 174: 107644. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107644 [18] 韩旭, 赵国荣, 王康. 基于线性编码补偿方法的非固定丢包率下的分布式融合估计器[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(6): 1229-1236.HAN X, ZHAO G R, WANG K. Distributed fusion estimator based on linear coding compensation method under unfixed packet loss rate[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(6): 1229-1236(in Chinese). [19] AVIANSH R, KANNAN S. Development of event-triggered-based minimum variance recursive estimator for the NLNS using multi-model approach[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2019, 13(9): 766-777. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2018.5546 [20] SUN S L, TIAN T, LIN H L. State estimators for systems with random parameter matrices, stochastic nonlinearities, fading measurements and correlated noises[J]. Information Sciences, 2017, 397-398: 118-136. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2017.02.048 [21] SUBIR G, GUO L, PENG L Y. Variance component estimators OPE, NOPE and AOPE in linear mixed effects models[J]. Australian & New Zealand Journal of Statistics, 2018, 60(4): 481-505. [22] GAO C, ZHAO G R, PAN S. Distributed multi-weight data-gathering and aggregation protocol in fleet wireless sensor networks: Optimal and heuristic algorithms[J]. International Journal of Intelligent Engineering and Systems, 2010, 3(2): 26-36. doi: 10.22266/ijies2010.0630.04 [23] YUAN P, ZHANG T T, YANG N, et al. Energy efficient network localisation using hybrid TOA/AOA measurements[J]. IET Communications, 2019, 13(8): 963-971. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2018.5419 -







 下载:
下载: