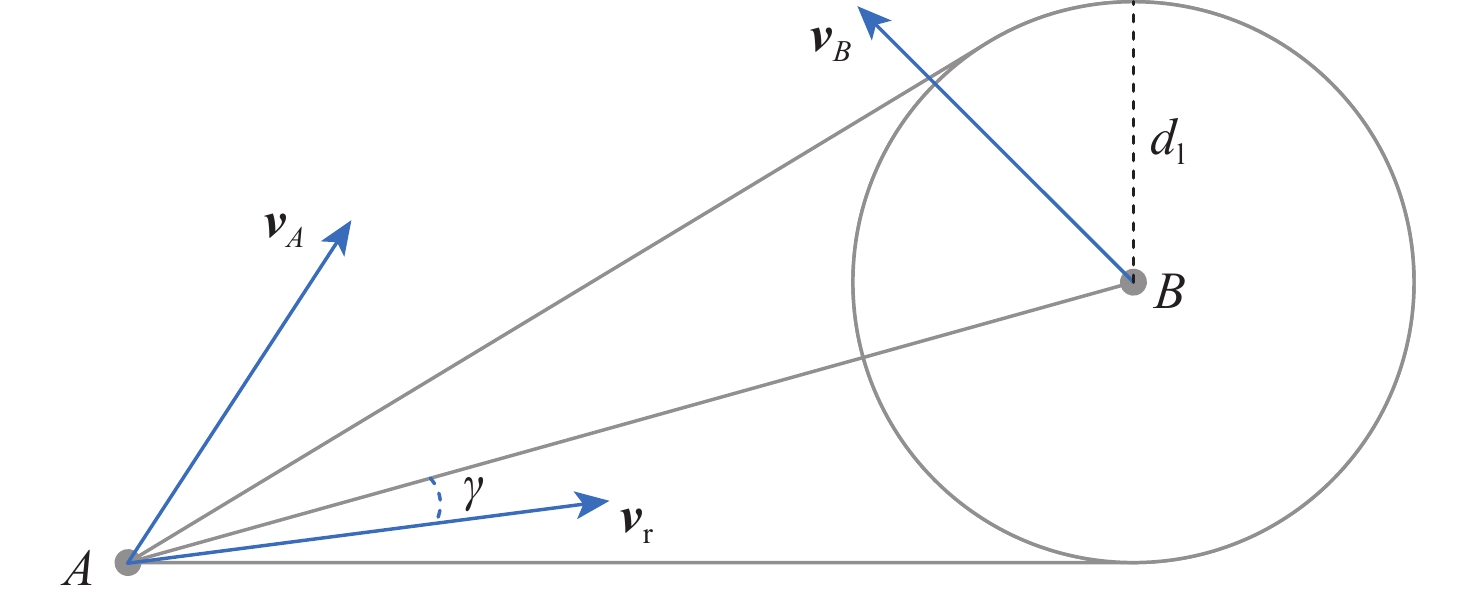
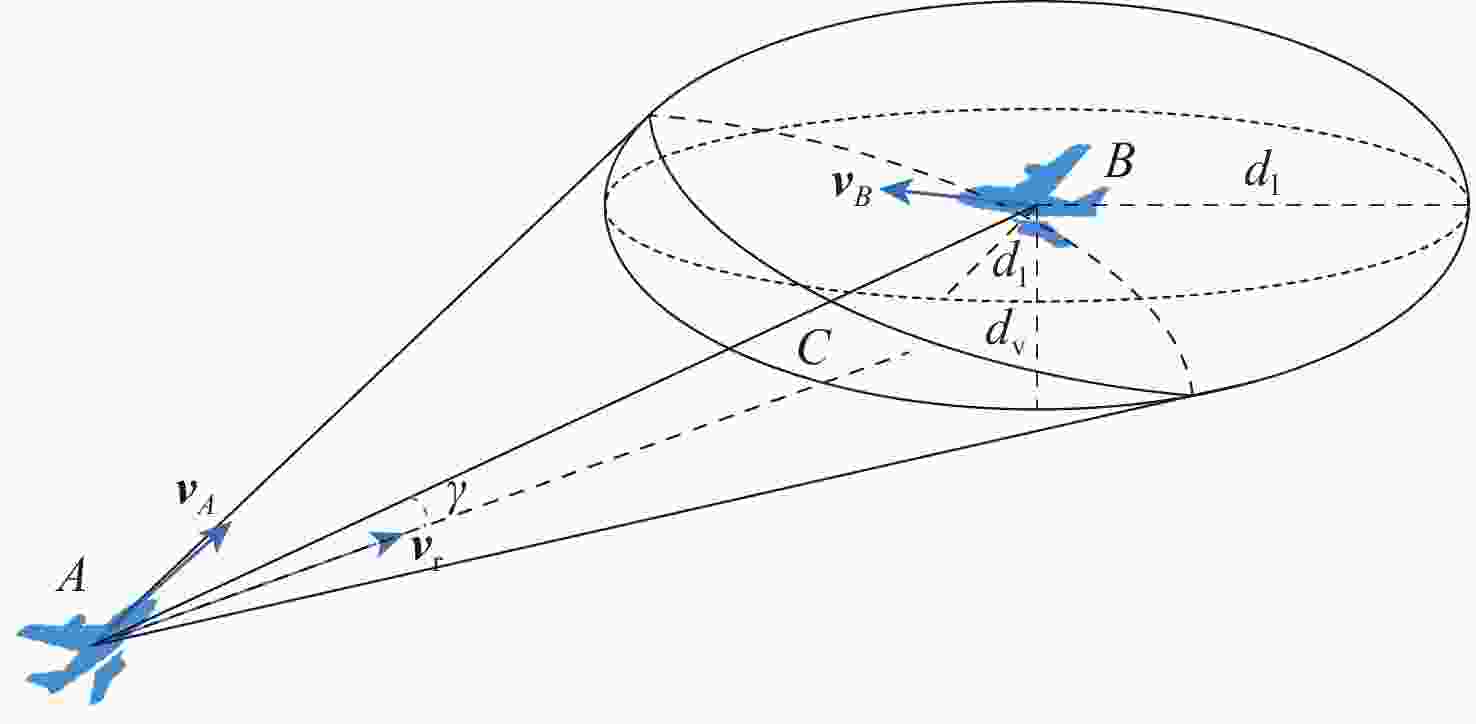
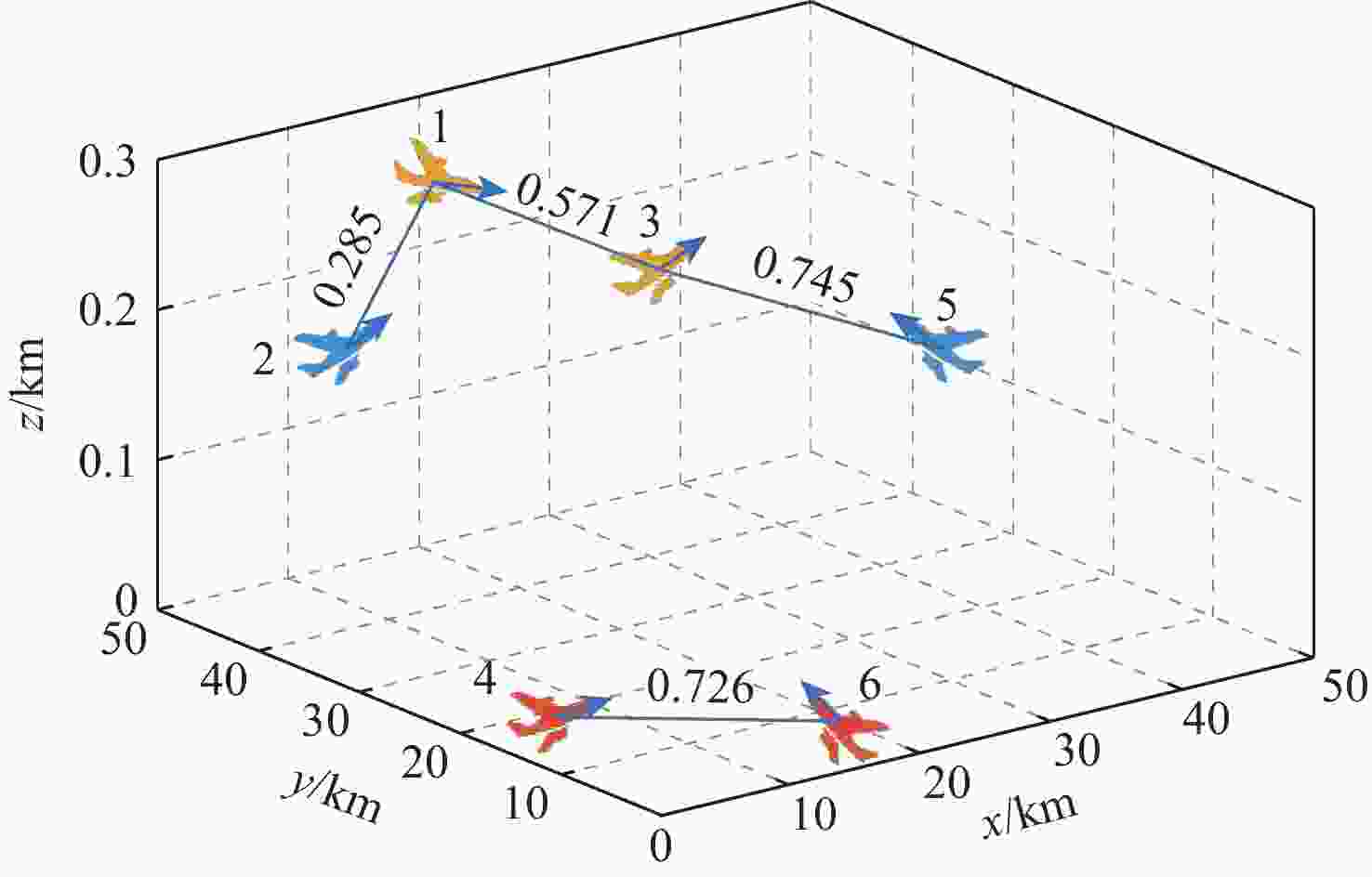
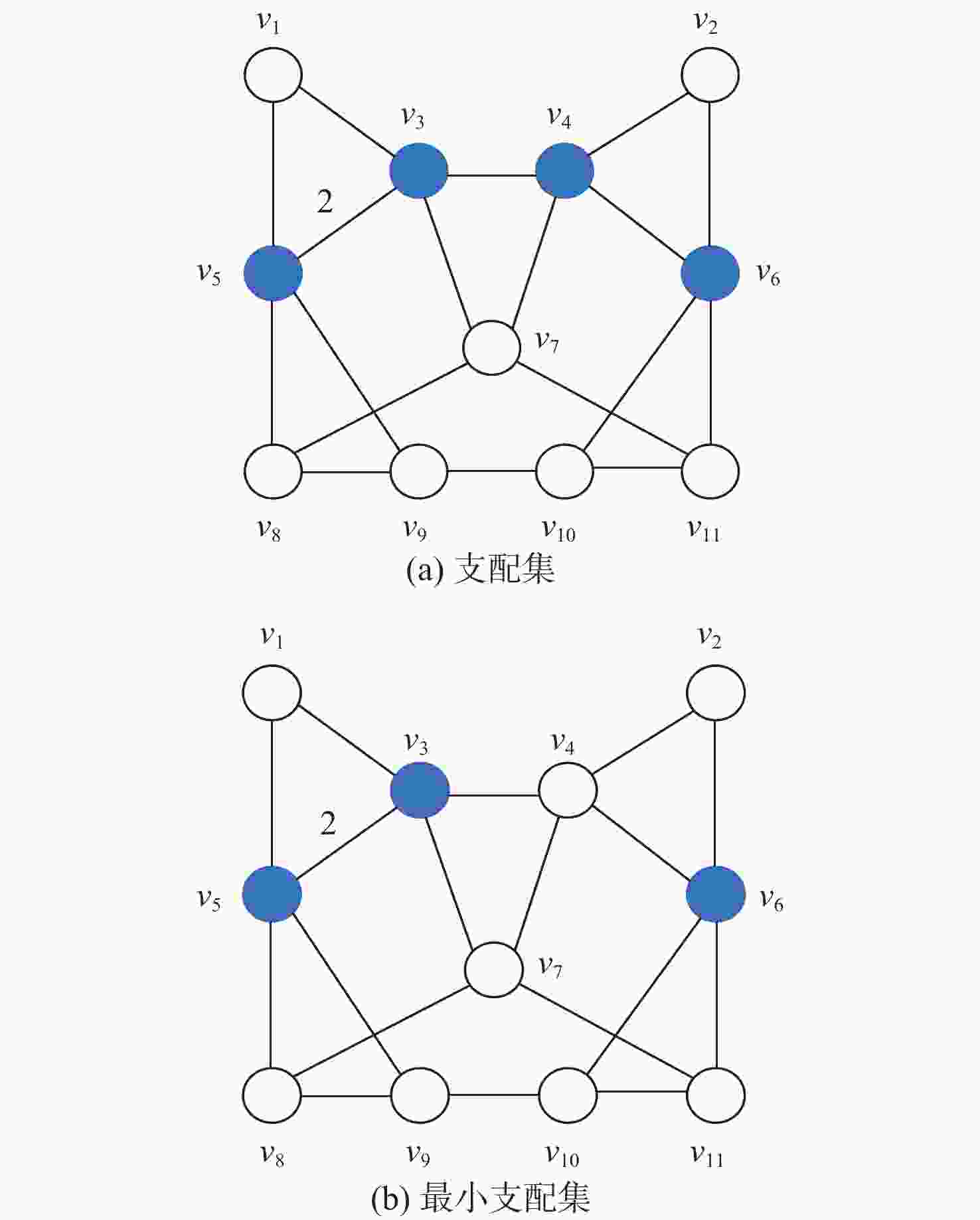
Conflict resolution strategy based on optimal dominating set of flight conflict networks
-
摘要:
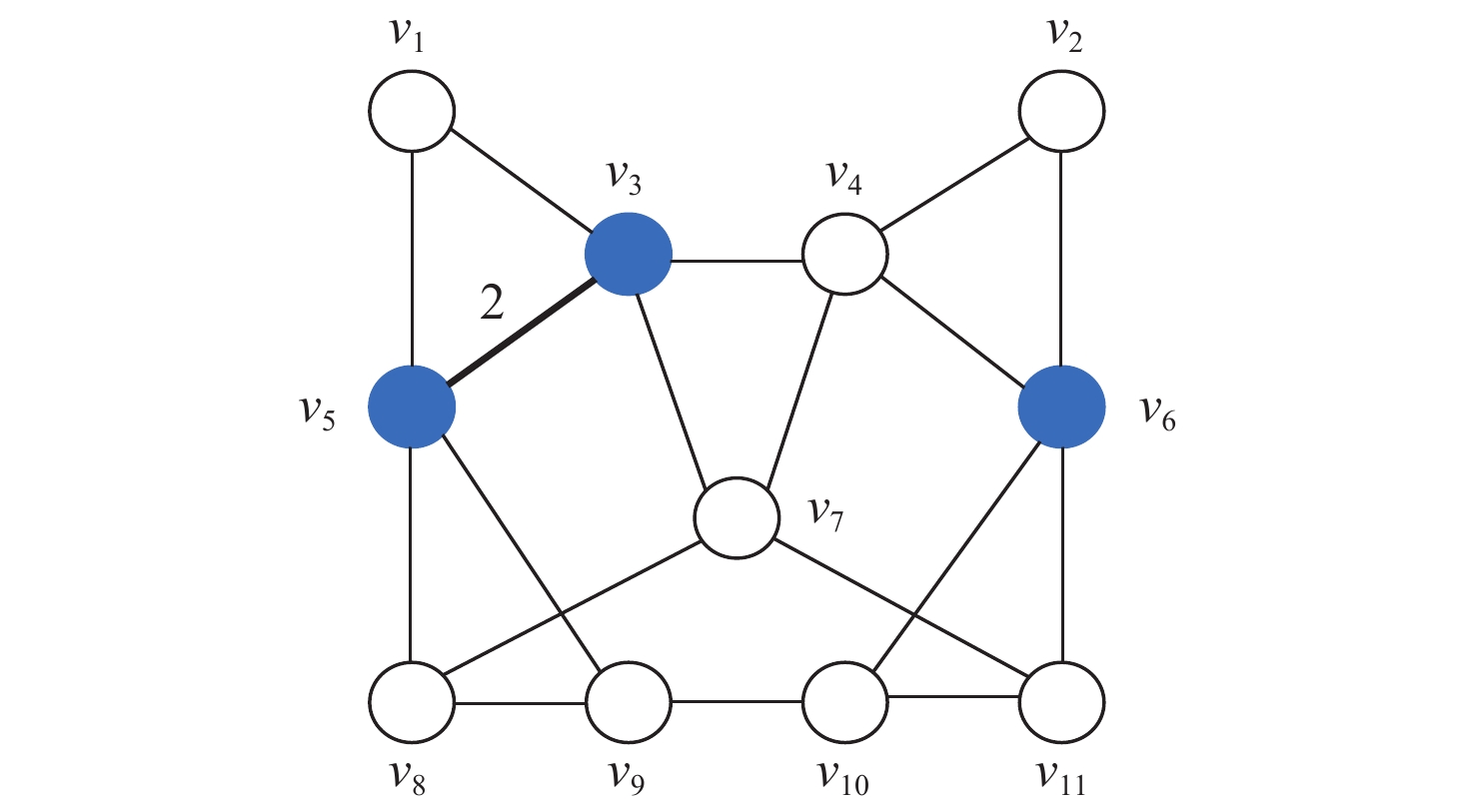
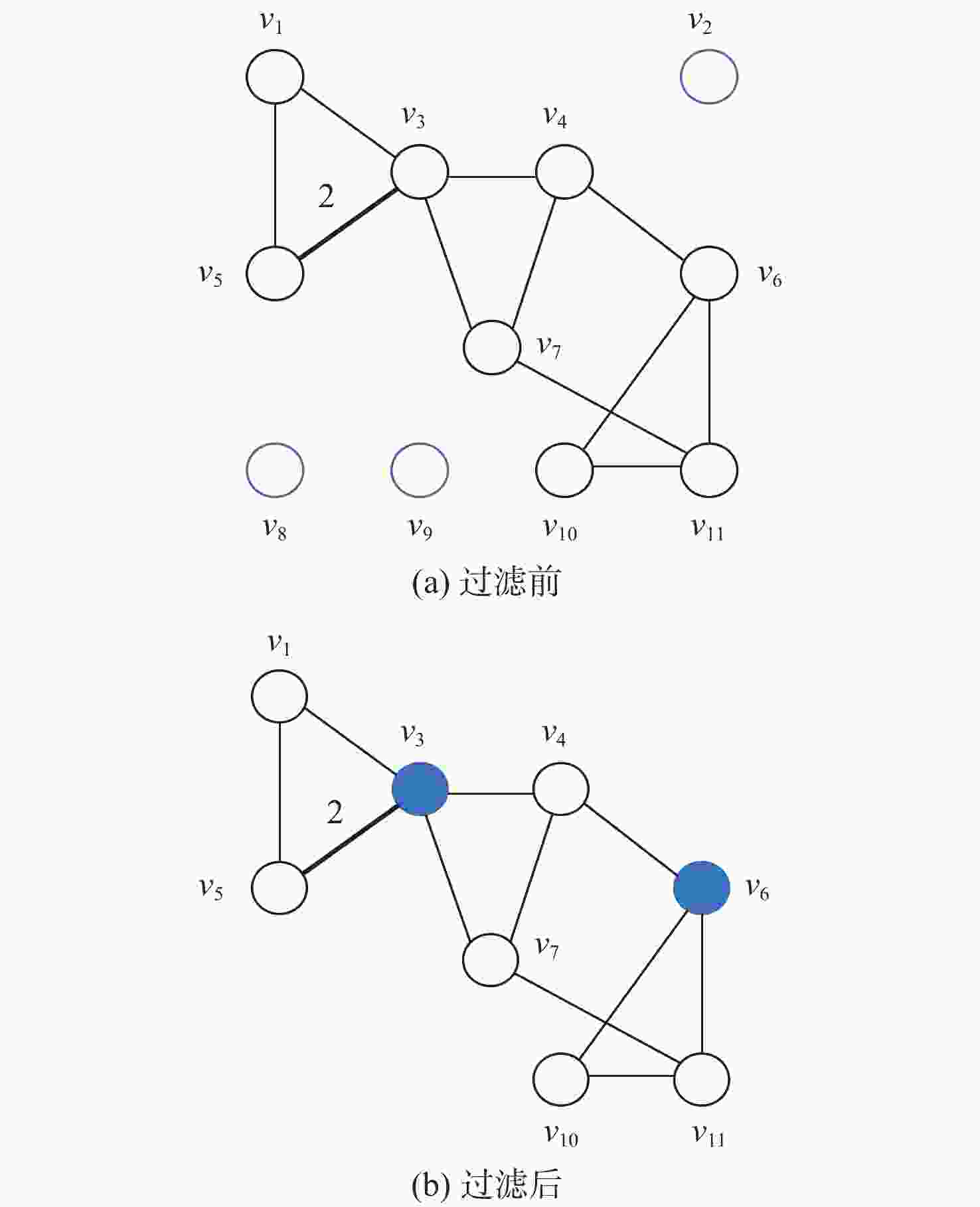
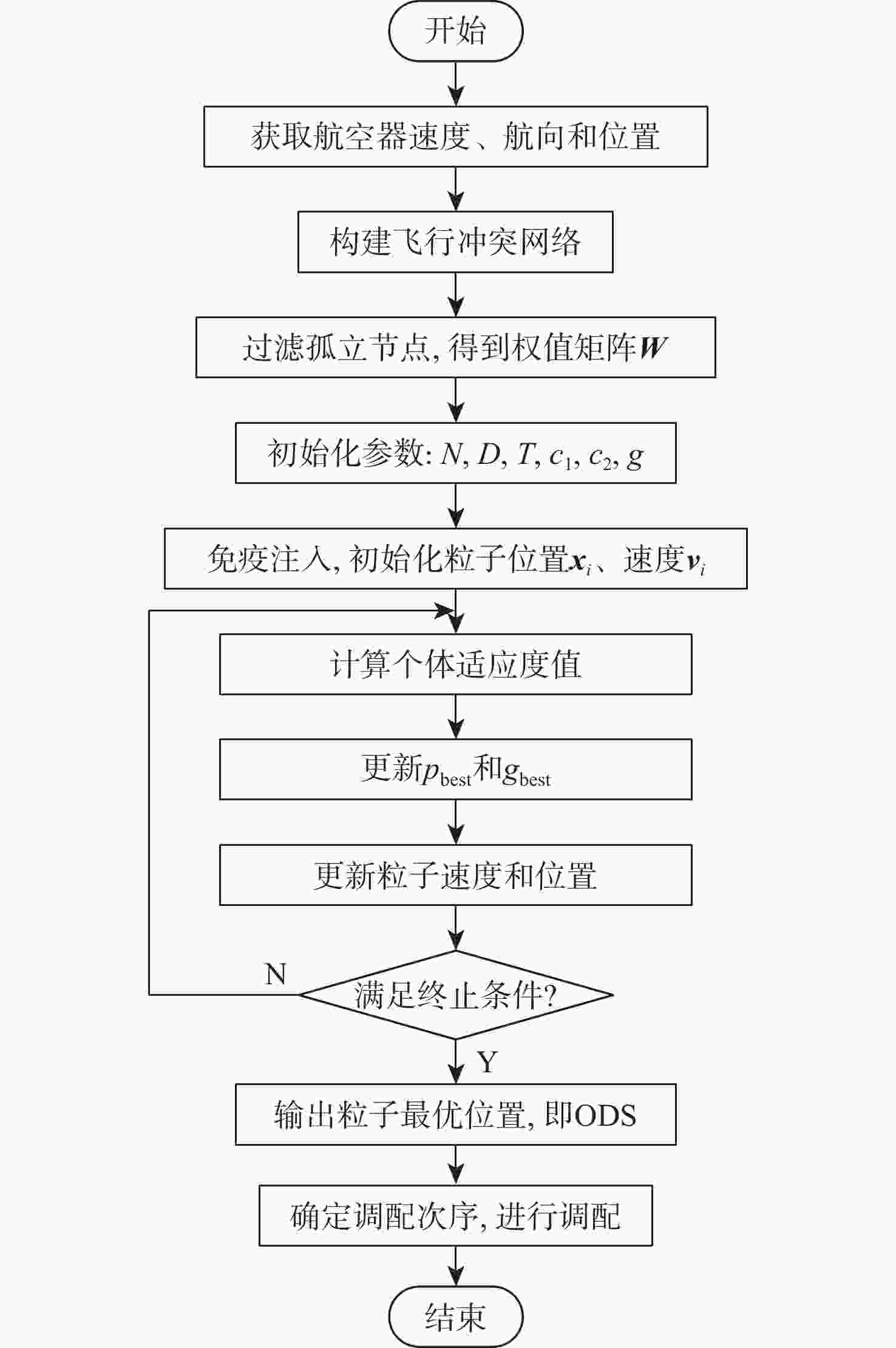
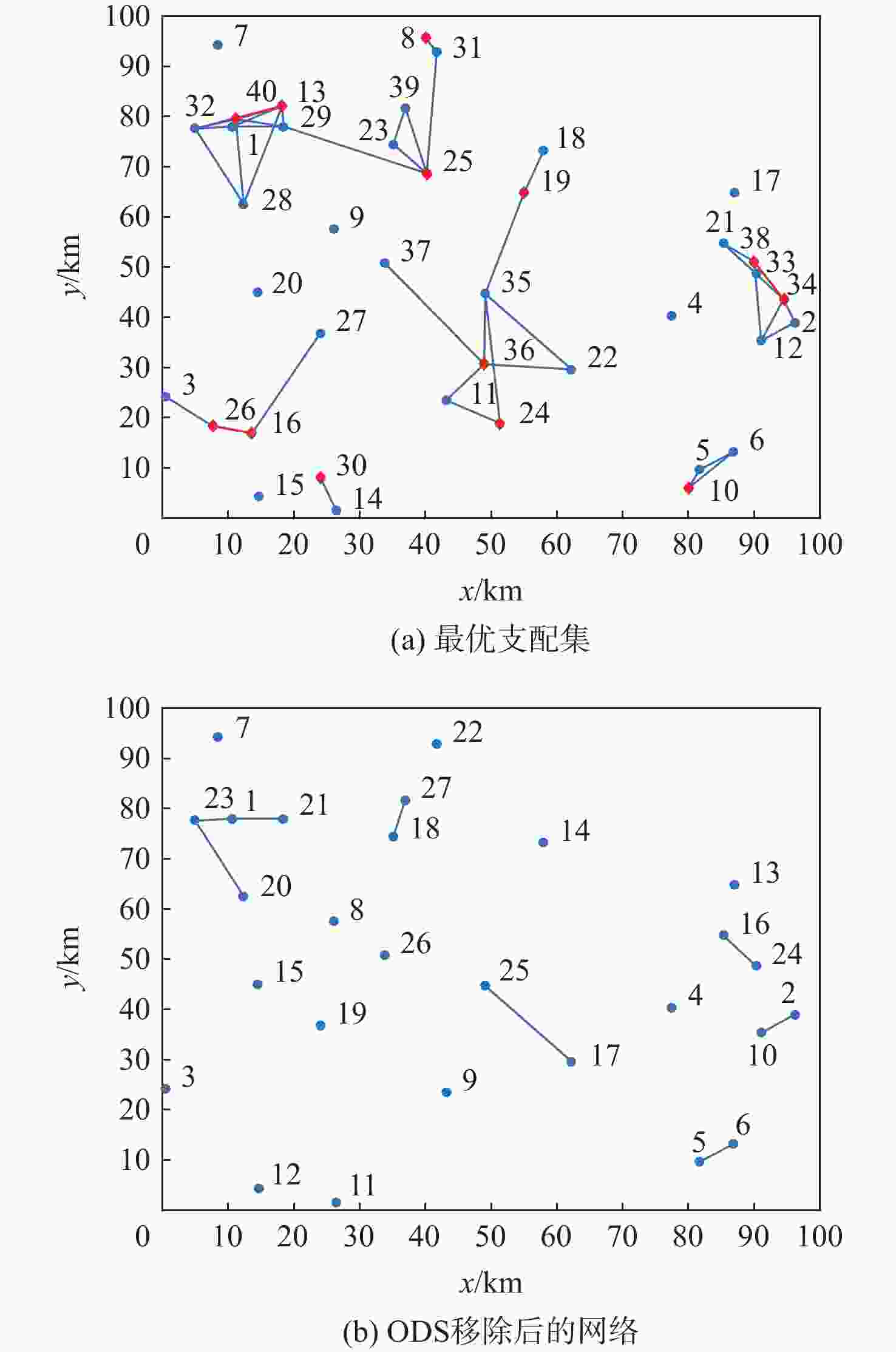
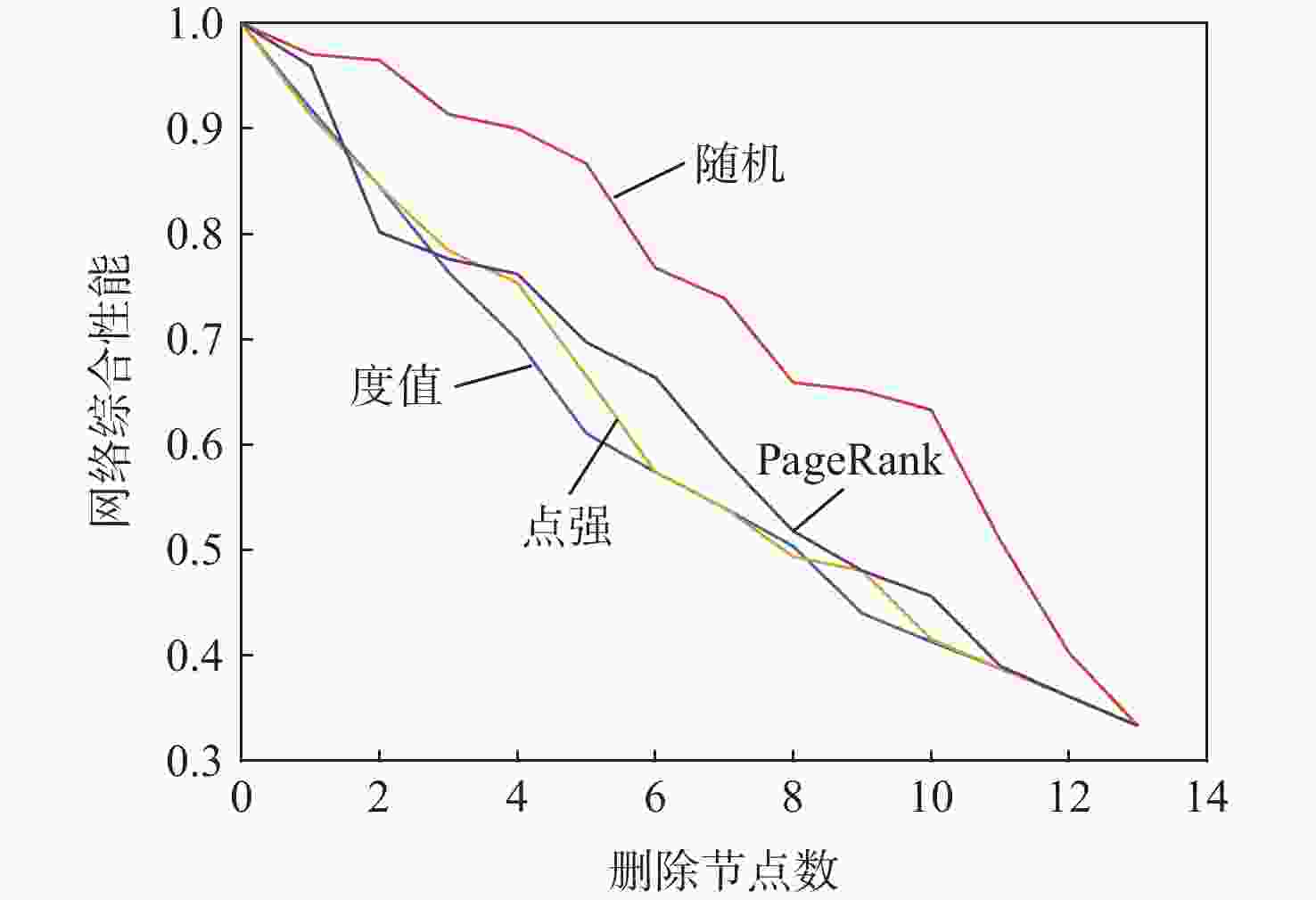
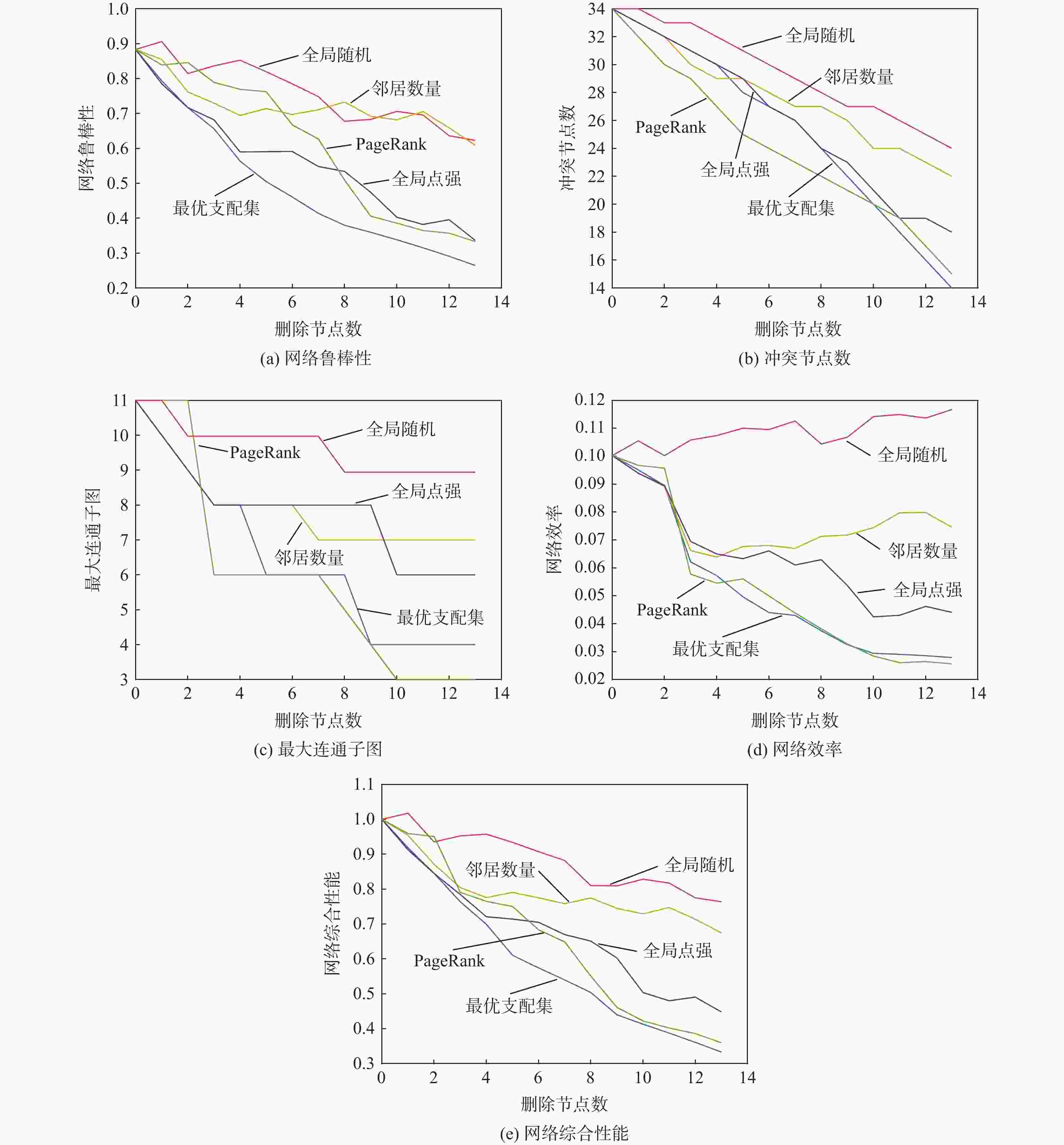
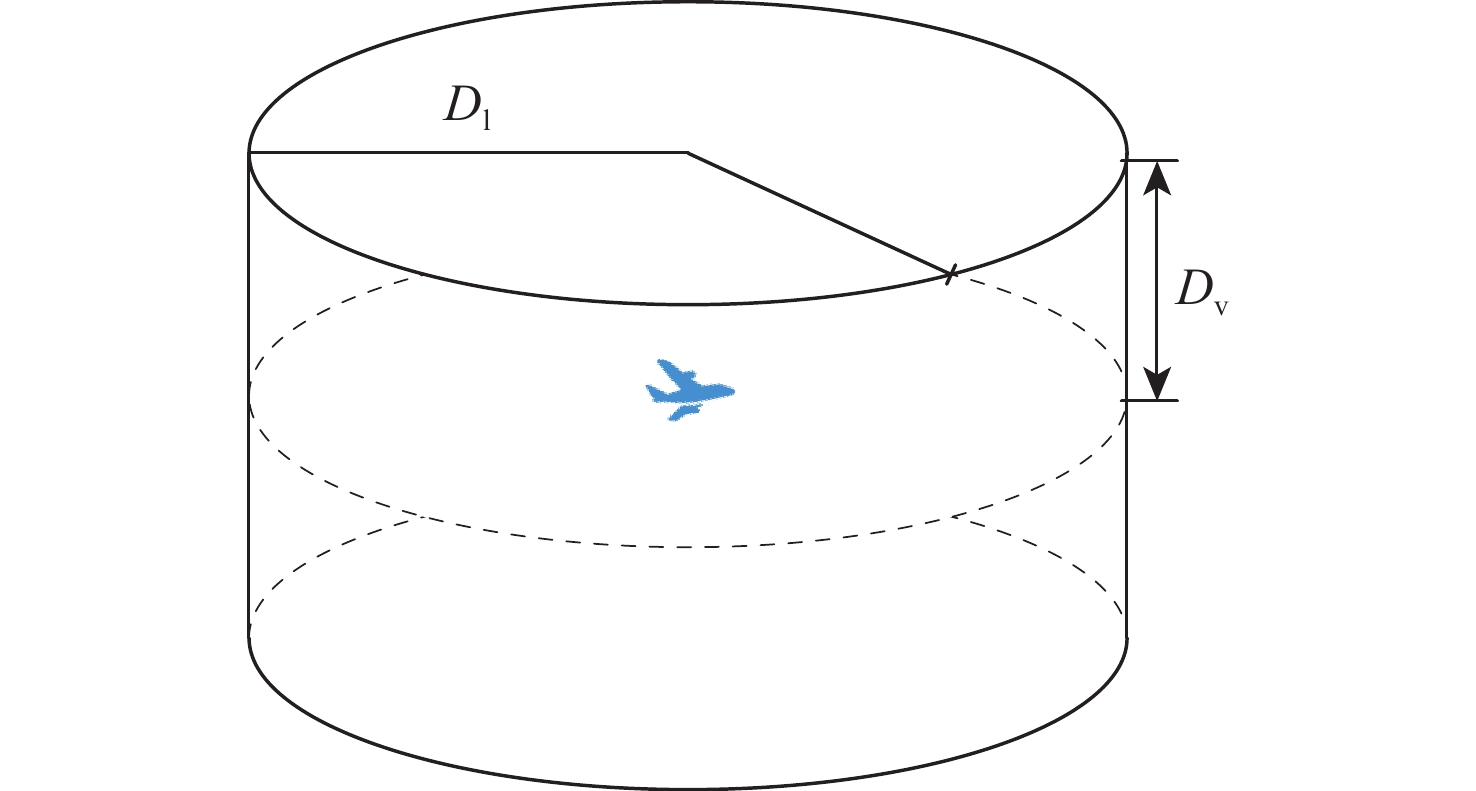
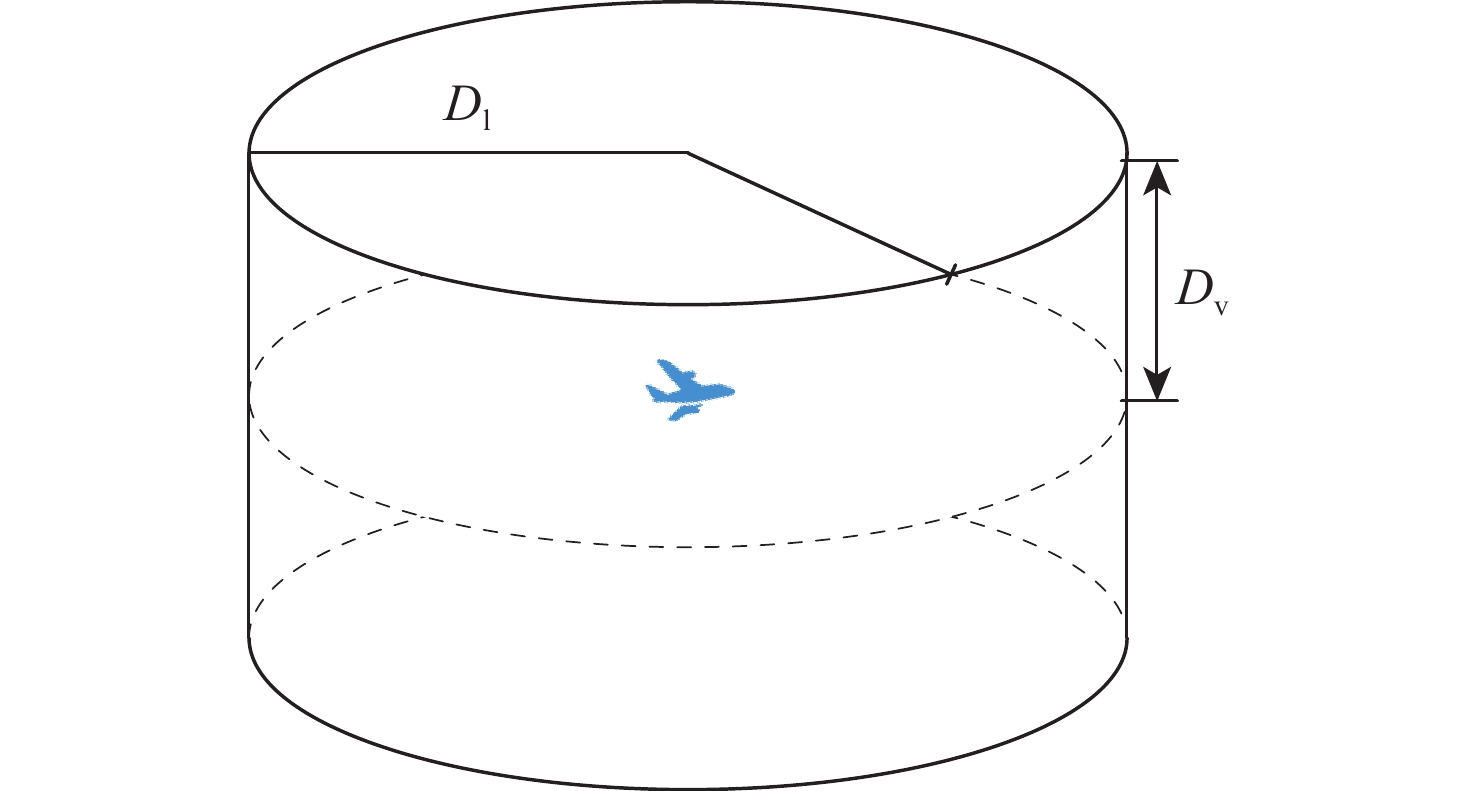
针对空中交通流量逐年上升、管制压力增大、飞行冲突难调配的问题,以航空器为节点,基于航空器之间的速度障碍关系建立飞行冲突网络。定义最优支配集的概念,通过移除飞行冲突网络的最优支配集节点,快速消解网络中的冲突,降低网络的复杂性。在使用粒子群(PSO)算法对网络最优支配集进行求解的过程中,引入免疫机制,设置节点和连边2种类型的抗原,保证对关键航空器和高风险冲突的优先调配。实验仿真表明:所提冲突调配策略相较于传统方法能够快速识别网络中的关键航空器节点,并对高风险的冲突连边具有较好的灵敏性,可为管制员和管制系统提供更加准确、可靠的信息和建议,在宏观上辅助进行飞行冲突的调配。
Abstract:As air traffic flow grows year by year, control pressure keeps rising and to find a resolution to flight conflict is increasingly difficult. This paper takes aircrafts as the nodes and establishes a flight conflict network based on the velocity obstacle relationship between aircrafts. Then, the concept of optimal dominating set is defined. By eliminating the nodes in the optimal dominating set of the flight conflict network, the conflict could be resolved quickly, thus reducing the complexity of the network. While particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm is used in solving the network optimal dominating set, the immune mechanism is introduced, with two types of antigens, node and edge, being set to ensure the priority resolution of critical aircraft and high-risk conflicts. Compared with traditional method, the conflict resolution strategy presented in this paper can quickly identify key aircraft nodes in the network, and has good sensitivity to high-risk conflict edges, which can offer controllers and control system more accurate and reliable information to achieve flight conflict resolution.
-
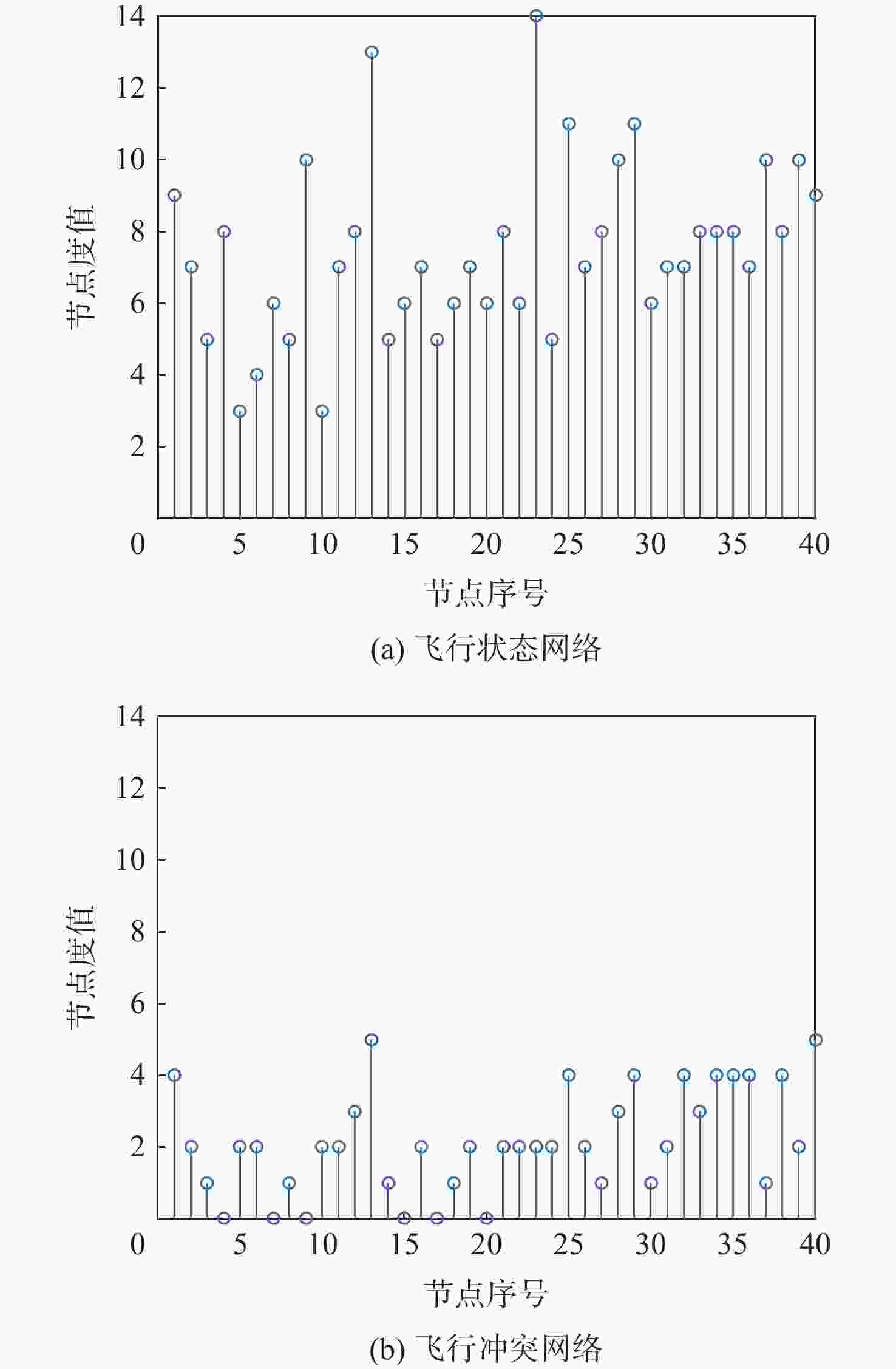
表 1 两种网络中节点的度值
Table 1. Node degrees in two networks
序号 节点度值 序号 节点度值 飞行状态网络 飞行冲突网络 飞行状态网络 飞行冲突网络 1 8 4 21 7 2 2 6 2 22 5 2 3 4 1 23 13 2 4 7 0 24 4 2 5 2 2 25 10 4 6 3 2 26 6 2 7 5 0 27 7 1 8 4 1 28 9 3 9 9 0 29 10 4 10 2 2 30 5 1 11 6 2 31 6 2 12 7 3 32 6 4 13 12 5 33 7 3 14 4 1 34 7 4 15 5 0 35 7 4 16 6 2 36 6 4 17 4 0 37 9 1 18 5 1 38 7 4 19 6 2 39 9 2 20 5 0 40 8 5 -
[1] CHE J J. Report of civil aviation airspace development in China 2019: CACC-2020-09[R]. Beijing: CAAC, 2020. [2] 张启钱, 王中叶, 张洪海, 等. 基于SMILO-VTAC模型的复杂低空多机冲突解脱方法[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2019, 19(6): 125-136.ZHANG Q Q, WANG Z Y, ZHANG H H, et al. SMILO-VTAC model based multi-aircraft conflict resolution method in complex low-altitude airspace[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2019, 19(6): 125-136(in Chinese). [3] 王泽坤, 吴明功, 温祥西, 等. 基于速度障碍法的飞行冲突解脱与恢复策略[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(7): 1294-1302.WANG Z K, WU M G, WEN X X, et al. Flight collision resolution and recovery strategy based on velocity obstacle method[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(7): 1294-1302(in Chinese). [4] 蒋旭瑞, 吴明功, 温祥西, 等. 基于合作博弈的多机飞行冲突解脱策略[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(11): 2482-2489. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.11.14JIANG X R, WU M G, WEN X X, et al. Conflict resolution of multi-aircraft based on the cooperative game[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(11): 2482-2489(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.11.14 [5] 陈伟锋, 邵之江. 基于析取关系直接变换的冲突解脱方法[J]. 航空学报, 2014, 35(4): 1122-1133.CHEN W F, SHAO Z J. Direct disjunction transcription based conflict resolution approach[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2014, 35(4): 1122-1133(in Chinese). [6] HUANG S M, FERON E, REED G, et al. Compact configuration of aircraft flows at intersections[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2014, 15(2): 771-783. [7] HONG Y, CHOI B, LEE K, et al. Conflict management considering a smooth transition of aircraft into adjacent airspace[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2016, 17(9): 2490-2501. [8] VALENZUELA A, RIVAS D. Conflict resolution in converging air traffic using trajectory patterns[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2011, 34(4): 1172-1189. [9] CAFIERI S, REY D. Maximizing the number of conflict-free aircraft using mixed-integer nonlinear programming[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2017, 80: 147-158. [10] WANG H Y, XU X H, ZHAO Y F. Empirical analysis of aircraft clusters in air traffic situation networks[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers. Part G:Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2017, 231(9): 1718-1731. doi: 10.1177/0954410016660870 [11] JIANG X R, WEN X X, WU M G, et al. A complex network analysis approach for identifying air traffic congestion based on independent component analysis[J]. Physica A-Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2019, 523: 364-381. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2019.01.129 [12] HUANG Y, TANG J, LAO S Y. Cooperative multi-UAV collision avoidance based on a complex network[J]. Applied Sciences-Basel, 2019, 9(19): 3943. doi: 10.3390/app9193943 [13] JENIE Y I, KAMPEN E J, VISSER C C, et al. Three-dimensional velocity obstacle method for uncoordinated avoidance maneuvers of unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2016, 39(10): 2312-2323. doi: 10.2514/1.G001715 [14] 王凯莉, 邬春学, 艾均, 等. 基于多阶邻居壳数的向量中心性度量方法[J]. 物理学报, 2019, 68(19): 235-245.WANK K L, WU C X, AI J, et al. Complex network centrality method based on multi-order K-shell vector[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2019, 68(19): 235-245(in Chinese). [15] 何明, 许元云, 刘锦涛, 等 基于k-shell分解的多智能体牵制控制算法[J]. 控制与决策, 2020, 35(10): 2556-2560.HE M, XU Y Y, LIU J T, et al. Multi-agent pinning control algorithm based on k-shell decomposition[J]. Control and Decision, 2020, 35(10): 2556-2560(in Chinese). [16] 王江盼, 郭强, 刘建国. 基于PageRank的合著论文中作者贡献分配算法[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2020, 49(6): 918-923.WANG J P, GUO Q, LIU J G. Credit allocation for each author in a multi-author paper based on PageRank[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020, 49(6): 918-923(in Chinese). [17] LI J W, WEN X X, WU M G, et al. Identification of key nodes and vital edges in aviation network based on minimum connected dominating set[J]. Physica A-Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2020, 541: 123340. [18] 殷剑宏, 吴开亚. 图论及其算法[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2003: 188-197.YIN J H, WU K Y. Graph theory and its algorithm[M]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China Press, 2003: 188-197 (in Chinese). [19] 高鹰, 谢胜利. 免疫粒子群优化算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2004(6): 4-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2004.06.002GAO Y, XIE S L. Particle swarm optimization algorithms with immunity[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2004(6): 4-6(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2004.06.002 -






 下载:
下载: